ZIO
Runtime
Contents
- Execution Model
- Fiber data type
- Sync execution
- Parallel execution
- Async execution
Simple program, right ?
// Simple for users, advanced inside
object Sync extends App {
val rt = Runtime.default // use sync runtime
val eff = ZIO.succeed(1) // define an effect type
val out = rt.unsafeRun(eff) // evaluate as a thunk
println(out)
}
Thunk evaluation
// by-name evaluation example
def when[A](test: Boolean, whenTrue: => A, whenFalse: => A): A =
test match {
case true => whenTrue
case false => whenFalse
}
// Try that again...
scala> when(1 == 1, println("foo"), println("bar"))
foo
scala> when(1 == 2, println("foo"), println("bar"))
bar
More info here
Thunk evaluation
ZIO Runtime evaluates effects by-value
final def unsafeRun[E, A]( zio: => ZIO[R, E, A] ): A
Sync Effect
// Program description with ZIO effects
val rt = Runtime.default
val data = List(1, 2, 3)
val foldEff = ZIO.foldLeft(data)(0)((acc, v) => ZIO.effect(acc + v))
// Effectful program execution on the edge
rt.unsafeRun(foldEff)
// 6Sync execution
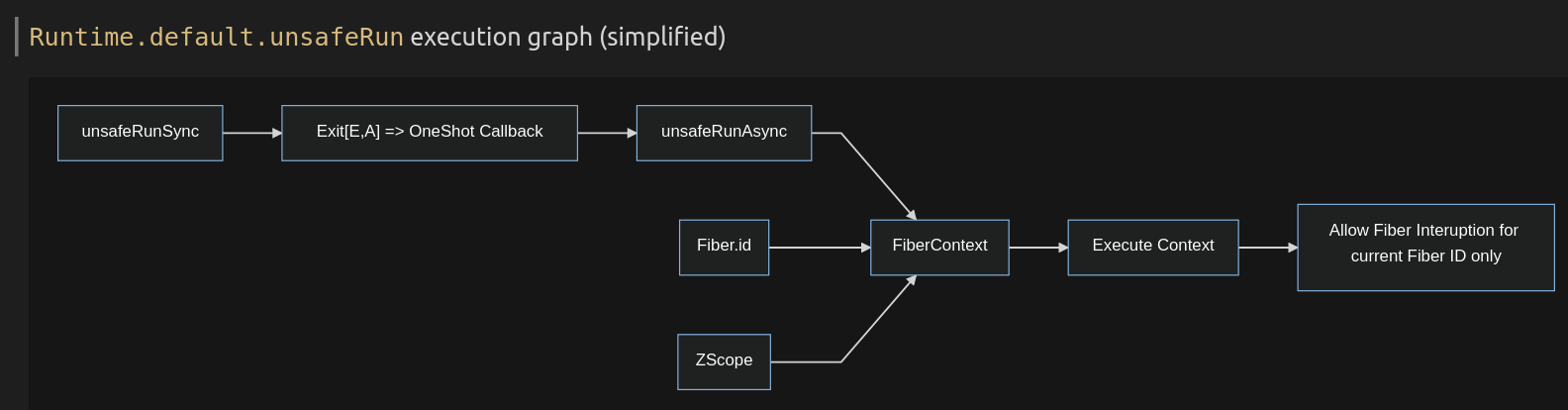
Parallel execution
object Par extends App {
val rt = Runtime.default
val data = List(1, 2, 3)
// executes in parallel with 8 fibers
val effPar = ZIO.foreachParN(8)(data)(el => ZIO.effect(el + 1))
val res0 = rt.unsafeRun(effPar)
println(res0)
// List(2,3,4)
}Par Execution
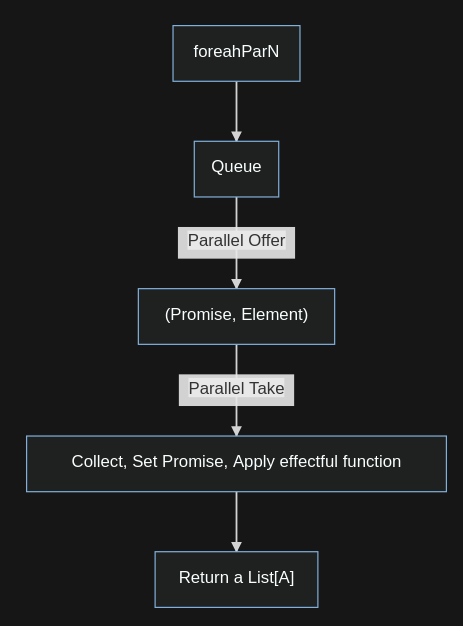
Sync and Par takeaways
-
Similar user semantics
-
Fiber based
-
Same Execution Context
Execution Contexts
import scala.concurrent.{ ExecutionContext }
import java.util.concurrent.{ Executors }
object Pools {
val cores = 4
// Fixed EC
val fixedEc = ExecutionContext.fromExecutor(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(cores))
// Scheduled TP EC
val schedTP = ExecutionContext.fromExecutor(Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(cores))
// Work Stealing (fork-join) EC
val workStealingEc = ExecutionContext.fromExecutor(Executors.newWorkStealingPool())
// Cached EC
val cachedEc = ExecutionContext.fromExecutor(Executors.newCachedThreadPool())
}Custom EC for Sync and Par
import scala.concurrent.{ ExecutionContext }
import java.util.concurrent.{ Executors }
object Effects {
val cores = 4
// Fixed EC
val fixedEc = ExecutionContext.fromExecutor(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(cores))
// Sync effect
val foldEff = ZIO.foldLeft(data)(0)((acc, v) => ZIO.effect(acc + v))
// Execute Sync effect on a custom Thread Pool
val syncCustomTP = foldEff.on(fixedEc)
}Why different thread pools ?
// Work Stealing (fork-join) EC
val workStealingEc = ExecutionContext.fromExecutor(Executors.newWorkStealingPool())
// Used fixed size thread pool
val syncCustomTP = foldEff.on(fixedEc)
// Executes on the blocking thread pool
val block = blocking(ZIO.succeed(Thread.sleep(Long.MaxValue)))
// Possible to reassign on another tread pool
val prog = syncCustomTP <* block // <-------- This Blocks indefinitely long
val out = rt.unsafeRun(prog)
// Hangs here
Blocking on another TP
// Work Stealing (fork-join) EC
val workStealingEc = ExecutionContext.fromExecutor(Executors.newWorkStealingPool())
// Used fixed size thread pool
val syncCustomTP = foldEff.on(fixedEc)
// Executes on the blocking thread pool
val block = blocking(ZIO.succeed(Thread.sleep(Long.MaxValue)))
// Possible to reassign on another tread pool
val prog = syncCustomTP <* block.on(workStealingEc) // <-------- Still Blocks here
val out = rt.unsafeRun(prog)
// Hangs here
Thread Profiling with VisualVM
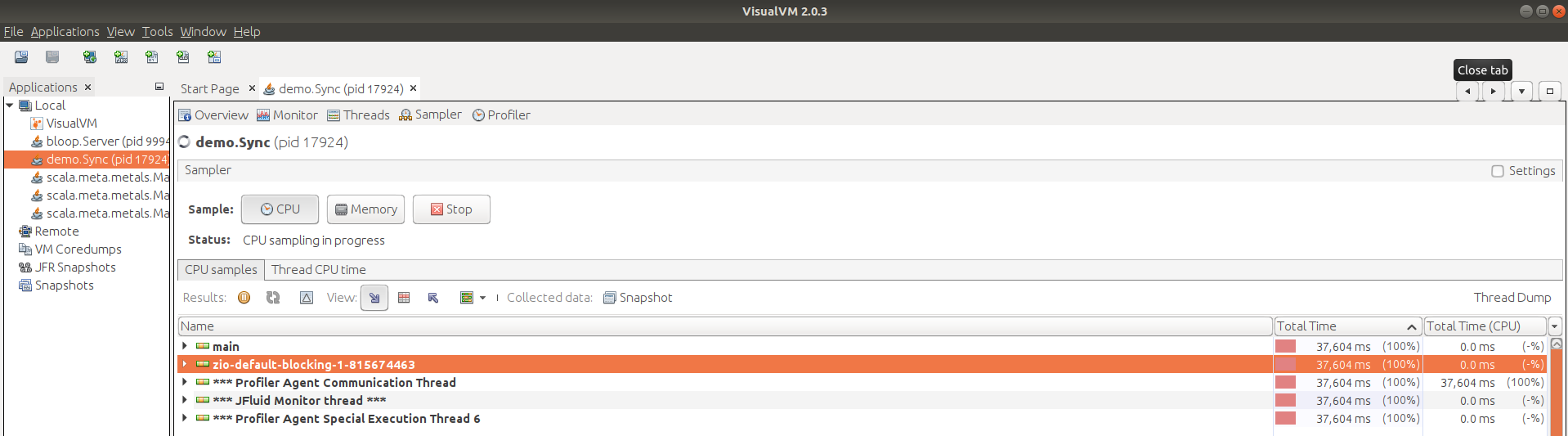
Async
val rt = Runtime.default
// Example 1
val effAsync = IO.effectAsync[Throwable, Int] { k =>
Thread.sleep(1000)
k(IO.succeed(11))
}
val res0 = rt.unsafeRun(effAsync)
println(res0)
// 11
// Example 2
def sayHello(str: String) = Future.successful(Message(str))
def res0(fut: Future[Message])(implicit ec: ExecutionContext): Task[Message] =
IO.effectAsync[Throwable, Message](cb =>
fut.onComplete(res =>
res match {
case Success(value) => cb(Task(value))
case Failure(exception) => Task.fail(exception)
}
)
)
val msg = sayHello("Boris")
val out0 = rt.unsafeRun(res0(msg)(cachedEc))
println(out0)
// Message(Boris)F
By ourcrew
F
- 72
