Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
RFC 2616
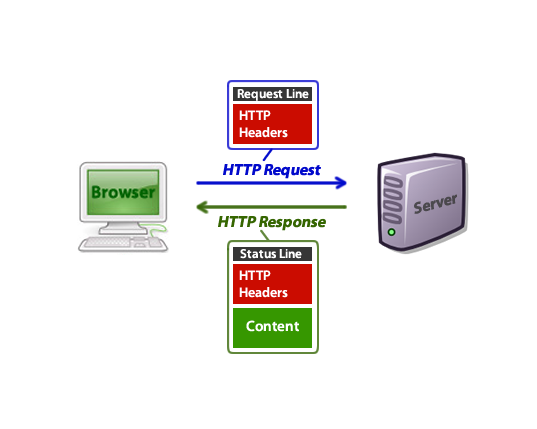
HTTP request header
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: google.com
Connection: close
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.0)
Accept-Encoding: gzip
Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,UTF-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7
Cache-Control: no-cache
Accept-Language: de,en;q=0.7,en-us;q=0.3
Referer: http://web-sniffer.net/HTTP request header
GET /tutorials/other/top-20-mysql-best-practices/ HTTP/1.1
Host: net.tutsplus.com
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-US; rv:1.9.1.5) Gecko/20091102 Firefox/3.5.5 (.NET CLR 3.5.30729)
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-us,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate
Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7
Keep-Alive: 300
Connection: keep-alive
Cookie: PHPSESSID=r2t5uvjq435r4q7ib3vtdjq120
Pragma: no-cache
Cache-Control: no-cacheMétodos HTTP
- GET: Obtener datos
- POST: Insertar datos
- PUT: Actualizar datos
-
DELETE: Borrar datos
- Otros: HEAD TRACE OPTIONS PATCH
HTTP response header
HTTP/1.x 200 OK
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Date: Sat, 28 Nov 2009 04:36:25 GMT
Server: LiteSpeed
Connection: close
X-Powered-By: W3 Total Cache/0.8
Pragma: public
Expires: Sat, 28 Nov 2009 05:36:25 GMT
Etag: "pub1259380237;gz"
Cache-Control: max-age=3600, public
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Last-Modified: Sat, 28 Nov 2009 03:50:37 GMT
X-Pingback: http://net.tutsplus.com/xmlrpc.php
Content-Encoding: gzip
Vary: Accept-Encoding, Cookie, User-Agent
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>Top 20+ MySQL Best Practices - Nettuts+</title>
<!-- ... rest of the html ... -->
Status code: 200
Métodos HTTP
- 200 (OK): The resource was found and all is well.
- 304 (NOT MODIFIED): The resource has not been modified since the last request. This is used most often for browser cache mechanisms.
- 401 (UNAUTHORIZED) : The clien is not authorized to handle the resource. Often, this will cause the browser to ask for a username and password to log in to the server.
- 403 (FORBIDDEN): The client failed to gain authorization. This typically happens if you fail to log in with the correct username and password after a 401.
- 404 (NOT FOUND): The resource does not exist at the given location.
200

401

403

404

500

Cliente HTTP
El navegador
Navegador por dentro

HTTP
By Pablo Bianchi
HTTP
Introducción a HTTP
- 802



