Publishing Library on NPM using Webpack


Authoring a Library
A JS Library should
Rubrics
Directory Structure
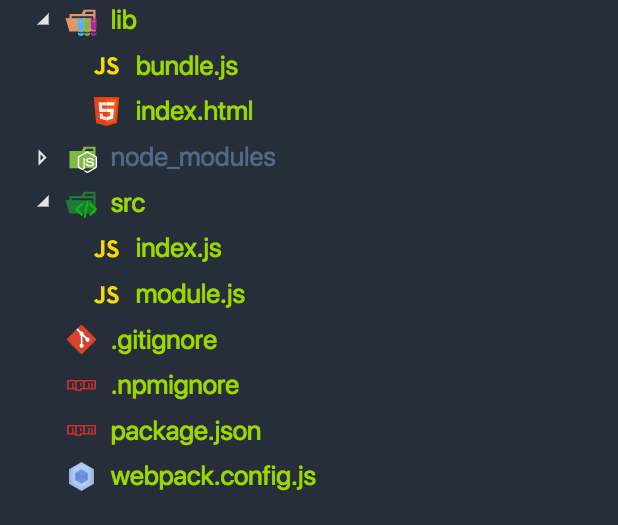
Webpack Bundling
Basic Webpack configuration
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: './index.js',
output: {
filename: 'bundle.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'lib')
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
loader: 'babel-loader'
},
{
test: /\.json$/,
loader: 'json'
},
]
},
plugins: [
new webpack.optimize.DedupePlugin()
]
};
Entry
entry: string | [string] | object { <key>: string | [string] }entry: './src/index.js'
// or
entry: {
home: "./home.js",
about: "./about.js",
contact: "./contact.js"
}
//or
entry: {
vendor: [
'moment',
'lodash',
'react',
'react-dom'
],
main: './client.js'
}
// or
entry: [
'polyfills',
'./src/index.js'
]Context
context: path.resolve(__dirname, 'src')
// Use this
entry: './index.js',
// Instead of
entry: './src/index.js',The base directory, an absolute path, for resolving entry points and loaders from configuration.
Output
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist')Contains set of options instructing webpack on how and where it should output your bundles, assets and anything else.
output.path
filename: '[name].bundle.js' | '[name]-[id].bundle.[hash].js'output.filename
libraryTarget: 'umd' | 'amd' | 'commonjs' | 'var' | 'global', 'window',output.libraryTarget
library: 'Dandelion'output.library
publicPath: "https://cdn.example.com/assets/" | "/assets/"output.publicPath
Module
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: [
['es2015']
]
}
},
{
test: /\.scss$/,
use: [{
loader: "style-loader" // creates style nodes from JS strings
}, {
loader: "css-loader" // translates CSS into CommonJS
}, {
loader: "sass-loader" // compiles Sass to CSS
}]
}
]
}These options determine how the different types of modules within a project will be treated.
module.rules
Array of rules which are matched to requests when modules are created
Plugins
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ title: 'Tree-shaking' }),
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: ['vendor', 'meta'],
minChunks: Infinity
})
]The plugins option is used to customize the webpack build process in a variety of ways
module.rules
Array of rules which are matched to requests when modules are created
Externals
externals : {
react: 'react'
}
// or
externals : {
lodash : {
commonjs: "lodash",
amd: "lodash",
root: "_" // indicates global variable
}
}
// or
externals : {
subtract : {
root: ["math", "subtract"]
}
}The externals configuration option provides a way of excluding dependencies from the output bundles.
Instead, the created bundle relies on that dependency to be present in the consumer's environment
package.json
{
"name": "node-js-sample",
"version": "0.2.0",
"description": "A sample Node.js app using Express 4",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "node index.js"
},
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.13.3"
},
"engines": {
"node": "4.0.0"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "https://github.com/heroku/node-js-sample"
},
"keywords": [
"node",
"heroku",
"express"
],
"author": "Mark Pundsack",
"contributors": [
"Zeke Sikelianos <zeke@sikelianos.com> (http://zeke.sikelianos.com)"
],
"license": "MIT"
}Title Text
Publishing Library on NPM using Webpack
By Param Singh
Publishing Library on NPM using Webpack
- 687



