Photon Maps
Oscar Ivarsson and Pär Eriksson
Global Illumination
using
- Overview
- Pass 1: Photon Map Construction
- Pass 2: Rendering
- Discussion
- Future Work
Introduction
Overview
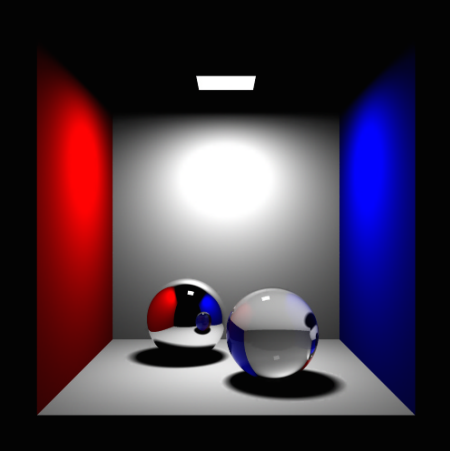

- View independent preprocessing
- More efficient than pure ray tracing
- Good for caustics
- Simulates diffuse reflections
Properties
Pass 1: Photon Map Construction
The Life of a Photon

"A photon checks in at a hotel and is asked if he needs any help with his luggage."
"No, I'm travelling light."
Pass 1: Photon Map Construction
1. Emission
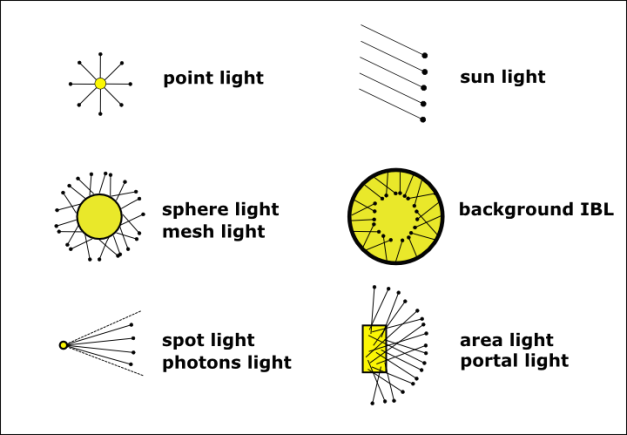
Pass 1: Photon Map Construction
2. Scattering
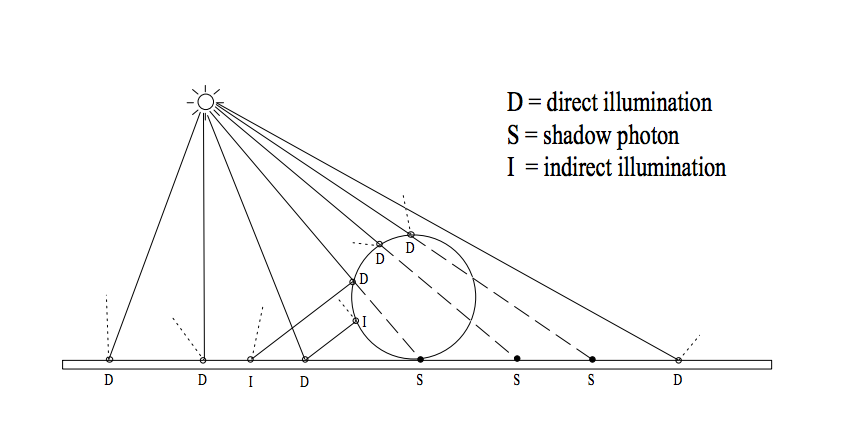
Pass 1: Photon Map Construction
3. Storage
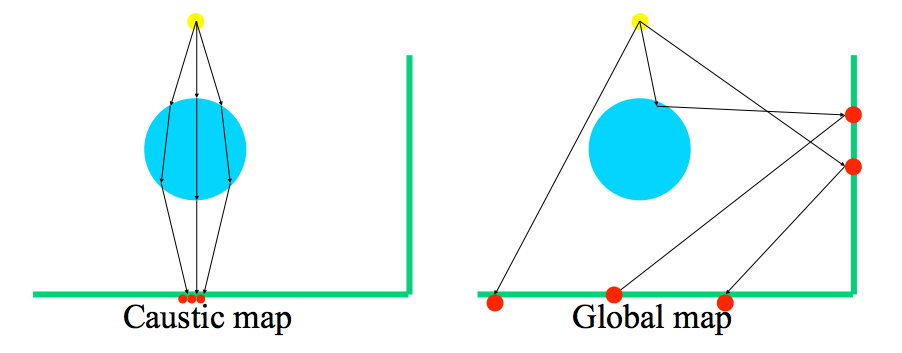
Rendering Equation
- Rendering Equation can be subdivided
-Lr can be split into a sum of components and defined as:
Pass 2: Rendering
-Direct illumination contribution
-Specular reflection contribution
- Caustics on diffuse & slightly glossy surfaces
- Soft indirect illumination
Pass 2: Rendering
Direct illumination (the first term)
Approximated:
- Radiance estimate obtained from the global photon map
Accurate:
- If all in shadow or not in shadow, assume the same
- If mixed, send shadow rays
Two methods used
Pass 2: Rendering
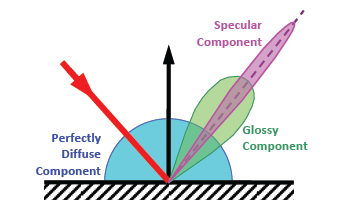
Specular reflection (the second term)
What:
-Radiance reflected of specular and higly glossy surfaces
How:
- Evaluated with Monte Carlo ray tracing
- Importance sampling based on BRDF minimizes computation
Pass 2: Rendering
Caustics (the third term)
What:
-Radiance reflected of specular and higly glossy surfaces
How:
- Evaluated with Monte Carlo ray tracing
- Efficient or time-consuming?
- Easy implementation?
- Smart emission?
Discussion
- Store photons in participating media
- Progressive photon map
- Stochastic progressive photon map
Future Work
Copy of Copy of Copy of Photon Mapping
By Pär Eriksson
Copy of Copy of Copy of Photon Mapping
- 163


