Что такое асинхронность, для чего она нужна и когда использовать. Разбор асинхронности в js
Что такое асинхронность? Это несовпадение чего-либо с чем-либо во времени.
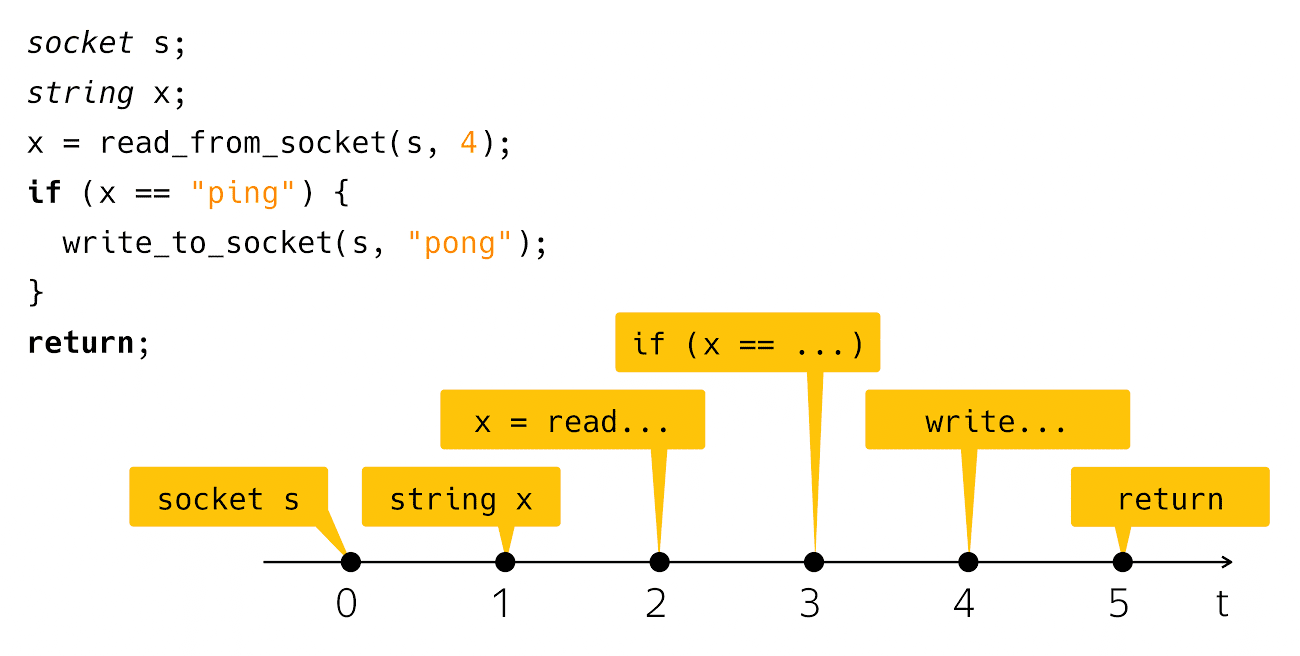

Под потоком, обычно, понимают одиночный процесс, который может использовать программа, для выполнения своих нужд. Каждый поток может выполнять только одну задачу в текущий момент времени:
Task A --> Task B --> Task C
Каждая задача будет выполнена последовательно; только когда текущая задача завершится, следующая сможет начаться.
Программные модели:
Синхронная однопоточная
Синхронная многопоточная
Асинхронная однопоточная
Асинхронная многопоточная
Text

Синхронная однопоточная
Синхронная многопоточная

Асинхронная однопоточная

Асинхронная многопоточная

// ajax(..) - некая библиотечная Ajax-функция
var response = ajax('https://example.com/api');
console.log(response);
// в переменной response не будет ответа от api
ajax('https://example.com/api', function(response) {
console.log(response); // теперь переменная response содержит ответ api
});Callbacks
fs.readdir(source, function (err, files) {
if (err) {
console.log('Error finding files: ' + err);
} else {
files.forEach(function (filename, fileIndex) {
console.log(filename);
gm(source + filename).size(function (err, values) {
if (err) {
console.log('Error identifying file size: ' + err);
} else {
console.log(filename + ' : ' + values);
var aspect = (values.width / values.height);
widths.forEach(function (width, widthIndex) {
var height = Math.round(width / aspect);
console.log('resizing ' + filename + 'to ' + height + 'x' + height);
this.resize(width, height).write(dest + 'w' + width + '_' + filename,
function (err) {
if (err) {
console.log('Error writing file: ' + err);
}
});
}.bind(this));
}
});
});
}
});
Callback hell
function first() {
console.log('first');
}
function second() {
console.log('second');
}
function third() {
console.log('third');
}
first();
setTimeout(second, 1000); // вызвать функцию second через 1000 миллисекунд
third();
// first
// third
// secondsetTimeout
Promises
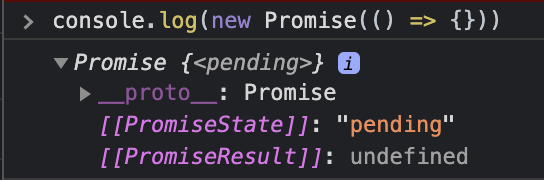
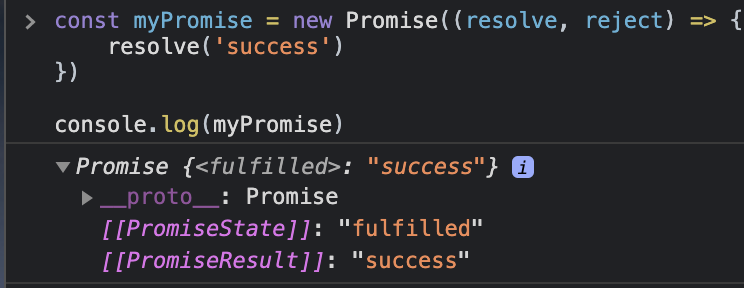
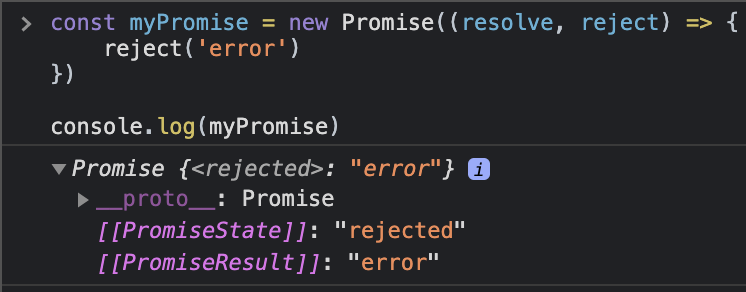
const resolvedPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('success')
})
resolvedPromise.then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
// success
const rejectedPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject('error')
})
rejectedPromise.then(res => {
console.log(res)
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err)
})
rejectedPromise.then(res => {
console.log(res)
}, err => {
console.log(err)
})
// errorconst resolvedPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
throw new Error('some error occured')
resolve('success')
})
resolvedPromise.then(res => {
console.log(res)
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err.message)
})
//some error occured
Promise.all()
Promise.allSettled()
Promise.any()
Promise.race()
Promise.reject()
Promise.resolve()
Promise.prototype.catch()
Promise.prototype.finally()
Promise.prototype.then()async/await
async function f() {
return 1;
}
f().then(alert); // 1
async function f() {
return Promise.resolve(1);
}
f().then(alert); // 1async function f() {
try {
let response = await fetch('http://no-such-url');
} catch(err) {
alert(err); // TypeError: failed to fetch
}
}
f();const fetchValue = (v) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const time = Math.random() * 1000;
console.log('time: ', time);
setTimeout(() => resolve(v), time);
})
}
const sum = (a,b) => a + b;
const main = async () => {
try {
const a = await fetchValue(4);
const b = await fetchValue(46);
console.log(sum(a, b))
} catch(err) {
console.log('some error: ', err)
}
}
main()
// main().catch(err => console.log('some error: ', err))
// "time: ", 597.2952118759335
// "time: ", 961.4652443525156
// 50

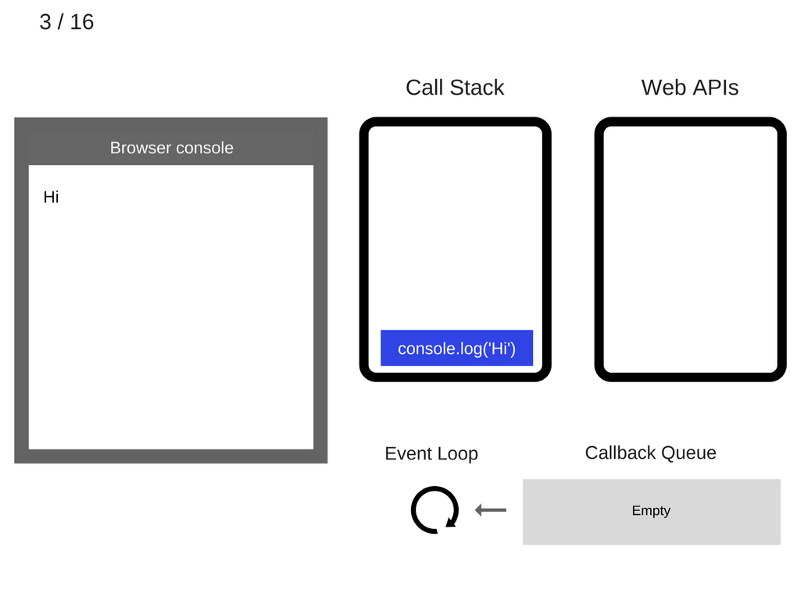
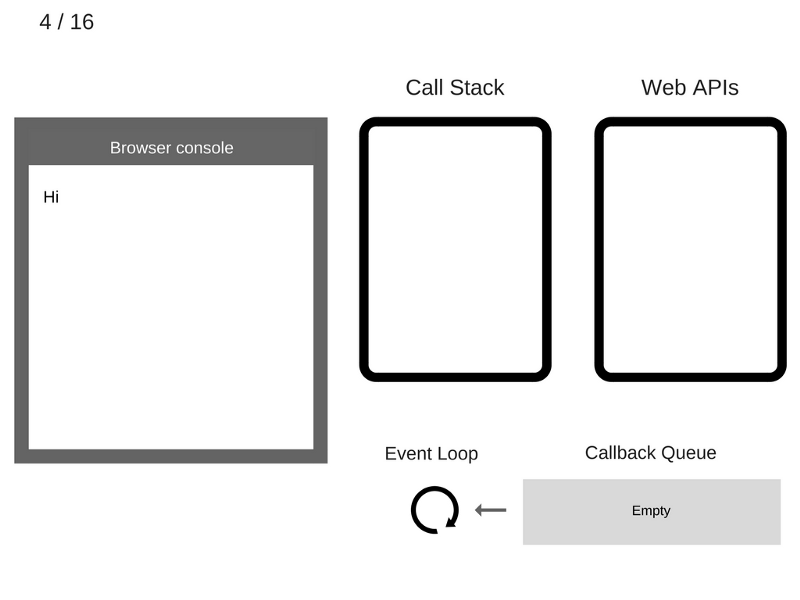
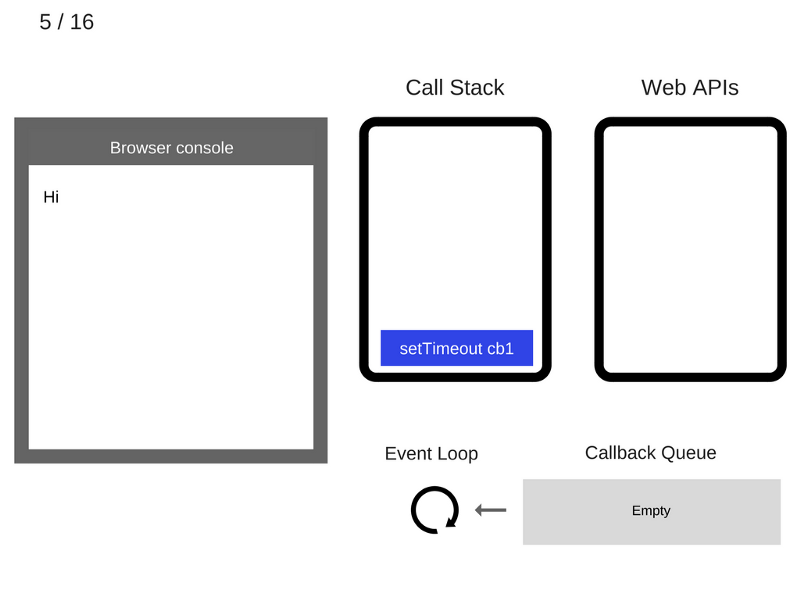
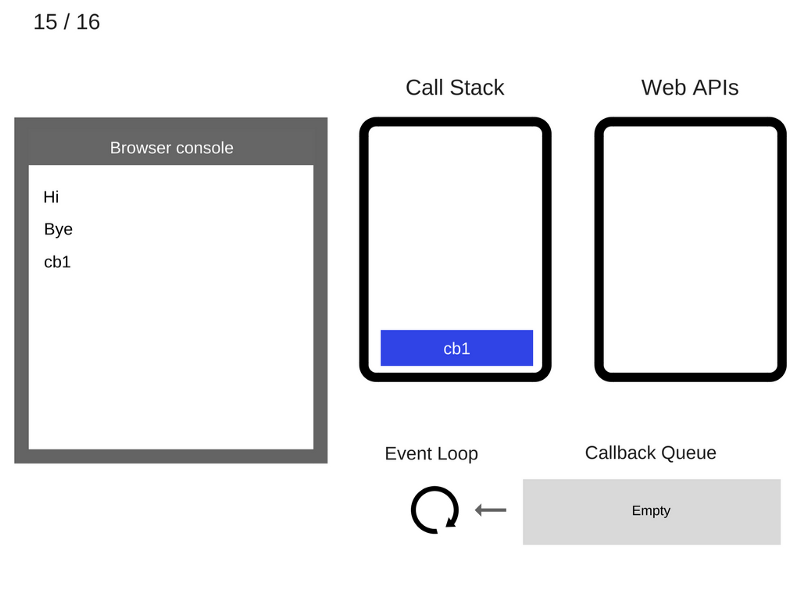
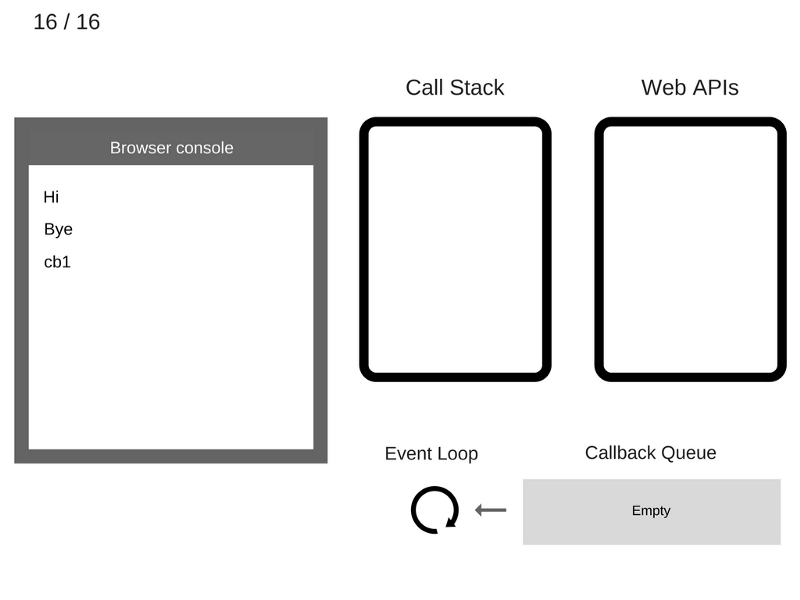
console.log('Hi');
setTimeout(function cb1() {
console.log('cb1');
}, 5000);
console.log('Bye');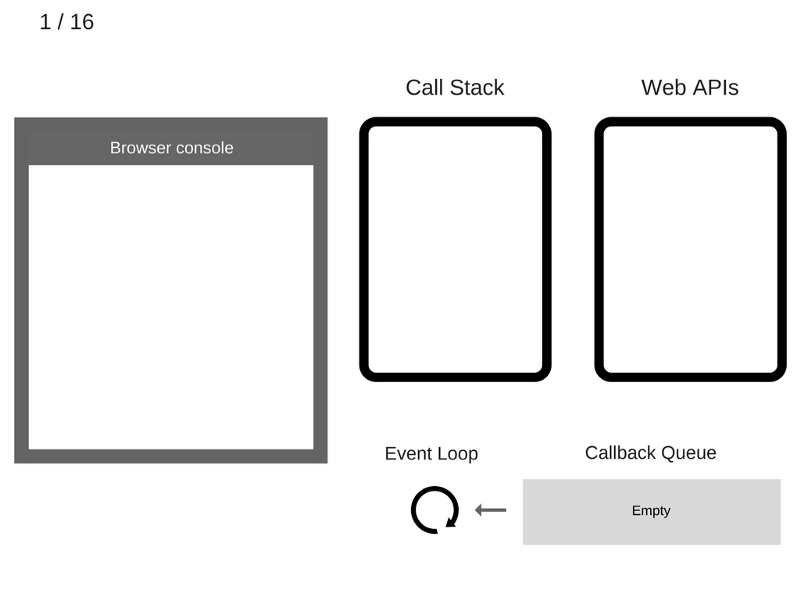


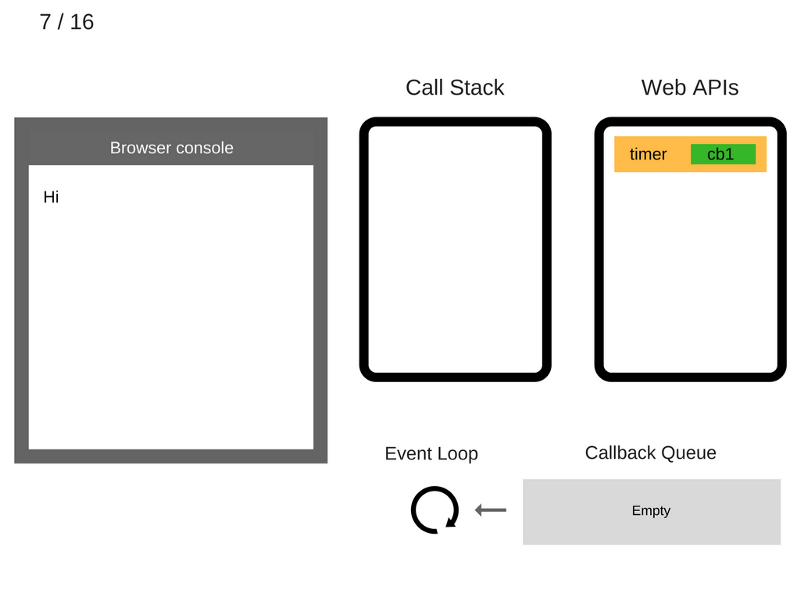
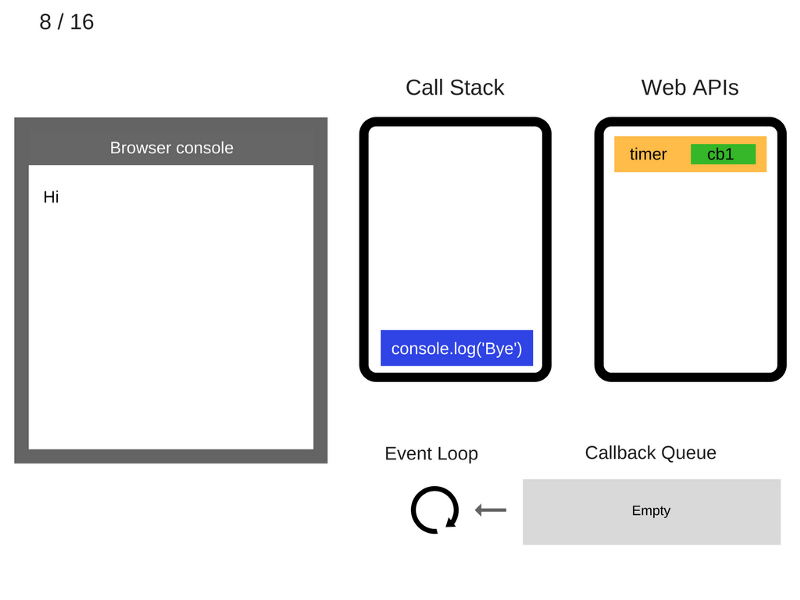
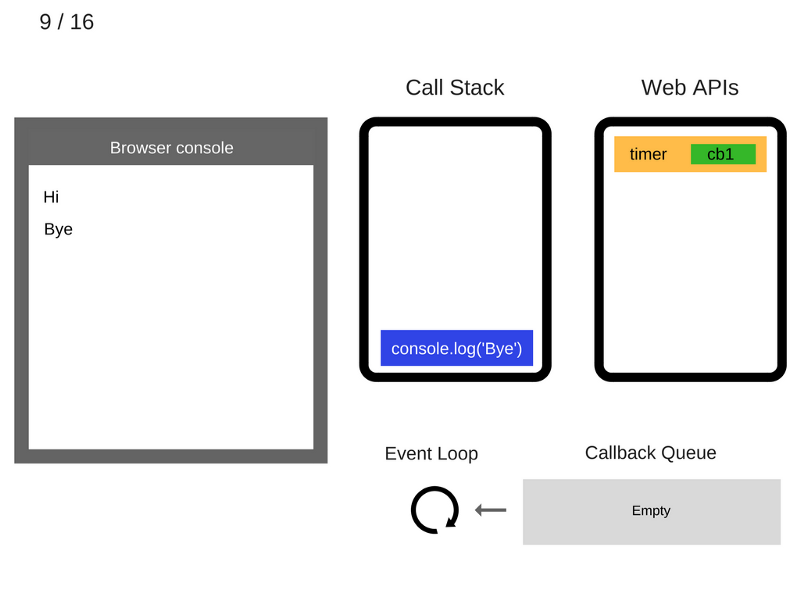
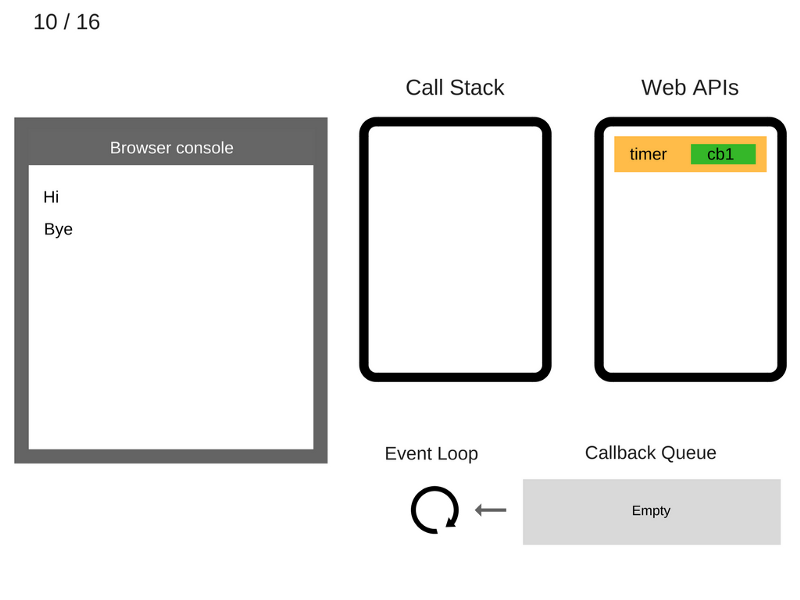
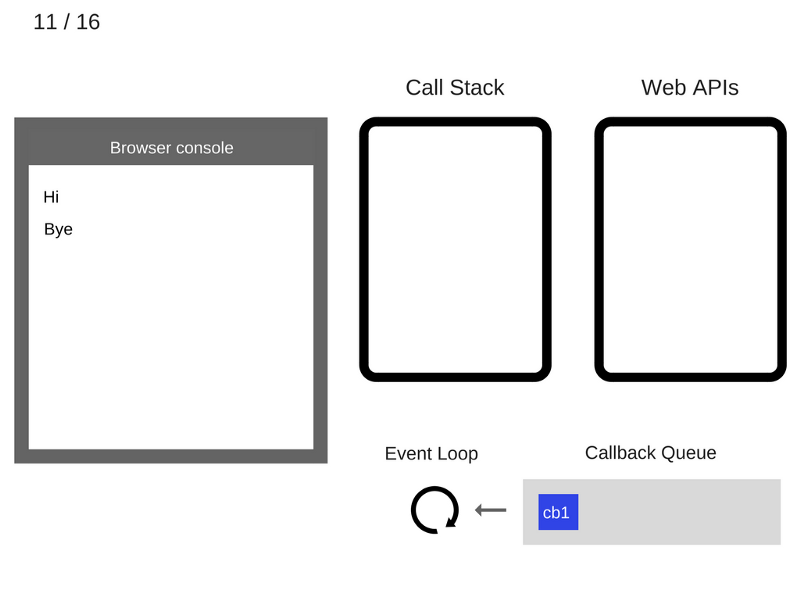
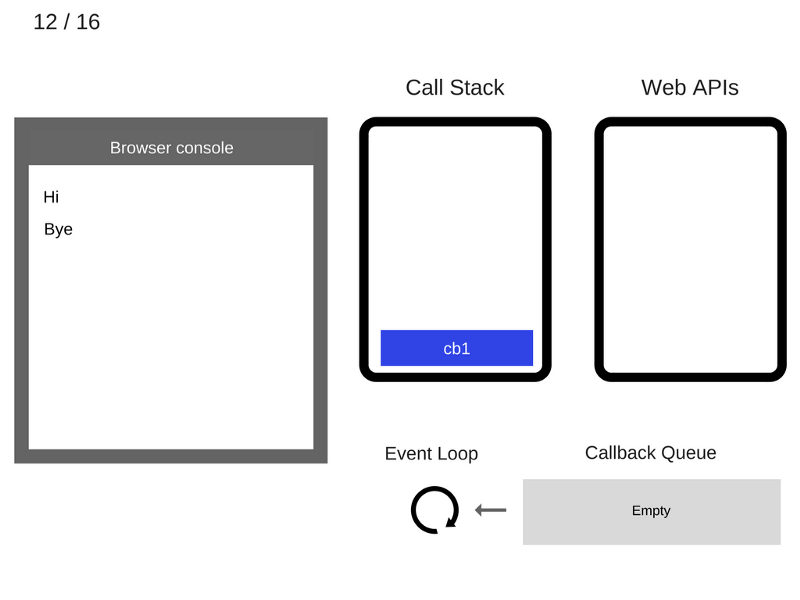
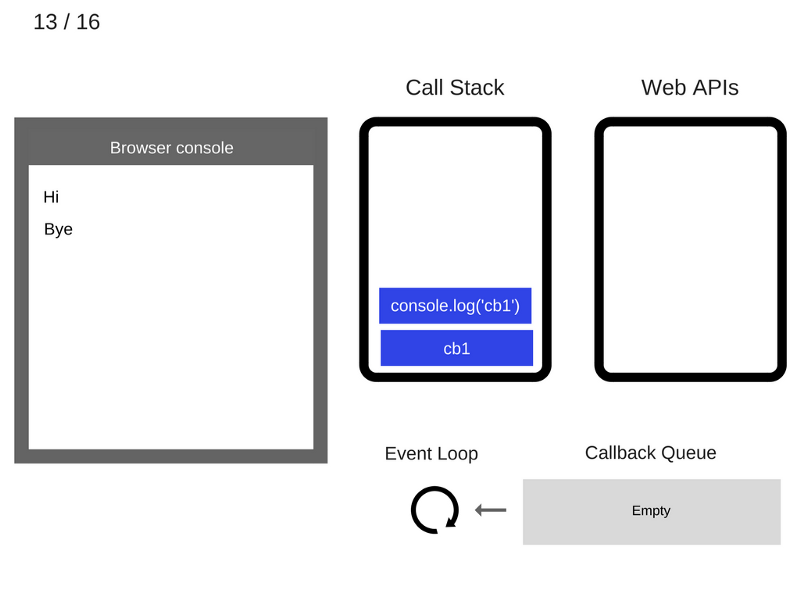
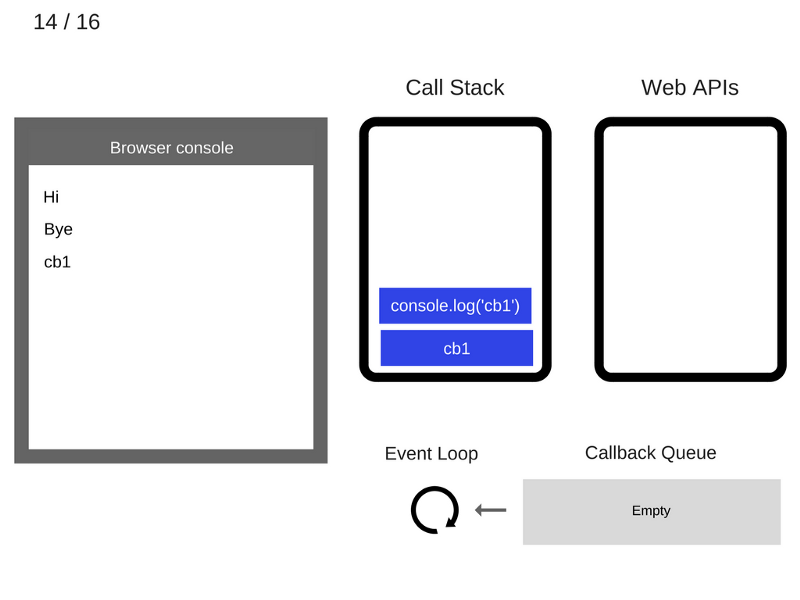

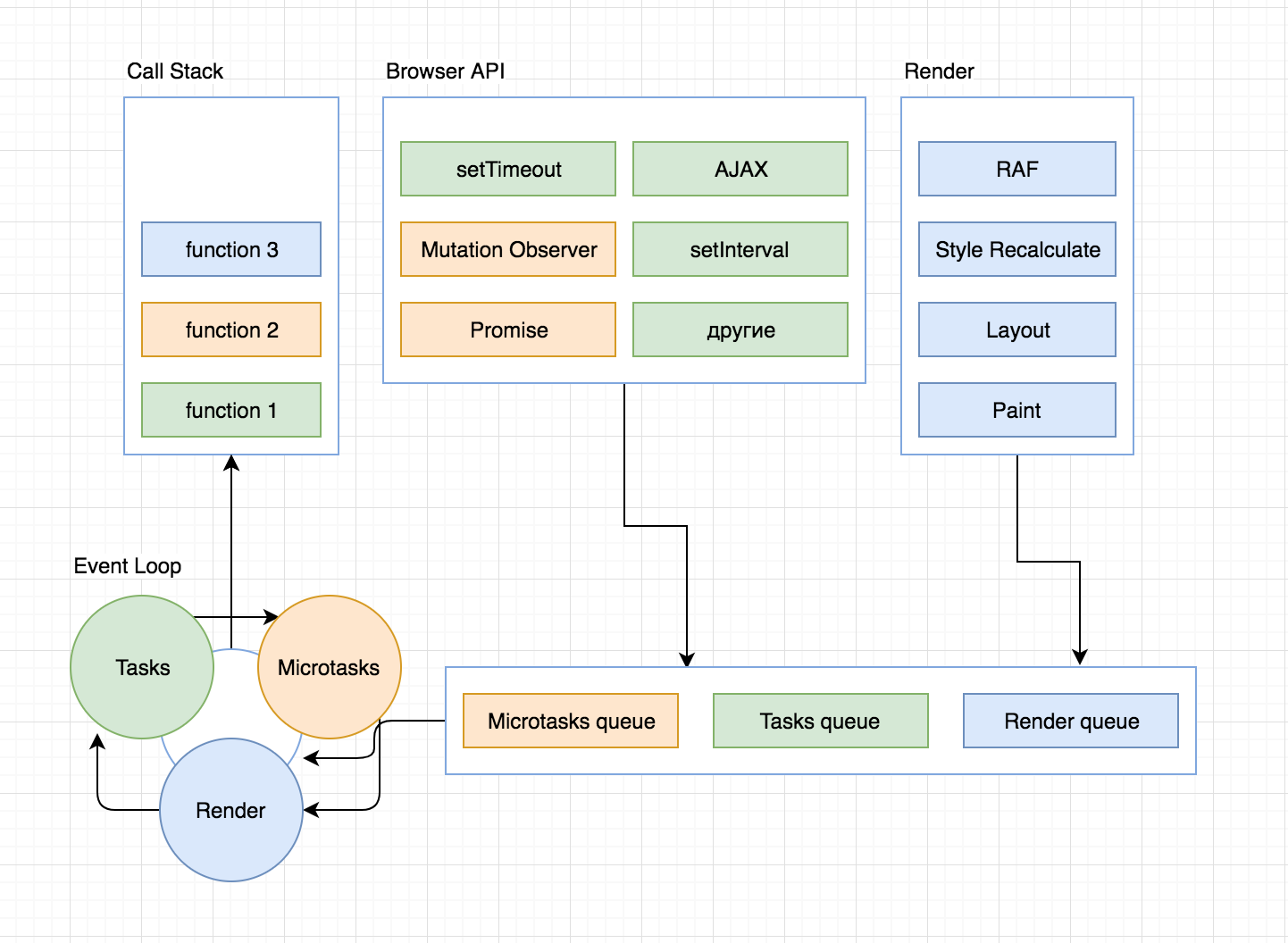

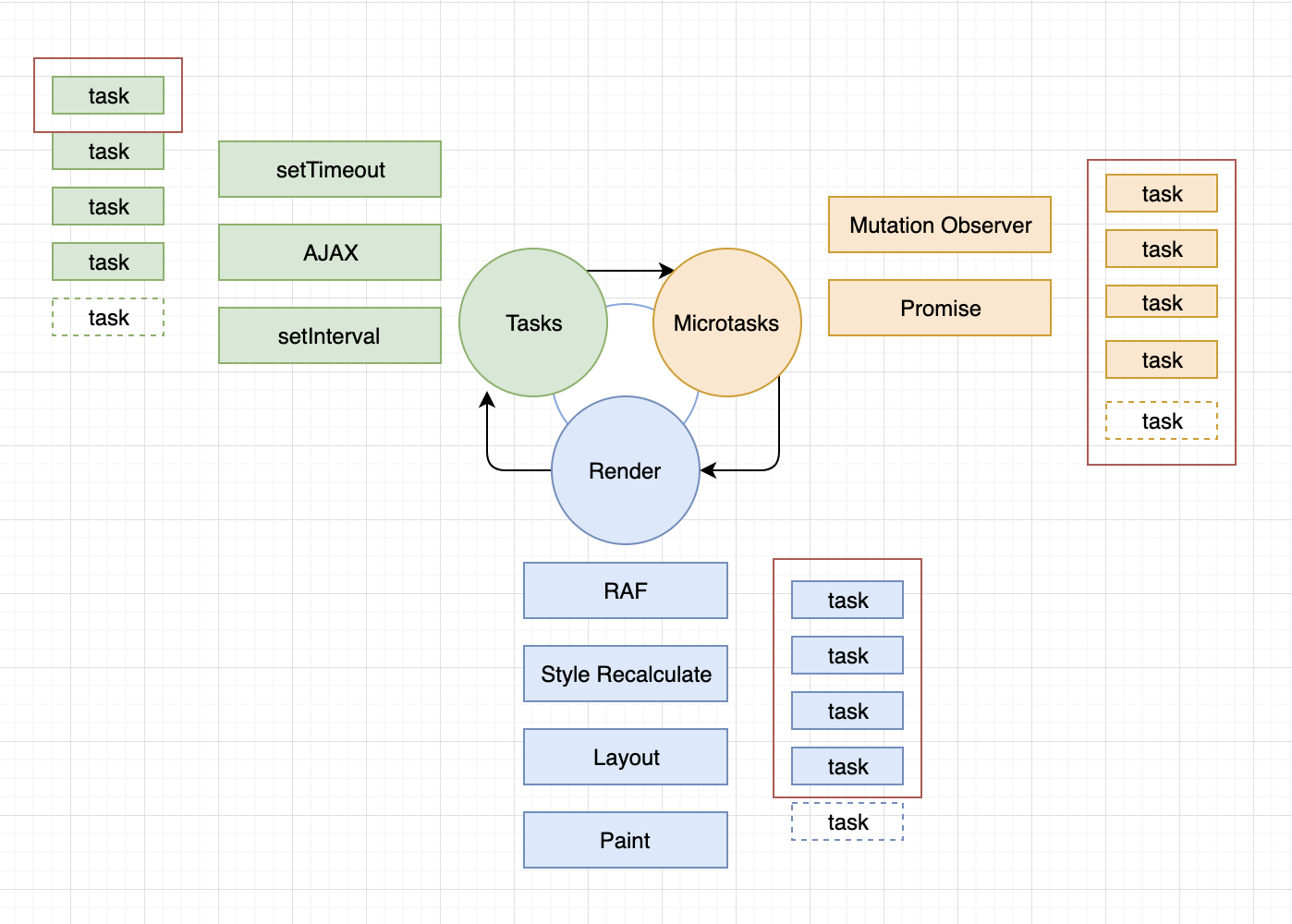
///////////////////////////////// Task 1 /////////////////////////////////
console.log('a')
setTimeout(() => console.log('b'), 0)
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('c')
reject();
}).catch(() => console.log('d')).then(() => console.log('e')).then(() => console.log('f'))
console.log('g');
///////////////////////////////// Task 2 /////////////////////////////////
Promise.reject(4)
.catch(r => r + 1)
.then(r => r + 4)
.then(r => r + 1)
.catch(r => r + 3)
.then(r => r = r + 6)
.finally(t => console.log('finally', t))
///////////////////////////////// Task 3 /////////////////////////////////
function foo() {
Promise.resolve().then(foo)
}
foo()
Асинхронность в js
By pavel_efimov
Асинхронность в js
- 239



