Zero Downtime Migrations for Postgres
on Django sample
Paveł Tyślacki
@tbicr
What is ZDM?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Downtime:
The term downtime is used to refer to periods when a system is unavailable.
My suggestion: postgres one time response time increasing less than a few seconds is not a downtime.
Infrastructure
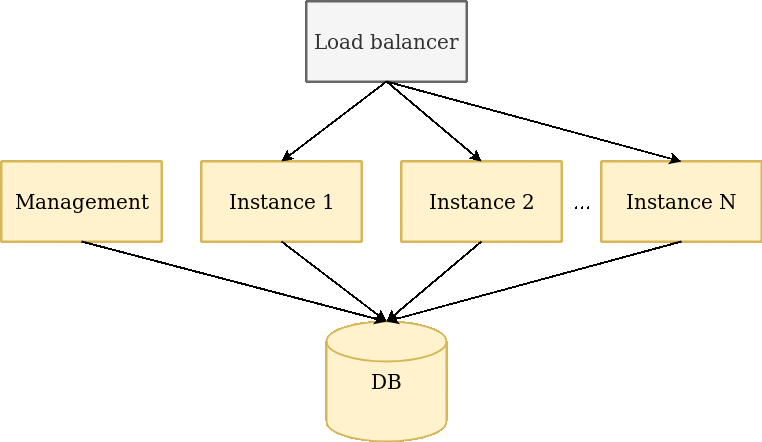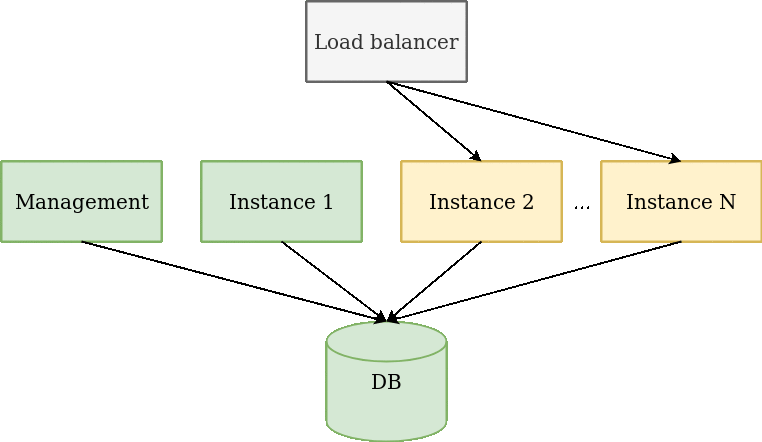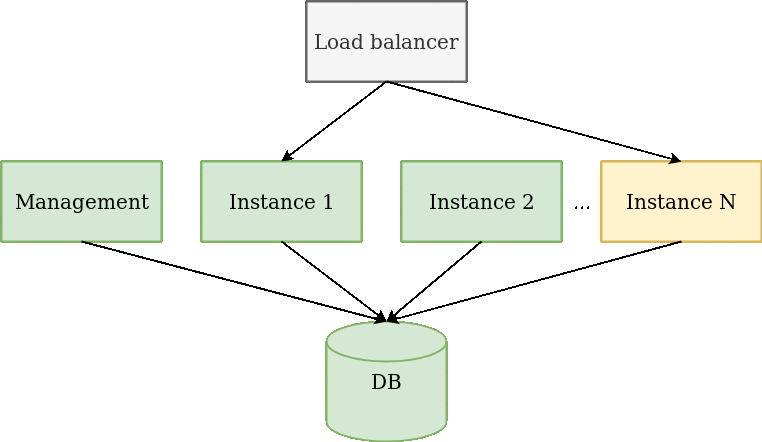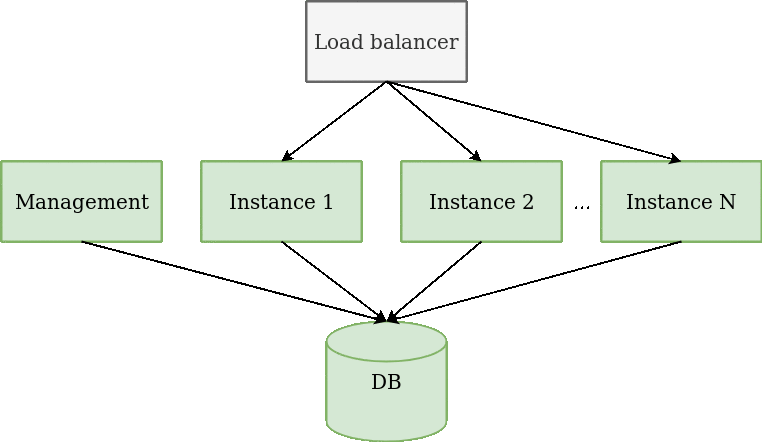
- We have several instances with application - application always should be available, even you restart one of instances;
- We have balancer before instances;
- We have one database.
Timeline
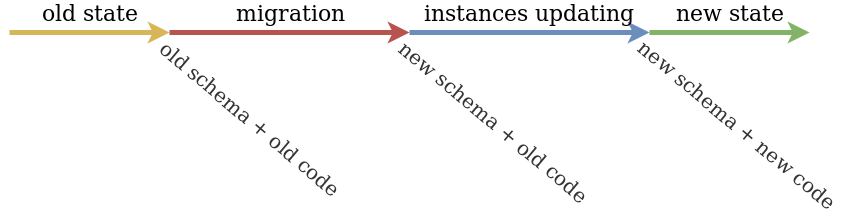
- Our application works fine before, on and after migration - old application works fine with old and new database schema version;
- Our application works fine before, on and after instance updating - old and new application versions work fine with new database schema version.
Migrations and Business Logic
| Schema Migrations | Data Migrations | Business Logic |
|---|---|---|
| CREATE TABLE, DROP TABLE, ALTER TABLE, CREATE INDEX, DROP INDEX | SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE | SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE |
| one thread | one thread | concurrent |
Transactions
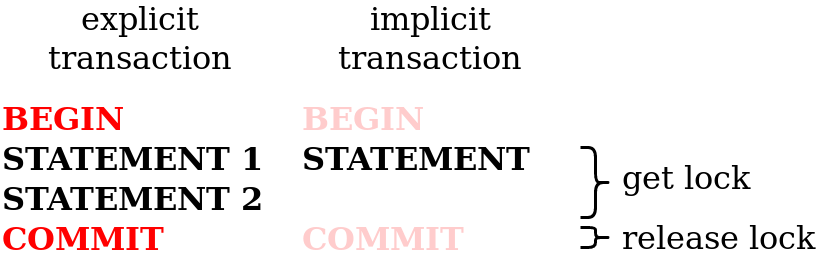
Table-level Locks
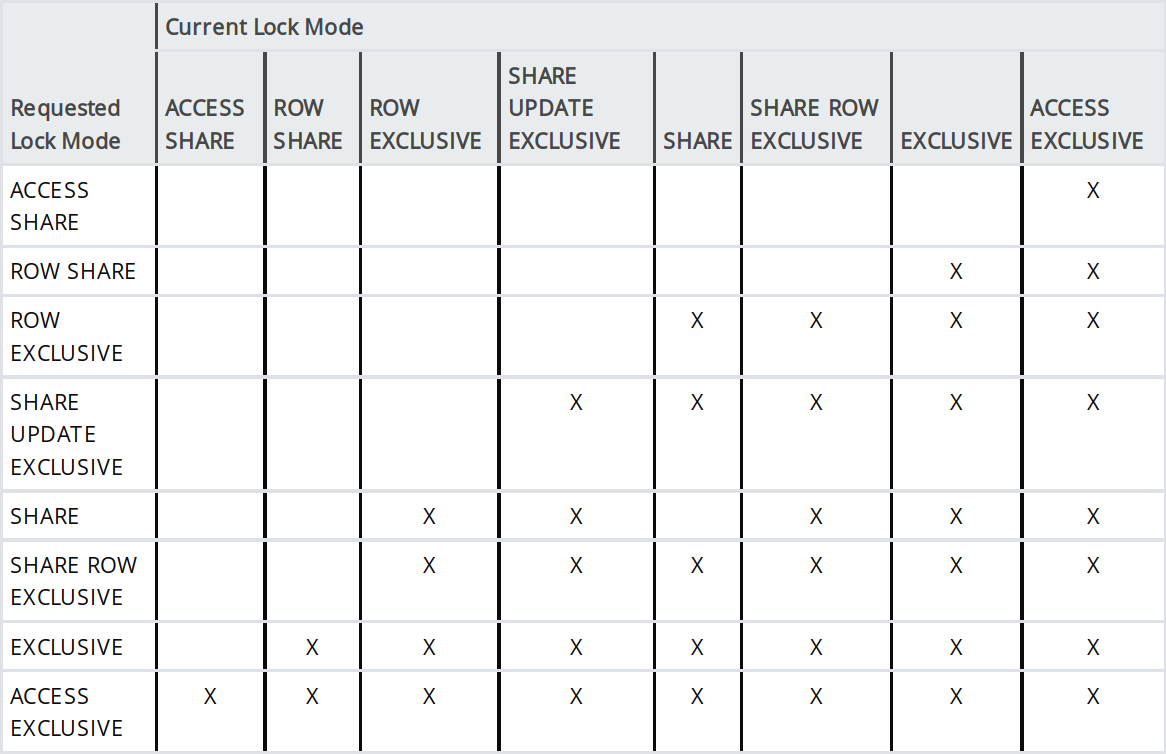
Table-level Locks for Migrations
| lock | operations |
|---|---|
| ACCESS EXCLUSIVE | CREATE SEQUENCE, DROP SEQUENCE, CREATE TABLE, DROP TABLE, ALTER TABLE, DROP INDEX |
| SHARE | CREATE INDEX |
| SHARE UPDATE EXCLUSIVE | CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY, DROP INDEX CONCURRENTLY, ALTER TABLE VALIDATE CONSTRAINT |
Table-level Locks for Business Logic
| lock | operations | conflict with locks | conflict with operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACCESS SHARE | SELECT | ACCESS EXCLUSIVE | ALTER TABLE, DROP INDEX |
| ROW SHARE | SELECT FOR UPDATE | ACCESS EXCLUSIVE, EXCLUSIVE |
ALTER TABLE, DROP INDEX |
| ROW EXCLUSIVE | INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE |
ACCESS EXCLUSIVE, EXCLUSIVE, SHARE ROW EXCLUSIVE, SHARE |
ALTER TABLE, DROP INDEX, CREATE INDEX |
Transactions Flow
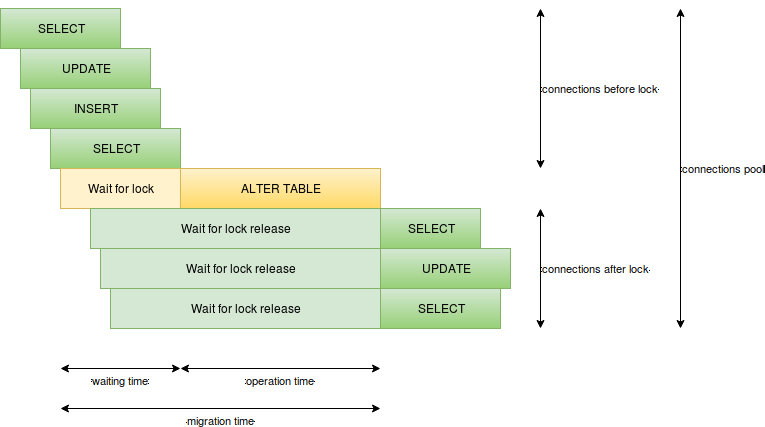
Migration Points
- decrease operation time for hard locks - use alternative operations with lighter lock or faster operations
- decrease waiting lock time - avoid slow business logic or analytic operation on migration time
- decrease queries count - run migrations when load minimal
- be careful with transactions for schema migrations - avoid too many operations in one transaction, especially for schema and data migrations
Timeouts
Use timeouts:
- SET lock_timeout TO '2s'
- SET statement_timeout TO '2s'
Be careful with global statement_timeout for CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY or ALTER TABLE VALIDATE CONSTRAINT (disable statement_timeout for them).
Deadlocks
Avoid too many operations in one transaction for schema migrations, especially for FOREIGN KEYS in active used tables (FOREIGN KEY constraint changes take ACCESS EXCLUSIVE lock for two tables).
Multiversion Concurrency Control
How transactions work.
Isolation levels.
Row user and hidden data (xmin, xmax).
- INSERT - create new row
- DELETE - mark row as dead
- UPDATE - mark previous row as dead and create new row
- dead rows will be free in AUTO VACUUM
- schema only changes do not change table rows data
Data Types Casting
rewrite whole table, except case
when data stored same way and do not lose precision:
- VARCHAR/TEXT
- DECIMAL
Row-level Locks

Use chunk changes for data migrations and business logic
Create/Drop Table
CREATE SEQUENCE,
DROP SEQUENCE,
CREATE TABLE,
DROP TABLE
- do not have conflict with business logic,
except dropping tables with FOREIGN KEYs
Add/Drop Column
ALTER TABLE ADD COLUMN (without
DEFAULT/NOT NULL/PRIMARY KEY/UNIQUE),
ALTER TABLE DROP COLUMN
- have ACCESS EXCLUSIVE lock, but change only schema
For DEFAULT/NOT NULL/PRIMARY KEY/UNIQUE add column and then add DEFAULT/constraint.
ALTER TABLE ADD COLUMN DEFAULT better in PG 11, but no luck with django.

Alter Column
ALTER TABLE ALTER COLUMN TYPE
- rewrite table, so better create new table and copy data, except:
- varchar(LESS) to varchar(MORE) or text
- numeric(LESS, SAME) to numeric(MORE, SAME)
ALTER TABLE ALTER COLUMN SET NOT NULL
- check whole table, can be replaced with CHECK IS NOT NULL
ALTER TABLE ALTER COLUMN DROP NOT NULL,
ALTER TABLE ALTER COLUMN SET DEFAULT,
ALTER TABLE ALTER COLUMN DROP DEFAULT
- have ACCESS EXCLUSIVE lock, but change only schema
Check/FK Constraints
ALTER TABLE ADD CONSTRAINT CHECK,
ALTER TABLE ADD CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY
- check whole table, but can be declared with NOT VALID keyword
and then validated with ALTER TABLE VALIDATE CONSTRAINT,
that do not have conflict with business logic
ALTER TABLE ADD CONSTRAINT CHECK NOT VALID,
ALTER TABLE ADD CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY NOT VALID,
ALTER TABLE DROP CONSTRAINT CHECK,
ALTER TABLE DROP CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY
- have ACCESS EXCLUSIVE lock, but change only schema
Indexes
CREATE INDEX
- lock table for write,
but can be replaced with CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY,
that do not have conflict with business logic
DROP INDEX
- have ACCESS EXCLUSIVE lock, but change only schema,
also can be replaced with DROP INDEX CONCURRENTLY,
that do not have conflict with business logic
Index Constraints
ALTER TABLE ADD CONSTRAINT PRIMARY KEY,
ALTER TABLE ADD CONSTRAINT UNIQUE
- create index under the hood,
but index can be created with CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY
and then constraints created with USING INDEX keyword
ALTER TABLE ADD CONSTRAINT PRIMARY KEY USING INDEX,
ALTER TABLE ADD CONSTRAINT UNIQUE USING INDEX,
ALTER TABLE DROP CONSTRAINT PRIMARY KEY,
ALTER TABLE DROP CONSTRAINT UNIQUE
- have ACCESS EXCLUSIVE lock, but change only schema
Hard to Support
ALTER TABLE SET TABLESPACE
- physically move data,
so better create new table and copy data
ALTER TABLE RENAME TO,
ALTER TABLE RENAME COLUMN
- change only schema, but hard to write logic
that support schema before, on and after schema changes,
so better create new table/column and copy data
Create new table/column and copy data is a good solution when your DB does not support so cool migrations like postgres.

Thanks
Zero Downtime Migrations for Postgres on Django
By Pavel Tyslacki
Zero Downtime Migrations for Postgres on Django
- 1,017



