Symfony Components

Part 1
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/index.html
Agenda
- Polyfills
- Finder
- ExpressionLanguage
- Serializer
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/index.html
Polyfils
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/polyfill_php71.html
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/polyfill_php72.html
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/polyfill_php73.html
Polyfils
- Polyfill / PHP 7.1 Component
- is_iterable(mixed $var): bool
- Polyfill / PHP 7.2 Component
- spl_object_id(object $obj): int
- utf_encode/decode(string $data): string
- stream_isatty(resource $stream): bool
- Polyfill / PHP 7.3 Component
- is_countable(mixed $var): bool
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/polyfill_php71.html
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/polyfill_php72.html
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/polyfill_php73.html
Finder
The Finder component finds files and directories via an intuitive fluent interface.
~Symfony doc.
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/finder.html
class Finder implements \IteratorAggregate, \Countable
{
// Creation
create() : Finder
// \IteratorAggregate implementation
getIterator(): \Iterator
// \Countable implementation
count(): int
// File type restriction
directories(): self
files(): self
ignoreUnreadableDirs(): self
ignoreDotFiles(bool): self
ignoreVCS(bool): self
addVCSPattern(string|string[]): self
// Filters
depth(string|string[]): self
date(string|string[]): self
{not}name(string|string[]): self
{not}contains(string|string[]): self
{not}path(string|string[]): self
size(string|int|string[]|int[]): self
exclude(string|string[]): self
filter(Closure): self
//Sorters
sortBy{Name|Type|AccessedTime|ChangedTime|Modified}(): self
sort(Closure): self
// Result
in(string|string[]): self
followLinks(): self
append(\Iterator)
hasResult(): bool
}https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/finder.html
Example: Log Rotator Cleaner
/
log/
2017/
01/
01/
log.log
02/
log.log
02/
01/
log.log
02/
log.log
[..]
2018/
01/
01/
log.log
02/
log.log
02/
01/
log.log
02/
log.log<?php
require vendor/autoload.php;
use Symfony\Component\Finder\Finder;
$finder = Finder::create()
->in('/log/')
->date("until 90 days ago")
->sort(function(\SplFileInfo $left, \SplFileInfo $right): int {
return - (strlen($left->getPathname()) <=> strlen($right->getPathname()));
})
;
// @var SplFileinfo $fileInfo
foreach ($finder as $fileInfo) {
if ($fileInfo->isDir()) {
echo $fileInfo.PHP_EOL;
@rmdir($fileInfo);
continue();
}
echo $fileInfo.PHP_EOL;
@unlink($fileInfo);
}
/*
/log/2017/01/01/log.log
/log/2017/01/02/log.log
[..]
/log/2018/04/30
/log/2018/04
/log/2018
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/finder.html
Expression Language
Expression Language component is a perfect candidate for the foundation of a business rule engine. [...] without introducing security problems
~Symfony Doc
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/expression_language.html
ExpressionLanguage
<?php
require 'vendor/autoload.php';
use Symfony\Component\ExpressionLanguage\ExpressionLanguage;
$expressionLanguage = new ExpressionLanguage();
var_dump($expressionLanguage->evaluate('1 + 2')); // displays 3
var_dump($expressionLanguage->compile('1 + 2')); // displays (1 + 2)https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/expression_language.html
Example
$expressionLanguage = new ExpressionLanguage();
//1
var_dump($expressionLanguage->evaluate(
'life + universe + everything',
array(
'life' => 10,
'universe' => 10,
'everything' => 22,
)
)); //42
//2
class User
{
public $name;
public function getName(): string { return $this->name;}
}
$user = new User();
$user->name = 'Paul';
var_dump($expressionLanguage->evaluate(
'user.name === user.getName()',
array(
'user' => $user,
)
)); //truehttps://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/expression_language.html
Possible Operators
Arithmetic Operators
- + (addition)
- - (subtraction)
- * (multiplication)
- / (division)
- % (modulus)
- ** (pow)
Bitwise Operators
- & (and)
- | (or)
- ^ (xor)
Logical Operators
-
not or !
-
and or &&
-
or or ||
Comparison Operators
-
== (equal)
-
=== (identical)
-
!= (not equal)
-
!== (not identical)
-
< (less than)
-
> (greater than)
-
<= (less than or equal to)
-
>= (greater than or equal to)
-
matches (regex match)
Functions
-
constant(constName)
String Operators
~ (concatenation)
Array Operators
in[] (contain)
not in[] (does not contain)
Numeric Operators
1..9 (range)
Ternary Operators
foo ? 'yes' : 'no'
foo ?: 'no' (equal to foo ? foo : 'no')
foo ? 'yes' (equal to foo ? 'yes' : '')
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/expression_language.html
Extending the ExpressionLanguage
use Symfony\Component\ExpressionLanguage\ExpressionLanguage;
$expressionLanguage = new ExpressionLanguage();
$expressionLanguage->register('lowercase', function ($str) {
return sprintf('(is_string(%1$s) ? strtolower(%1$s) : %1$s)', $str);
}, function ($arguments, $str) {
if (!is_string($str)) {
return $str;
}
return strtolower($str);
});
var_dump($expressionLanguage->evaluate('lowercase("HELLO")'));
// this will print: hellohttps://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/expression_language.html
Using Expression in validation
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Mapping\ClassMetadata;
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Constraints as Assert;
class BlogPost
{
public static function loadValidatorMetadata(ClassMetadata $metadata)
{
$metadata->addConstraint(new Assert\Expression(p
'expression' =>
'this.getCategory() in ["php", "symfony"] or !this.isTechnicalPost()',
'message' =>
'If this is a tech post, the category should be either php or symfony!',
]));
$metadata->addPropertyConstraint('isTechnicalPost', new Assert\Expression([
'expression' => 'this.getCategory() in ["php", "symfony"] or value == false',
'message' => 'If this is a tech post, the category should be either php or symfony!',
]));
}
}
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/expression_language.html
Using Expression in validation
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<constraint-mapping xmlns="http://symfony.com/schema/dic/constraint-mapping"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://symfony.com/schema/dic/constraint-mapping http://symfony.com/schema/dic/constraint-mapping/constraint-mapping-1.0.xsd">
<class name="App\Model\BlogPost">
<constraint name="Expression">
<option name="expression">
this.getCategory() in ['php', 'symfony'] or !this.isTechnicalPost()
</option>
<option name="message">
If this is a tech post, the category should be either php or symfony!
</option>
</constraint>
<property name="isTechnicalPost">
<constraint name="Expression">
<option name="expression">
this.getCategory() in ['php', 'symfony'] or value == false
</option>
<option name="message">
If this is a tech post, the category should be either php or symfony!
</option>
</constraint>
</property>
</class>
</constraint-mapping>https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/expression_language.html
Using Expression in validation
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Constraints as Assert;
/**
* @Assert\Expression(
* "this.getCategory() in ['php', 'symfony'] or !this.isTechnicalPost()",
* message="If this is a tech post, the category should be either php or symfony!"
* )
*/
class BlogPost
{
/**
* @Assert\Expression(
* "this.getCategory() in ['php', 'symfony'] or value == false",
* message="If this is a tech post, the category should be either php or symfony!"
* )
*/
private $isTechnicalPost;
}https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/expression_language.html
Serializer
The Serializer component is meant to be used to turn objects into a specific format (XML, JSON, YAML, ...)
~Symfony Doc
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/serializer.html
Workflow
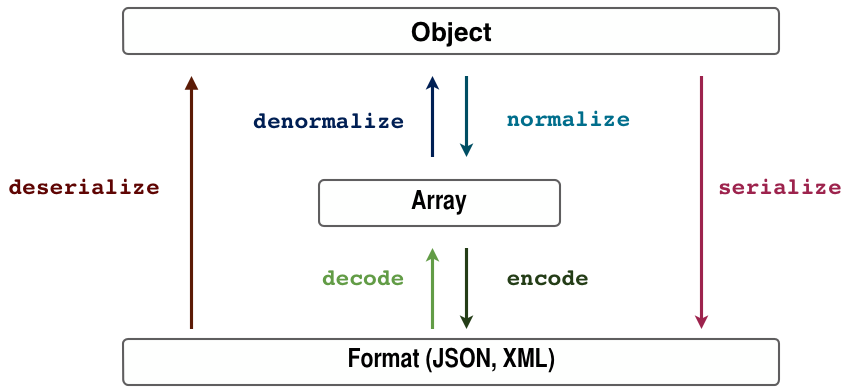
© Symfony Documentation, The Serializer Component
https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/serializer.html
Workflow
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Serializer;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Encoder\XmlEncoder;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Encoder\JsonEncoder;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Normalizer\ObjectNormalizer;
$encoders = array(new XmlEncoder(), new JsonEncoder());
$normalizers = array(new ObjectNormalizer());
$serializer = new Serializer($normalizers, $encoders);class Person
{
private $age;
private $name;
private $sportsperson;
private $createdAt;
/* Settters, getters, issers */
}$person = new Person;
$person->setName('foo');
$person->setAge(99);
$person->setSportsperson(false);
$jsonContent = $serializer->serialize(
$person,
JsonEncoder::FORMAT //json
);
/*
{
"name":"foo",
"age":99,
"sportsperson":false,
"createdAt":null
}
$data = <<<EOF
<person>
<name>foo</name>
<age>99</age>
<sportsperson>false</sportsperson>
</person>
EOF;
$newPerson = $serializer->deserialize(
$data,
Person::class,
XmlEncoder::FORMAT
);
$newPerson == $person //truehttps://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/serializer.html
Deserializing in an Existing Object
$person = new Person;
$person->setName('foo');
$person->setAge(99);
$person->setSportsperson(false);
$data = <<<EOF
<person>
<name>foo</name>
<age>69</age>
<sportsperson>1</sportsperson>
</person>
EOF;
$serializer->deserialize(
$data,
Person::class,
XmlEncoder::FORMAT,
['object_to_populate' => $person]
);
// $person = App\Model\Person(name: 'foo', age: '69', sportsperson: true)https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/serializer.html
Selecting specific attributes
$person = new Person;
$person->setName('foo');
$person->setAge(99);
$person->setSportsperson(false);
$serializer->normalize(
$person,
null,
['attributes' => ['name', 'age']]
);
// ['name' => 'foo', 'age' => 99]https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/serializer.html
Ignoring attributes
$normalizer = new ObjectNormalizer();
$normalizer->setIgnoredAttributes(array('age'));
$encoder = new JsonEncoder();
$serializer = new Serializer(array($normalizer), array($encoder));
$serializer->normalize(
$person
);
// ['name' => 'foo', 'sportsperson' => false]https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/serializer.html
Custom property names
$nameConverter = new class implements NameConverterInterface
{
public function normalize($propertyName)
{
return 'custom_'.$propertyName;
}
public function denormalize($propertyName)
{
return 'custom_' === substr($propertyName, 0, 7)
? substr($propertyName, 7) : $propertyName;
}
}
$normalizer = new ObjectNormalizer(null, $nameConverter);
$serializer = new Serializer(array($normalizer), array(new JsonEncoder()));
$json = $serializer->serialize($person, 'json');
// { "custom_name": "foo", "custom_age": 99, "custom_sportperson": false}
$serializer->deserialize($json, Company::class, 'json') == $person; // truehttps://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/serializer.html
Using Callbacks
$encoder = new JsonEncoder();
$normalizer = new GetSetMethodNormalizer(); // <-- Implments Normalizer only
$callback = function ($dateTime) {
return $dateTime instanceof \DateTime
? $dateTime->format(\DateTime::ISO8601)
: '';
};
$normalizer->setCallbacks(array('createdAt' => $callback));
$serializer = new Serializer(array($normalizer), array($encoder));
$person = new Person();
$person->setName('cordoval');
$person->setAge(34);
$person->setCreatedAt(new \DateTime('now'));
$serializer->serialize($person, 'json');
// Output: {"name":"foo", "age": 99, "sportperson": false, "createdAt": "2014-03-22T09:43:12-0500"}https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/serializer.html
XmlEncoder
['response' => ['foo' => [1, 2], 'bar' => true];
// <?xml version="1.0"?>
// <response>
// <foo>1</foo>
// <foo>2</foo>
// <bar>1</bar>
// </response>
['response' => ['foo' => ['@bar' => 'value']];
// is encoded as follows:
// <?xml version="1.0"?>
// <response>
// <foo bar="value" />
// </response>
['response' => ['foo' => ['@bar' => 'value'. '#' => 'baz']];
// is encoded as follows:
// <?xml version="1.0"?>
// <response>
// <foo bar="value">
// baz
// </foo>
// </response>https://symfony.com/doc/3.4/components/serializer.html
Symfony Components Part 1
By Paweł Radzikowski
Symfony Components Part 1
- 232



