A modular, extensible and flexible tool to build, monitor and report nextflow pipelines
C I Mendes
@ines_cim

cimendes




Enables scalable and reproducible scientific workflows using software containers. It simplifies the deployment of complex parallel and reactive workflows.
Reactive workflow framework
Programming DSL
Containerized
Create pipelines with asynchronous (and implicitly parallelized) data streams
Has it's own language for building a pipeline
Integration with container engines (Docker, Singularity, Shifter) out of the box
Nextflow | What is it?
Nextflow | Requirements
Requirements
- Bash
- Java 1.8
- Nextflow
Ubiquitous on UNIX. Windows: Cygwin or Linux subsystem... maybe...sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdkcurl -s https://get.nextflow.io | bashOptional (but recommended)
- Container engine (Docker, Singularity...)
Creation of Nextflow pipelines was designed for bioinformaticians familiar with programming.
Execution of Nextflow pipelines if for everyone
The motivation
The game changing combination of nextflow + containers:
- Fast pace of bioinformatics software landscape
- Continuous need for benchmarking and comparative analyses
- The need for agile and dynamic pipeline building
- Remove the pain of changing inner workings of workflows
- Portability
- Reproducible
- Scalability
- Multi-scale containerization
- Native cloud support
But substantial challenges persist:



The FlowCraft project
The premise:
Workflow based development
Component based development
Components are modular pieces of nextflow code with some basic rules:

Component A
- Input/Output
- Parameters
- Resources
Component B

- Input/Output
- Parameters
- Resources
The component
IN_adapters_{{ pid }} = Channel
.value(params.adapters{{ param_id }})
process fastqc2 {
tag { fastq_id }
input:
set fastq_id, file(fastq_pair) from {{ input_channel }}
val ad from IN_adapters
output:
set fastq_id, file(fastq_pair) into {{ output_channel }}
script:
template "fastqc.py"
}
{{ forks }}Nextflow template file
- Standard nextflow code (1 or more processes, channels, etc)
- Addition of placeholders that allow the engine to orchestrate components into a workflow
The component
class Fastqc(Process):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.input_type = "fastq"
self.output_type = "fastq"
self.params = {
"adapters": {
"default": "'None'",
"description":
"Path to adapters files, if any."
}
}
self.directives = {"fastqc2": {
"cpus": 2,
"memory": "'4GB'",
"container": "flowcraft/fastqc",
"version": "0.11.7-1"
}}Python declarative class
Specify input/output types so components can be connected
Add any number/type of parameters
Add process directives for one or more processes
And many other attributes that let you easily configure your component:
https://flowcraft.readthedocs.io/en/latest/dev/create_process.html#process-attributes
Crafting pipelines
With this framework, building workflows becomes simple:
flowcraft build -t 'trimmomatic fastqc spades pilon' -o my_nextflow_pipeline
Results in the following workflow DAG
$ nextflow run my_nextflow_pipeline.nf --help
N E X T F L O W ~ version 0.32.0
Launching `my_nextflow_pipeline.nf` [jovial_swirles] - revision: b4473f5a12
============================================================
F L O W C R A F T
============================================================
Built using flowcraft v1.4.0
Usage:
nextflow run my_nextflow_pipeline.nf
--fastq Path expression to paired-end fastq files. (default: fastq/*_{1,2}.*) (default: 'fastq/*_{1,2}.*')
Component 'INTEGRITY_COVERAGE_1_1'
----------------------------------
--genomeSize_1_1 Genome size estimate for the samples in Mb. It is used to estimate the coverage and other assembly parameters andchecks (default: 1)
--minCoverage_1_1 Minimum coverage for a sample to proceed. By default it's setto 0 to allow any coverage (default: 0)
Component 'TRIMMOMATIC_1_2'
---------------------------
--adapters_1_2 Path to adapters files, if any. (default: 'None')
--trimSlidingWindow_1_2 Perform sliding window trimming, cutting once the average quality within the window falls below a threshold (default: '5:20')
--trimLeading_1_2 Cut bases off the start of a read, if below a threshold quality (default: 3)
--trimTrailing_1_2 Cut bases of the end of a read, if below a threshold quality (default: 3)
--trimMinLength_1_2 Drop the read if it is below a specified length (default: 55)
--clearInput_1_2 Permanently removes temporary input files. This option is only useful to remove temporary files in large workflows and prevents nextflow's resume functionality. Use with caution. (default: false)
Component 'FASTQC_1_3'
----------------------
--adapters_1_3 Path to adapters files, if any. (default: 'None')
Component 'SPADES_1_4'
----------------------
--spadesMinCoverage_1_4 The minimum number of reads to consider an edge in the de Bruijn graph during the assembly (default: 2)
--spadesMinKmerCoverage_1_4 Minimum contigs K-mer coverage. After assembly only keep contigs with reported k-mer coverage equal or above this value (default: 2)
--spadesKmers_1_4 If 'auto' the SPAdes k-mer lengths will be determined from the maximum read length of each assembly. If 'default', SPAdes will use the default k-mer lengths. (default: 'auto')
--clearInput_1_4 Permanently removes temporary input files. This option is only useful to remove temporary files in large workflows and prevents nextflow's resume functionality. Use with caution. (default: false)
--disableRR_1_4 disables repeat resolution stage of assembling. (default: false)
Component 'ASSEMBLY_MAPPING_1_5'
--------------------------------
--minAssemblyCoverage_1_5 In auto, the default minimum coverage for each assembled contig is 1/3 of the assembly mean coverage or 10x, if the mean coverage is below 10x (default: 'auto')
--AMaxContigs_1_5 A warning is issued if the number of contigs is overthis threshold. (default: 100)
--genomeSize_1_5 Genome size estimate for the samples. It is used to check the ratio of contig number per genome MB (default: 2.1)
Component 'PILON_1_6'
---------------------
--clearInput_1_6 Permanently removes temporary input files. This option is only useful to remove temporary files in large workflows and prevents nextflow's resume functionality. Use with caution. (default: false)Help and parameters tailor-made to the pipeline
Crafting pipelines
It's easy to get experimental:
flowcraft build -t 'trimmomatic fastqc skesa pilon' -o my_nextflow_pipeline
Switch spades for skesa
flowcraft build -t 'trimmomatic fastqc skesa pilon (abricate | prokka)' -o my_nextflow_pipelineAdd genome annotation components in the end

Crafting pipelines
It's easy to get wild:
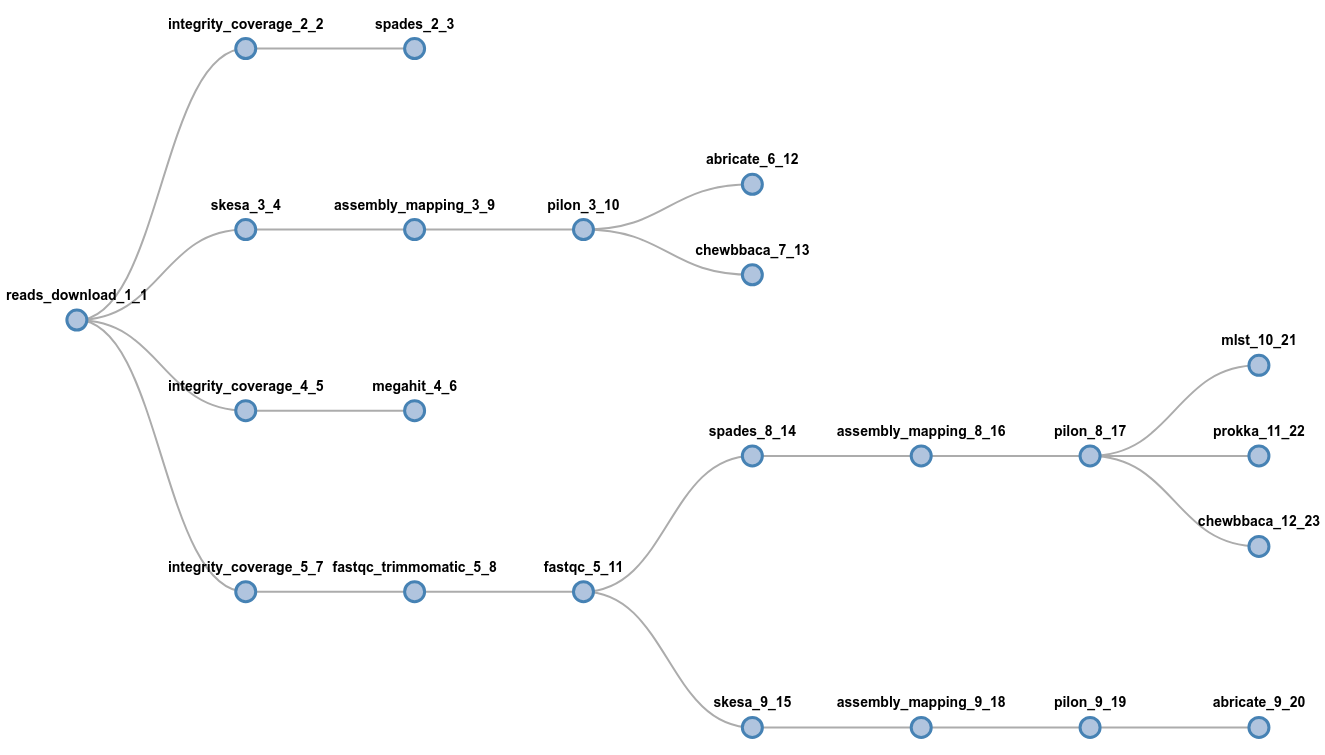
flowcraft build -t 'reads_download (
spades | skesa pilon (abricate | chewbbaca) | megahit |
fastqc_trimmomatic fastqc (spades pilon (
mlst | prokka | chewbbaca) | skesa pilon abricate))' -o my_nextflow_pipelinewait, what?
More building features
Forks
Connect one component to multiple
Secondary channels
Connect non-adjacent components
Extra inputs
Inject user input data anywhere
Recipes
Curated and pre-assembled pipelines for specific needs
Workflow live monitoring
Tracks execution in real time
Minimal requirements for general nextflow pipelines
Workflow live reports
Dynamic generation of interactive report page
Reports can be updated live or viewed at the end of the run
The future
Multiple Raw Input Types
Not limited to paired-end FastQ or Fasta
Dynamic Input in Components
One component, multiple inputs
Expand Building Features
New merge operators
- Component that receives multiple input types
- Component that merges multiple inputs from different branches




Diogo N Silva
Tiago F Jesus
Inês Mendes
Bruno
Ribeiro-Gonçalves
Core developers

Advisors
Prof. Mário Ramirez

Prof. João André Carriço
The team

Thank you for your attention
and happy pipeline building
Join the fun!



conda install flowcraftpip install flowcraftFCT PhD Grant SFRH/BD/129483/2017
Funding and Acknowledgements






Copy of CBBS 2019 - FlowCraft
By Pedro Cerqueira
Copy of CBBS 2019 - FlowCraft
Slide presentation for the Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Seminars about FlowCraft
- 413



