The Semantic Web
Presented By:
Piyush Agarwal
Masters of Computer Science
University of North Carolina at Greensboro
"Remember the parable about the man who built his house on sand? Or the pigs who made their houses out of straw and sticks?
LOSERS
They lost because they didn't put enough value on the importance of STRUCTURE"
as cited by Peter Gasston in his book 'The Modern Web'
Structure before Semantics
- Structure is the most important feature of a website and on the Web that starts with the use of good HTML.
- The ways one marks-up his web pages gives them a solid structure both now and in the future.
- A Solid structure, makes your website more accessible and easy to manage and maintain.
Example
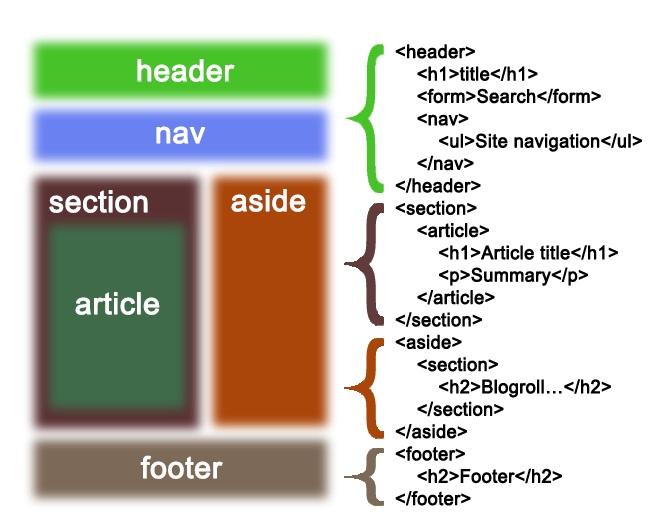
Semantics
- Beyond simple structure lies the richness of a good Semantic;
- Semantic means to give your web page content and extra meaning which is very beneficial;
- Some benefits of Semantics include:
- Better understanding of the page for anyone
- Easier for search-engines to crawl and understand your data
- Long-term benefits, which are still hidden
- The Semantic Web is a collaborative movement led by international standards body the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) which promotes common data formats on the World Wide Web.
- By encouraging the inclusion of semantic content in web pages, the Semantic Web aims at converting the current web, dominated by unstructured and semi-structured documents into a "web of data".
- The Semantic Web stack builds on the W3C's Resource Description Framework (RDF).
citation - Wikipedia: Semantic Web
Resource Description Framework (RDF)
- RDF is a family of W3C specifications which was originally designed as a metadata data model.
- It has come to be used as a general method for conceptual description or modeling of information that is implemented in web resources, using a variety of syntax notations and data serialization formats.
- RDF is based upon the idea of making statements about the resource, especially web-resource, in the form of subject-predicate-object expressions
RDF (Contd...)
- Subject denotes the resource; Predicate denotes traits or aspects of the resource and expresses a relationship between the Subject and the Object .
- Example - one way to represent the notion "The basket-ball is round in shape" in RDF is as the triple: a subject denoting "the basket-ball", a predicate denoting "the shape", and an object denoting "round".
- The same example above can also be represented in the classical notation of entity-attribute-value model as entity (basket-ball), attribute (shape) and value (round).
- The RDF Vocabulary
Importance of Semantics
"Our boat is safely anchored by the shore,
And there will safely ride when we are gone;
The flowering shrubs that deck our humble door
Will prosper, though untended and alone:
Fields, goods, and far-off chattels we have none:
These narrow bounds contain our private store
Of things earth makes, and sun doth shine upon;
Here are they in our sight--we have no more."
-William Wordsworth - A Farewell
- We know that the above is a paragraph from the poem 'A Farewell' but the search engine does not knows it because the word Farewell is never mentioned in the paragraph.
Semantics with HTML
- Created by Grassroots Coalition of Developers
- Add extra meaning to content through standardized markup patterns using existing HTML attributes
-
Example:
<div class="vcard">
<p><a href="https://www.facebook.com/piyushagarwal11" class="url fn">Piyush Agarwal</a>
is a student at <a href="http://uncg.edu" class="url org">UNCG</a>.</p>
</div> -
A crawler which recognizes the hcard pattern will see the vcard class and know that the content inside is the information for the person it is looking for. First link contains the full name(fn) of the contact and the second link contains the organization(org) the contact is related to
Semantics with HTML(Contd...)
- Is an extension of HTML which provides context to content using a whole new set of attributes.
- Relies on a predefined schema to describe the content.
- Example:
- The value of the attribute is the URL of the relevant description of the term "creator" from a schema which is part of a standardized vocabulary known as Dublin Core.
<p property="http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/creator">Piyush Agarwal</p>Semantics with HTML5
- HTML5 has addressed the semantic issue with the creation of a simple syntax called the Microdata.
- A series of name-value pairs that provide meaningful machine-readable data
- Example:
- We can test our semantic on the Google's Structured Data Testing Tool.
<p itemscope>Hello, my name is <span itemprop="given-name">Piyush</span>
and I'm<span itemprop="role"> a student</span> at <span itemprop="university">UNCG</span>.
</p>What should I use?
-
One can use any of the three Semantic types, which he/she is comfortable with, but I prefer Microdata.
- The reason for this preference is that it is widely accepted on Web so one can get the web page content easily noticed and promoted by search engines.
- In 2011 four big Web Giants - Google, Microsoft, Yahoo! and Yandex - launched a new Website, Schema.org, which introduced a set of shared vocabularies for marking up common patterns using microdata.
Conclusion
- A well-structured web page makes it easy to maintain it.
- Semantics provide meaning to the content on the web page so that it is easily understood by Search Engines as well as a user
- Semantic Web is a collaborative movement started by W3C
- We can use RDF, Microformat, RDFa and Microdata for providing Semantic to our web-content
- Schema.org is a website built by four big Web Giants which provides shared vocabularies which help in adding semantics
The Semantic Web
By Piyush Agarwal
The Semantic Web
An Introduction to the Semantic Web
- 1,288
