
Part-1
Agenda
- Introduction about Kafka
- Kafka Core Components
- Kafka Setup in local machine
- Redpanda/Conduktor tool
- Simple Use case: pub-sub
- Retry Use Case
- Reflow Use Case
- Reflow with Retry Use case
What is Kafka?
-
Apache Kafka is a Message Broker. -
Kafka is a middleman between producers and the consumers. -
Apache Kafka is an open-source distributed publish-subscribe messaging platform that has been purpose-built to handle real-time streaming data for distributed streaming, pipelining, and replay of data feeds for fast, scalable operations. -
Apache Kafka is a horizontally scalable, fault-tolerant, distributed steaming platform.
Producers
- Producers are the publisher of messages to one or more Kafka topics. Producers send data to Kafka brokers. Every time a producer publish a message to a broker, the broker simply appends the message to the last segment file. Actually, the message will be appended to a partition. Producer can also send messages to a partition of their choice.
- When the new broker is started, all the producers search it and automatically sends a message to that new broker.
- Kafka producer doesn’t wait for acknowledgements from the broker and sends messages as fast as the broker can handle.
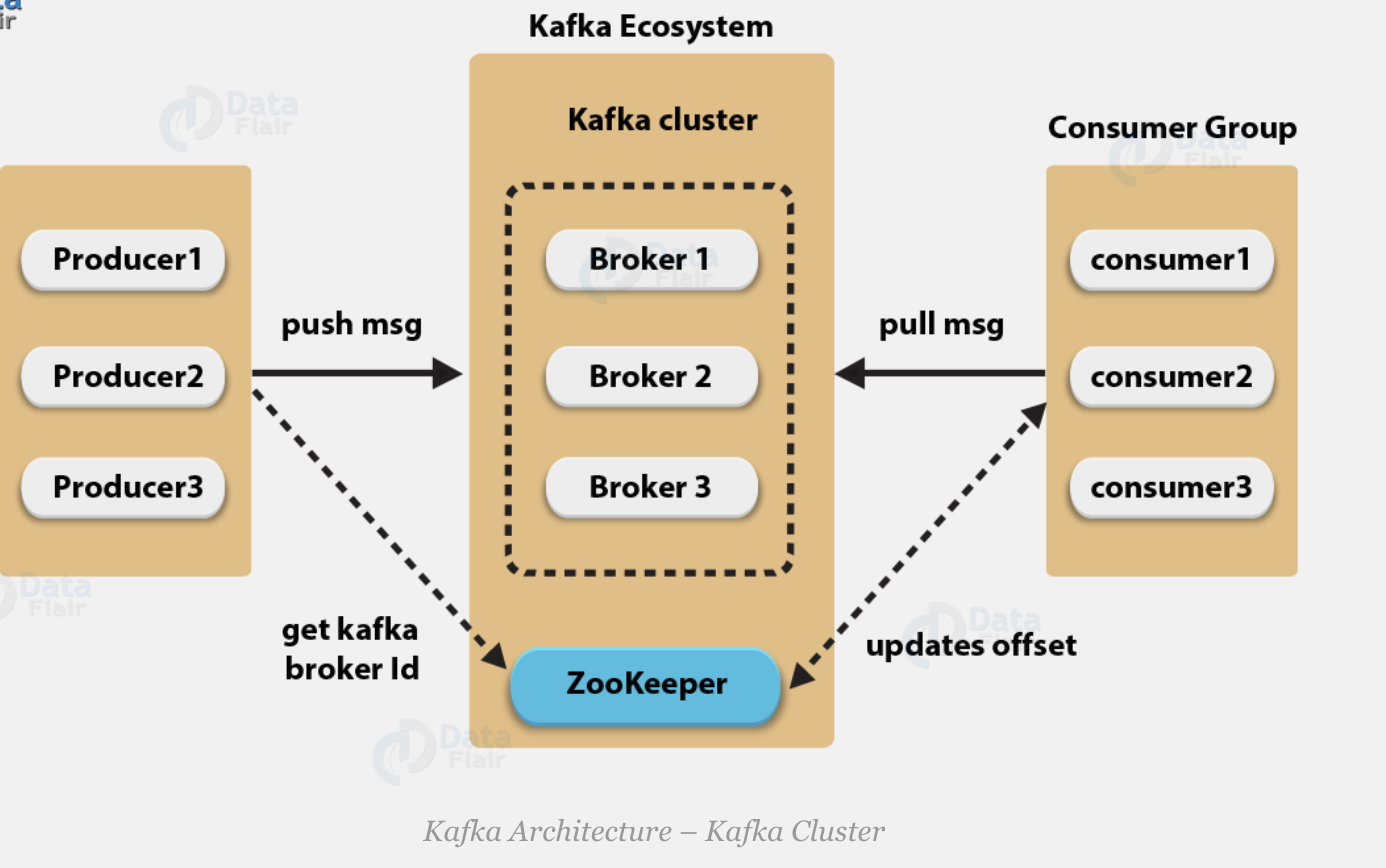
- Kafka cluster typically consists of multiple brokers to maintain load balance.
- Kafka brokers are stateless, so they use ZooKeeper for maintaining their cluster state.
- One Kafka broker instance can handle hundreds of thousands of reads and writes per second and each bro-ker can handle TB of messages without performance impact.
Kafka Broker

Consumers
-
Consumers read data from brokers. Consumers subscribes to one or more topics and consume published messages by pulling data from the brokers -
Since Kafka brokers are stateless, which means that the consumer has to maintain how many messages have been consumed by using partition offset. -
If the consumer acknowledges a particular message offset, it implies that the consumer has consumed all prior messages. -
The consumers can rewind or skip to any point in a partition simply by supplying an offset value. Consumer offset value is notified by ZooKeeper.

- Kafka Cluster: a Cluster is nothing but a group of brokers that work together to share the workload. And that’s how Kafka becomes a distributed and scalable system.
- ZooKeeper is used for managing and coordinating Kafka broker.
- ZooKeeper service is mainly used to notify producer and consumer about the presence of any new broker in the Kafka system or failure of the broker in the Kafka system.
- As per the notification received by the Zookeeper regarding presence or failure of the broker then pro-ducer and consumer takes decision and starts coordinating their task with some other broker.

Kafka Components
- Topics
- partitions
- partitions offset
- Replicas of partitions
Topic
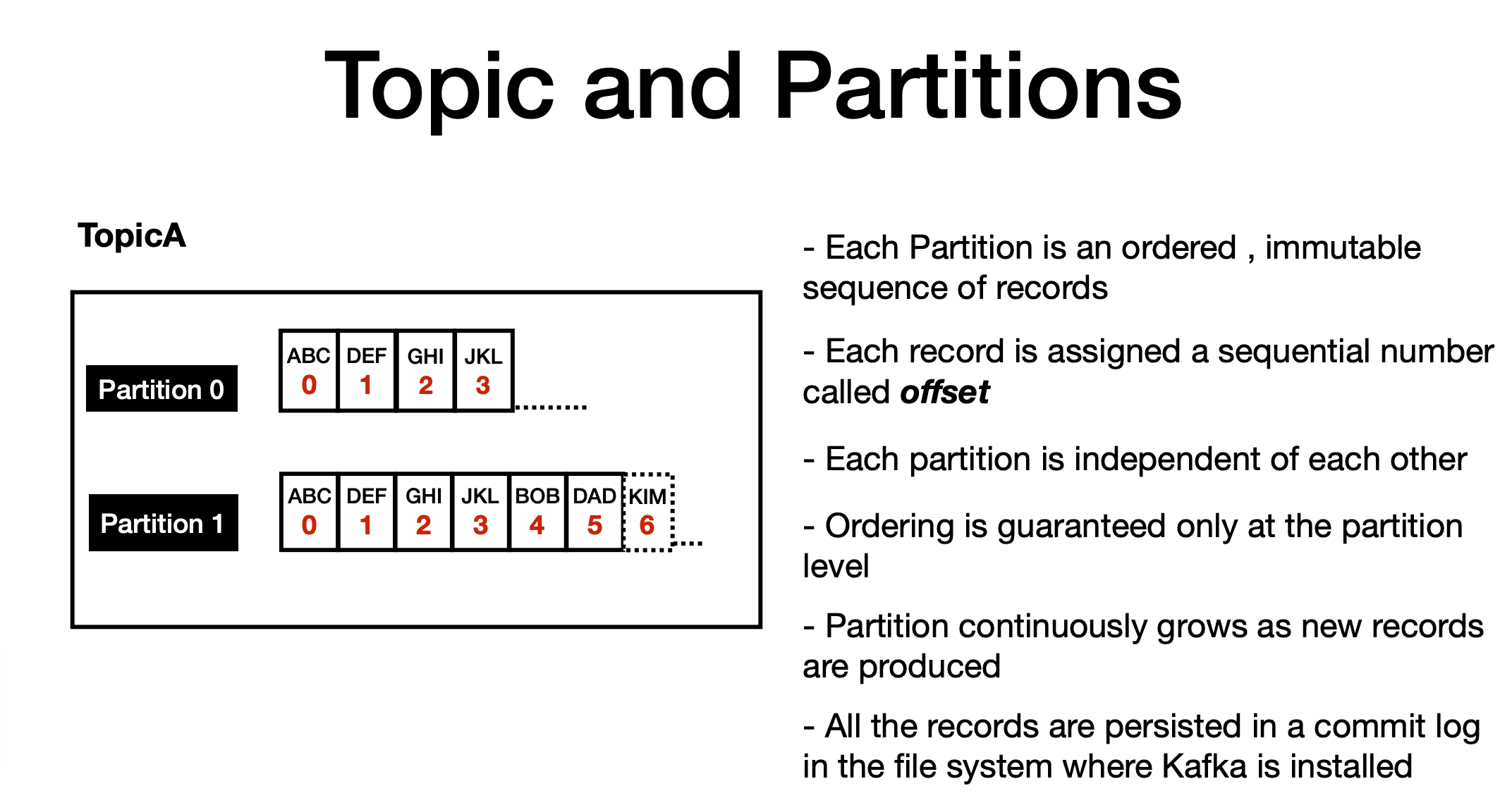
- A stream of messages belonging to a particular category is called a topic. Data is stored in topics.
-
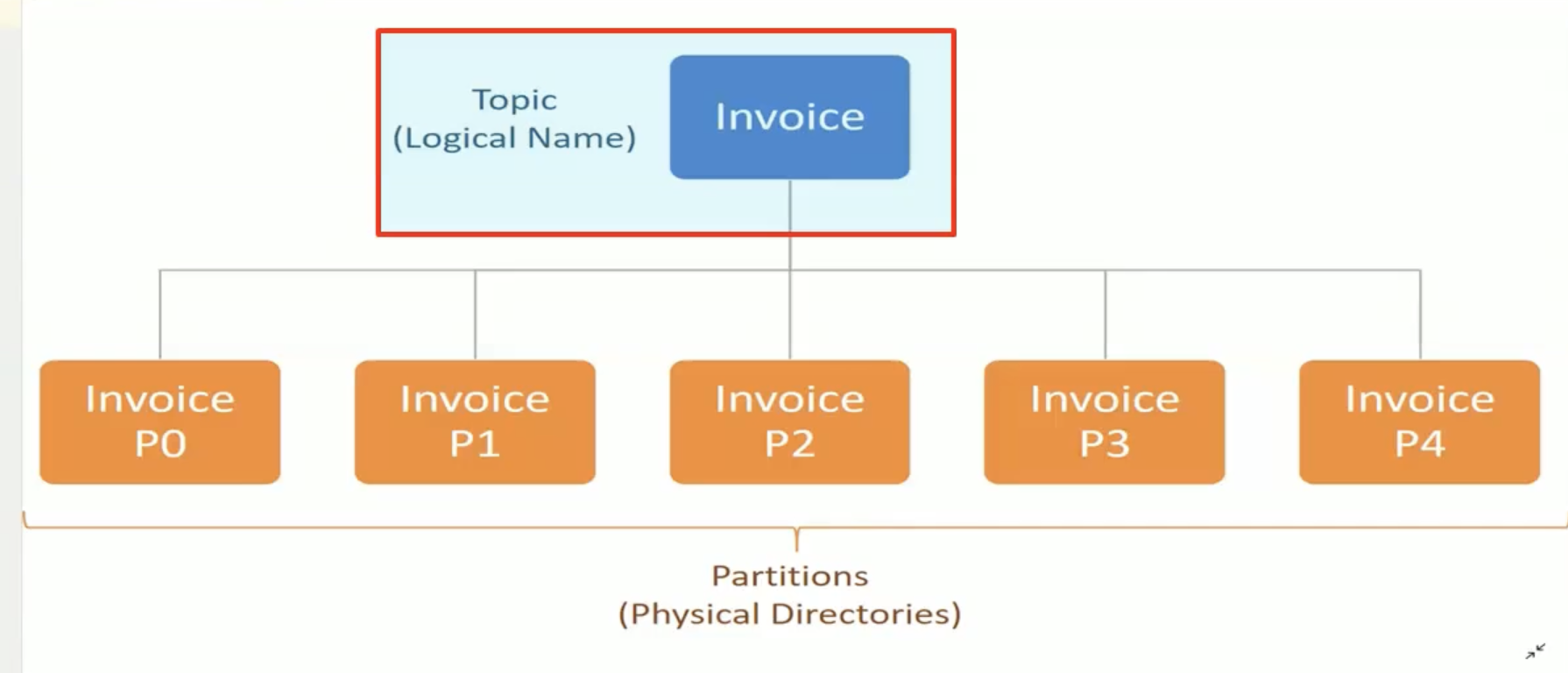
or A Topic is a Logical Name to group messages.like in your database , you must create a table to store your data records.
In Kafka , you must create topic to store messages - Topics are split into partitions.
- For each topic, Kafka keeps a mini-mum of one partition. Each such partition contains messages in an immutable ordered sequence.
- A partition is implemented as a set of segment files of equal sizes.



Kafka Setup
- Install Docker
- Download docker-compose file
- run docker-compose up command
- after 1 min, Kafka Cluster should be up and running
- Download RedPanda/conductor GUI tool for Kafka Cluster
- Now Go ahead with Sample Application
Kafka GUI tool
- Conductor
- RedPanda
Pub-sub Message Flow Demo
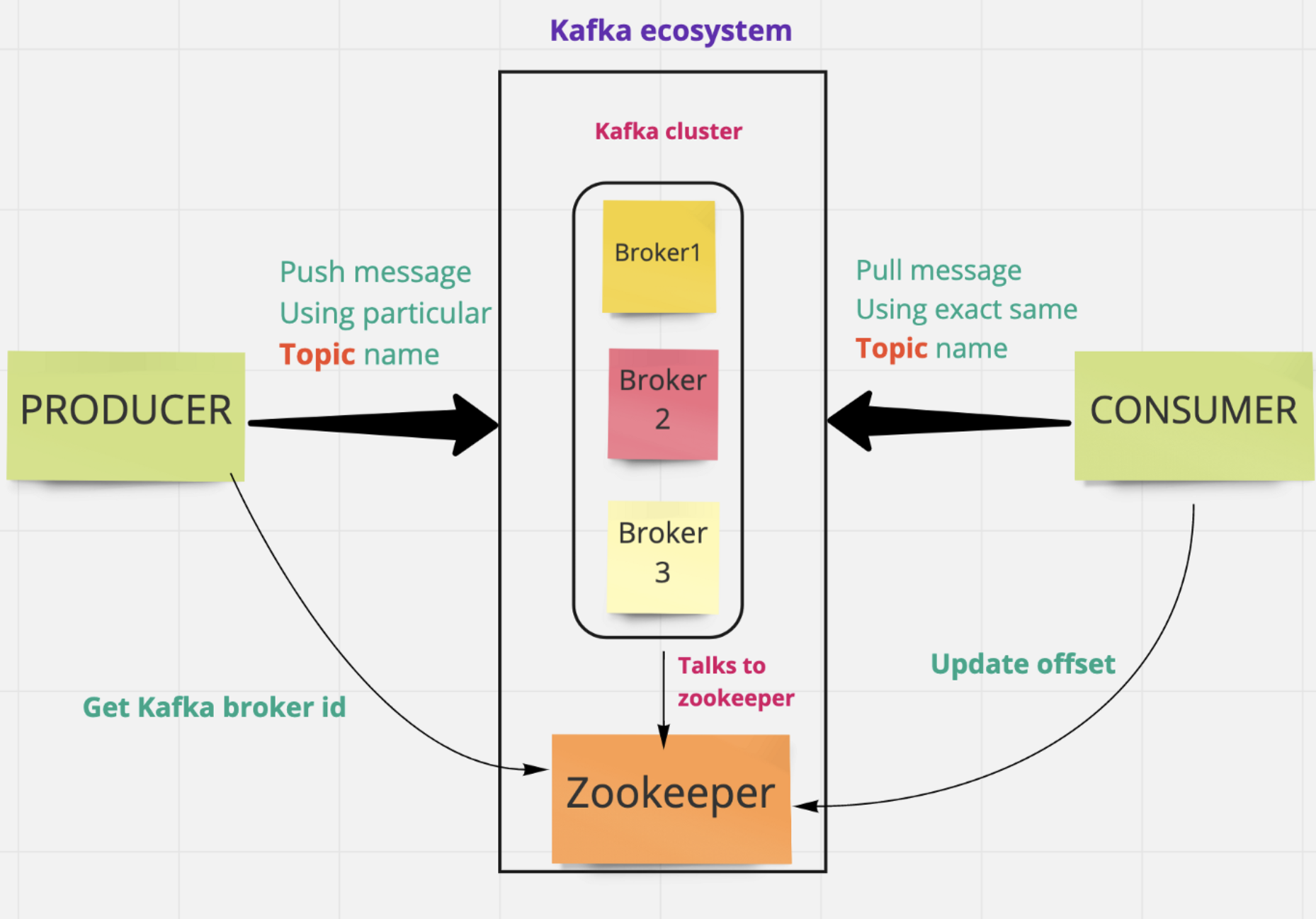
Workflow of Pub-Sub Messaging
-
Producers send message to a topic at regular intervals or as per your business needs. -
Kafka broker stores all messages in the partitions configured for that particular topic. It ensures the messages are equally shared between partitions. If the producer sends two messages and there are two partitions, Kafka will store one message in the first partition and the second message in the second partition. -
Consumer subscribes to a specific topic. -
Once the consumer subscribes to a topic, Kafka will provide the current offset of the topic to the consumer and also saves the offset in the Zookeeper ensemble. -
Consumer will request the Kafka in a regular interval (like 100 Ms) for new messages. -
Once Kafka receives the messages from producers, it forwards these messages to the consumers. -
Consumer will receive the message and process it. -
Once the messages are processed, consumer will send an acknowledgement to the Kafka broker. -
Once Kafka receives an acknowledgement, it changes the offset to the new value and updates it in the Zookeeper. Since offsets are maintained in the Zookeeper, the consumer can read next message correctly even during server outrages. -
This above flow will repeat until the consumer stops the request. -
Consumer has the option to rewind/skip to the desired offset of a topic at any time and read all the subsequent messages.
-
This above flow will repeat until the consumer stops the request.
-
Consumer has the option to rewind/skip to the desired offset of a topic at any time and read all the subsequent messages.
Retry Use Case flow
Replay or Reflow Usecase
Thank you
Kafka Part-1
By Product Engineer
Kafka Part-1
- 136
