Introduction to Serverless in Amazon Web Services
Piotr Grzesik
Agenda
- Amazon Web Services
- What do we define as "serverless"?
- AWS Lambda
- API Gateway
- SQS
- EventBridge
- SNS
- DynamoDB
- Cognito
- S3
Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services is a Cloud Computing platform from Amazon. It was introduced in March 2006, offering at first only three services (Amazon Simple Storage Service, Amazon Simple Queue Service, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud), while as of 2025 it's offering more than 300 different services in domains such as Compute, Storage, Database, Migration, Network and Content Delivery, Management Tools, Messaging, Security, Identity & Compliance
Czym jest "serverless"?
Serverless is a cloud-architecture model in which a user can run applications or services without having to manage the underlying infrastructure, typically paying only for actual usage (“pay-per-use”).
Pros of serverless
-
No need for manual infrastructure management
-
“Infinite” scalability
-
High availability
-
Automatic environment adjustment to current traffic
-
Greater focus on the application’s business logic
-
Pay-per-use billing model
Cons of Serverless
-
Performance limitations of individual instances
-
Difficult testing, debugging, and monitoring
-
Solution complexity due to distributed processing
-
Vendor lock-in
-
Pay-per-use billing model
Example use cases for Serverless
-
Image processing (e.g., in response to an image upload)
-
Reacting to database changes (e.g., change auditing)
-
Processing IoT sensor readings (e.g., temperature data from sensors)
-
Stream processing (e.g., handling message streams from multiple applications)
-
Executing scheduled actions (e.g., performing backups)
-
REST or GraphQL APIs (e.g., web applications)
When serverless might not be the best choice
-
Applications that demand very low latency (e.g., trading systems)
-
Applications with high, highly predictable traffic (e.g., batch processing of fixed data sets)
-
Applications requiring hardware acceleration (e.g., training machine-learning models)
-
Long-running tasks (e.g., a job that runs for more than an hour and cannot be easily decomposed)
AWS Lambda
-
Serverless compute platform
-
Natively supports runtimes such as Python, Node.js, .NET, and Java, plus any custom runtime
-
Pay-per-use billing model
-
Execution time limit – 15 minutes
-
Maximum available memory of 10,240 MB and 6 vCPUs per single instance
-
Easy integration with other AWS services such as SQS, API Gateway, and S3
Model AWS Lambda
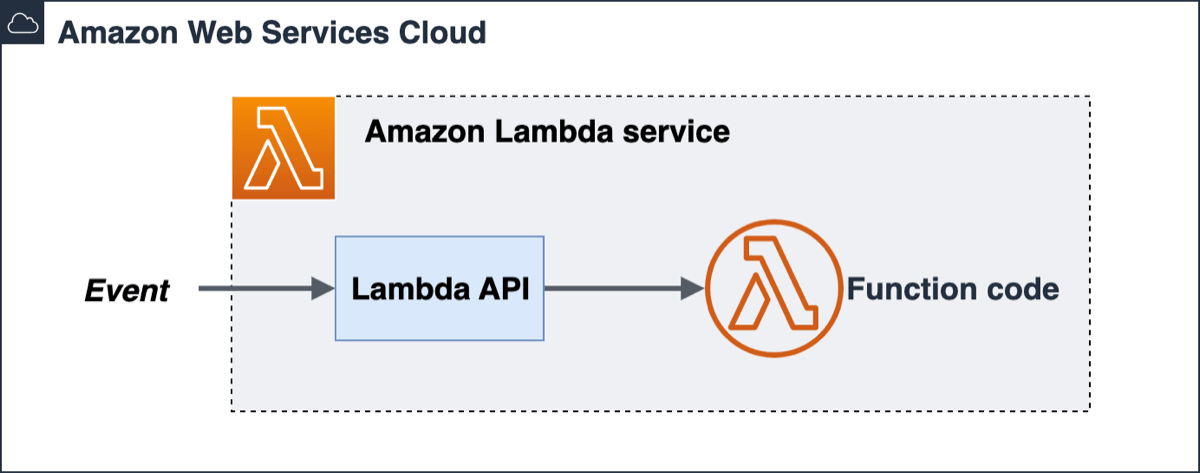
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/images/serverless/latest/devguide/images/s_lambda/lambda-arch-overview.png
Event sources supported by AWS Lambda
- Amazon API Gateway
- Amazon SQS
- Amazon S3
- Amazon SNS
- Amazon EventBridge
- Amazon DynamoDB
- ... and many more
Live Demo
Amazon API Gateway
-
Service for creating and managing APIs
-
Automatically scalable, supporting thousands of concurrent connections
-
Provides API authentication/authorization support
-
Integrates with various AWS services, including AWS Lambda
-
Allows versioning and defining “stages” for an API
Live Demo
Amazon S3
-
Service that provides disk space for storing files (object storage)
-
Supports multiple storage classes that differ in price, durability, and data-access speed
-
Offers automatic file-lifecycle rules (e.g., deletion after 30 days)
-
Can be used as an event source for Lambda functions
Live Demo
Amazon SQS
-
Queue service for sending messages between services
-
Provides support for FIFO (First In, First Out) queues
-
Requires no management or manual scaling
-
Allows messages to be retained in the queue for up to 14 days
Live Demo
Amazon EventBridge
-
Service that provides an event bus between services
-
Allows multiple applications to react to an event simultaneously
-
Supports advanced message-filtering rules
-
Offers persistence and the ability to replay events
-
Supports scheduling events for execution at a specified time (cron-like)
-
Does not guarantee event-processing order
Live Demo
Amazon SNS
-
Service that enables message exchange between publishers and subscribers
-
Based on asynchronous communication through “topics”
-
Supports the FIFO model
-
Limited message-filtering capabilities
-
Supports direct publishing of mobile push notifications
Live Demo
Amazon DynamoDB
-
Serverless NoSQL database, fully managed and scaled by AWS
-
Supports read/write operations with single-digit millisecond latency
-
Offers “on-demand” or “provisioned” billing models
-
Handles millions of requests per second
-
Enables reacting to table changes via DynamoDB Streams
-
Supports global data replication through global tables
Live Demo
Amazon Cognito
-
Service for managing users, authorization, and authentication
-
Lets users obtain temporary access to AWS services
-
Integrates with Facebook, Google, and other external identity providers
-
Supports SAML and OpenID Connect
-
Supports Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Live Demo
Example diagram of a serverless architecture

Popular frameworks for building serverless applications on AWS
- AWS SAM - https://aws.amazon.com/serverless/sam/
- SST - https://sst.dev/
- Serverless Framework - https://github.com/serverless/serverless
- Serverless.TF - https://serverless.tf/
- Architect - https://arc.codes/
- AWS CDK - https://aws.amazon.com/cdk/
Q&A + Contact
@p_grzesik
contact@pgrzesik.com
Introduction to Serverless in Amazon Web Services
By progressive
Introduction to Serverless in Amazon Web Services
- 157



