Pointer
指標
by一直想去搭伙署名的某江
1.
指標 pointer
2.
取址符 '&'
3.
指標變數
4.
取值符 '*'
5.
參考 reference
目錄
Pointer
定義說明:
指標,也就是位置
是電腦儲存東西的地方,
而這個地方的地址
用文言來說就是指標
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a;
cout<<&a;
return 0;
}
//0x7ffde917c584a的地址





Text
取址符'&'
顧名思義
是用來取資料的地址的
只要在你想要知道地址的資料前
簡單的加個'&'就可以囉!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b;
cout<<&a;//取得a的地址
cout<<"\n";
cout<<&b;//取得b的地址
return 0;
}
//0x7ffc0fc41130
//0x7ffc0fc41134指標變數
定義說明:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a;
int* p=&a;
cout<<p;
return 0;
}
//0x7ffc7919739c用來儲存指標的變數
也只能儲存指標喔!
如何宣告:
int* ap;
如何賦值:
int* ap = &a ;
int* -> 宣告指標變數
int型態a的位置
也要用int的指標變數
指標變數
定義說明:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a;
int* p=&a;
cout<<p;
return 0;
}
//0x7ffc7919739c用來儲存指標的變數
也只能儲存指標喔!
如何宣告:
int* ap;
如何賦值:
int* ap = &a ;
int型態a的位置
也要用int的指標變數
int* -> 宣告指標變數
Like This
a
0x7ffc7919739c
指標變數
Try Try See!
給你們5分鐘試試看喔!
凍凍腦
那有辦法在知道地址後
取得那個地址上的資料嗎?

當然是OK啦!
凍凍腦
那有辦法在知道地址後
取得那個地址上的資料嗎?

當然是OK啦!
取值符 '*'
顧名思義
就是用來取得地址上的資料(數值)
只要在你想取得數值的指標變數前
簡單的加個 ' * ' 就好囉!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=4;
int* ap = &a;
cout<<*ap;
return 0;
}
//4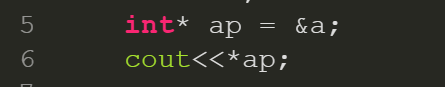



雙胞胎?
比較指標變數與取值符的 ' * '
指標變數:
取值符:
放在變數型態後
<ex> int* , float*
放在指標變數前
<ex> *ap
順帶一提
更改已取值的指標變數時,原變數的質也會被更改到
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=2;
int* p=&a;
cout<<a<<endl; //2
*p=5;
cout<<a<<endl; //5
return 0;
}Try to see see
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=2;
int* p=&a;
cout<<a<<endl;
cout<<&a<<endl;
cout<<*a<<endl;
cout<<*&a<<endl;
cout<<p<<endl;
cout<<*p<<endl;
cout<<&p<<endl;
return 0;
}See see answer
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=2;
int* p=&a;
cout<<a<<endl;
cout<<&a<<endl;
cout<<*a<<endl;
cout<<*&a<<endl;
cout<<p<<endl;
cout<<*p<<endl;
cout<<&p<<endl;
return 0;
}
//2
//0x7ffc7e112b9c
//error
//2
//0x7ffc7e112b9c
//2
//0x7ffc7e112ba0參考 reference
也就是幫變數娶小明
使他擁有另一個名字
指標跟陣列也都可以娶小明喔!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=2;
int &r=a;
int *p=&a;
int *&rp=p;
cout<<a<<endl;
cout<<r<<endl;
cout<<p<<endl;
cout<<rp<<endl;
return 0;
}
//2
//2
//0x7ffd358c5f1c
//0x7ffd358c5f1c語法:
原變數的型態 &小名=原變數;
like右邊
參考 reference
也就是幫變數娶小明
使他擁有另一個名字
指標跟陣列也都可以娶小明喔!
語法:
原變數的型態 &小名=原變數;
like右邊
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=2;
int &r=a;
int *p=&a;
int *&rp=p;
cout<<a<<endl;
cout<<r<<endl;
cout<<p<<endl;
cout<<rp<<endl;
return 0;
}
//2
//2
//0x7ffd358c5f1c
//0x7ffd358c5f1c也就是說他們是同個人喔!
也就代表改變參考的值,原本的值也會被改到喔!
但必須在設定變數時就告訴他那個小名代表的是誰
也就代表他們的位址是一樣的!
Like this
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=2;
int &r=a;
int *p=&a;
int *&rp=p;
cout<<a<<" "<<r<<endl; //2 2
r=66666;
cout<<a<<endl; //66666
cout<<r<<endl; //66666
cout<<rp<<" "<<p<<endl; //0x7ffdaa658928 0x7ffdaa658928
cout<<*rp<<" "<<*p<<endl; //66666 66666
int b=9;
rp=&b;
cout<<rp<<endl; //0x7ffdaa65892c
cout<<p<<endl; //0x7ffdaa65892c
cout<<*rp<<endl; //9
cout<<*p<<endl; //9
return 0;
}Like this
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=2;
int &r=a;
int *p=&a;
int *&rp=p;
cout<<a<<" "<<r<<endl; //2 2
r=66666;
cout<<a<<endl; //66666
cout<<r<<endl; //66666
cout<<rp<<" "<<p<<endl; //0x7ffdaa658928 0x7ffdaa658928
cout<<*rp<<" "<<*p<<endl; //66666 66666
int b=9;
rp=&b;
cout<<rp<<endl; //0x7ffdaa65892c
cout<<p<<endl; //0x7ffdaa65892c
cout<<*rp<<endl; //9
cout<<*p<<endl; //9
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=3;
int &r=a;
int* p=&a;
int* &rp=p;
cout<<a<<endl;
cout<<r<<endl;
r=6;
cout<<a<<endl;
cout<<rp<<endl;
cout<<*p<<endl;
int b=r;
rp=&b;
cout<<p<<endl;
cout<<*rp<<endl;
return 0;
}Try try see
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=3;
int &r=a;
int* p=&a;
int* &rp=p;
cout<<a<<endl; //3
cout<<r<<endl; //3
r=6;
cout<<a<<endl; //6
cout<<rp<<endl; //0x7fffcd9d5f48
cout<<*p<<endl; //6
int b=r;
rp=&b;
cout<<p<<endl; //0x7fffcd9d5f4c
cout<<*rp<<endl; //6
return 0;
}See see answer
Kahoot!
現在是痛苦卡戶時間
各位加油(•ˋ _ ˊ•)
pointer
By problemsolvemaster_kaitochiang
pointer
- 135



