Essential AWS Services with Spring Cloud
Pulkit Pushkarna
Dynamo DB
-
DynamoDB is an easy to use and fully managed NoSQL database service provided by Amazon.
-
It provides fast and consistent performance, highly scalable architecture, flexible
data structure,
DynamoDB Component
Tables : DynamoDB stores data in an entity called a table. A table consists of a set of data.
Item : A table consists of multiple items. An item consists of a group of attributes.
An item is like a record or row in an RDBMS table.
Attributes : An item in a table consists of multiple attributes. An attribute is a basic data element of an item. It is similar to a field or a column in an RDBMS.
Primary key
- It is mandatory to define a primary key in the DynamoDB table. A primary key is a mechanism to uniquely identify each item in a table.
-
There are two types of primary keys:
-
Partition Key :
-
It is a simple primary key that is composed of a single attribute named partition key.
-
DynamoDB partitions the data in sections based on the partition key value.
-
The partition key value is used as an input to an internal hash functions, which determines in which partition the data is stored.
-
This is the reason partition key is also called the hash key.
-
No two items in a table can have the same partition key.
-
-
- Partition key and sort key :
-
Partition key and sort key are composed of two attributes and that's why it is also called as a composite primary key.
-
As the name suggest, the first attribute of the key is the partition key and the second attribute is the sort key.
-
DynamoDB stores all items with the same partition key together.
-
In a partition, items are ordered based on a sort key value. Thus, the partition key determines the first level of sort
order in a table whereas the sort key determines the secondary sort order of the data stored in a partition.
-
A sort key is also called a range key.
-
A table with both partition key and sort key can have more than one item with the same partition key value; however, it must have a different sort key.
-
Secondary indexes
-
DynamoDB allows you to create secondary indexes on a table.
-
It is an alternate way to query table data in addition to querying it using the primary key.
-
DynamoDB allows you to create 5 GSI and 5 LSI on a table. There are two types of secondary indexes:
-
Global Secondary Index (GSI) :
It consists of a partition key and a sort key,
which has to be different from the primary keys defined on the table
-
Local Secondary Index (LSI) :
It uses the same partition key as of the table but
uses a different sort key
-
Naming rules
-
Names are case-sensitive and must be encoded in UTF-8
-
A table name and an index name may range between 3 to 255 characters
-
Names may contain only the following characters:
-
a-z
-
A-Z
-
0-9
- _ (underscore)
-
- (dash)
-
. (dot)
-
Attributes can have a number of characters between 1 to 255.
-
Data Types
-
Scalar types: Scalar data type represents one value. It includes data types such as number, string, binary, boolean, and null.
-
Document types: A document data type contains of a complex structure with nested attributes. Examples of such structures are JSON and XML. DynamoDB
supports list and map document data types.
-
Set types: A set data type contains a group of scalar values. The set types supported by DynamoDb are string set, number set, and binary set.
AWS console demo for Dynamo DB
build.gradle
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.4.0'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.6'
}
group = 'com.aws.demo'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
java {
toolchain {
languageVersion = JavaLanguageVersion.of(21)
}
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation platform("io.awspring.cloud:spring-cloud-aws-dependencies:3.0.0")
// Replace the following with the starter dependencies of specific modules you wish to use
implementation 'io.awspring.cloud:spring-cloud-aws-starter-sqs'
implementation 'io.awspring.cloud:spring-cloud-aws-starter-dynamodb'
implementation 'io.awspring.cloud:spring-cloud-aws-starter-s3'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher'
}
tasks.named('test') {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
package com.aws.demo.aws_services.entity;
import software.amazon.awssdk.enhanced.dynamodb.mapper.annotations.DynamoDbBean;
import software.amazon.awssdk.enhanced.dynamodb.mapper.annotations.DynamoDbPartitionKey;
import java.util.UUID;
@DynamoDbBean
public class Person {
private UUID id;
private String name;
private String lastName;
public Person() {
}
public Person(UUID id, String name, String lastName) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@DynamoDbPartitionKey
public UUID getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(UUID id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
}package com.aws.demo.aws_services.Controller;
import com.aws.demo.aws_services.entity.Person;
import io.awspring.cloud.dynamodb.DynamoDbTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import software.amazon.awssdk.enhanced.dynamodb.Expression;
import software.amazon.awssdk.enhanced.dynamodb.model.Page;
import software.amazon.awssdk.enhanced.dynamodb.model.ScanEnhancedRequest;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.dynamodb.model.AttributeValue;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@RestController
public class PersonController {
@Autowired
DynamoDbTemplate dynamoDbTemplate;
@GetMapping("/person/save")
public void savePerson(){
dynamoDbTemplate.save(new Person(UUID.randomUUID(), "John", "Doe"));
}
@GetMapping("/persons")
public void getPersons(){
dynamoDbTemplate.scanAll(Person.class).forEach(System.out::println);
}
@GetMapping("/persons/{id}")
public List<Person> deletePerson(@PathVariable String id){
ScanEnhancedRequest request = ScanEnhancedRequest.builder()
.consistentRead(true)
.filterExpression(Expression.builder()
.expression("id >= :id")
.expressionValues(
Map.of( ":id", AttributeValue.builder().s(id).build()))
.build())
.build();
return dynamoDbTemplate.scan(request, Person.class).stream().map(Page::items).flatMap(e->e.stream()).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
Amazon SQS
- A message queue is a queue of messages exchanged between applications.
- Messages are data objects that are inserted in the queue by sender applications and received
by the receiving applications. - SQS is a highly reliable, scalable, and distributed message queuing service provided by
Amazon
Use cases for SQS
-
Asynchronous data processing : SQS allows you to process the messages asynchronously. That means, you can add a message on the queue but do not need to process it immediately.
-
Building resilience in the system : If some processes in your application environment go down, your entire environment does not go down with it. Since SQS decouples the processes, if a client processing a message goes down, the message is re-added to the queue after a specific duration.
-
Bringing elasticity to application with SQS : Using SQS you can build elasticity into your application. Data publisher and data consumer resources can be scaled up when there is a high
amount of traffic and the resources can be scaled down when the traffic is low.
-
Building redundancy with SQS : Sometimes processes do fail while processing the data. In such scenarios, if the data is not persisted, it is lost forever. SQS takes care of such a data risk by persisting the data till it's completely processed.
How Queue works ?
-
The publishing application pushes message into the queue.
-
The consuming application pulls the message from the queue and processes it.
-
The consuming application confirms to the SQS queue that processing on the message is completed and deletes the message from the SQS queue.
Type of SQS
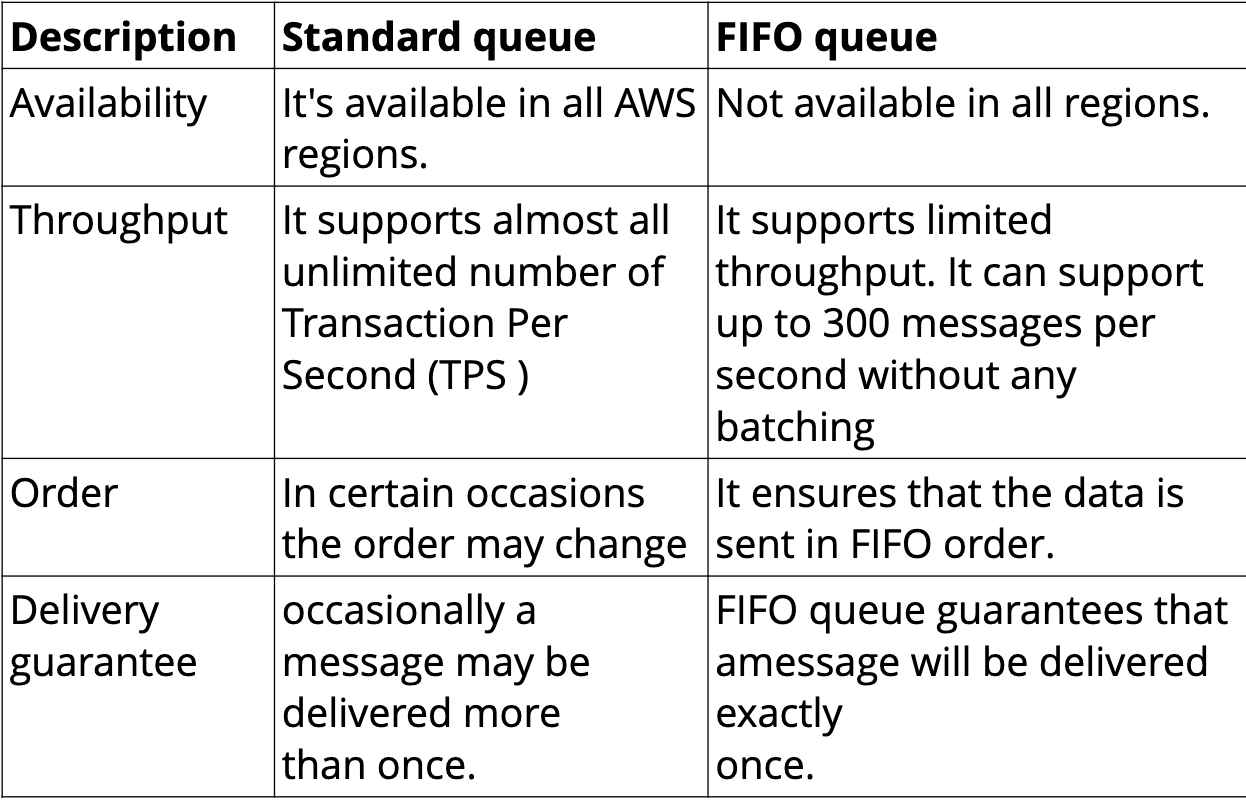
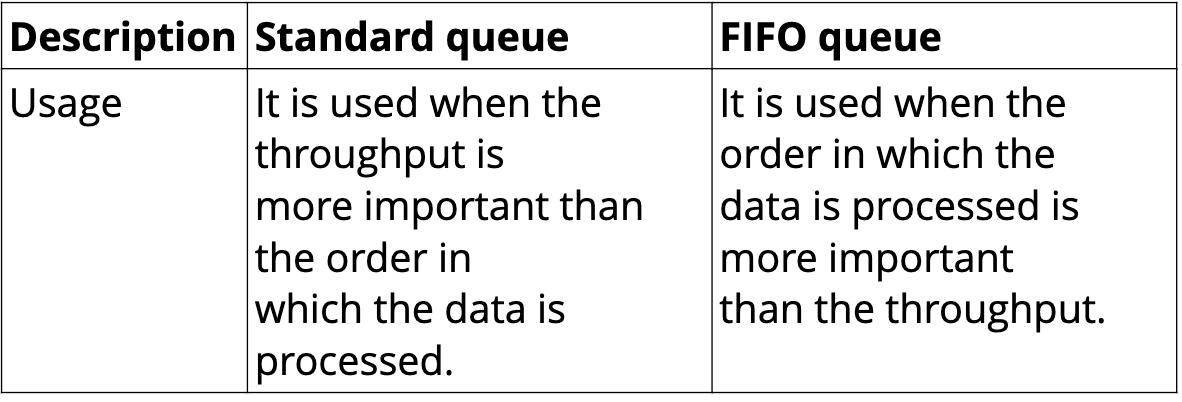
Dead Letter Queue
-
A DLQ is used by other queues for storing failed messages that are not successfully consumed by consumer processes.
-
You can use a DLQ to isolate unconsumed or failed
messages and subsequently troubleshoot these messages to determine the reason for their
failures.
-
SQS uses redrive policy to indicate the source queue, and the scenario in which SQS transfers messages from the source queue to the DLQ.
-
If a queue fails to process a message for a predefined number of times, that message is moved to the DLQ.
Queue Attributes
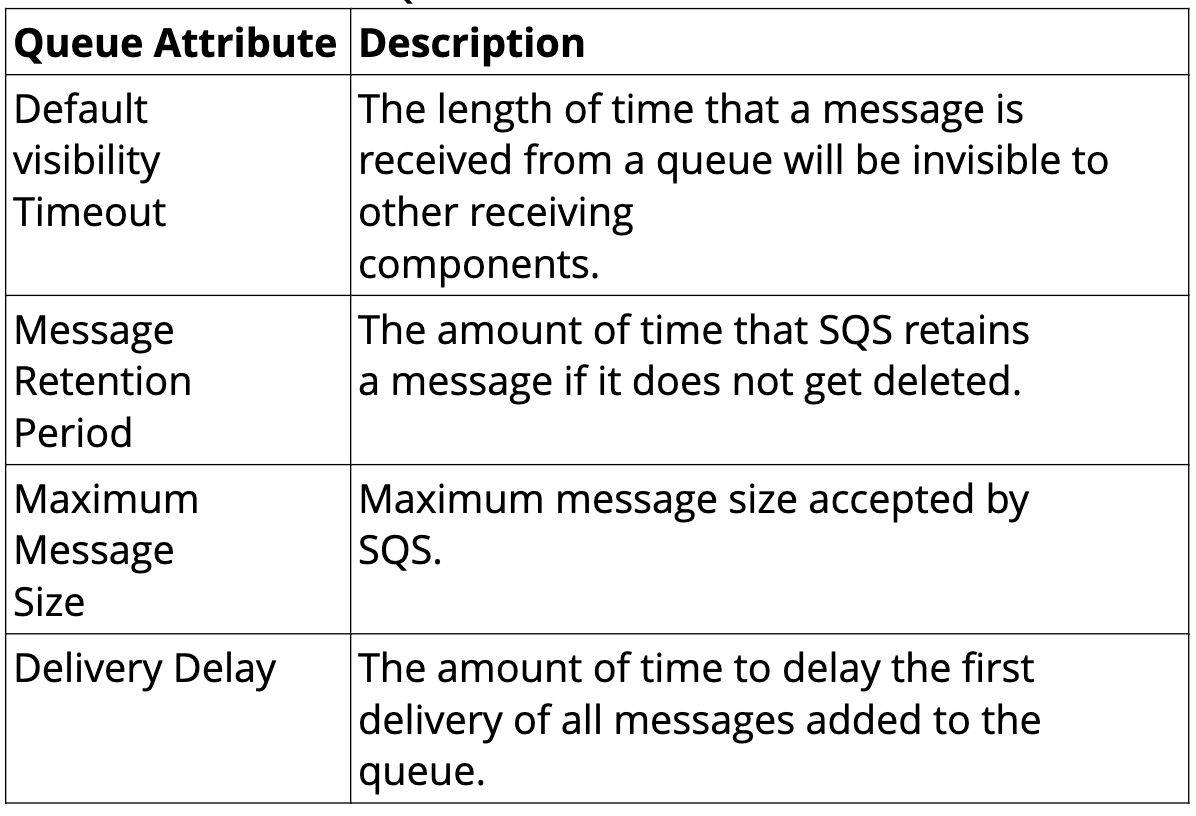
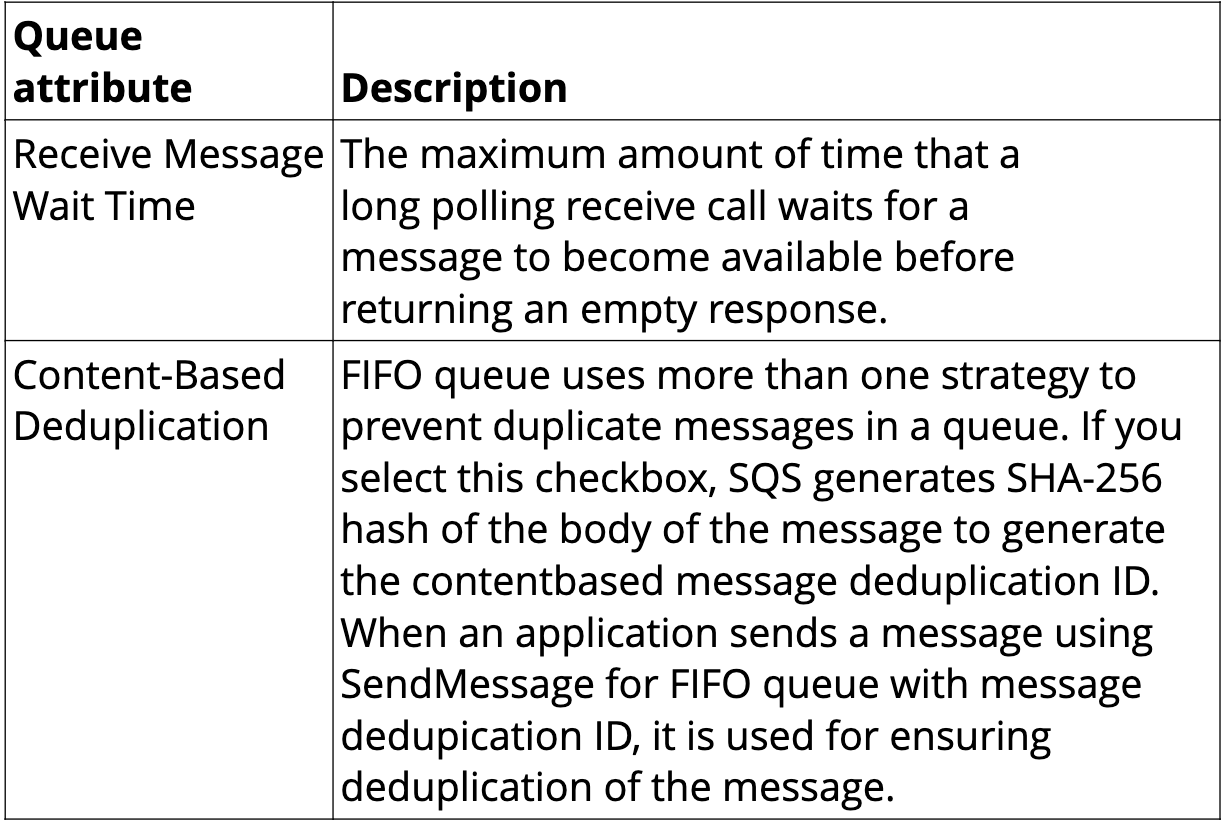
AWS Console SQS Demo
package com.aws.demo.aws_services;
import io.awspring.cloud.sqs.annotation.SqsListener;
import io.awspring.cloud.sqs.operations.SendResult;
import io.awspring.cloud.sqs.operations.SqsTemplate;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.sqs.SqsAsyncClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class AwsServicesApplication {
@GetMapping("/{message}")
public String index(@PathVariable String message){
SqsTemplate template = SqsTemplate.newTemplate(SqsAsyncClient.builder().build());
template.send("myQueue", message);
return "Success";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AwsServicesApplication.class, args);
}
@SqsListener("myQueue")
public void listen(String message) {
System.out.println("recieving message>>"+message);
}
}
S3 - Simple Storage Service
- Amazon S3 is storage for the internet. It is a simple storage service that offers software developers a highly scalable reliable, low latency data storage infrastructure at very low costs.
- S3 often known as key value data store.
- S3 provides a simple web service interface that you can use to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time, from anywhere on the web.
- Using this service developers can easily build applications that make use of internal storage
- It is secure and highly reliable object store from AWS
- S3 objects can range from 0 bytes to 5 terabyte
Types of S3 Storage classes
- Amazon S3 Standard : General purpose storage for frequent access of data.
- Amazon S3 Standard - Infrequent Access : Long Lived but less frequently accessed data.
- Amazon Glacier : For long term archive
- Reduced Redundancy Storage (RRS) is an Amazon S3 storage option that enables customers to reduce cost by storing non critical reproducible data at lower levels of redundancy than amazon S3 standard storage.
package com.aws.demo.aws_services;
import io.awspring.cloud.s3.S3Resource;
import io.awspring.cloud.s3.S3Template;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.time.Duration;
@RestController
public class S3Controller {
@Autowired
private S3Template s3Template;
String bucketName = "my-bucket-pulkit-pushkarna";
@GetMapping("/s3/createBucket")
public String createBucket(){
return s3Template.createBucket("my-bucket-pulkit-pushkarna");
}
@GetMapping("/s3/uploadFile")
public S3Resource uploadFile() throws FileNotFoundException {
return s3Template.upload("my-bucket-pulkit-pushkarna", "myFile2", new FileInputStream("/Users/pulkitpushkarna/Downloads/TXT.txt"));
}
@GetMapping("/s3/url")
public URL signedUrl() throws FileNotFoundException {
return s3Template.createSignedGetURL("my-bucket-pulkit-pushkarna", "myFile2", Duration.ofMinutes(60));
}
}
AWS Lambda
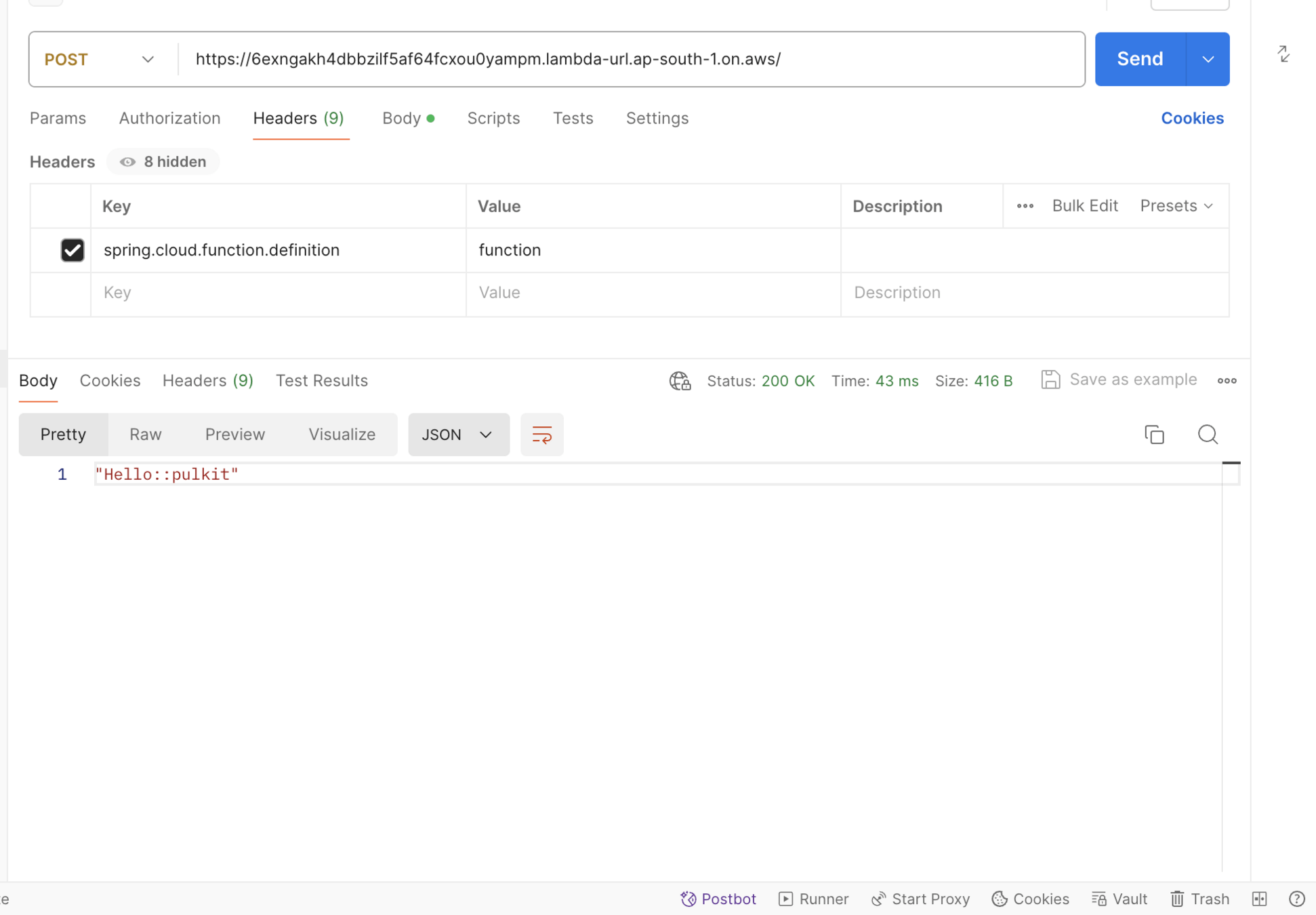
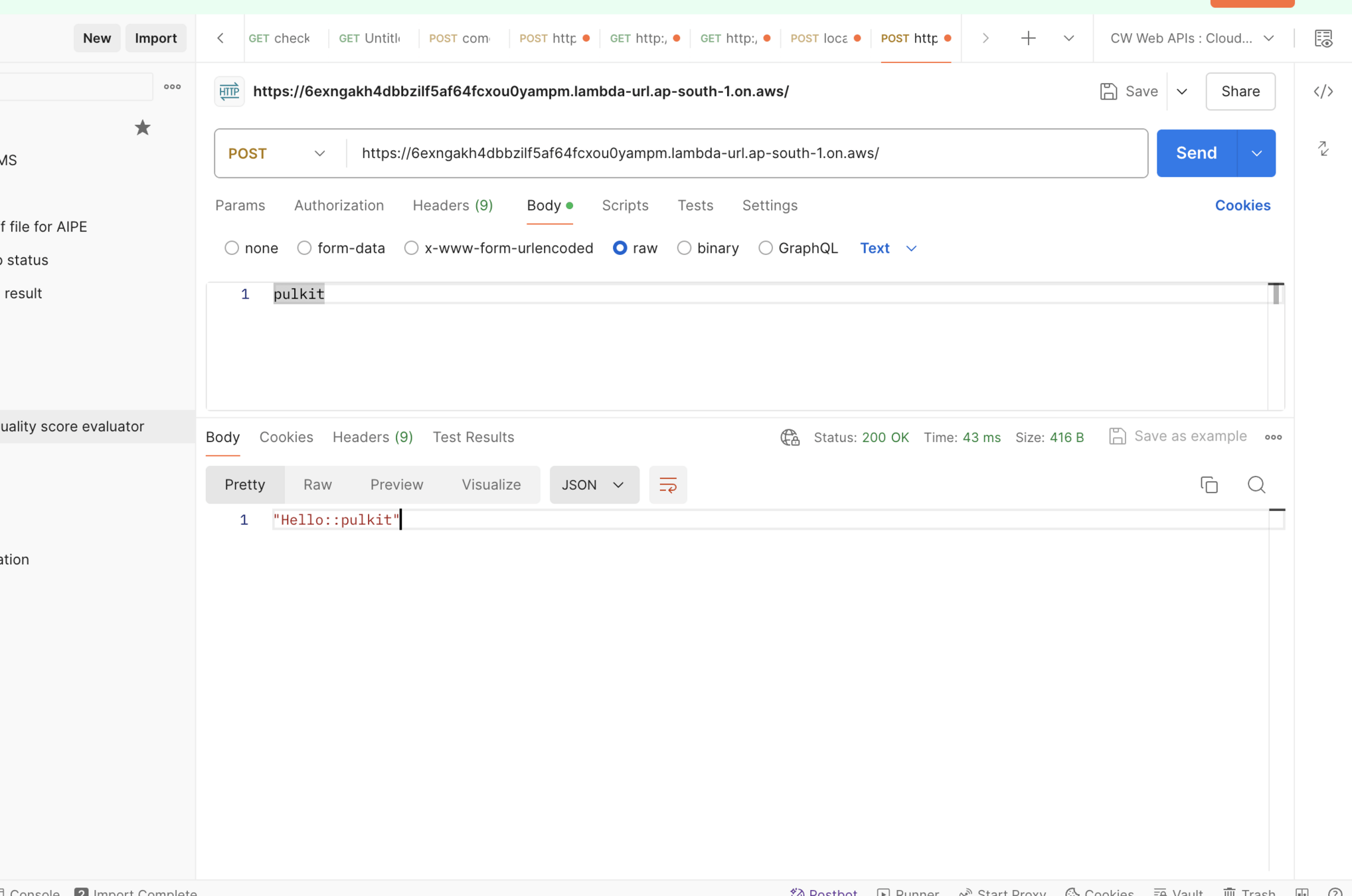
- AWS Lambda is a serverless and event-driven compute service. It allows you to upload a piece of source code to execute against a valid event. The uploaded piece of code is called a Lambda function.
-
AWS Lambda functions includes source code along with all dependencies.
-
Each Lambda function has its own configuration informations, such as runtime, environment variables,
handler, IAM role, tag(s), memory, timeout, VPC, and many other details that are defined at the time of creating.
-
Lambda function can be configured to execute in between 1 to 900 seconds. Lambda function execution time is called timeout. If the Lambda function is running after the defined timeout, it is automatically terminated.
While creating a Lambda function along with memory, here are few more parameters that need to be defined:
-
Maximum execution time (timeout):
The maximum it can be 15 minutes. It helps to prevent the Lambda function from running indefinitely. When timeout has been reached, the Lambda function execution terminates.
-
IAM role (execution role):
Lambda can assume an IAM role at the time of execution. Based on the privileges granted to the IAM role, the Lambda function can inherit the privileges for executing the function.
-
Handler name :
It refers to the method name to be used by AWS Lambda to start the execution. AWS Lambda passes an event information that triggers the invocation as a parameter to the handler method.
Lambda Function Invocation Types
-
AWS Lambda supports two invocation methods: synchronous and asynchronous.
-
The invocation type can be only specified at the time of manually executing a Lambda function.
-
This Lambda function execution is called on-demand invocation.
-
On-demand invocation is done by the invoke operation. It allows you to specify the invocation type, synchronous or asynchronous.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>io.spring.sample</groupId>
<artifactId>function-sample-aws</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version><!-- @releaser:version-check-off -->
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>function-sample-aws</name>
<description>Spring Cloud Function Sample for AWS Lambda</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.4.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<wrapper.version>1.0.29.RELEASE</wrapper.version>
<aws-lambda-events.version>3.9.0</aws-lambda-events.version>
<spring-cloud-function.version>4.2.0-SNAPSHOT</spring-cloud-function.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-function-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-function-adapter-aws</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-lambda-java-events</artifactId>
<version>${aws-lambda-events.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-lambda-java-core</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-function-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-function.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot.experimental</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-thin-layout</artifactId>
<version>${wrapper.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<createDependencyReducedPom>false</createDependencyReducedPom>
<shadedArtifactAttached>true</shadedArtifactAttached>
<shadedClassifierName>aws</shadedClassifierName>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</project>pom.xml
package com.aws.spring_cloud.aws_spring_cloud_mvn;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
@SpringBootApplication
public class AwsSpringCloudMvnApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AwsSpringCloudMvnApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Supplier<String> supply(){
return () ->"Hello";
}
@Bean
public Consumer<String> consume(){
return (name) -> System.out.println("Hello::"+name);
}
@Bean
public Function<String, String> function(){
return (name) -> "Hello::"+name;
}
}
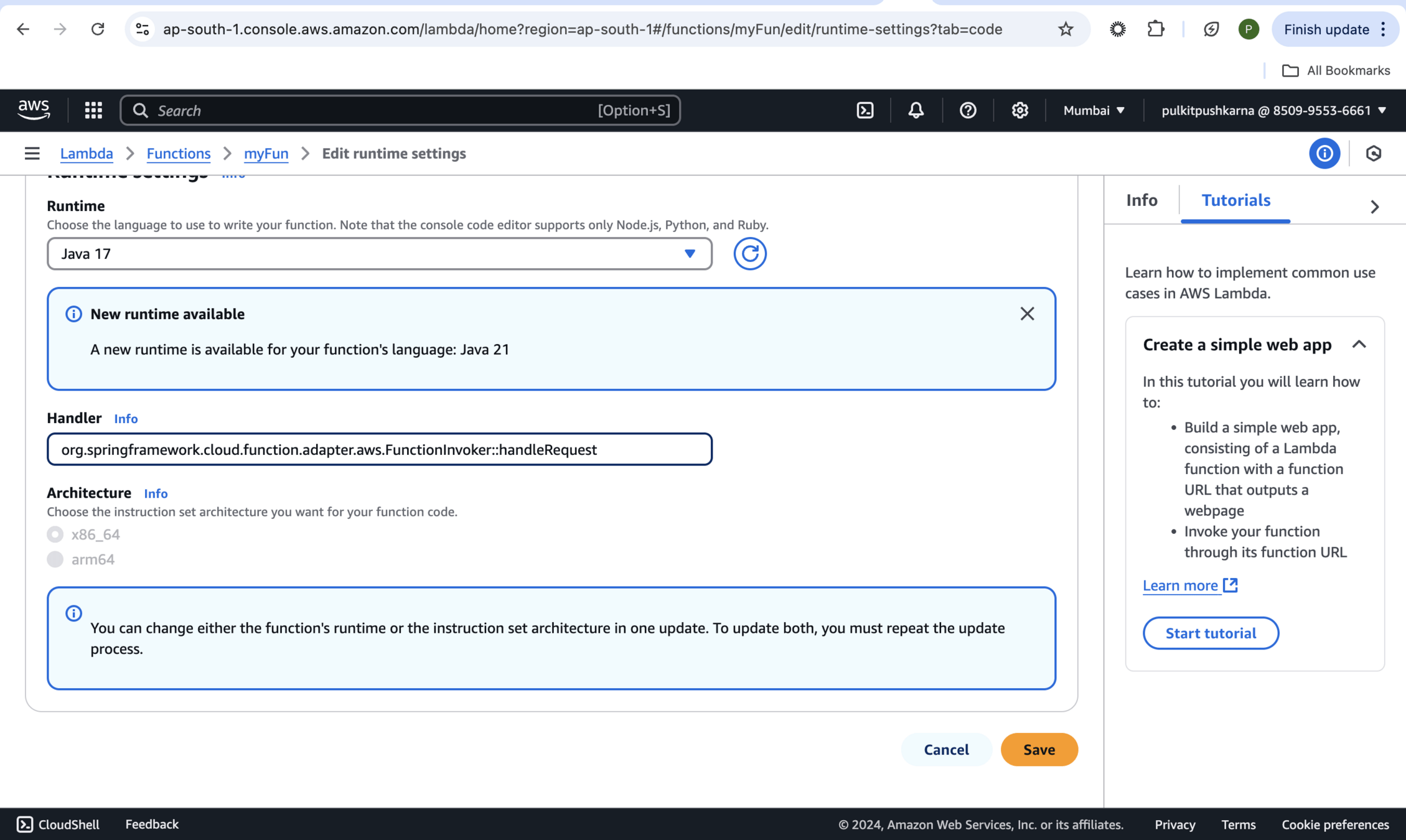
org.springframework.cloud.function.adapter.aws.FunctionInvoker::handleRequest

Essential AWS Services with Spring Cloud
By Pulkit Pushkarna
Essential AWS Services with Spring Cloud
- 75



