배열 (2)
지난 시간
다차원 배열
축이 두개 이상인 배열
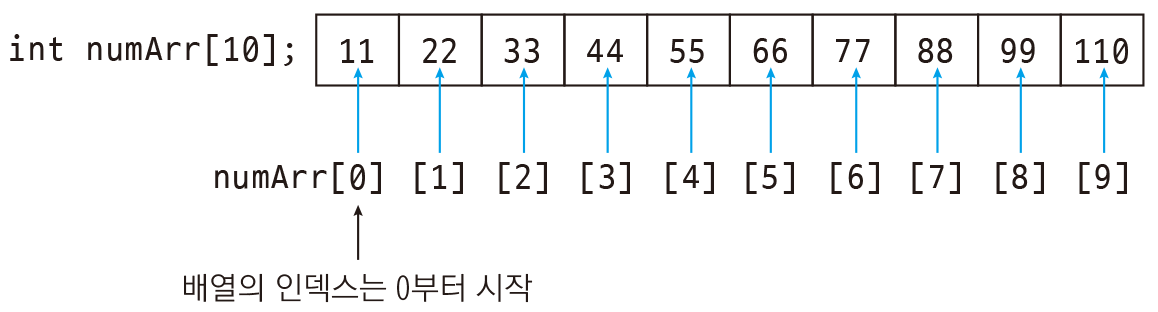
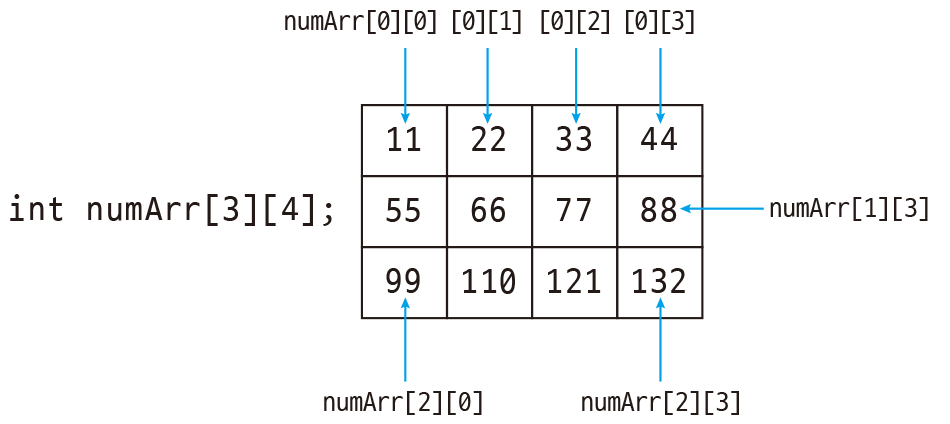
요소(element)
[0, n]
[1, n]
[2, n]
[n, 0]
[n, 1]
[n, 3]
선언
자료형[,...,] 변수명
ex) int[,] array, char[,,]
초기화
변수명 = new 자료형[1차원 크기,..., n차원 크기]
ex) array = new int[2, 2]{{1, 2}, {3, 4}}
array = new char[5, 6, 7]
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[,] intArray;
char[,,] charArray;
intArray = new int[5, 3];
charArray = new char[5, 6, 7];
}
}
접근
변수명[1차원 인덱스, ... , n차원 인덱스]
ex) array[1, 2], array[1, 5, 6]
범위 접근
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(array[i, j]);
}
}
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[,] intArray = new int[2, 2]{{1, 2}, {3, 4}};
Console.WriteLine(intArray[1, 1]);
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(intArray[i , j]);
}
}
}
}
Q.
2차원 배열([9, 9])에서 [n, m]에 n*m의 값을 넣자.
hint.
예전에 푼 구구단 출력문제와 똑같다.
대신 출력을 하지 않고 배열안에 넣을 뿐이다.
가변 배열
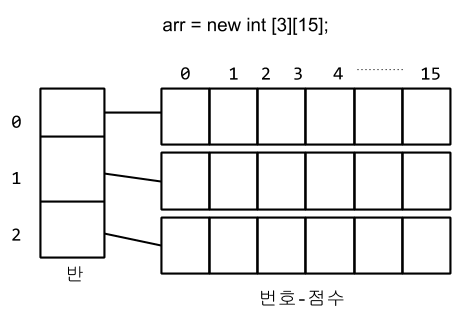
배열의 요소가 배열
선언과 초기화
자료형[][] = new 자료형[크기][]
{
new int[크기]{요소,...}
new int[크기]{요소,...}
....
};
자료형[][] = new 자료형[크기][];
(자료형[])[] = new (자료형[크기])[];
선언과 초기화 예시
int[][] array = new int[3][]
{
new int[2]{1, 2},
new int[3]{1, 4, 2},
new int[3]{3, 4, 2)
};
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[][] array = new int[3][]
{
new int[2]{1, 2},
new int[3]{1, 4, 2},
new int[3]{3, 4, 2)
};
Console.WriteLine(array[0][1]);
}
}접근
자료형[1차원 인덱스][2차원인덱스];
ex) array[3][4], array[5][3][4]
범위 접근
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(array[i][j]);
}
}
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[,] intArray = new int[2][2]
{
new int[2]{1, 2},
new int[2]{3, 4}
};
Console.WriteLine(intArray[1][1]);
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(intArray[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
Q.
2차원인 가변 배열([9, 9])에서 [n][m]에 n*m의 값을 넣자.
다차원 배열 vs 가변 배열
메모리 낭비를 줄이기 위해
가변배열 사용!
리스트(list)

원소를 추가할 때마다 크기가 늘어나는 배열
선언 및 초기화
List<자료형> 변수명 = new List<자료형>();
ex) List<int> list = new List<int>();
List<char> list = new List<char>();
추가
리스트변수명.Add(자료형 값);
ex) list.Add(1); list.Add('A');
접근
리스트변수명[인덱스]
ex) list[0]; list[1];
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> list = new List<int>();
list.Add(1);
list.Add(2);
list.Add(4);
Console.WriteLine(list[0]);
}
}제거
특정 원소 제거: 리스트명.Remove(원소 값);
특정 인덱스의 원소 제거: 리스트명.RemoveAt(인덱스);
ex)
list => [0, 1, 2, 3]
list.Remove(0);
list.RemoveAt(0);
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> list = new List<int>();
list.Add(1);
list.Add(2);
list.Add(3);
list.Remove(1);
list.RemoveAt(2);
foreach(int i in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.WriteLine(list.Count);
}
}요소 수 세기
리스트명.Count;
ex) list.Count;
원리
Q. 고객 추첨이벤트를 위해 고객들이 방문할때마다 고객들의 이름을 저장하려고 한다.
고객 리스트 제작 프로그램을 만들어 보자.
입력: 이름이 주어진다.
이때 이 이름을 list에 저장하고 "끝"이라는 단어가 주어지면 입력을 그만둔다.
출력: 입력이 멈춘후 지금까지 있었던 고객의 이름을 한줄마다 모두 출력한다.
Q. 입력받은 값을 거꾸로 출력해보자.
입력: 문자열이 한 줄에 주어진다.
ex) 이것은 문자열 입니다.
출력: 입력된 문자열을 거꾸로 출력한다.
ex) .다니입 열자문 은것이
힌트 1) 문자열은 char형 배열과 같이 접근할 수 있다.
ex)
string str = "이것은 문자열 입니다."
str[0] = '이', str[5]= '자'
힌트 2) 문자열의 길이를 얻을 수 있는 코드가 존재한다.
ex)
string str = "이것은 문자열 입니다."
str.length == 12
배열 (2)
By qwd0214
배열 (2)
- 109



