CI/CD & Tool Jenkins
Agenda
- General Terminology & concepts
- CI, CD , CD
- Why CI & benefits
- What is Pipeline
- Client Environment View
- Jenkins History & Details
- Sample Setup and playing around
CI- Continuous Integration
"Continuous Integration is a software development practice where members of a team integrate their work frequently; usually each person integrates at least daily leading to multiple integrations per day." --Martin Fowler

CD- Continuous Delivery
"Continuous Delivery is a software development discipline where you build software in such a way that the software can be released to production at any time" --Martin Fowler
CD- Continuous Deployment
Continuous Deployment is a third term that's sometimes confused with Continuous Delivery. Where Continuous Delivery provides a process to create frequent releases but not necessarily deploy them, Continuous Deployment means that every change you make automatically gets deployed through the deployment pipeline.
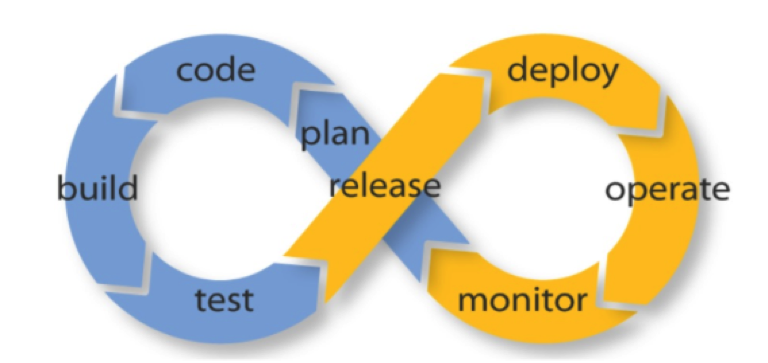
CI – What does it really mean?
At a regular frequency (ideally at every commit), the system is:
Integrated:
All changes up until that point are combined into the project
Built:
The code is compiled into an executable or package
Tested:
Automated test suites are run
Archived:
Versioned and stored so it can be distributed as
Deployed:
Loaded onto a system where the developers can interact with it
CI – Benefits
- Immediate bug detection
- No integration step in the lifecycle
- A deployable system at any given point
- Record of the evolution of the project
Best practices
- Maintain a code repository
- Automate the build
- Make the build self-testing
- Everyone commits to the baseline every day
- Every commit (to baseline) should be built
- Keep the build fast
- Test in a clone of the production environment
- Make it easy to get the latest deliverables
- Everyone can see the results of the latest build
- Automate deployment
What is pipeline?

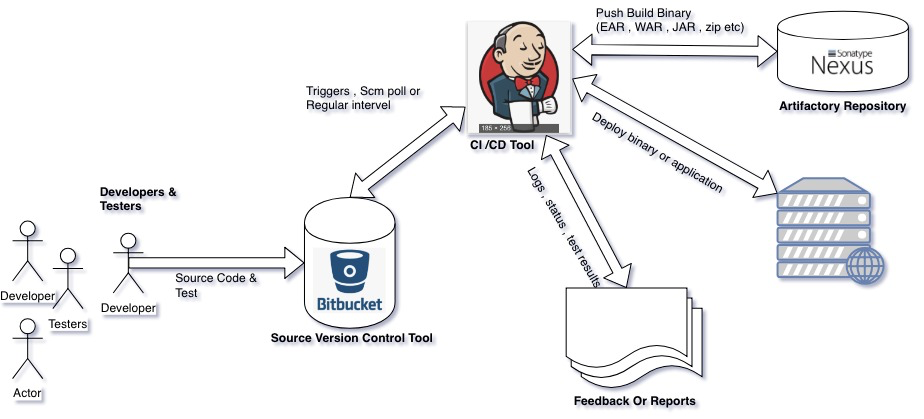
Overview of Sample CI & Tools
History
2005 - Hudson was
2010 – Oracle bought Sun Microsystems Due to a naming dispute, Hudson was renamed to Jenkins Oracle continued development of Hudson (as a branch of the original)
Details
Jenkins - History & details
- Branched from Hudson
- Current version LST - 2.150.1
- JVM-based continuous build system
-
Runs in a servlet container
- Glassfish, Tomcat
-
Under development since 2005
-
Plugins: https://plugins.jenkins.io/
-
Download: https://jenkins.io/download/
-
Source: https://github.com/jenkinsci
Jenkins 1 vs 2
-
The pipeline as a code.
-
New job creation page with icon based on the job
-
New Job Configuration page with tab view
-
Backwards Compatible.
More details: https://jenkins.io/2.0/
Jenkins Pipeline
Prerequisite :
- Working version of Jenkins.
- Build slaves if required.
- You can use Docker images or OVA virtual box image
- Test if you are able to logging, install plugin & right to add build job.
Add MultiPipeline job
- Fork GitHub repo and add multi-branch build job.
- Include and exclude branches.
- Run the build.
- Add polling for checking changes.
Update Jenkins file
- Use snippet code generator
- And update Jenkins file
- Run build and complete all stages.
Alternative for Jenkins
-
Tools that are used in RABO
- VSTS - now as Azure devops
- concourse - https://concourse-ci.org/
- Other Tools
- Bamboo
- Travis
- CircleCI
- TeamCity





CI/CD & Tool Jenkins
By Rajesh Manoharan
CI/CD & Tool Jenkins
- 1,144


