Angular ChatApp using FireStore

Manav Goel
Software Engineer at
GeekyAnts

- Observable based - Use the power of RxJS, Angular, and Firebase.
- Realtime bindings - Synchronizes data in realtime.
- Authentication - Log users in with a variety of providers and monitor authentication state in realtime.
- Offline Data - Store data offline automatically with AngularFirestore.
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AngularFireModule.initializeApp(firebaseConfig)
AngularFirestoreModule.enablePersistence() /// <--- update this line
],
bootstrap: [
AppComponent
]
})
export class AppModule { }- ngrx friendly - Integrate with ngrx using AngularFire's action based APIs.
Introduction to Angular FireStore (AngularFire)
Firebase offers two cloud-based, client-accessible database solutions that support realtime data syncing:
-
Realtime Database is Firebase's original database. It's an efficient, low-latency solution for mobile apps that require synced states across clients in realtime.
- Cloud Firestore is Firebase's new flagship database for mobile app development. It improves on the successes of the Realtime Database with a new, more intuitive data model. Cloud Firestore also features richer, faster queries and scales better than the Realtime Database.
Database? : Cloud Firestore or Realtime Database
Cloud Firestore vs Realtime Database
(Data Model)
Realtime Database-:
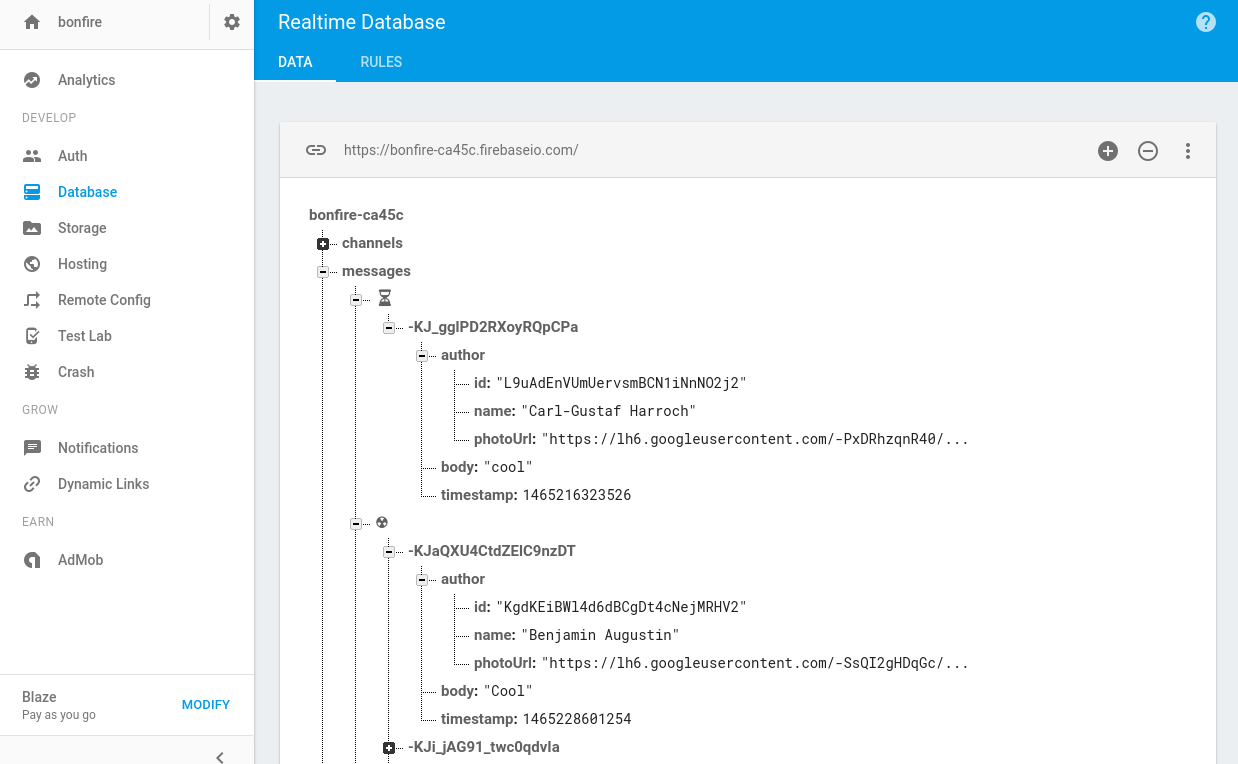
- Stores data as one large JSON tree.
- Complex, hierarchical data is harder to organize at scale.
Cloud Firestore -:
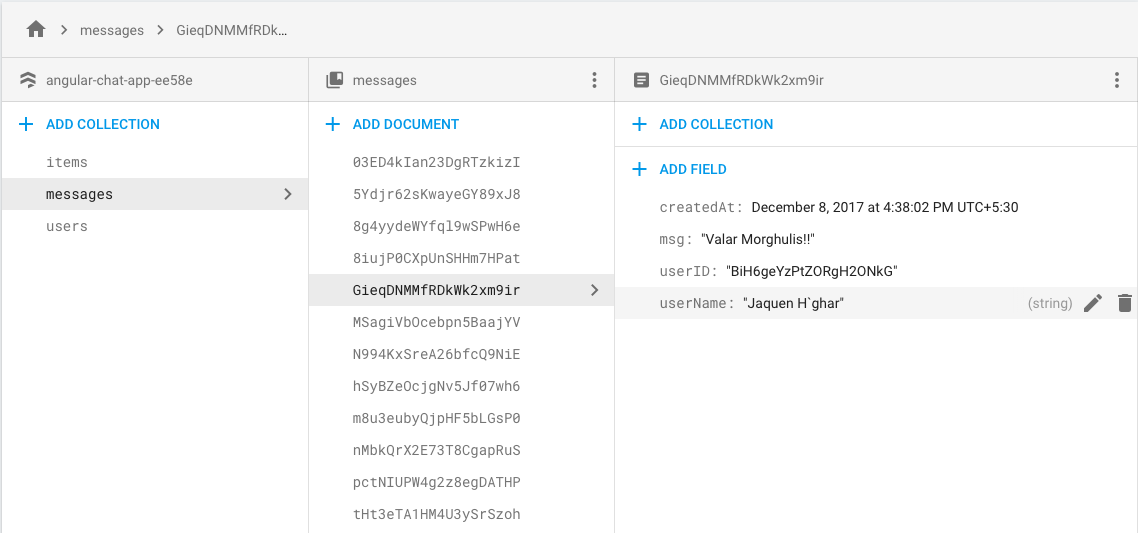
- Stores data in documents organized in collections.
- Complex, hierarchical data is easier to organize at scale, using sub-collections within documents.
Cloud Firestore vs Realtime Database
(Data Model)
npm install firebase angularfire2 --save
Copy the above command in the terminal, Hit enter and you are ready to go.....
How to install Angularfire
Step 1: Create a new database project
Setting Up Firebase
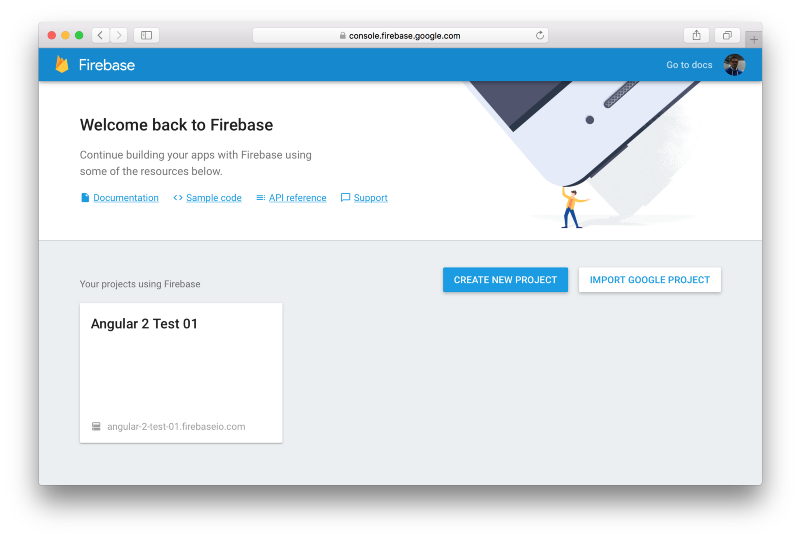
Step 2: Database dashboard.
Setting Up Firebase (Contd.)
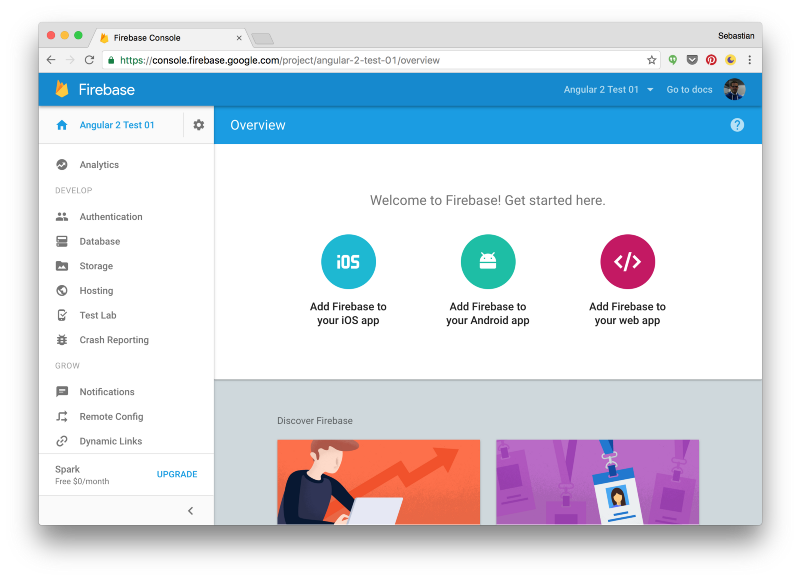
Step 3: Config.
Setting Up Firebase (Contd.)
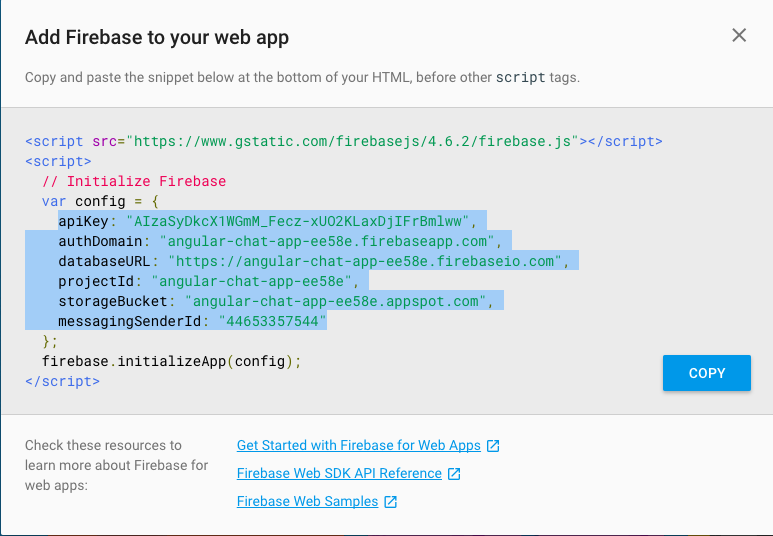
Step 4: Add FireStore configs to environment variable
(/src/environments/environment.ts).
Setting Up Firebase (Contd.)
export const environment = {
production: false,
firebase: {
apiKey: '<your-key>',
authDomain: '<your-project-authdomain>',
databaseURL: '<your-database-URL>',
projectId: '<your-project-id>',
storageBucket: '<your-storage-bucket>',
messagingSenderId: '<your-messaging-sender-id>'
}
};Step 5: Setup @NgModule for the AngularFireModule.
Setting Up Firebase (Contd.)
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { AngularFireModule } from 'angularfire2';
import { environment } from '../environments/environment';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AngularFireModule.initializeApp(environment.firebase)
],
declarations: [ AppComponent ],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule {}Step 6: Setup individual @NgModules
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { AngularFireModule } from 'angularfire2';
import { AngularFirestoreModule } from 'angularfire2/firestore';
import { AngularFireAuthModule } from 'angularfire2/auth';
import { environment } from '../environments/environment';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AngularFireModule.initializeApp(environment.firebase, 'my-app-name'), // imports firebase/app needed for everything
AngularFirestoreModule, // imports firebase/firestore, only needed for database features
AngularFireAuthModule, // imports firebase/auth, only needed for auth features
],
declarations: [ AppComponent ],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule {}For example if your application was using both Firebase authentication and the Firebase database you would add:
Setting Up Firebase (Contd.)
Step 7: Inject AngularFirestore.
Setting Up Firebase (Contd.)
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { AngularFirestore } from 'angularfire2/firestore';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: 'app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
constructor(db: AngularFirestore) {
}
}Step 8: Bind to a list.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { AngularFirestore } from 'angularfire2/firestore';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs/Observable';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: 'app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
items: Observable<any[]>;
constructor(db: AngularFirestore) {
this.items = db.collection('items').valueChanges();
}
}<ul>
<li class="text" *ngFor="let item of items | async">
{{item.name}}
</li>
</ul>/src/app/app.component.ts
/src/app/app.component.html
Setting Up Firebase (Contd.)
Chat App
Get Data with Cloud Firestore
There are two ways to retrieve data stored in Cloud Firestore -:
- Call a method to get the data
this.db.collection("users")
.doc(this.currentUserID)
.get()
.then((data)=> {
this.currentUser = doc.data() as User;
}).catch(function(error) {
console.error("Error removing document from users: ", error);
});constructor(private db: AngularFirestore) {}interface User{
user_name: string;
joinedAt: Date;
}Get Data with Cloud Firestore
2. Set a listener to receive data-change events.
2.1. Use valueChanges()
this.messageList = this.msgCollection.valueChanges();
this.users = this.usersCollection.valueChanges();- valueChanges() returns current state of the collection.
- Returns an Observable of data as a synchronized array of JSON objects.
- All Snapshot metadata is stripped.
msgCollection: AngularFirestoreCollection<Message>;
messageList: Observable<Message[]>;
users: Observable<User[]>;Interface Message{
msg: string;
createdAt: Date;
id?: string;
}Get Data with Cloud Firestore
this.db.collection("users")
.snapshotChanges()
.map(arr=>{
this.usersArrObj = {};
arr.map((ab)=>{
const data = ab.payload.doc.data() as User;
const id = ab.payload.doc.id;
this.usersArrObj[id] = {...data}.user_name;
});
}).subscribe();2. Set a listener to receive data-change events.
2.2. Use snapshotChanges()
- Also returns current state of the collection. Returns an Observable of data as a synchronized array of DocumentChangeAction[]
- Data along with the metadata
- Metadata provides you the underyling DocumentReference, document id, and array index of the single document
Get Data with Cloud Firestore
Output of snapshotChanges()

Add Data In Cloud Firestore
this.db.collection("messages").add({
msg: data,
createdAt: new Date(),
userID: this.currentUserID,
userName: this.currentUser
})
.then((docRef)=> {
this.messageBox.nativeElement.value = "";
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.error("Error adding document: ", error);
});There are several ways to write data to Cloud Firestore:
- Set the data of a document within a collection, explicitly specifying a document identifier.
- Add a new document to a collection. In this case, Cloud Firestore automatically generates the document identifier.
- Create an empty document with an automatically generated identifier, and assign data to it later.
Delete Data From Cloud Firestore
Using delete() method:
this.db.collection("users")
.doc(this.currentUserID)
.delete()
.then((data)=> {
this.userService.setUserID('');
}).catch(function(error) {
console.error("Error removing document from users: ", error);
});Realtime Updates in Cloud Firestore
Using stateChanges() method:
- Returns an Observable of the most recent changes as a DocumentChangeAction[].
- It emits changes as they occur rather than syncing the query order.
this.usersCollection.stateChanges(['added'])
.map(actions => {
if(actions.length === 1){
actions
.map(a => {
this.newUser = true;
const data = a.payload.doc.data() as User;
this.newlyAddedUser = data.user_name.toString();
const id = a.payload.doc.id;
return { id, ...data };
})
}
}).subscribe();Querying Collections in Cloud Firestore
Firestore Collection ≈ RealtimeDB List
Collections are just containers of documents.
They have their own query methods that are way more developer-friendly than the realtimeDB.
Here are some of the cool things you can do that were previously difficult -:
this.msgCollection = this.db.collection('messages', ref=>{
return ref
.orderBy('createdAt')
.where('createdAt', '>=' , this.currentUserDate? this.currentUserDate : new Date());
});Important Links
Cloud Firestore Docs ->
https://firebase.google.com/docs/firestore/
THANK YOU!

@manav1020goel
FireStore :D
By Ratnam Pandey
FireStore :D
- 1,407


