Virtual Private Networks
Agenda
-
What is a VPN?
-
Characteristics of VPNs
-
Types of VPNs?
VPN is
An emulation of a private Wide Area Network (WAN) using shared or public IP facilities, such as the Internet or private IP backbones
definition by IETF
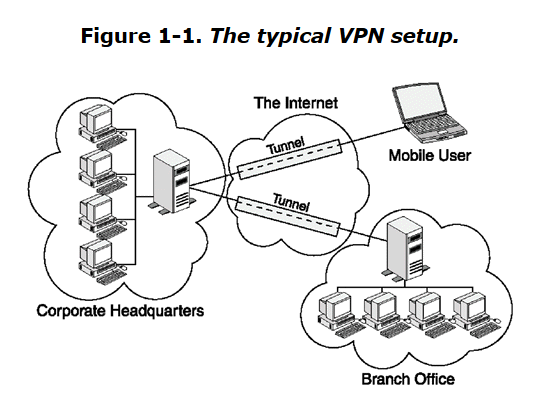
Safety mechanisms
-
Encryption
-
Authentication
-
Authorization
Characteristics of an Effective VPN
-
Data confidentiality
-
Data integrity
-
Sender non-repudiation
-
Message authentication
Confidentiality and Authenticity in Encrypted Communications
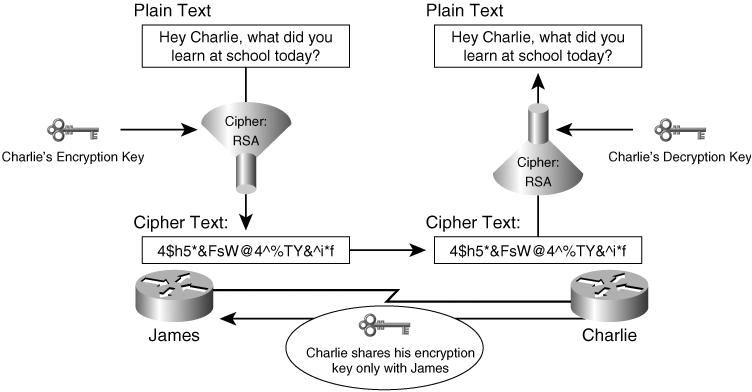
Data Integrity, Secure Hashes
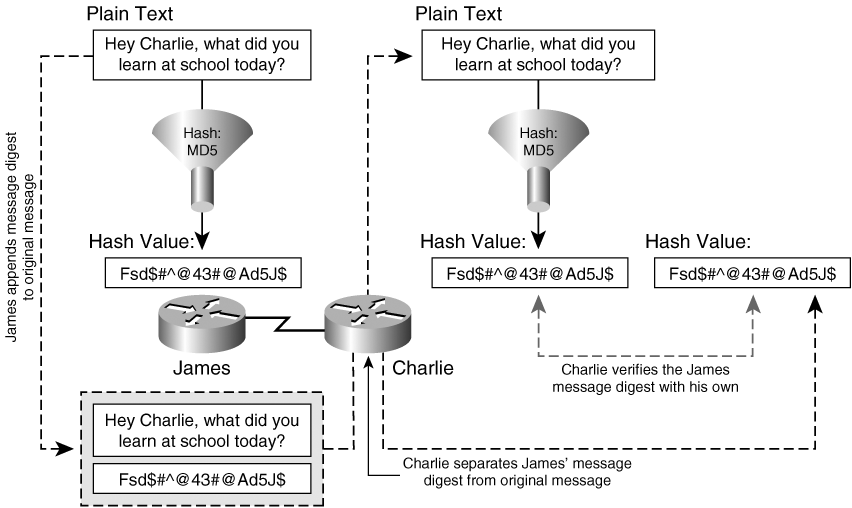
Message Authenticity and Data Non-Repudiation with Digital Signatures

VPN Tunneling Protocols
-
IP Security (IPSec)
-
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
-
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
-
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
VPNs types:
-
Site-to-site VPNs
-
Remote access VPNs
Typical Site-to-Site VPN
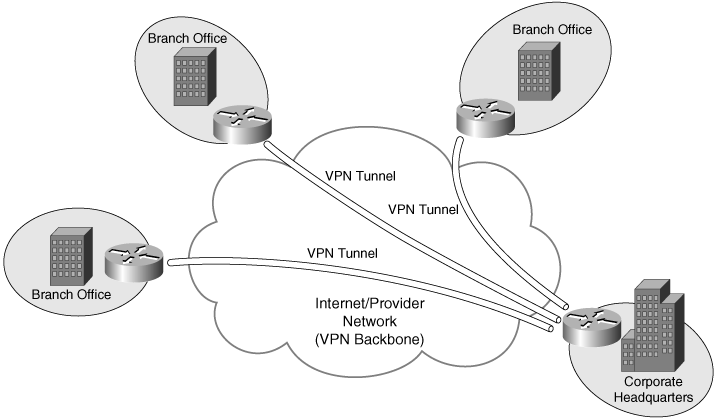
There are two types of site-to-site VPN:
-
Intranet VPNs— Allow connectivity between sites of a single organization
-
Extranet VPNs— Allow connectivity between organizations such as business partners or a business and its customers
Remote Access VPNs

References
-
Gupta, M. (2003) Building a Virtual Private Network
-
Lewis, M. (2006) Comparing, Designing, and Deploying VPNs
-
Carmouche, J. H. (2006) IPsec Virtual Private Network Fundamentals
Advantages of VPNs
-
Reduced cost of implementation
-
Reduced management and staffing costs
-
Enhanced connectivity
-
Security of transactions
-
Effective use of bandwidth
-
Enhanced scalability
Advantages of VPNs
-
High dependence on the Internet
-
Lack of support to the legacy protocols
Q & A
Thank You
VPN
By rav
VPN
- 709

