Microsoft Fabric
SQL Database
(preview)
Jeff Taylor


jssug.org
Every 3rd Wednesday 6-8pm
Except for May, November and December


Annual Free Data Conference
May 2nd & 3rd, 2025

JSSUG
January Sponsor
Jeff Taylor
Principal Data Consultant
Database Consulting, LLC






Jeff Taylor
Microsoft Fabric
SQL Database
(preview)

Introduction to Microsoft Fabric SQL Database
-
Overview: Developer-friendly transactional database based on Azure SQL Database.
-
Integration: Integrated with development frameworks and analytics.
-
Replication: Automatic data replication into OneLake for analytics.
- Performance: Intelligent performance features like automatic index creation.
Key Features of Microsoft Fabric SQL Database
-
OLTP Workloads: Home for OLTP workloads, easy to configure and manage.
-
Analytics Setup: Automatically replicates data into OneLake in near real-time.
-
Development Tools: Supports SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), Azure Data Studio, and web-based editor in the Fabric portal.
- Intelligent Performance: Features like automatic tuning and index creation.
Analytical Endpoint
-
Paired Endpoint: Each Fabric SQL database has a paired SQL analytics endpoint.
-
Reporting Queries: Run reporting queries against the OneLake copy of the data.
- Access Methods: Accessible via the Fabric portal, SSMS, and Visual Studio Code.
Connecting to the Database
-
Web-Based Editor: Use the web-based editor in the Fabric portal.
-
SSMS and Azure Data Studio: Connect using SQL Server Management Studio and Azure Data Studio.
- Connection Strings: Provided for various tools including ADO.NET, JDBC, ODBC, PHP, and Go.
Semantic Model
-
Default Model: Automatically created for each SQL database.
-
Custom Models: Ability to create multiple models from one database.
-
Business-Friendly: Enables deeper analysis with metrics and business-friendly terminology.
- Integration: Integrated with Power BI for visualizations and analysis.
Cross-Database Queries
- Querying Across Databases: Write cross-database queries joining data from other SQL databases, mirrored databases, warehouses, and the SQL analytics endpoint.
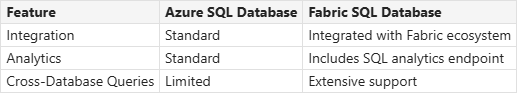
Azure SQL vs. Fabric SQL Database
- Common Code Base: Both share a common code base with the latest stable version of the Microsoft SQL Database Engine.
Differences
- Always Encrypted: Supported in Azure SQL but not in Fabric SQL.
- Change Data Capture (CDC): Supported in Azure SQL but not in Fabric SQL.
- Elastic Pools: Available in Azure SQL but not in Fabric SQL.
- Provisioning Control: Detailed control in Azure SQL, autonomous management in Fabric SQL.
- Integration: Fabric SQL is fully integrated with other workloads in the Microsoft Fabric platform by default
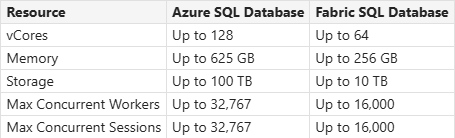
Azure SQL vs. Fabric SQL Database
Azure SQL Database
Fabric SQL Database
- Compute Tiers: Provisioned or serverless.
- Hardware Configurations: Gen5, Fsv2, DC.
- Elastic Pools: Yes.
- Maximum Resource Limits: Higher limits for vCores, DTUs, and storage.
- Compute Tiers: Serverless.
- Hardware Configurations: Latest configurations.
- Elastic Pools: No.
- Maximum Resource Limits: Lower limits compared to Azure SQL Database, subject to change before general availability.
Azure SQL vs. Fabric SQL Database
Demo
Create a SQL database in the Fabric portal
Demo
Use SQL Analytics Endpoint
Demo
Connect to the Database - SSMS, Azure Data Studio
Demo
Semantic Model
Resources
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/fabric/database/sql/overview
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/shows/data-exposed/sql-integration-with-microsoft-fabric-data-exposed
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/fabric/data-warehouse/tutorial-sql-cross-warehouse-query-editor
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/fabric/database/sql/mirroring-limitations
Questions?
Thank you
Jeff Taylor
Thank you for attending my session today. If you have any additional questions please don't hesitate to reach out. My contact information is below.


Microsoft Fabric SQL Database (private preview)
By reviewmydb
Microsoft Fabric SQL Database (private preview)
- 195



