Jeff Taylor
How To Tune A Multi-Terabyte Database For Optimum Performance
ABOUT ME
- Jeff Taylor
- Data/Software Architect
- SQL Server Since SQL 6.5
- 24+ years working with Microsoft SQL Server
- President of Jacksonville SQL Server Users Group
- Contact: Jeff@ReviewMyDB.com, @reviewmydb
- Blog: https://blog.reviewmydb.com

Questions
- What is your role (How many DBA's)?
- What Versions of SQL Server are you using in Production?
- What Editions of SQL Server are you using in Production?
Problems Encountered
- Queries take minutes to run, hours for processes to finish, application timeouts extended.
- Databases so large, index maintenance cannot be finished nightly, let alone started
- New Indexes take 4-8 hours to create on one table with billions of records.
- Full backups take 12+ hours
- Database log mode kept in Simple mode due to transaction log backups not being able to keep up
- Using nested Virtual Hard Drives for data in a VM Host VHD
First things First
- Hire a DBA
- Preferably one who knows servers and storage (SANs)
- Move to Enterprise Edition
Agenda
-
Assess/Test Network/Server/Database Configuration.
- Determine What Kind of Data You Have.
- Determine Queries and Filters Used.
- Review and Adjust Data Types.
- Data Types/Data Sizes.
- Moving/Fixing Data.
- Cleanup
Would you rather use This?

Or This?

Would you rather use This?

Or This?

Would you rather use This?

Or This?

Or better yeT?

First we need better design

First we need better design
- Assess and Test Current System
- Infrastructure Design
- Data Types
- Logical Separation/Physical Location
Measure Throughput
- SQL Server File IO Per DB
WITH Agg_IO_Stats
AS
(
SELECT
DB_NAME(database_id) AS database_name,
CAST(SUM(num_of_bytes_read + num_of_bytes_written) / 1048576 / 1024.
AS DECIMAL(12, 2)) AS io_in_gb
FROM sys.dm_io_virtual_file_stats(NULL, NULL) AS DM_IO_Stats
GROUP BY database_id
),
Rank_IO_Stats
AS
(
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY io_in_gb DESC) AS row_num,
database_name,
io_in_gb,
CAST(io_in_gb / SUM(io_in_gb) OVER() * 100
AS DECIMAL(5, 2)) AS pct
FROM Agg_IO_Stats
)
SELECT R1.row_num, R1.database_name, R1.io_in_gb, R1.pct,
SUM(R2.pct) AS run_pct
FROM Rank_IO_Stats AS R1
JOIN Rank_IO_Stats AS R2
ON R2.row_num <= R1.row_num
GROUP BY R1.row_num, R1.database_name, R1.io_in_gb, R1.pct
ORDER BY R1.row_num;Measure Throughput
- SQL Server File IO Per DB

Latency Per DB File
- SQL Server Latetency Per File
SELECT
--virtual file latency
[ReadLatency] =
CASE WHEN [num_of_reads] = 0
THEN 0 ELSE ([io_stall_read_ms] / [num_of_reads]) END,
[WriteLatency] =
CASE WHEN [num_of_writes] = 0
THEN 0 ELSE ([io_stall_write_ms] / [num_of_writes]) END,
[Latency] =
CASE WHEN ([num_of_reads] = 0 AND [num_of_writes] = 0)
THEN 0 ELSE ([io_stall] / ([num_of_reads] + [num_of_writes])) END,
--avg bytes per IOP
[AvgBPerRead] =
CASE WHEN [num_of_reads] = 0
THEN 0 ELSE ([num_of_bytes_read] / [num_of_reads]) END,
[AvgBPerWrite] =
CASE WHEN [io_stall_write_ms] = 0
THEN 0 ELSE ([num_of_bytes_written] / [num_of_writes]) END,
[AvgBPerTransfer] =
CASE WHEN ([num_of_reads] = 0 AND [num_of_writes] = 0)
THEN 0 ELSE
(([num_of_bytes_read] + [num_of_bytes_written]) /
([num_of_reads] + [num_of_writes])) END,
LEFT ([mf].[physical_name], 2) AS [Drive],
DB_NAME ([vfs].[database_id]) AS [DB],
--[vfs].*,
[mf].[physical_name]
FROM
sys.dm_io_virtual_file_stats (NULL,NULL) AS [vfs]
JOIN sys.master_files AS [mf]
ON [vfs].[database_id] = [mf].[database_id]
AND [vfs].[file_id] = [mf].[file_id]
ORDER BY [WriteLatency] DESC;
GOLatency Per DB File
- SQL Server Latetency Per File

Measure Throughput
- Crystal Disk Mark
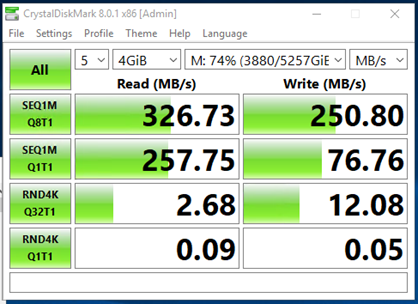
Initial Server Results
Sequential 1 MB 8 threads 1 process
Sequential 1MB 1 thread 1 process
Random 4k 32 processes 1 thread
Random 4k 1 thread 1 thread
Measure Throughput
- Crystal Disk Mark
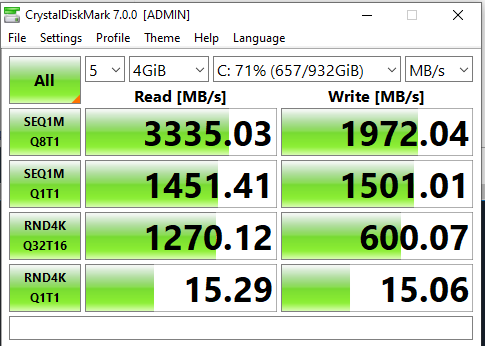
My Laptop Results
Sequential 1 MB 8 threads 1 process
Sequential 1MB 1 thread 1 process
Random 4k 32 processes 16 threads
Random 4k 1 thread 1 thread
Measure Throughput
- Crystal Disk Mark

Comparison - Initial Server vs. My Laptop

Measure Throughput
- Crystal Disk Mark
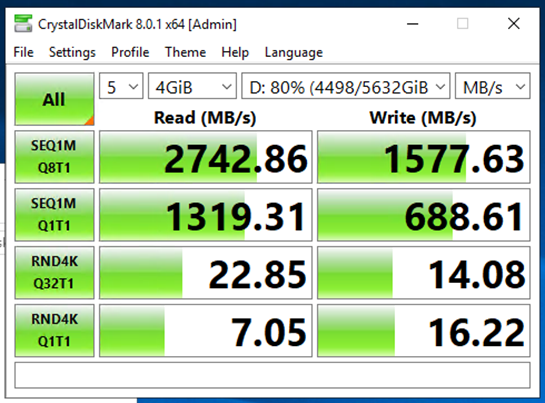
Server After Upgrades
Measure Throughput
- Crystal Disk Mark
Comparison - Initial Server vs. After Adjustments


Measure Throughput
- diskspd - (formally sqlio) - Before Test - Reads 64k
Command Line: diskspd -b64K -d300 -o32 -t10 -h -r -w0 -L -Z1G -c20G M:\test.dat
Input parameters:
timespan: 1
-------------
duration: 300s
warm up time: 5s
cool down time: 0s
measuring latency
random seed: 0
path: 'M:\test.dat'
think time: 0ms
burst size: 0
software cache disabled
hardware write cache disabled, writethrough on
write buffer size: 1073741824
performing read test
block size: 65536
using random I/O (alignment: 65536)
number of outstanding I/O operations: 32
thread stride size: 0
threads per file: 10
using I/O Completion Ports
IO priority: normalMeasure Throughput
- diskspd - (formally sqlio) - Before Test - 64K Reads
Read IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev | file
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 | 3436183552 | 52432 | 10.92 | 174.77 | 182.901 | 882.749 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
1 | 3441950720 | 52520 | 10.94 | 175.07 | 182.813 | 879.862 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
2 | 3442933760 | 52535 | 10.94 | 175.12 | 183.085 | 879.030 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
3 | 3436445696 | 52436 | 10.92 | 174.79 | 183.459 | 883.685 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
4 | 3442606080 | 52530 | 10.94 | 175.10 | 182.791 | 876.278 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
5 | 3439525888 | 52483 | 10.93 | 174.94 | 182.975 | 890.304 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
6 | 3437494272 | 52452 | 10.93 | 174.84 | 183.032 | 890.014 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
7 | 3438608384 | 52469 | 10.93 | 174.90 | 182.996 | 882.304 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
8 | 3440115712 | 52492 | 10.94 | 174.97 | 183.638 | 890.562 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
9 | 3440115712 | 52492 | 10.94 | 174.97 | 182.891 | 877.021 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
total: 34395979776 | 524841 | 109.34 | 1749.47 | 183.058 | 883.195Measure Throughput
- diskspd - (formally sqlio) - After Test - 64k Reads
Command Line: diskspd -b64K -d300 -o32 -t10 -h -r -w0 -L -Z1G -c20G J:\test.dat
Input parameters:
timespan: 1
-------------
duration: 300s
warm up time: 5s
cool down time: 0s
measuring latency
random seed: 0
path: 'J:\test.dat'
think time: 0ms
burst size: 0
software cache disabled
hardware write cache disabled, writethrough on
write buffer size: 1073741824
performing read test
block size: 65536
using random I/O (alignment: 65536)
number of outstanding I/O operations: 32
thread stride size: 0
threads per file: 10
using I/O Completion Ports
IO priority: normalMeasure Throughput
- diskspd - (formally sqlio) - After Test - 64k Reads
Read IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev | file
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 | 69446729728 | 1059673 | 220.74 | 3531.88 | 9.055 | 11.633 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
1 | 80267247616 | 1224781 | 255.14 | 4082.18 | 7.837 | 7.692 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
2 | 79802073088 | 1217683 | 253.66 | 4058.52 | 7.883 | 8.170 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
3 | 79711305728 | 1216298 | 253.37 | 4053.91 | 7.892 | 7.596 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
4 | 11169824768 | 170438 | 35.50 | 568.07 | 55.935 | 403.657 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
5 | 80384884736 | 1226576 | 255.51 | 4088.16 | 7.825 | 6.320 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
6 | 80713220096 | 1231586 | 256.55 | 4104.86 | 7.794 | 7.703 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
7 | 10342301696 | 157811 | 32.87 | 525.98 | 60.756 | 198.219 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
8 | 81465507840 | 1243065 | 258.94 | 4143.12 | 7.722 | 5.959 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
9 | 403767296 | 6161 | 1.28 | 20.53 | 1570.195 | 2666.786 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
total: 573706862592 | 8754072 | 1823.58 | 29177.21 | 10.964 | 103.685Measure Throughput
- diskspd - (formally sqlio) - Before Test - 64k Writes
Command Line: diskspd -b64K -d300 -o32 -t10 -h -r -w100 -L -Z1G -c20G M:\test.dat
Input parameters:
timespan: 1
-------------
duration: 300s
warm up time: 5s
cool down time: 0s
measuring latency
random seed: 0
path: 'M:\test.dat'
think time: 0ms
burst size: 0
software cache disabled
hardware write cache disabled, writethrough on
write buffer size: 1073741824
performing write test
block size: 65536
using random I/O (alignment: 65536)
number of outstanding I/O operations: 32
thread stride size: 0
threads per file: 10
using I/O Completion Ports
IO priority: normalMeasure Throughput
- diskspd - (formally sqlio) - Before Test - 64k Writes
Write IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev | file
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 | 2722496512 | 41542 | 8.65 | 138.47 | 231.917 | 45.290 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
1 | 2722693120 | 41545 | 8.66 | 138.48 | 231.933 | 45.672 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
2 | 2723217408 | 41553 | 8.66 | 138.51 | 231.896 | 45.642 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
3 | 2723217408 | 41553 | 8.66 | 138.51 | 231.891 | 45.729 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
4 | 2721775616 | 41531 | 8.65 | 138.43 | 231.934 | 45.574 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
5 | 2722234368 | 41538 | 8.65 | 138.46 | 231.977 | 45.615 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
6 | 2723282944 | 41554 | 8.66 | 138.51 | 231.900 | 45.705 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
7 | 2722889728 | 41548 | 8.66 | 138.49 | 231.897 | 45.448 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
8 | 2723020800 | 41550 | 8.66 | 138.50 | 231.919 | 45.629 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
9 | 2721579008 | 41528 | 8.65 | 138.42 | 232.005 | 45.789 | M:\test.dat (20GiB)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
total: 27226406912 | 415442 | 86.55 | 1384.79 | 231.927 | 45.609Measure Throughput
- diskspd - (formally sqlio) - After Test - 64k Writes
Command Line: diskspd -b64K -d300 -o32 -t10 -h -r -w100 -L -Z1G -c20G J:\test.dat
Input parameters:
timespan: 1
-------------
duration: 300s
warm up time: 5s
cool down time: 0s
measuring latency
random seed: 0
path: 'J:\test.dat'
think time: 0ms
burst size: 0
software cache disabled
hardware write cache disabled, writethrough on
write buffer size: 1073741824
performing write test
block size: 65536
using random I/O (alignment: 65536)
number of outstanding I/O operations: 32
thread stride size: 0
threads per file: 10
using I/O Completion Ports
IO priority: normalMeasure Throughput
- diskspd - (formally sqlio) - After Test - 64k Writes
Write IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev | file
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 | 10689511424 | 163109 | 33.98 | 543.68 | 58.842 | 55.344 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
1 | 10661265408 | 162678 | 33.89 | 542.25 | 58.982 | 61.204 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
2 | 10862985216 | 165756 | 34.53 | 552.51 | 57.889 | 47.318 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
3 | 10706419712 | 163367 | 34.03 | 544.54 | 58.736 | 59.966 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
4 | 10694164480 | 163180 | 33.99 | 543.92 | 58.814 | 51.372 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
5 | 10790567936 | 164651 | 34.30 | 548.82 | 58.263 | 57.034 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
6 | 10759634944 | 164179 | 34.20 | 547.25 | 58.445 | 59.746 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
7 | 10420158464 | 158999 | 33.12 | 529.98 | 60.330 | 61.604 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
8 | 10647830528 | 162473 | 33.85 | 541.56 | 59.015 | 70.884 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
9 | 10049814528 | 153348 | 31.95 | 511.15 | 62.517 | 61.650 | J:\test.dat (20GiB)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
total: 106282352640 | 1621740 | 337.85 | 5405.66 | 59.157 | 58.894Measure Throughput
- diskspd - (formally sqlio) - Comparison 64k
Read Random 64k IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Before total: 34395979776 | 524,841 | 109.34 | 1749.47 | 183.058 | 883.195
After total: 573706862592 | 8,754,072 | 1,823.58 | 29,177.21 | 10.964 | 103.685
Write Random 64k IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Before total: 27226406912 | 415,442 | 86.55 | 1,384.79 | 231.927 | 45.609
After total: 106282352640 | 1,621,740 | 337.85 | 5,405.66 | 59.157 | 58.894
Read Sequential 64k IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Before total: 51745456128 | 789,573 | 164.49 | 2,631.90 | 121.740 | 324.619
After total: 558304985088 | 8,519,058 | 1,774.71 | 2,8395.44 | 11.227 | 116.484
Write Sequential 64k IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Before total: 20625096704 | 314,714 | 65.57 | 1,049.05 | 304.779 | 158.935
After total: 89771278336 | 1,369,801 | 285.37 | 4,565.85 | 70.075 | 174.488Measure Throughput
- diskspd - (formally sqlio) - Comparison 8k
Read Random 8k IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Before total: 5604122624 | 684,097 | 17.81 | 2,280.32 | 140.317 | 26.689
After total: 417648984064 | 50,982,542 | 1,327.67 | 169,942.24 | 1.881 | 19.345
Write Random 8k IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Before total: 4747075584 | 579,477 | 15.09 | 1,931.58 | 165.717 | 107.243
After total: 25027559424 | 3,055,122 | 79.56 | 10,183.72 | 31.420 | 11.481
Read Sequential 8k IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Before total: 9096527872 | 1,110,416 | 28.92 | 3,701.38 | 86.442 | 16.131
After total: 404835688448 | 49,418,419 | 1,286.94 | 16,4728.37 | 1.941 | 15.316
Write Sequential 8k IO
thread | bytes | I/Os | MiB/s | I/O per s | AvgLat | LatStdDev
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Before total: 6630064128 | 809,334 | 21.08 | 2,697.77 | 118.605 | 21.490
After total: 24726937600 | 3,018,425 | 78.60 | 10,061.40 | 31.803 | 10.447Verify Network Setup
- Do you have Multi-Path Setup from SAN To Host or SAN to Physical?
- What is your connection speed from your server/host to SAN?
- 1GB?
- 8GB?
- 10GB?
- 25GB?
- 40GB?
- 100GB?
- Connections X Bandwidth = more throughput
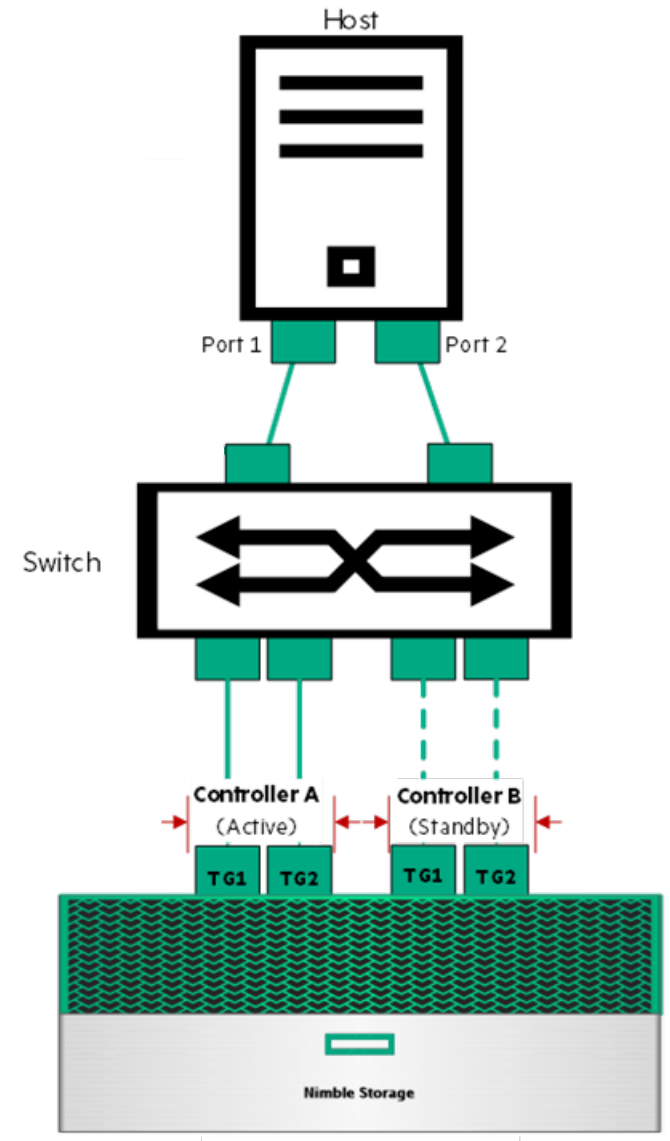
Verify Network Setup
- Are Jumbo Frames Enabled?
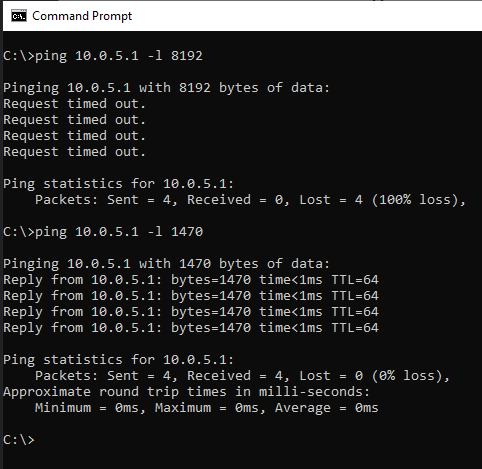
Drive Configuration
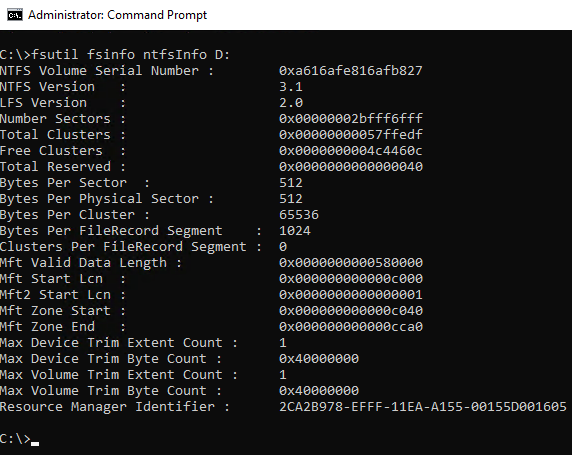
- Are your Data drives formatted in 64k blocks?
fsutil fsinfo ntfsInfo D: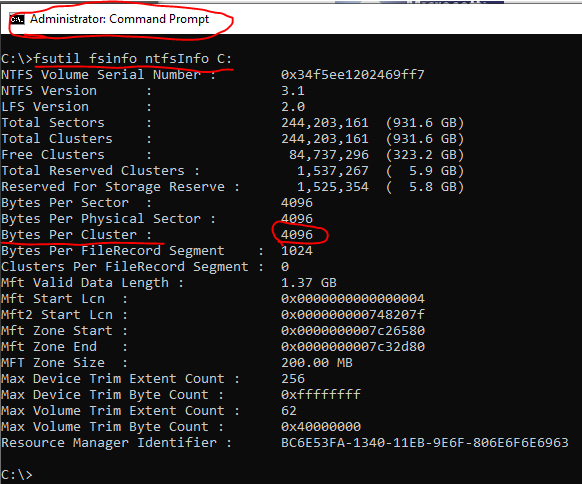
Drive Configuration
- Are your Log drives formatted in 8k blocks?
fsutil fsinfo ntfsInfo L: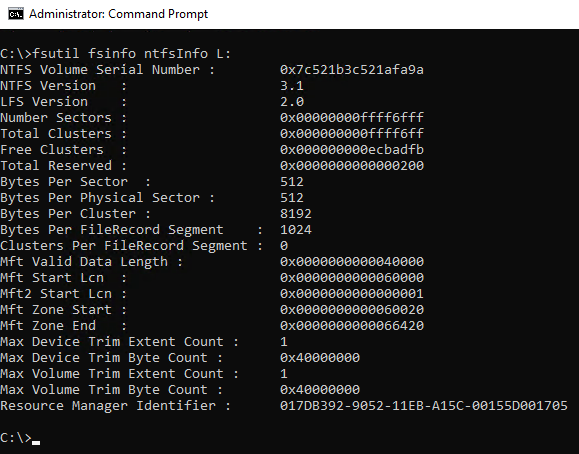
Drive Configuration
Disk Partition Alignment Best Practices for SQL Server - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/sql/sql-server-2008/dd758814(v=sql.100)
Disk performance may be slower than expected when you use multiple disks - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-US/troubleshoot/windows-server/performance/disk-performance-slower-multiple-disks
- Disk Offset
- 20-30% performance enhancement fixing offset
Drive Configuration
- For older OS, is your drive alignment correct? - Consult your SAN best practices
wmic partition get BlockSize, StartingOffset, Name, Index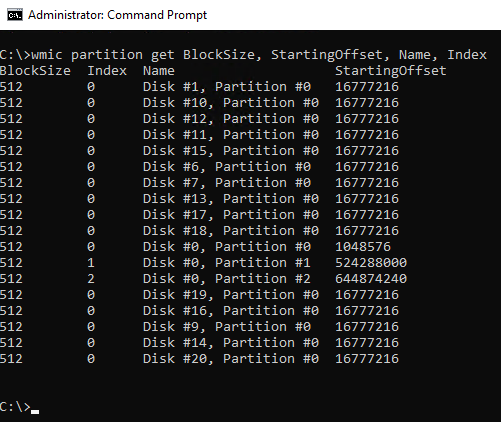
Know Your DATA
- Inserting, Updating, Deleting (CRUD) OLTP
- Insert Only (i.e. Logging)
- Does it make sense to Partition?
- Data Warehouse
How do you query and or filter your data?
- If partitioning, what column makes sense? Primary Key Id? Datetime?
- Date
- Bit (Active? Unfulfilled?)
- Int (Identifier, Status)
- Are you using your clustered keys in queries and are your indexes supporting your queries?
Data Retention - Partioning
- Do you really need 2.5+ billion records in that table?
- Determine your retention periods (1 year? 2 years? 7 years?)
- Does all of the data need to be on hot storage?
- Determine your typical searching range. Month, Quarter, Year)
- Based on number of records per period may also determine partitioning structure.
Does your application/database use any unicode characters?
- nchar
- nvarchar
- ntext
(n Stands for National Language)
Does your database use TEXt/NText/Image?
- They are Deprecated!
- Move the data to a new varchar(max)/varbinary(max) column.
- Just changing the data type won't help performance or space savings. I tried!
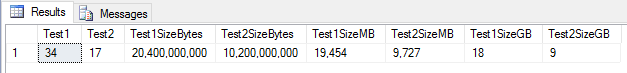
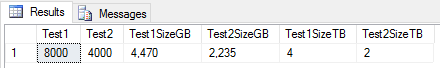
Is there a size difference between nvarchar vs. varchar?
- nvarchar uses 2 bytes (or more) per character
- varchar uses 1 byte per character
DECLARE @test1 NVARCHAR(4000), @test2 VARCHAR(4000),
@test1size BIGINT, @test2size BIGINT;
SET @test1 = 'My Text Data Test';
SET @test2 = 'My Text Data Test';
SET @test1size = DATALENGTH(@test1)
SET @test2size = DATALENGTH(@test2)
SELECT
DATALENGTH(@test1) AS Test1
,DATALENGTH(@test2) AS Test2
,FORMAT(@test1size * 600000000,'###,###') AS Test1SizeBytes
,FORMAT(@test2size * 600000000,'###,###') AS Test2SizeBytes
,FORMAT((@test1size * 600000000)/1024/1024,'###,###') AS Test1SizeMB
,FORMAT((@test2size * 600000000)/1024/1024,'###,###') AS Test2SizeMB
,FORMAT((@test1size * 600000000)/1024/1024/1024,'###,###') AS Test1SizeGB
,FORMAT((@test2size * 600000000)/1024/1024/1024,'###,###') AS Test2SizeGBSize Difference
Datetime & Datetime2 Difference
- Datetime - 8 Bytes, Accuracy Rounded to increments of .000, .003, or .007 seconds
- Datetime2(#) - 0 to 7 digits, with an accuracy of 100ns.
- The default precision is 7 digits.
- 6 bytes for precisions less than 3
- 7 bytes for precisions 3 and 4.
- All other precisions require 8 bytes.
Data Size
DECLARE @test1 DATETIME, @test2 DATETIME2(0), @test3 DATETIME2(3), @test1size BIGINT,
@test2size BIGINT, @test3size BIGINT, @samedt DATETIME;
SET @samedt = GETDATE();
SET @test1 = @samedt;
SET @test2 = @samedt;
SET @test3 = @samedt;
SET @test1size = DATALENGTH(@test1);
SET @test2size = DATALENGTH(@test2);
SET @test3size = DATALENGTH(@test3);
SELECT
@test1, @test2, @test3,
DATALENGTH(@test1) AS Test1,
DATALENGTH(@test2) AS Test2,
DATALENGTH(@test3) AS Test3
SELECT
FORMAT((@test1size * 600000000)/1024/1024,'###,###') AS Test1SizeMB
,FORMAT((@test2size * 600000000)/1024/1024,'###,###') AS Test2SizeMB
,FORMAT((@test3size * 600000000)/1024/1024,'###,###') AS Test3SizeMB
,FORMAT((@test1size * 600000000)/1024/1024/1024,'###,###') AS Test1SizeGB
,FORMAT((@test2size * 600000000)/1024/1024/1024,'###,###') AS Test2SizeGB
,FORMAT((@test3size * 600000000)/1024/1024/1024,'###,###') AS Test3SizeGB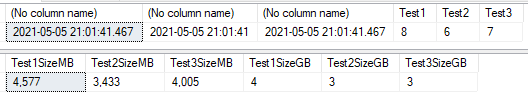
Table Data Size Example
- CreatedDatetime - 8 vs. 6
- ModifiedDatetime - 8 vs. 6
- OrderDate - 8 vs. 6 (or 3)
- FullfilledDate - 8 vs. 6 (or 3)
- ReturnDate - 8 vs. 6 (or 3)
- nvarchar - 8000 vs. 4000
- 5 Datetime Columns = 20GB down to 10 or 5GB
- 1 nvarchar to varchar column 4TB to 2TB
- Per Table!
- Save on space, backup, restore time and bytes transfered.
1 Table with 600 million Rows
Instant File INITIALIZATION
- Before data migration turn on Instant File Initialization for the service and group/account which is executing the scripts, or be in the administrative group when creating the filegroups.
- Why? Speed up file growth on disk. Doesn't zero write-out files. It will affect query performance. You may see long wait latches on page allocations during growth.
- It will also speed up restoring databases
Instant File INITIALIZATION
- Check to see if it is already enabled
SELECT
servicename AS Service_Display_Name,
service_account AS Service_Account,
instant_file_initialization_enabled
FROM
sys.dm_server_services
WHERE
servicename LIKE 'SQL Server (%';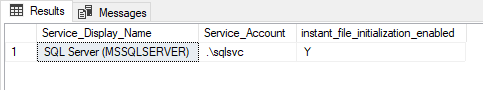
Instant File INITIALIZATION
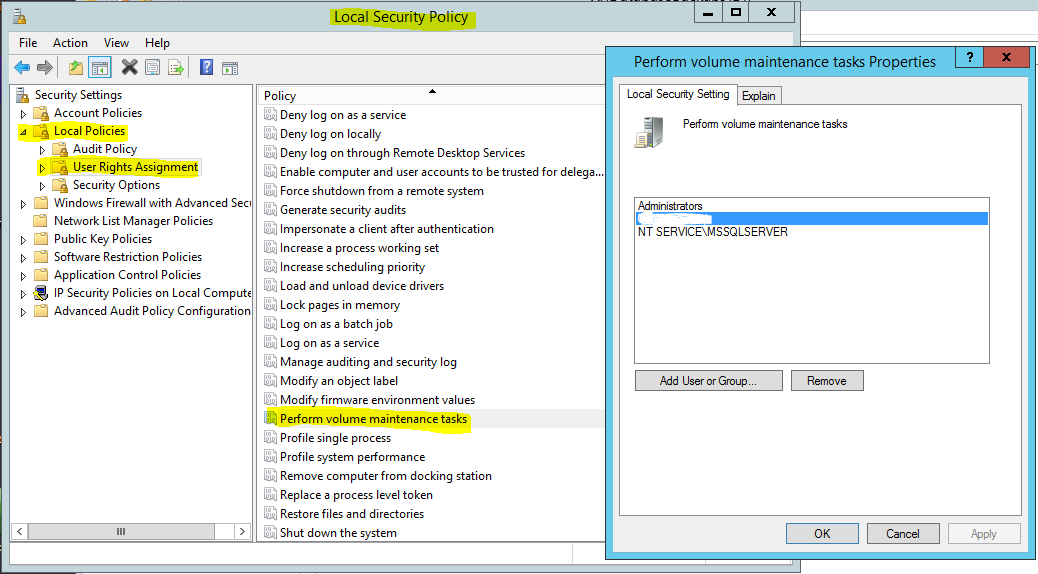
Local Security Policy
Instant File INITIALIZATION
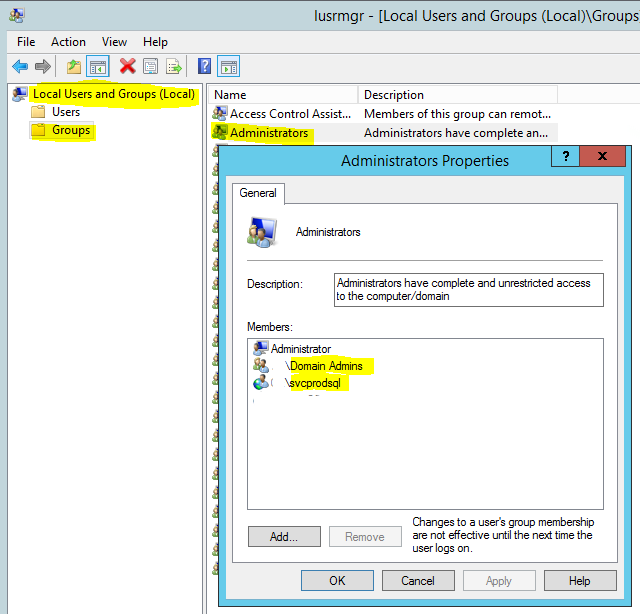
Local Administrative Group
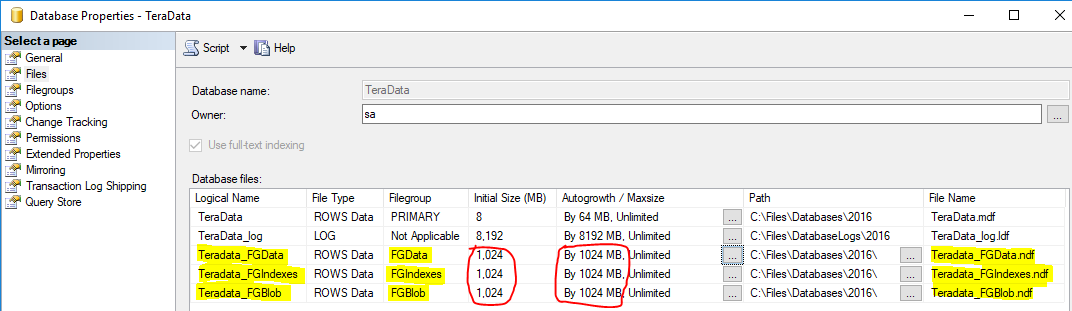
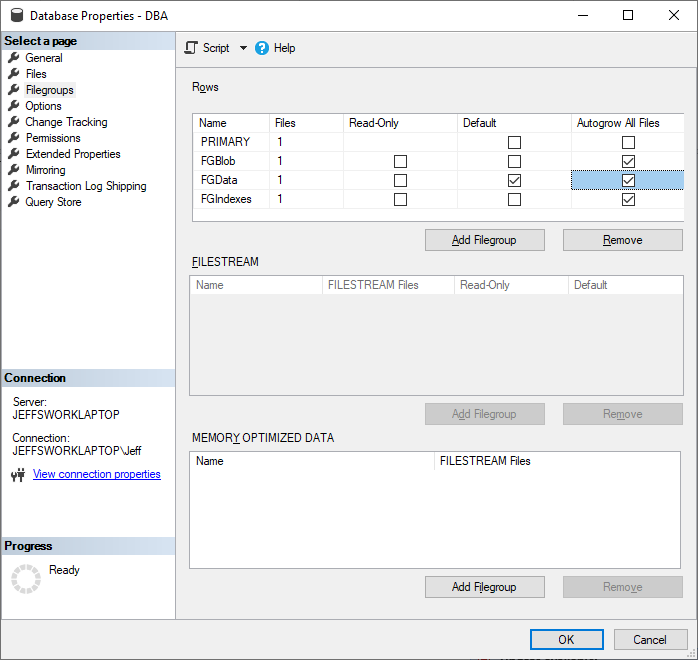
Create File Groups
- File Group for Data - FGData
- File Group for Indexes - FGIndexes
- File Group for Blob Data - FGBlob
- Partition File Groups - (Examples: PSMonth201610, PSYear2016, PSMonthly90)
- Change Default File Group to FGData for new objects.
Create File Groups
USE [master]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [FGBlob]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [FGData]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [FGIndexes]
GO
USE [TeraData]
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT name FROM sys.filegroups
WHERE is_default=1 AND name = N'FGData')
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData]
MODIFY FILEGROUP [FGData] DEFAULT
GOCreate File Groups
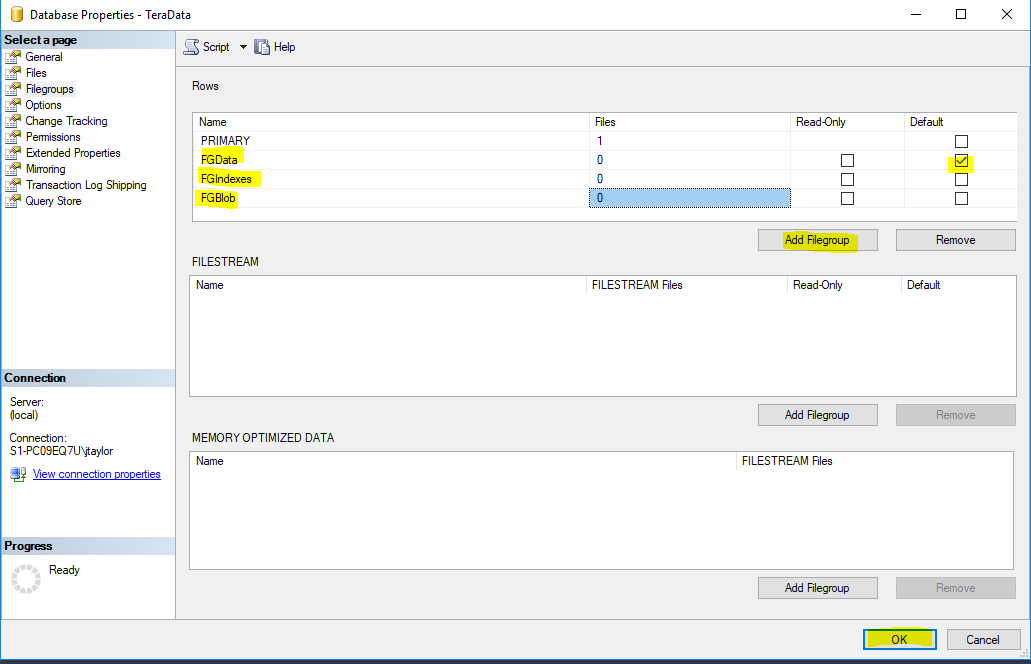
Create Files
- Create at least one file for each file group. - Place on separate drives.
USE [master]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = 'TeraData_FGBlob',
FILENAME = N'D:\Databases\TeraData_FGBlob.ndf' ,
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGBlob]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = 'TeraData_FGData',
FILENAME = N'E:\Databases\TeraData_FGData.ndf' ,
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGData]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = 'TeraData_FGIndexes',
FILENAME = N'F:\Databases\TeraData_FGIndexes.ndf' ,
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGIndexes]
GOCreate Files
Partitioning
USE [TeraData]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_Empty]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2017_10]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2017_11]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2017_12]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2018_01]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2018_02]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2018_03]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2018_04]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2018_05]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2018_06]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2018_07]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2018_08]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2018_09]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILEGROUP [PG_2018_10]
GOPartitioning
USE [TeraData]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_Empty',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_Empty.ndf' , SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_Empty]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2017_10',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2017_10.ndf' , SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2017_10]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2017_11',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2017_11.ndf' , SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2017_11]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2017_12',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2017_12.ndf' , SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2017_12]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2018_01',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2018_01.ndf' , SIZE = 1MB , FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2018_01]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2018_02',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2018_02.ndf', SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2018_02]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2018_03',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2018_03.ndf', SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2018_03]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2018_04',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2018_04.ndf', SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2018_04]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2018_05',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2018_05.ndf', SIZE = 1MB , FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2018_05]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2018_06',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2018_06.ndf', SIZE = 1MB , FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2018_06]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2018_07',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2018_07.ndf', SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2018_07]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2018_08',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2018_08.ndf', SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2018_08]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2018_09',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2018_09.ndf', SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2018_09]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_PG_2018_10',
FILENAME = N'C:\Files\Databases\TeraData_PG_2018_10.ndf', SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 128MB)
TO FILEGROUP [PG_2018_10]
GOPartitioning
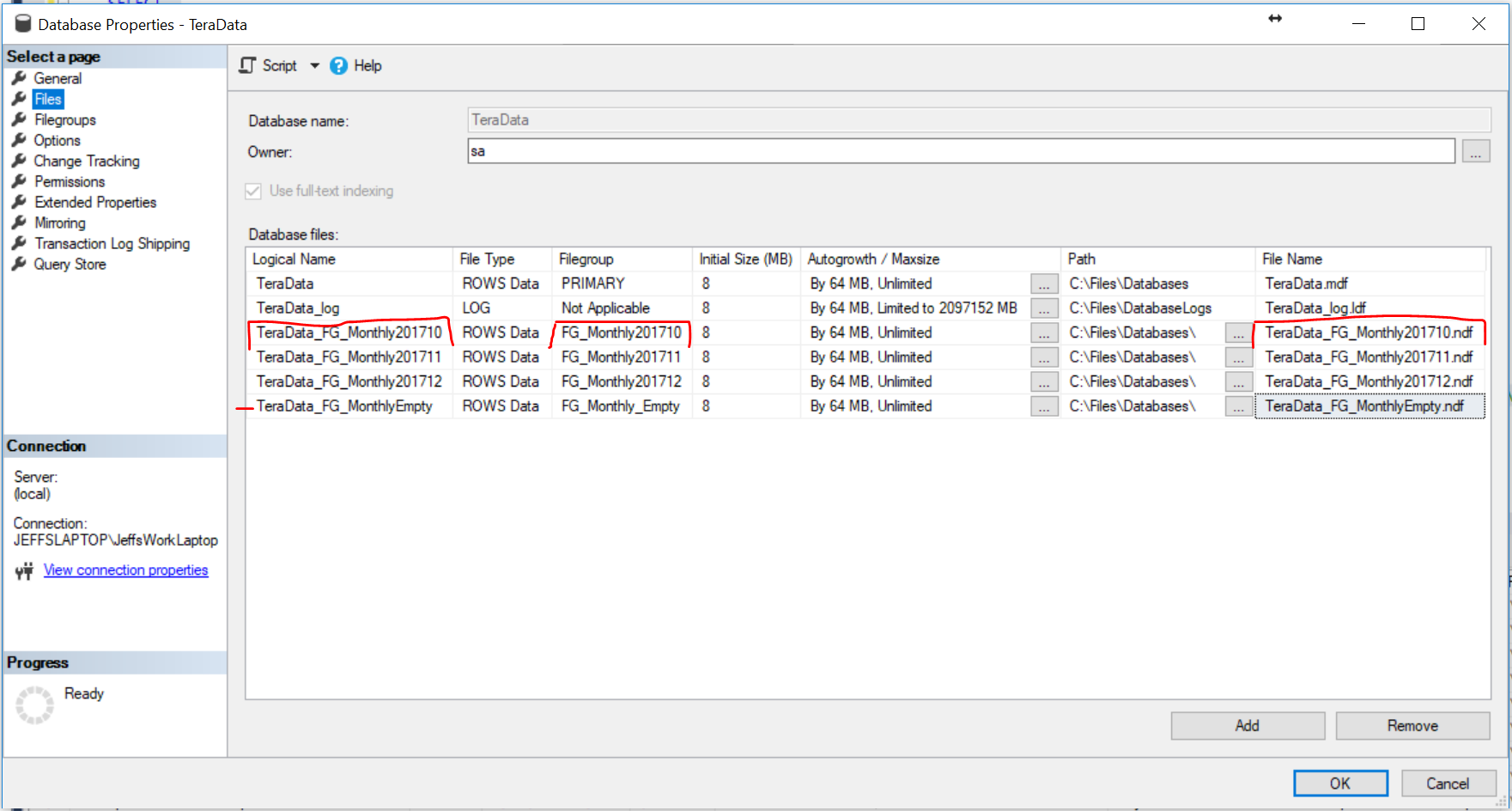
Partitioning
USE [TeraData]
GO
CREATE PARTITION FUNCTION [PF_Monthly](datetime) AS RANGE Right FOR VALUES (
N'2017-10-01',
N'2017-11-01',
N'2017-12-01',
N'2018-01-01',
N'2018-02-01',
N'2018-03-01',
N'2018-04-01',
N'2018-05-01',
N'2018-06-01',
N'2018-07-01',
N'2018-08-01',N'2018-09-01',N'2018-10-01')
GO
CREATE PARTITION SCHEME [PS_Monthly] AS PARTITION [PF_Monthly] TO (
[PG_Empty],
[PG_2017_10],
[PG_2017_11],
[PG_2017_12],
[PG_2018_01],
[PG_2018_02],
[PG_2018_03],
[PG_2018_04],
[PG_2018_05],
[PG_2018_06],
[PG_2018_07],
[PG_2018_08],[PG_2018_09],[PG_2018_10])
GOPartitioning
USE [TeraData]
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[ErrorLog](
[ErrorLogId] [INT] IDENTITY(-2147483648,1) NOT NULL,
[PageName] [VARCHAR](200) NULL,
[ErrorLabel] [VARCHAR](100) NULL,
[CustomErrorMessage] [VARCHAR](200) NULL,
[ExecutedDatetime] [DATETIME] NOT NULL,
[ExecutionMessage] [VARCHAR](MAX) NULL,
[CreatedDatetime] [DATETIME] NOT NULL,
[ServerName] [VARCHAR](20) NULL,
[ServerIPAddress] [VARCHAR](16) NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_ErrorLog] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[ErrorLogId] ASC,
[CreatedDatetime] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF,
ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE)
ON [PS_Monthly]([CreatedDatetime])
) ON [PS_Monthly]([CreatedDatetime])
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[ErrorLog] ADD CONSTRAINT [DF_ErrorLog_CreatedDatetime]
DEFAULT (GETDATE()) FOR [CreatedDatetime]
GOMore Performance
- If greater performance is needed create multiple files per file group.
- Place multiple files on multiple LUNS/Drives
Create Multiple Files
USE [master]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGBlob1', FILENAME = N'D:\Databases\TeraData_FGBlob1.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGBlob]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGBlob2', FILENAME = N'E:\Databases\TeraData_FGBlob2.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGBlob]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGBlob3', FILENAME = N'F:\Databases\TeraData_FGBlob3.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGBlob]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGBlob4', FILENAME = N'G:\Databases\TeraData_FGBlob4.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGBlob]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGData1', FILENAME = N'G:\Databases\TeraData_FGData1.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGData]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGData2', FILENAME = N'F:\Databases\TeraData_FGData2.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGData]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGData3', FILENAME = N'E:\Databases\TeraData_FGData3.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGData]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGData4', FILENAME = N'D:\Databases\TeraData_FGData4.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGData]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGIndexes1', FILENAME = N'D:\Databases\TeraData_FGIndexes1.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGIndexes]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGIndexes2', FILENAME = N'E:\Databases\TeraData_FGIndexes2.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGIndexes]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGIndexes3', FILENAME = N'F:\Databases\TeraData_FGIndexes3.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGIndexes]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [TeraData] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'TeraData_FGIndexes4', FILENAME = N'G:\Databases\TeraData_FGIndexes4.ndf',
SIZE = 8192KB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB ) TO FILEGROUP [FGIndexes]
GOCreate Multiple Files
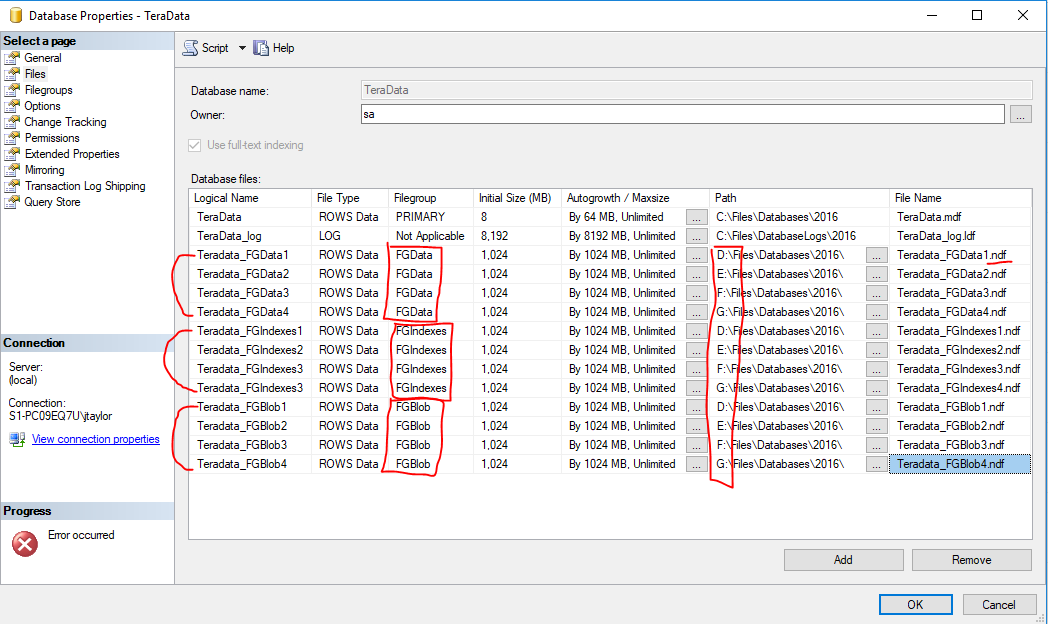
File Size
- Pre-Grow Files - Attempt to determine size of new files, based on data size, index size and blob storage, so you don't have to have file growths during the data migration process.
- Divide the total by however many files you end up selecting.
File Size
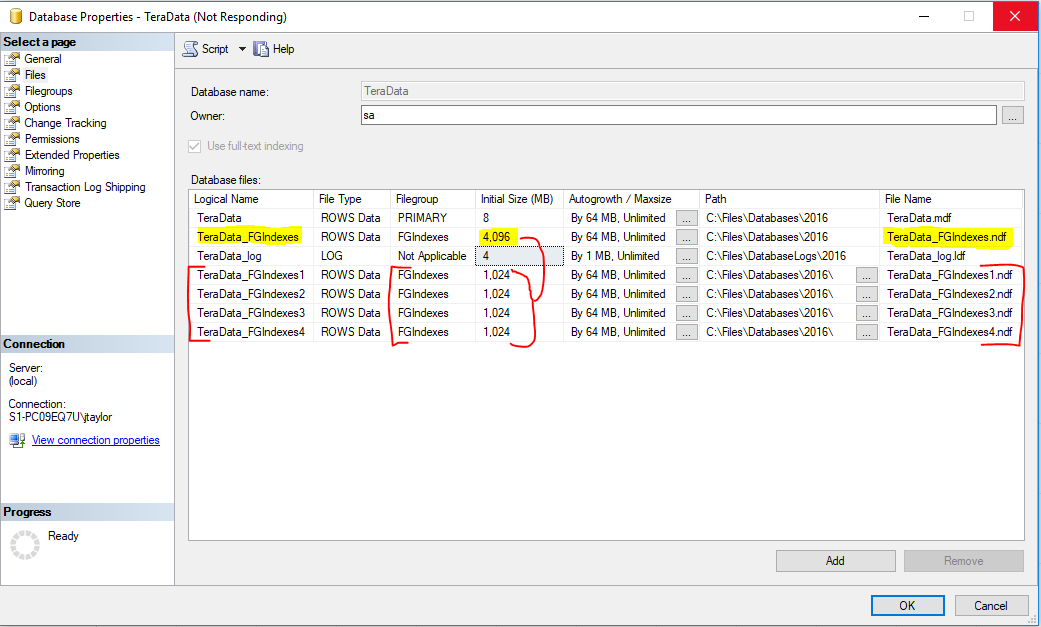
File Growth
- Ensure all files in the filegroup have the same auto-growth setting.
- If multiple files in one filegroup make sure you enabled the flag which distributes the data evenly between all files in a filegroup. Trace Flag T1117 (not required now in 2016 and newer).
File Growth
* note - Autogrow All Files Flag - Single User Mode
Do you have any heap tables?
- Create clustered indexes on the heap tables. - Insure created on the correct new FGData Filegroup with compression if possible.
Moving Blob Data Types
-
You have to create a new table to relocate blob storage.
- Create a new table.
- Copy data to the new table.
- Check table record counts.
- Drop old table.
- Rename the new table.
- Create Indexes.
Moving data
-
If you have millions/billions of records, batching records to move may be appropriate. If you can schedule a maintenance window, perhaps use simple mode for faster performance as well.
- Always batch by your clustered key for best performance.
Compression
- Use Page Compression for Tables and Indexes
- Use Columnstore compression for Data Warehouse or archive tables
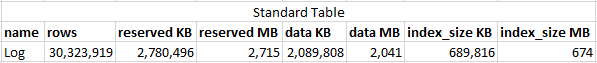
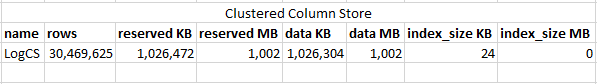
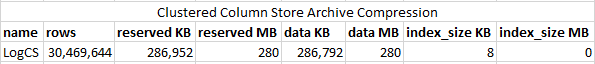
63.1% Space Savings
89.7% Space Savings
Compression
- Estimate compression for tables
EXEC sp_estimate_data_compression_savings 'dbo','Votes',NULL,NULL,'PAGE'
EXEC sp_estimate_data_compression_savings 'dbo','Votes',NULL,NULL,'COLUMNSTORE'
EXEC sp_estimate_data_compression_savings 'dbo','Votes',NULL,NULL,'COLUMNSTORE_ARCHIVE'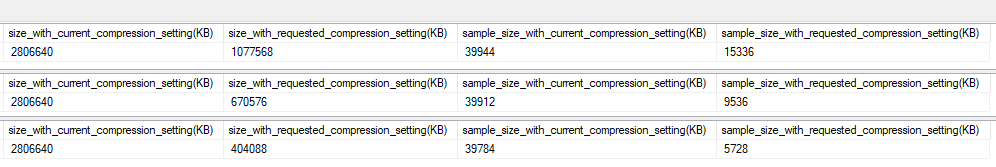
- Estimation will also include indexes
Compression
-
When Building/Rebuilding Tables, and Clustered Indexes use Compression (DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE) and place in FGData filegroup. Don't forget (TEXTIMAGE_ON FGBlob) for LOB
-
When Building/Rebuilding Non-clustered Indexes use Compression (DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE) and place in FGIndexes filegroup
-
Columnstore is best for Archive/Log Tables - (DATA_COMPRESSION = COLUMNSTORE or DATA_COMPRESSION = COLUMNSTORE_ARCHIVE) and place in FGData filegroup
-
Sort In TempDB to minimize file bloat - SORT_IN_TEMPDB = ON
- Don't use Fillfactor
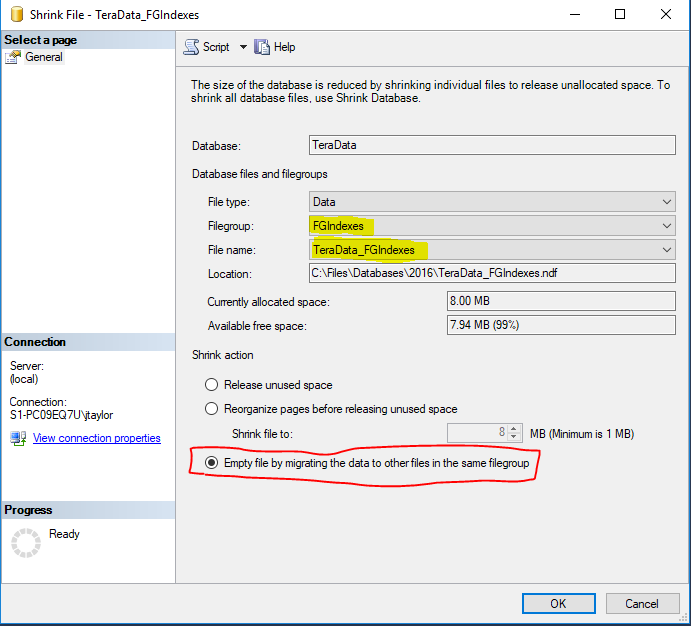
Redistribute 1 to 4 files
- If you end up needing more performance, you can add more files to each file group.
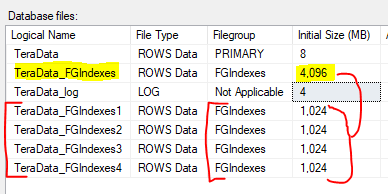
- Your file groups are now lopsided.
- There is a way to fix that.
USE [MyDatabase]
GO
DBCC SHRINKFILE (N'MyDatabase_FGIndexes' , EMPTYFILE)
GO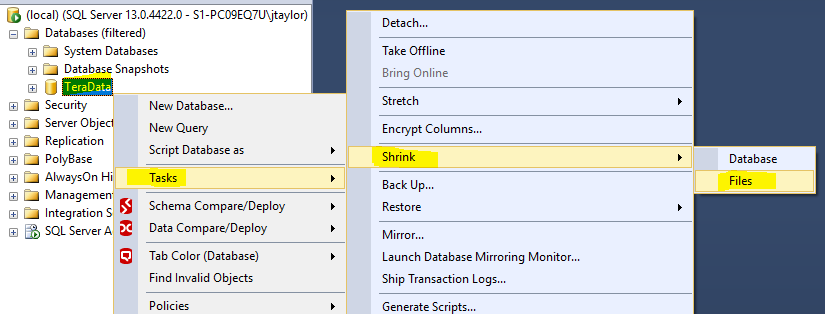
Redistribute 1 to 4 files
Redistribute 1 to 4 files
Fixing Data Types
- Create new column.
- Copy data to new column.
- Check that values match 100% for column.
- Drop old column.
- Rename new column.
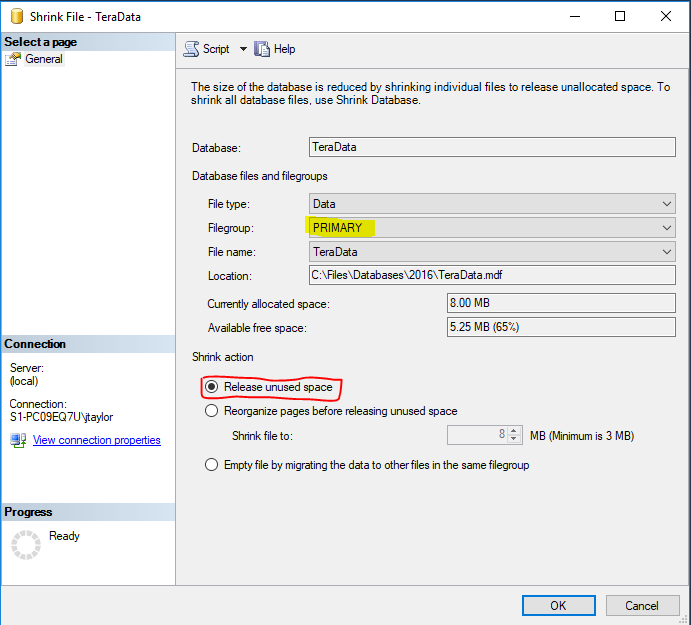
Shrink Primary
- Shrink Primary File Group
USE [MyDatabase]
GO
DBCC SHRINKFILE (N'MyDatabase' , 0, TRUNCATEONLY)
GOShrink Primary
Overall Results
- Overall database size cut in less than half original size using better data types (varchar, datetime2) (4TB to 1.55TB)
- Overall database size down further to 1/3rd of the original size using Page/Columnstore Compression. (4TB down to 500GB)
- Single file database file now spread across multiple LUNS/Disks with multiple (12) files reducing latency from 1,000+ms to less than 20ms.
- Backup speed and restore speed cut in half. (Compression, data types, Instant File Initialization)
- Throughput went from 200/300MBPS to over 2,000mbps (Multi-Path, Jumbo Frames, 1GB to 8GB Fiber/10GB/25GB/40GB Ethernet.)
Questions?
Resources
-
DateTime Data Types/Sizes
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms186724.aspx
-
nchar/nvarchar Data Types/Sizes
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms186939.aspx
-
text/ntext/image
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms187993.aspx
Contact
How To Tune A Multi-Terabyte Database For Optimum Performance
By reviewmydb
How To Tune A Multi-Terabyte Database For Optimum Performance
This session will cover how to tune a multi-terabyte database where all of the data is stored a single file, primary file group. We will look at file groups, managing indexes and moving large amounts of data.
- 720



