Welcome to Electrical
Mentors
Austin Russell
Ricardo Ortiz
James Corcoran


Austin
- Network & Cyber Security Engineer
- Groton Utilities
- Student on the team for 2013 & 2014 season, now mentor for the past year
- New England Institute for Technology, September 2017
- Associate of Science, Network Engineering
- Bachelor of Science, Network Engineering & Cyber Security
- Other than just electrical, I manage the IT and computer systems for the team, as well as anything else that needs to be done

Ricardo
- TODO
James
- Software Engineer at Electric Boat
- Move air, water, and metal with electrons and dinosaurs
- Electrical/Programming mentor on FRC2168 since 2008
- BS Computer Engineering from Rochester Institute of Technology
- I like to learn about new & random stuff:
- Space, 3D Printing, Computer Vision, Flat Earth Society
- Micro controllers, Artificial Organs, Information Security
- CNC, Lego, Cheap stuff from China, Linux, Pyrotechnics,
- Test Automation, Wood working, primitive technologies
- Robotics!, Web Design, Statistics, Photo editing, ...
Course Topics
- Motor Controllers
- Motors
- DC Motors
- Servos (Rotary/Linear)
- RoboRIO
- VRM
- Radio
- Sensors
- Encoders, Gyro, potentiometers
- Boolean (Mechanical Switches, Hall effects, IR proximity)
- IR rangingsensors
- Pneumatics
- PCM
- Solenoids
- Acutators
Overview
Topics to cover
- Team role
- Interfacing with other disciplines
- Build season role
- Prototype support
- Final wiring
- Criticality of our work
- Aware of design decisions for seamless autos
- Hardware overview
Team Role / Discipline Interaction
- Electrical
- Mechanical
- Aid prototype development
- Programming
- Determine the right sensors for the job
- CAD
- Plan component placement
- Drive Team
- Custom controls & Automation
- Mechanical
Build Season Role
- Week 1 - 3
- Test which sensors work for detecting game elements
- Source components for games specific features
- Support prototype wiring
- Week 4 - 6
- Plan out electrical layout for comp bot
- Wire practice & comp bot
- Week 6+
- Keep the robot running at events
- Fix broken wires, sensors, etc
- Wire up new mechanisms & design revisions
- Figure out what doesn't work, find solutions
- Keep the robot running at events
Hardware Overview

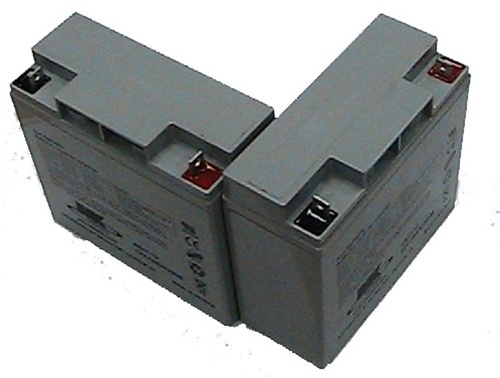
Battery
The brains of the operation.
- 12V Sealed Lead Acid Battery
- Like what you'd find on a motorcycle or lawnmower
- All power for robot operation must come from ONE battery.
- Can supply 100s of Amps
- Respect the batteries and don't get hurt!
Main Breaker
High current (120A) circuit breaker.
- Main robot power switch
- OFF - Depress red button
- ON - Close black lever
- Open circuits when high current drawn for long duration of time
- Prevents fires, causes tears
- Design bot to never pop

Power Distribution Panel (PDP)
Distributes power from the battery to all components on the robot.
- Up to 8 40A circuts
- Up to 8 30A circuits
- Special 10A & 20A circuits for peripherals

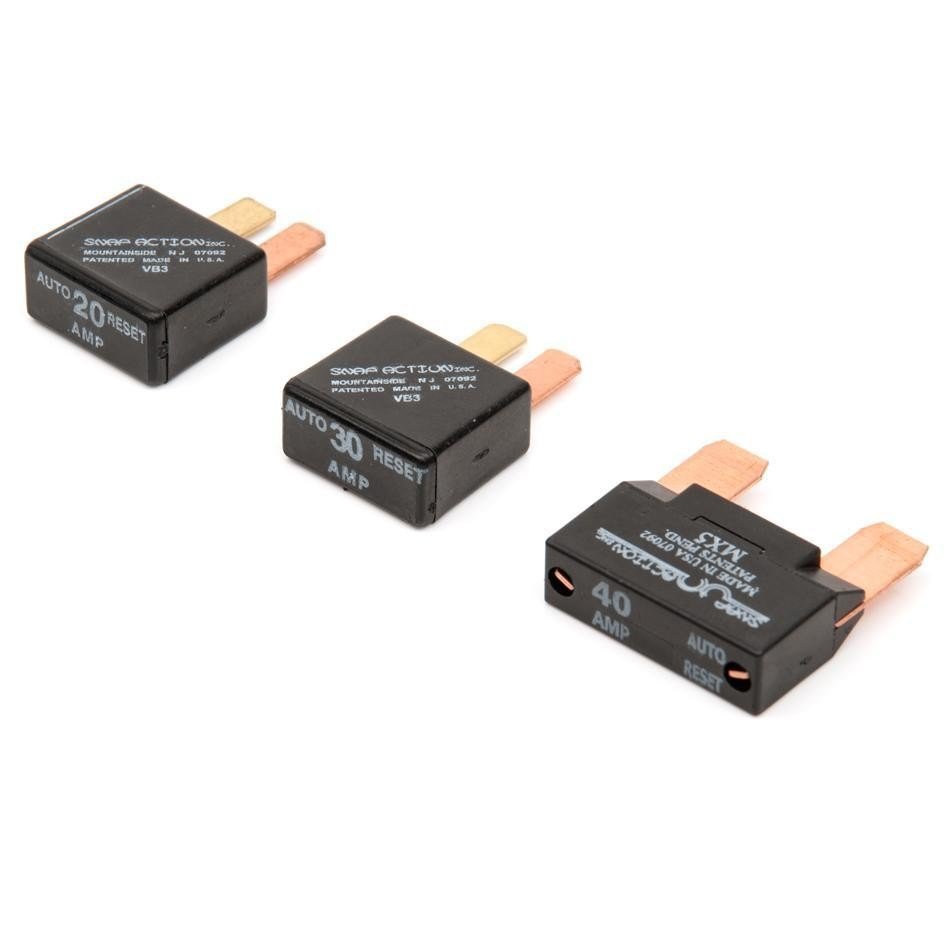
Auto-Resetting Circuit Breaker
Different sizes (40A, 30A, 20A)
- Protect hardware from blowing
- 40A breakers for powerful motors
- 30/20A breakers for
- After heating up (high current), these open circuit
- Once cool they will automatically close and send power back to downstream componet
Pneumatics Control Module (PCM)
Allows control of pneumatics components over CAN bus
- Control up to 8 solenoid channels
- Turn compressor on/off compressor

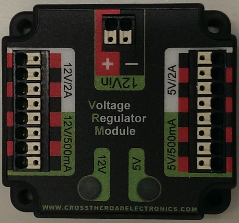
Voltage Regulator Module (VRM)
Provides regulated supply voltages
- 12V 2A
- 500mA section counts towards 2A limit
- 5V 2A
- 500mA section counts towards 2A limit
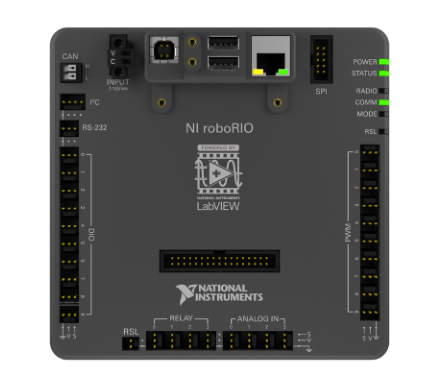
RoboRIO
The brains of the operation.
- Runs our code
- Controls all outputs
- Reads all inputs
- Talks back to driver station laptop
- Interfaces
- PWM
- Digital Inputs/Outpus
- Relay Channels
- Analog inputs
- MXP expansion header
Motor Controllers
Control speed and direction of motors
- Many different kinds
- SPARK, Victor 888, Talon, Victor SP, Talon SRX
- Controlled by roboRIO over
- PWM
- CAN
- Don't plug in backwards
- Expensive learning experience





Robot Radio
Standard WIFI Radio (802.11)
- Can be configured as Access Point
- For use at home
- Wireless Client
- For use at competitions

SPIKE Relay module
Contains two relays (switches)
- Not terribly common
- Can be used to control anything that just needs to be turned on/off (12V).
- Compressor
- LEDs
- Low power motor with no speed control
- Contains its own 20A fuse

Cameras
Ethernet / USB
- Used for:
- Operator feedback
- Object detection
- Camera feed can be fed back to driver station or processed locally on the roboRIO

Motors
Topics to cover
-
Intro on voltage, current, resistance
-
Review FRC parts
-
Battery
-
PD board
-
Breakers
-
Motor controllers
-
-
DC Motors
- Servo Motors

Voltage/Current/Resistatnce
FRC Parts - Refresher

Find them:
- Battery
- PD Board
- Breakers
- Motor Controllers
- RoboRIO
- Radio
- VRM
- PCM

A B C
D
E
F
G H

MOTOR CONTROLLERS

Motor Controllers
- Allow motors to be... controlled by the roboRIO
- Varying degrees of features
- Some are very simple just speed/direction control
- Some are complex and can interface directly to sensors and have internal position/speed controllers
- Brake/Coast setting
- High RPM >> Use COAST!



Brushed DC MOTORS

DC MOTORS
- Magnets mounted around the exterior
- "stator"
- Coil of wire at center
- "rotor"
- When current flows through the coil it creates a magnetic field that reacts against the field created by the magnets and causes rotary motion
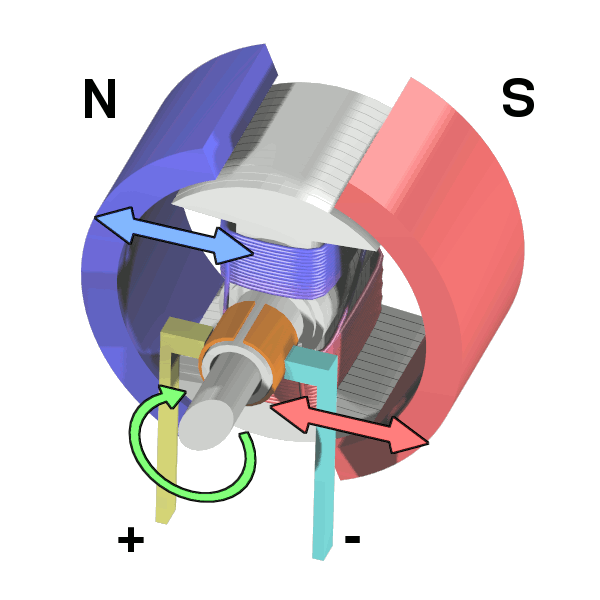
Brushed DC Motors: the most common type of motors used on our robots.
Brushed DC Motors
Lab
Materials Needed
- Motor tester board with PWM generator
Procedure:
- Wire up motor tester board to DC Motor
- Hook up multimeter across input and output of motor controller.
- Monitor voltage output as motor speed is changed
How does the Brake/Coast jumper affect operation?
What happens when the load is applied to the motor?
SERVO MOTORS

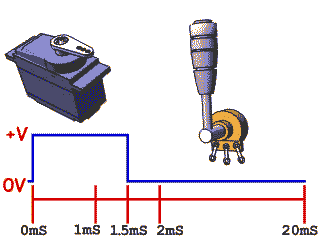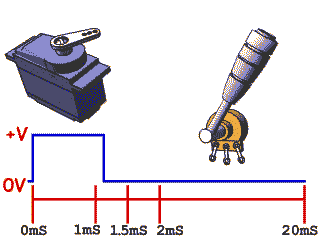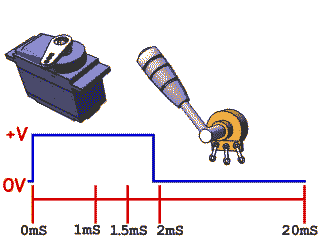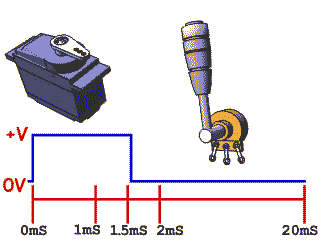
Rotary Position Servos
Command motor to specific angle
- Can be used for controlling mechanism to specific position
- Need to take external forces into consideration when choosing part to prevent stripped gears and backdriving
Continuous Rotation Servos
Same as position servos but, control circuitry is modified.
- Instead of controlling position...
input controls speed and direction (sound familiar?) - These aren't the solution to all out problems though, remember there's still a very small DC motor inside the servo.
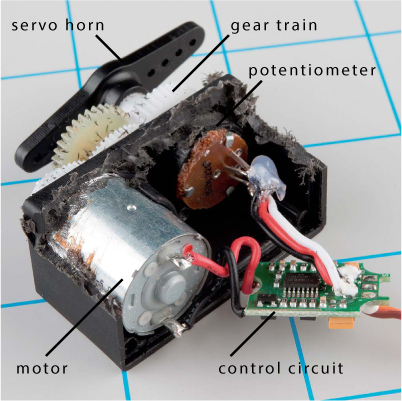
Linear Servo Motors
Command motor to extension

Similar to rotary servo, but extends and retracts
- Gear boxes in some of them can provide a large toque multiplier.
- Surprisingly strong
- Easy to break when side loaded
Lab
Materials Needed
- Motor tester board with PWM generator
Procedure:
- Wire up motor tester board to servo (directly to PWM generator)
- Monitor position of servo as the PWM generator moved.
What will happen when an external force is applied?
Sensors

Topics to cover
- Discrete Sensors
- Switches, Hall effect,
- Analog Sensors
- Potentiometer, SHARP IR, Pressure Sensor
- Position Sensors
- Encoders, Gyros, IMUs
- Cameras
Discrete Sensors
- Report a Boolean status to the control system
- On/Off, True/False
- Examples:
- Limit switch (Mechanical contact)
- Hall Effect Sensor (Magnetic field)
- Proximity Sensor (Metal presence)
- Photo Detector/Emitter (Light)




Analog Sensors
- Voltage varies over sensed range
- Can be used to measure
- distance, pressure, current, position, etc
- Analog sensors can be turned into Boolean statuses with logic in robot code:
- e.g. If voltage >= 2.5 true; else false;
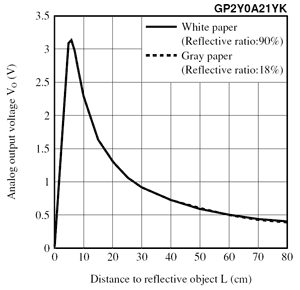
Analog Sensors (cont)
- Examples:
- SHARP IR
- Pressure Sensor
- Potentiometer
- Ultrasonic




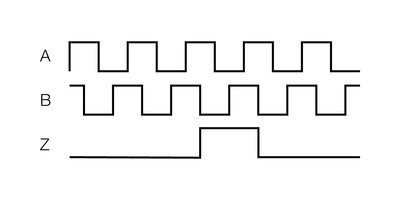
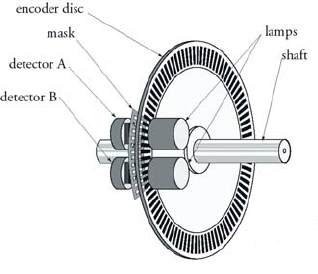
Encoders
- Incremental or absolute indication of position
- Produce a train of pulses
- Number of pulses can be counted to determine position or speed of component

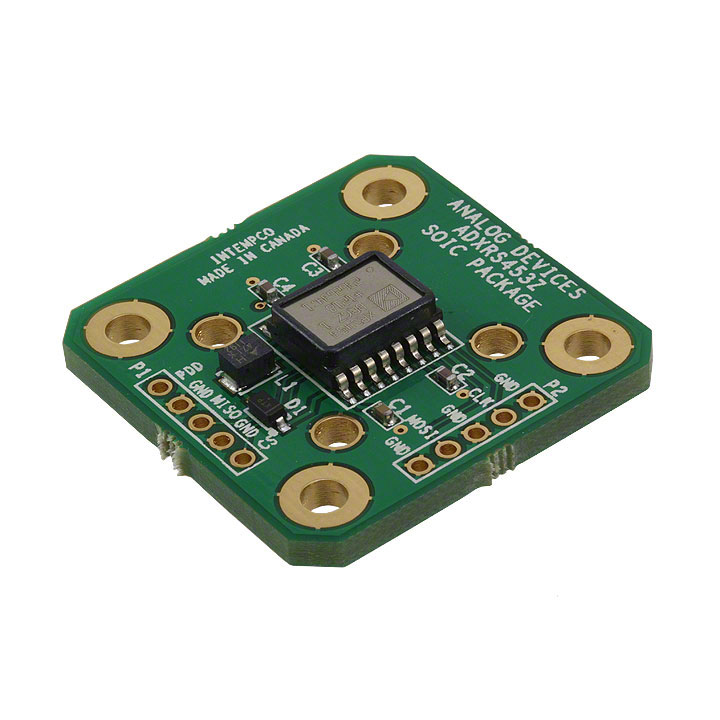
Gyros
- Gyro
- A gyro can be used to measure the robots heading (which way it's facing), usually relative to a calibrated zero
- Value reported as a rotation rate which is integrated to determine heading
- Interface can be serial (ADXRS450) or analog (ADW22307)

IMUs
- Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)
- Combine multiple sensors for multi-axis position indication
- Typically at least a Gyro and Accelerometer
- Can also include Magnetometers, temperature sensors, etc.
- Typically provides roll/pitch/heading
- Some can also provide translation/offset relative to starting position (field oriented).


Camera
- Used for drive team situational awareness and Autonomous robot navigation
- Connect to robot over Ethernet or USB
- Important performance characteristics
- Resolution (more is not nesc. better)
- Exposure (calibratable)
- Image latency


Pneumatic Systems

Topics to cover
- Pneumatic components
- Pneumatic controls
Air Compressor

- Convert electric energy into compressed air
- VIAR 90C
- Runs off 12VDC, ~10A
- Rated at 9% duty cycle!!!
Nason Pressure Switch

- Used by control system to turn compressor on and off
- Note the labels "NC" and "C"
- Remember what those mean from our discrete sensors class?
- Closed circuit when pressure is low
Air Tanks

- Clippard tanks store 574ml of air ea.
- Max 125 PSI
Pressure Regulator
- Similar to voltage regulator but for air
- Allows stepping high pressures down to lower pressures
- 120 PSI -> 60 PSI
- 60 PSI -> 30 PSI

Pressure relief vlave
- Releases pressure out of system when above "safe" set point
Pressure Gauge
- Indicates the pressure accumulated within the system.
- Can be used to indicate pressure before (high side) or after (low side) regulators


Pneumatic Actuator (Cylinder)
- Linear actuator
- Two "ports", one at each end
- Rod down the middle
- Tail end of rod seals against inner wall of cylinder
- Pressure difference across the seal causes rod to extend/retract

Pneumatic Actuator (Cylinder)
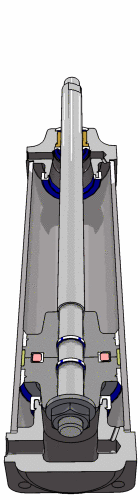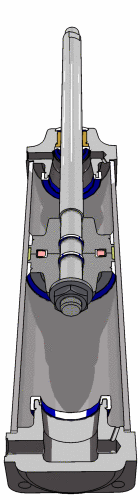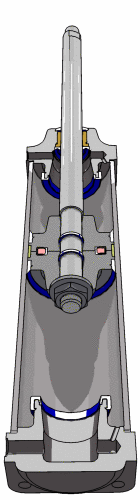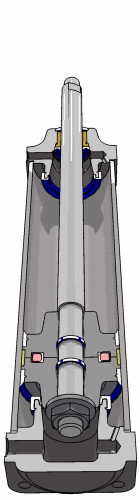
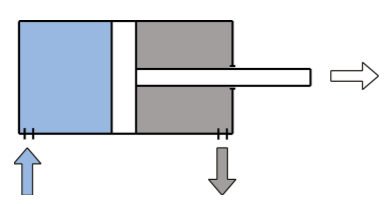
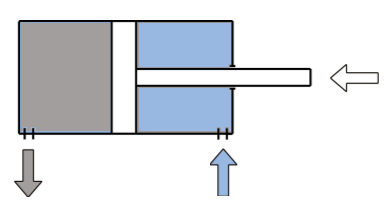
- Extend cylinder
- Apply pressure to the left of the seal
- Vent pressure from the right of the seal
- Retract cylinder
- Apply pressure to the right of the seal
- Vent pressure from the left of the seal
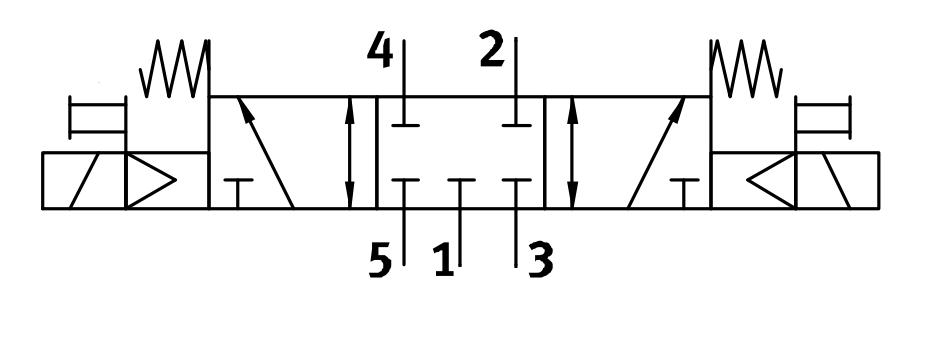
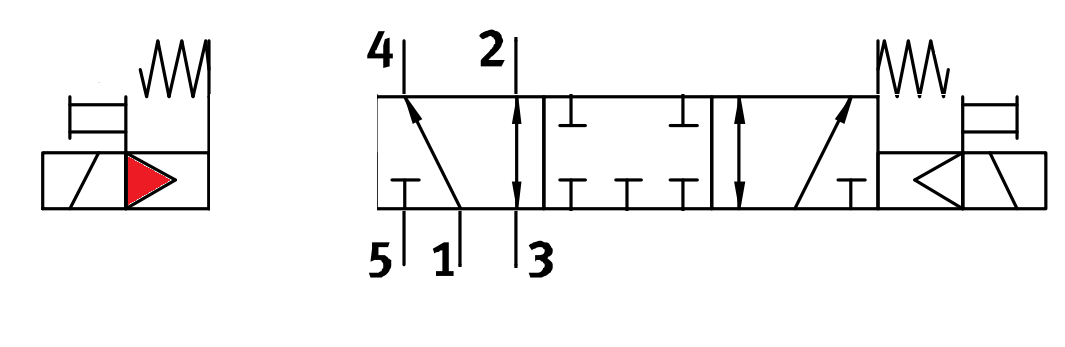
Solenoid Valve

Electrically control air flow.
- Solenoids in FRC are either 12 or 24V
- We typically use "5/3" double solenoid valves
- 5 physical ports (holes) on it
- 3 positions the valve can be in
- Called "double" solenoids because each valve has two solenoids.
- The solenoids are coils of wire
- When electricity flows through them it creates a magnetic field.
- The magnetic field causes the valve to port air in different directions
Solenoid Valve


B: Spring return
A: Solenoid
What do these symbols mean?!@#
C: Depicting how air will flow between numbered ports for different valve positions
D: Manual actuator
Solenoid Valve Positions

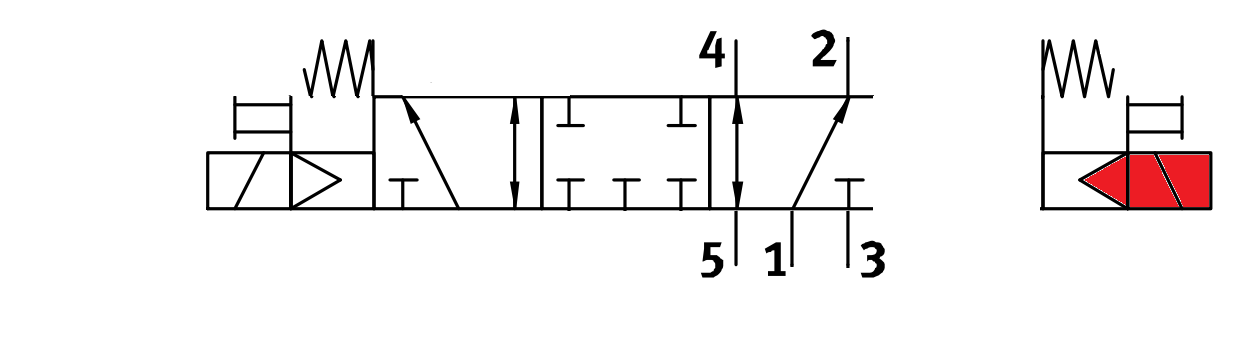

- Left solenoid energized
- Valve shifts
- Pressure flows from 1 to 4
- 2 and 3 are connected allowing 2 to vent
- Right solenoid energized
- Valve shifts
- Pressure flows from 1 to 2
- 4 and 5 are connected allowing 4 to vent
Pneumatics Control Module (PCM)
Allows control of pneumatics components over CAN bus
- Turn compressor on/off compressor
- Control up to 8 solenoid channels
- 8 single acting solenoids
- 4 Double solenoids

Lab
Wire & Plumb up a simple pneumatic system
- Compressor turned on/off by Nason pressure switch (through relay for example)
- Air tank to store pressure from pump
- Plumb pressurized tank to regulator
- Set regulator to ~30 PSI
- Plumb regulator to 5/3 valve (port 1 on previous slide)
- Plumb outputs of valve (ports 2 & 4) to cylinder
- Apply power to system and verify compressor turns off at right pressure
- Energize solenoids one at a time
- Observe behavior of cylinder

Safety
Topics to cover
- Personal Safety
- Robot Safety
- Yes, Robots have feelings too
Personal Safety
- Safety is always a number one priority
- We want to keep ourselves safe at all times
Tools that can hurt
-
Cutting tools
- Flush cutters
- Scissors
- Strippers



Tools that can hurt
-
Heating tools
- Soldering Iron
- Heat gun


Tools that can hurt
-
Crushing/Impact tools
- Crimpers

Tools that can hurt
-
Common shop tools
- Screw drivers
- Wrenches
- Pliers
- etc.

Tools that can hurt
-
Machinery
- Band Saw
- Drill Press
- Drills



How to be safe
-
Always have a mentor present
- If not sure about something, ask a mentor or student lead
- Use Personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Use common sense
- Think before doing
PPE
-
Safety Glasses
- Always to be used in shop when machinery is run or mechanical is working
- Always to be used when soldering
- Hot liquid metal in the eye is not good
- Gloves
- Used when needed
- Sometimes helpful when soldering when holding wire so you don't burn hands, but can hinder hand articulation and mobility
- Used when needed


Robot Safety
- Robots are expensive
- Electrical components are almost always the most expensive parts of an FRC robot
- We want to keep them working

Robot Safety
- Double check all wiring before robot power is applied
- When making changes to the electrical or control systems, be sure to have a mentor or student lead verify the changes
-
Mentors qualified to check work
- James
- Austin
- Kevin H
- Ricardo
- Student leads qualifed to check work
- Deidra Hall
-
Mentors qualified to check work
Robot Safety
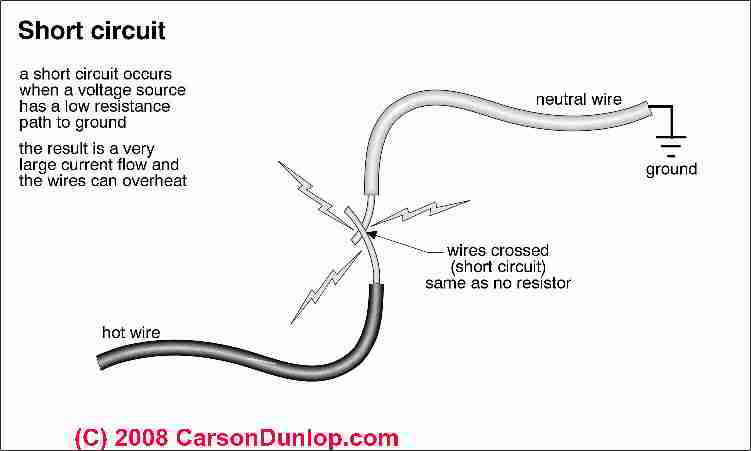
- Don't short connections
- A short circuit is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or a very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive amount of current flowing into the circuit
- Verify that the chassis is isolated from the battery power and ground before the main breaker is turned on
Robot Safety
- Pay attention to what you are doing
- What
- Where
- When
- Why
- How
- Some of the simplest and sometimes biggest mistakes can be due to not following this structure
Robot Safety
- Pay attention to what is going on around you and the robot
- Listen for ENABLING
- RSL will blink when robot is enabled
- Ensure others are not repairing/tampering/controlling things that will effect what you are doing
- Ensure that others are not in/around the robot when enabling the robot
- Listen for ENABLING
Robot Safety
- Robots can be dangerous
- Have many different types of mechanisms that can cause injury
- Always pay attention to whats going on when working in the robot
- Look out for others
- Sometimes other students may be doing something unsafe or can lead to injury
- Let them know, and/or the Safety lead, and/or a mentor
The End
Questions?
Electrical_Team2168
By ricardo2168
Electrical_Team2168
Off season electrical course for FRC team 2168
- 166