"Advanced"
Functional Programming
For the absolute beginner
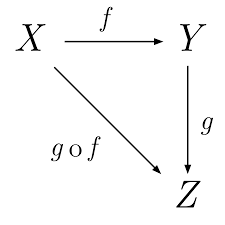
(a → F[b]) → F[a] → F[b]
(a -> b) → F[a] → F[b]
λx.x
Algebraic Data Types
> let a = (false, false);;
val a : bool * bool = (false, false)> let b = (false, true);;
val b : bool * bool = (false, true)> let c = (true, false);;
val c : bool * bool = (true, false)> let d = (true, true);;
val d : bool * bool = (true, true)Product Types
type Result =
| Success of int
| Failure of string
let half x =
if x % 2 = 0 then Success (x/2)
else Failure "That's not an even number"
Sum Types
> half 8;;
val it : Result = Success 4
> half 7;;
val it : Result = Failure "That's not an even number"val half : x:int -> ResultObject Inheritance Hierarchy
Lambda Calculus
λ
Lambda Calculus
The world's smallest universal programming language
<expression := <name> | <function> | <application>
<function> := λ<name>.<expression>
<application> := <expression><expression>
Lambda Calculus
Functions
λx.x
(λx.x)y
≡ y
Lambda Calculus
Application
(λxy.x)E1E2
≡ E1
(λxy.x)E1
≡ λy.E1
(λxy.y)E1E2
≡ E2
(λxy.y)E1
≡ λy.y
Lambda Calculus
Application
a b c d
≡
((a b) c) d
> printf "%s" "Hello\n";;
Hello
val it : unit = ()> printf "%s";;
val it : (string -> unit) = <fun:it@19-7>
> printf "%d";;
val it : (int -> unit) = <fun:it@20-8>2 + 3 + 5 = 10
(2 + 3) + 5 = 10
2 + (3 + 5) = 10
2 + (3 + 5)
("Hello," + " ") + "World!"
([1; 2] @ [2; 3; 4]) @ [3; 4; 5]
(2 + 3) + 5
"Hello," + (" " + "World!")
[1; 2] @ ([2; 3; 4] @ [3; 4; 5])
SEMIGROUP
So What?
2 + 3 = 5
2 + 0 = 2
n + 0 = n
Identity
2 * 3 = 6
2 * 1 = 2
n * 1 = n
Identity
MONOID
So What?
[1; 2; 3; 4; 5]
[2; 3; 4; 5; 6]
x → x + 1
List [Int]
List [Int]
Int → Int
List [Int]
List [String]
Int → String
F#
> List.map (fun x -> x + 1) [1; 2; 3];;
val it : int list = [2; 3; 4]>>> [x + 1 for x in [1, 2, 3]]
[2, 3, 4]Python
(map (fn [x] (+ x 1)) [1 2 3])
=> (2 3 4)Clojure
λ map (+1) [1, 2, 3]
[2,3,4]Haskell
λ [i+1 | i <- [1, 2, 3]]
[2,3,4]>>> map (lambda x: x+1, [1, 2, 3])
[2, 3, 4]
for {x <- List(1, 2, 3)} yield x+1
List(2, 3, 4)Scala
(fun a → b) → List[a] → List[b]
let currencyCodes = ["EUR"; "GBP"; "USD"; "CAD"; "JPY"]
let id x = x
let toLower (s: string) =
s.ToLower()
let addPrefix s =
"x." + s
List.map id currencyCodes
val it : string list = ["EUR"; "GBP"; "USD"; "CAD"; "JPY"]
List.map toLower currencyCodes
val it : string list = ["eur"; "gbp"; "usd"; "cad"; "jpy"]List.map addPrefix currencyCodes
val it : string list = ["x.EUR"; "x.GBP"; "x.USD"; "x.CAD"; "x.JPY"](fun a → b) → List[a] → List[b]
currencyCodes
|> List.map toLower
|> List.map addPrefix
val it : string list = ["x.eur"; "x.gbp"; "x.usd"; "x.cad"; "x.jpy"]> let listToLower = List.map toLower
val listToLower : (string list -> string list)> let convertCode = toLower >> addPrefix
val convertCode : (string -> string)
> List.map convertCode currencyCodes
val it : string list = ["x.eur"; "x.gbp"; "x.usd"; "x.cad"; "x.jpy"]> let convertCodes = listToLower >> listAddPrefix;;
val convertCodes : (string list -> string list)> convertCodes currencyCodes;;
val it : string list = ["x.eur"; "x.gbp"; "x.usd"; "x.cad"; "x.jpy"]> listToLower currencyCodes;;
val it : string list = ["eur"; "gbp"; "usd"; "cad"; "jpy"]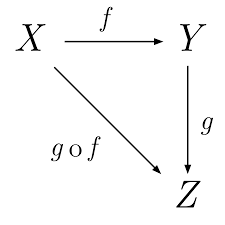
It's not just Lists
let codesByCountry = Map.ofList [
("Ireland", "EUR")
("England", "GBP")
("Scotland", "GBP")
("United States", "USD")
("Canada", "CAD")
("Japan", "JPY")
("Switzerland", "CHF")
]
codesByCountry.["Ireland"];;
val it : string = "EUR"(fun a → b) → Option[a] → Option[b]
let findInMap map key =
Map.tryFind key map
> let findCode = findInMap codesByCountry
val findCode : (string -> string option)
> findCode "Ireland"
val it : string option = Some "EUR"
> findCode "Australia"
val it : string option = None> let irlCode = findCode "Ireland";;
val irlCode : string option = Some "EUR"(fun a → b) → Option[a] → Option[b]
> let ausCode = findCode "Australia";;
val ausCode : string option = None
> Option.map convertCode ausCode;;
val it : string option = None> Option.map toLower irlCode;;
val it : string option = Some "eur"> Option.map addPrefix irlCode;;
val it : string option = Some "x.EUR"> Option.map convertCode irlCode;;
val it : string option = Some "x.eur"(fun a → b) → Option[a] → Option[b]
(fun a → b) → List[a] → List[b]
(fun a → b) → F[a] → F[b]
List.map
Option.map
fmap (aka map)
Functor
So What?
findCode: string → Option[string]
findCode: string → string
Composition
findRate: string → decimal
findRate: string → Option[decimal]
findCode >> findRate
✔︎
findCode >> findRate
✘
Composition
let codesByCountry = Map.ofList [
("Ireland", "EUR")
("England", "GBP")
("Scotland", "GBP")
("United States", "USD")
("Canada", "CAD")
("Japan", "JPY")
("Switzerland", "CHF")
]
let rates = Map.ofList [
("x.eur", 1M)
("x.gbp", 0.78883M)
("x.jpy", 123.94M)
("x.usd", 1.13804M)
("x.cad", 1.47397M)
]
let findCode = findInMap codesByCountry
val findCode : (string -> string option)
let findRate = findInMap rates
val findRate : (string -> decimal option)
> Option.bind
val it : (('a -> 'b option) -> 'a option -> 'b option)(fun a → Option[b]) → Option[a] → Option[b]
"United States" // String|> findCode // Option[String]
|> Option.map convertCode // Option[String]|> Option.bind findRate // Option[Decimal]
val it : decimal option = Some 1.13804M"Australia"
|> findCode
|> Option.map convertCode
|> Option.bind findRate
val it : decimal option = None"Switzerland"
|> findCode
|> Option.map convertCode
|> Option.bind findRate
val it : decimal option = None(fun a → Option[b]) → Option[a] → Option[b]
(fun a → List[b]) → List[a] → List[b]
(fun a → F[b]) → F[a] → F[b]
List.collect
Option.bind
bind (aka flatmap)
a → F[a]
return (just wrap a value)
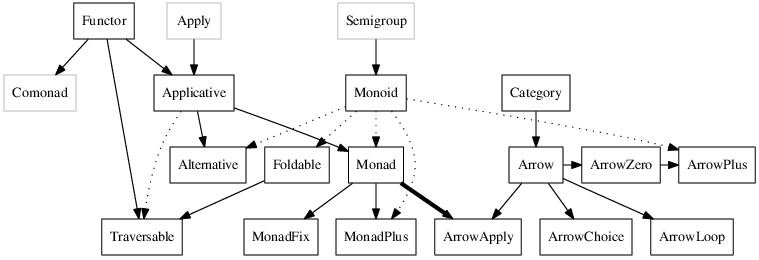
Monad
That's It?
Polymorphism
Inheritance
Easy to add new types, hard to add new behaviour
Parametric
Easy to add new behaviour, hard to add new types
Polymorphism
Typeclasses
Add behaviour to things who's code you don't have access to
Almost like duck typing, but behaviour only for those types for which a typeclass "instance" is available
Still type-safe, compiler checked
Advanced Functional Programming for the absolute beginner
By richardadalton
Advanced Functional Programming for the absolute beginner
- 3,470