Mathematical Art
&
Complex Analysis
Mathematical Art
Dr. Robert Jacobson
Roger Williams University
22 March 2016
http://goo.gl/xmbzcX
Follow along on your device at this address.
Complex Numbers
where
and
real numbers, and .
are ordinary
The number is called the real part while is called the imaginary part.
Every real number is also a complex number.
Complex Arithmetic
Addition:
Multiplication:
"Complexification" of functions:
The Complex Plane

Conformal Maps
A map is conformal at a point
if preserves the angle between any two curves passing through .
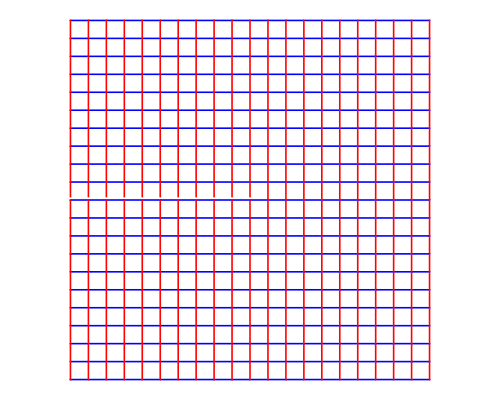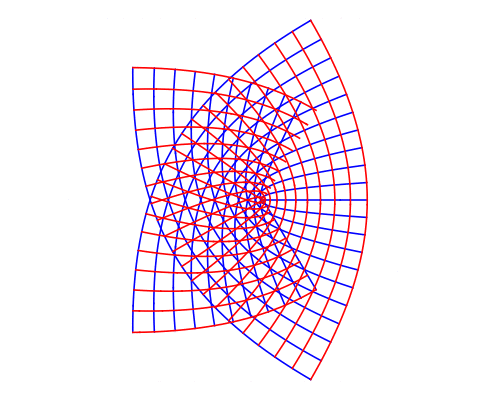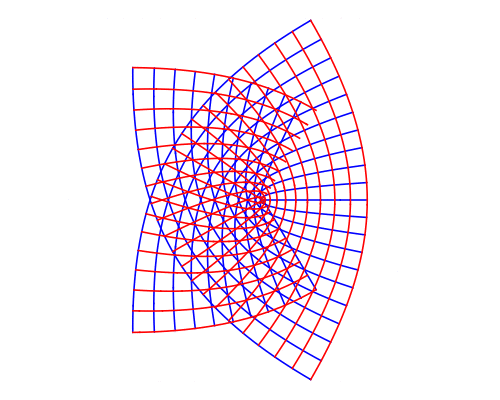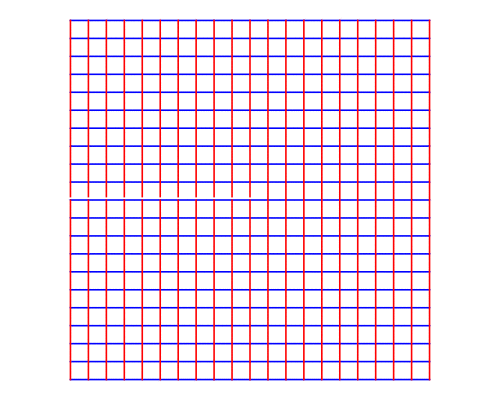


Conformal
Map
Viewer
Spherical Video
Spherical Video
Euclidean Geometry
In a plane, given a line and a point not on it, at most one line parallel to the given line can be drawn through the point.
Hyperbolic Geometry
For any given line R and point P not on R, in the plane containing both line R and point P there are at least two distinct lines through P that do not intersect R.

Hyperbolic Geometry
Poincaré Disk Model

Hyperbolic Geometry
Poincaré Disk Model
Go check out this other guy's math talk.
M. C. Escher (1898-1972)

Circle Limit III, woodcut, 1959
Hyperbolic Geometry
Upper Half Plane Model

Hyperbolic Geometry
Upper Half Plane Model
Poincaré Disk Model

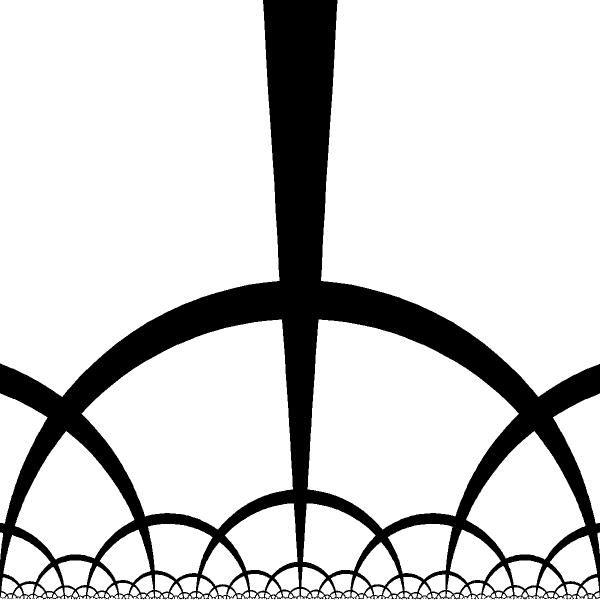
Hyperbolic Geometry

Upper Half Plane Model
Upper Half Plan Limit III
Hyperbolic Crochet

It's on Amazon: http://amzn.com/1568814526.
Hyperbolic Coral

Yellow Fiji Leather Coral

The Professor Spiral I
The Professor Spiral II
The Professor Spiral III
Mathematics of The Droste Spiral
"What magic is this?!"
M. C. Escher (1898-1972)

M. C. Escher (1898-1972)
Print Gallery, 1956
Print Gallery, 1956



The Mathematical Structure of Escher's Print Gallery
B. de Smit and H. W. Lenstra Jr.
Notices of the AMS, volume 50, number 4, pages 446-451, 2007.

De-Escherization

The Mathematical Structure of Escher's Print Gallery

De-Escherization
"The map \(h(w)\) is given by the easy formula \(h(w)=w^{(2\pi i + \log 256)/(2\pi i)}\)."
Stereographic Projection
Stereographic Projection
Stereographic Projection
Point on sphere to point on plane:
Point on plane to point on sphere:

Stereographic Projection
Stereographic Projection
Mathematical Art and Complex Analysis
By Robert Jacobson
Mathematical Art and Complex Analysis
Listen to a complex analyst explain how mathematicians and artists use ideas from the field of complex analysis to create art.
- 1,142



