Title Text



Software engineer, team lead at DA-14

Cyber Security - beginning for beginners
- Web Apps Evolution
- Secure App: myth or fact
NodeJS Vulnerabilities
- Brute-Force Attacks
- Database Injections
- Regular Expression DOS
- Memory Leaks
- Hijacking the require chain
- Rainbow Table attack
- Hash Table Collision attack
- Timing attack
It's show time (c) Ben Richards
Painkiller
- Best Practice
- Helpful Modules

CONTENTS

Okay, now it's secure enough (c) noone ever
CYBER SECURITY - BEGINNING FOR BEGINNERS

Application evolution
Before
Now



CYBER SECURITY - BEGINNING FOR BEGINNERS
What's now

CYBER SECURITY - BEGINNING FOR BEGINNERS





Is this application secure enough?
- SSL is not the silver bullet

CYBER SECURITY - BEGINNING FOR BEGINNERS
Is this application secure enough?
- Broken authentication
- Broken access controls
- Database injection
- Cross-site scripting
- Information leakage
- Cross-site request forgery

CYBER SECURITY - BEGINNING FOR BEGINNERS

User can:
- submit arbitrary input
- send requests in any sequences
- interact with any pieces of transmitted data
- send requests in any sequences
- submit parameters at different stages
- use different tools to access application

CYBER SECURITY - BEGINNING FOR BEGINNERS
User/Attacker can initiate a process of:
- modifying a session token
- modifying amount of provided parameters
- altering input to process by back-end

CYBER SECURITY - BEGINNING FOR BEGINNERS
BEFORE WE START
Good developers code; Best developers copy (c) stack overflow


3rd party dependencies
your code
APP

MODERN JAVA SCRIPT APPLICATION
The most guaranteed but time-consuming method to crack a password


BRUTE-FORCE ATTACK
Guess:
- 1.000.000.000 passwords/sec
Conditions:
- 8 character password
- 96 characters

BRUTE-FORCE ATTACK
Guess:
-
1.000.000.000 passwords/sec
Conditions:
- 8 character password
- 96 characters
Result:
- ~ 80 days

BRUTE-FORCE ATTACK
Guess:
- 400.000.000.000 passwords/sec
Result:
- up to 6 hours


BRUTE-FORCE ATTACK
Best Practice:
- Require strong passwords
- Rate-limiting
- Invalid login attempts locker
- Logging
- Secure password recover
- Requires the old password
- Secret question
- Do not reveal the current password

BRUTE-FORCE ATTACK
Painkiller
- node-rate-limiter
-
load balancing
- queue solution(RabbitMQ, Kafka, Redis etc. )
- hardware-based balancing
- proxy-based request limiting (Nginx)

BRUTE-FORCE ATTACK
DB injection has been around for almost 20 years and is still a big issue


DATABASE INJECTIONS
Examples:
DELETE /users/?id=<userId>UserModel.remove({ _id: req.query.id }); 
DATABASE INJECTIONS
UserModel.remove({ _id: { '$exists': true } });DELETE /users/?id={ '$exists': true }
Examples:
DELETE /users/?id=<userId>UserModel.remove({ _id: req.query.id }); DATABASE INJECTIONS
Examples:
.find( { $where: "this.<key> == 'a; sleep(1000000)'" } );.find( { $where: "this.<key> == <value>" } );
DATABASE INJECTIONS
Best Practice:
- validate incoming body and query parameters
- be careful with the executable incoming data
- create strict rules for incoming data
- validate data type
- check length
- use value enumeration if it's possible - use ORM/ODM for database queries

DATABASE INJECTIONS

DATABASE INJECTIONS
RE implementations may reach extreme situations


REGULAR EXPRESSION DOS

What the hell is the state machine and NFA?

REGULAR EXPRESSION DOS

Regular Expression: ^(a+)+$
Result:
aaaaX - 16 possible paths
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaX - 65536 possible paths

REGULAR EXPRESSION DOS
Evil Regular Expressions:
- grouping with repetition
-
inside the repeated group
- repetition
- alternation with overlapping


REGULAR EXPRESSION DOS
Painkiller:
Helpers:

REGULAR EXPRESSION DOS
Tracking down memory leaks has always been a challenge


MEMORY LEAKS

heap
stack
resident set
retained size
shallow size
mark-sweep
scavenge
old space
new space

MEMORY LEAKS
Common Reasons:
- forgotten timers or callbacks
- weak closures
- insecure dependencies
- buggy technology
- new Buffer(size) (deprecated, but still)


MEMORY LEAKS
Painkiller:

MEMORY LEAKS
Hooking all asynchronous core methods is definitely possible


HIJACKING THE REQUIRE CHAIN


HIJACKING THE REQUIRE CHAIN
A
B
C

HIJACKING THE REQUIRE CHAIN
A
B
C
D
C
E

HIJACKING THE REQUIRE CHAIN
A
B
C
D
C
E
PATCH

HIJACKING THE REQUIRE CHAIN
- wait for D module to be included first
- require() is synchronous

HIJACKING THE REQUIRE CHAIN
B
A
D
C
E
C
APPLICATION
CACHED

HIJACKING THE REQUIRE CHAIN

HIJACKING THE REQUIRE CHAIN
Rain Bow Table attack must be weird enough...


RAINBOW TABLE


Theory:
- a precomputed table of <password> - <hash> pairs for reversing cryptographic hash functions
- can be generated according to encryption type/way and existing hash

RAINBOW TABLE

RAINBOW TABLE
The fourth letter of your password is wrong, please try again

TIMING ATTACK


TIMING ATTACK
- tired of slides
- just keep talking
- they won't notice


HASH TABLE COLLISION (FLOOD) ATTACK
That moment when you realize we're in trouble


HASH TABLE COLLISION (FLOOD) ATTACK

Hash table?

HASH TABLE COLLISION (FLOOD) ATTACK
Hash table?


HASH TABLE COLLISION (FLOOD) ATTACK
Hash table collision :(


HASH TABLE COLLISION (FLOOD) ATTACK
Hash table collision :(


HASH TABLE COLLISION (FLOOD) ATTACK
Hash table collision :(
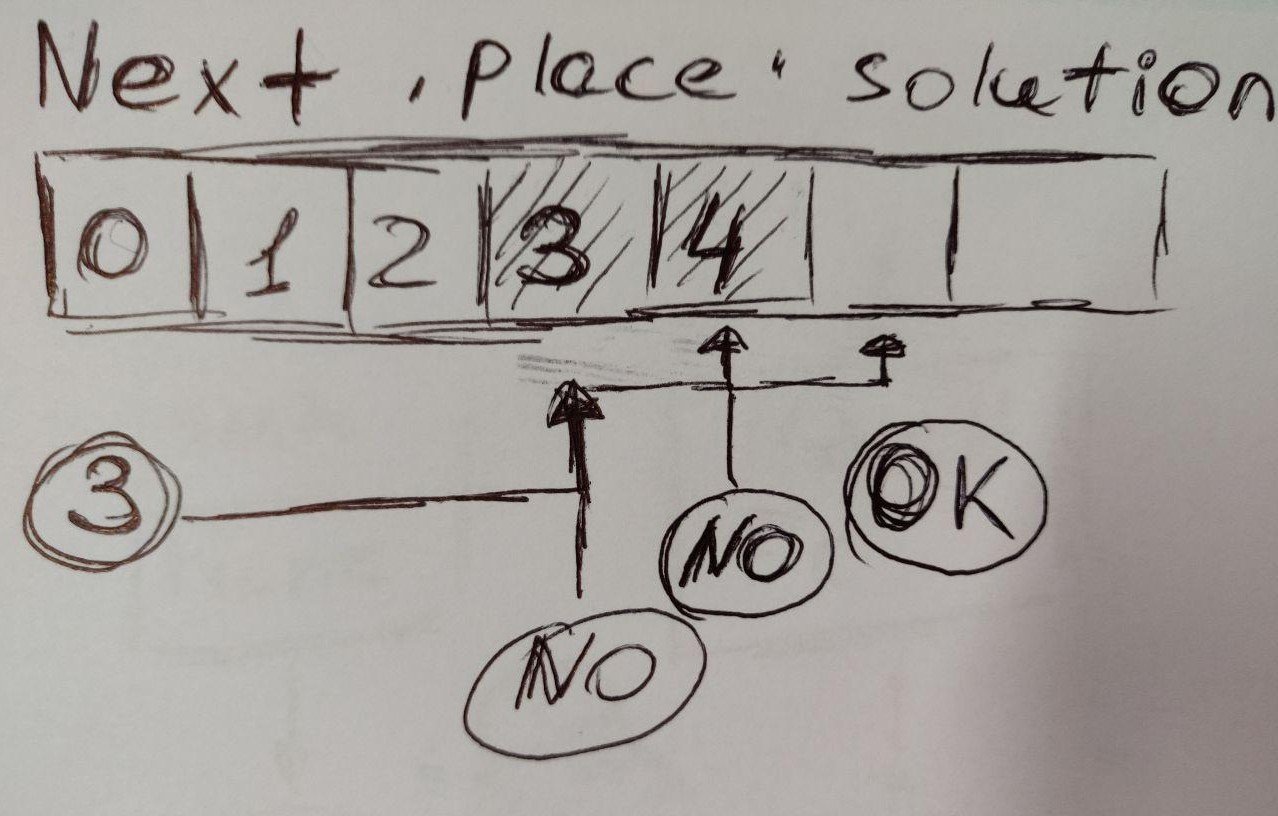

HASH TABLE COLLISION (FLOOD) ATTACK
Hash table collision :(


HASH TABLE COLLISION (FLOOD) ATTACK
Hash table collision attack?


HASH TABLE COLLISION (FLOOD) ATTACK
Best Practice:
- check/limit input data size (ex. body size)
- validate headers
- use strong cryptographic algorithms
- !important: bcrypt vs crypto

BEFORE YOU GO

The thing to show I've got for you (c) Yoda parodist

BEFORE YOU GO
// package.json
"config": {
"ghooks": {
"pre-push": "npm test && npm audit",
"pre-commit": "npm run lint"
}
},Security starts from quality

BEFORE YOU GO
Security starts from quality

May the 4th be with you


BEST PRACTICE
- Limit requests frequency
- Don't accept or use carefully query params as database query items
- Validate incoming body, query params
- Hide 'X-Powered-By' header
- Set a strong access control system
- Use SSL
- Be careful with expressions
- Use Security check tools
- User secure WebSocket connection
- OWASP top 10 (http://nodegoat.herokuapp.com/tutorial)

BEST PRACTICE
Let off some steam


HELPFUL MODULES
Rate Limiting
Memory Check
Other

HELPFUL MODULES

Do they speak English in What?

ARTICLES
Security 'musts'
Memory Leak
Require Chain

ARTICLES
*and again I couldn't find a funny meme for this page

roman.sachenko@gmail.com
roman.sachenko

https://twitter.com/rsachenko
https://github.com/roman-sachenko/
Security in NodeJS: Symphony of Destruction
By Roman Sachenko
Security in NodeJS: Symphony of Destruction
There are dozens of mistakes that can be easily made and lead to huge security problems. On the other hand, there are even more ways to break an application, such as DB injections, brute-force attacks, regular expression DOS, memory leaks, and hijacking require chain, just to name a few. During the presentation, I’ll list the most common security problems, talk about the current situation in WEB and will explain how to deal with safety concerns. What can we do to decrease the level of 'insecurity'? I'll teach the audience to deal with security holes and will explain the must-steps which should be performed before launching a new application.
- 1,726



