Angular. Overview



Let me introduce myself



Roman
Front End Developer at TechMagic
Angular Lviv Meetup Co-organizer
@graniron
roman.yavoriv@gmail.com
graniron

How and Why


- Teach/Learn
- Practice
- Laugh(at least invoke smile few times)
- Assign homework




Agenda
1. Intro
2. Angular CLI
3. Typescript
4. Rxjs
5. Angular Building Blocks
6. Router
7. Http


1. Intro


History Time




Angular Core Team








10/2010
First Release
09/2016
Documentation
Speed
Joy


Key features
- Framework By Google
- SPA
- Speed & Performance
- Rich Ecosystem
- Large Community
- And Little Bit Of...









Magic
Current State
- Version: 8.2.14
- Open Source (1053 contributors)
- Github Stars (54400)



2. Angular CLI


CLI - Command Line Interface



1. Install the Angular CLI:

2. Generate New Project

3. Run



Let's try


Automate Tasks


Generate Angular Building Blocks

- component
- pipe
- directive
- service


Simplify regular tasks
- Linting

- Unit Testing

- Build


3. Typescript


ES5
ES6
TypeScript
Typescript Structure


"TypeScript is a typed superset of JavaScript that compiles to plain JavaScript"
Why?
- ~15% reduction in bugs
- TypeScript tools
- ES-next compliance
- Types are one of the best forms of documentation


Let's Define Some Types
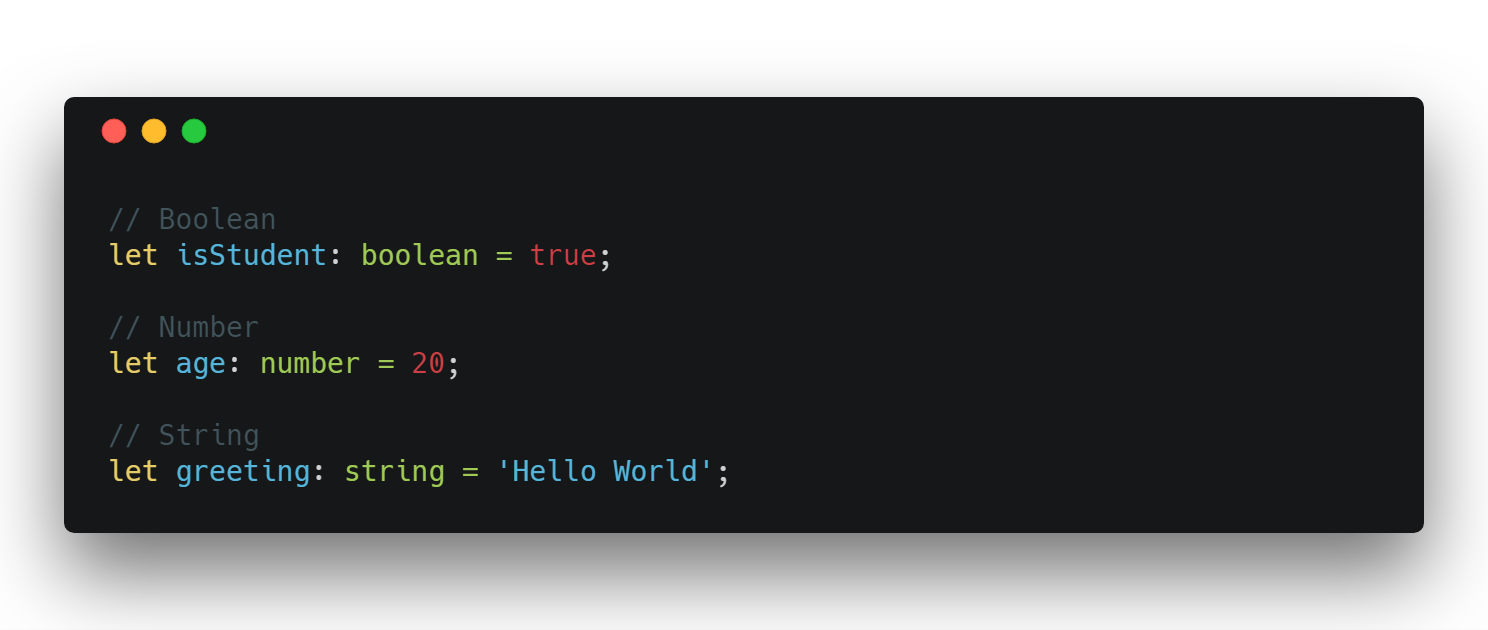
Primitives
Non Primitives
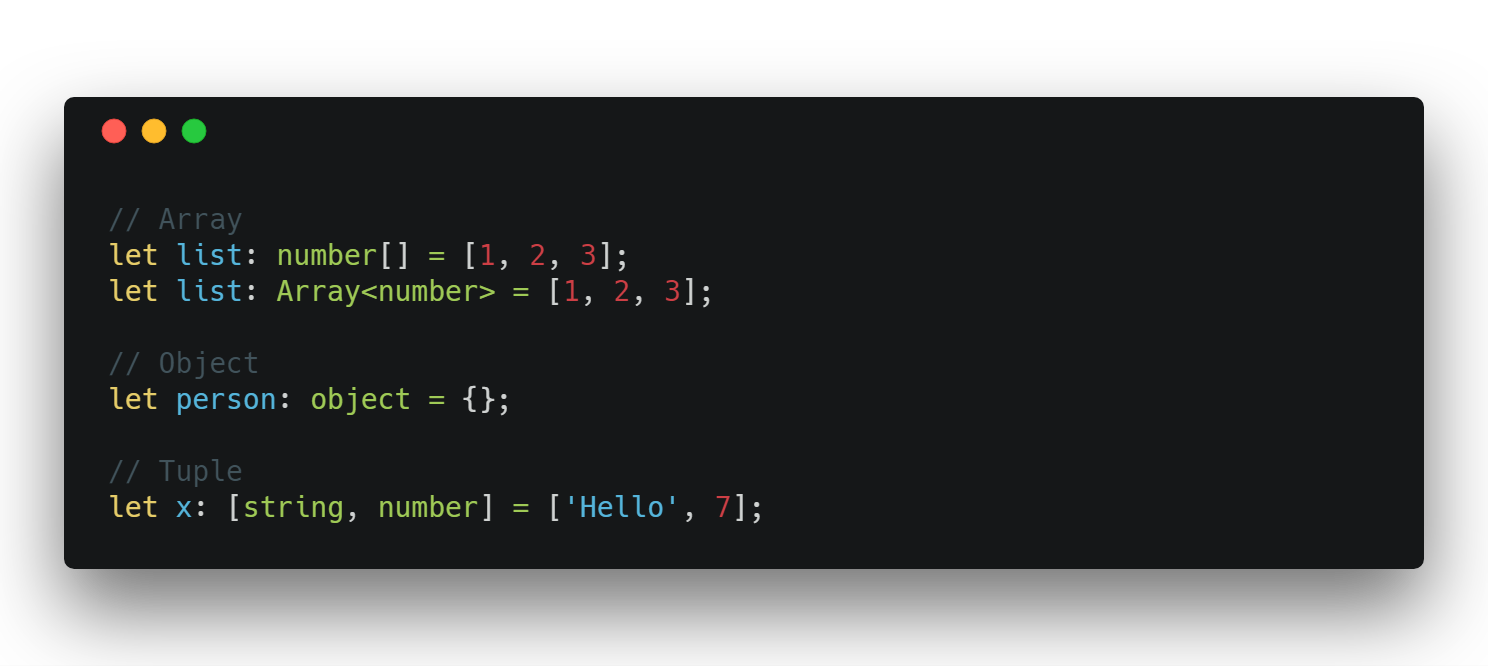


string
number
Not defined types



Working with Functions



Enum



Interface
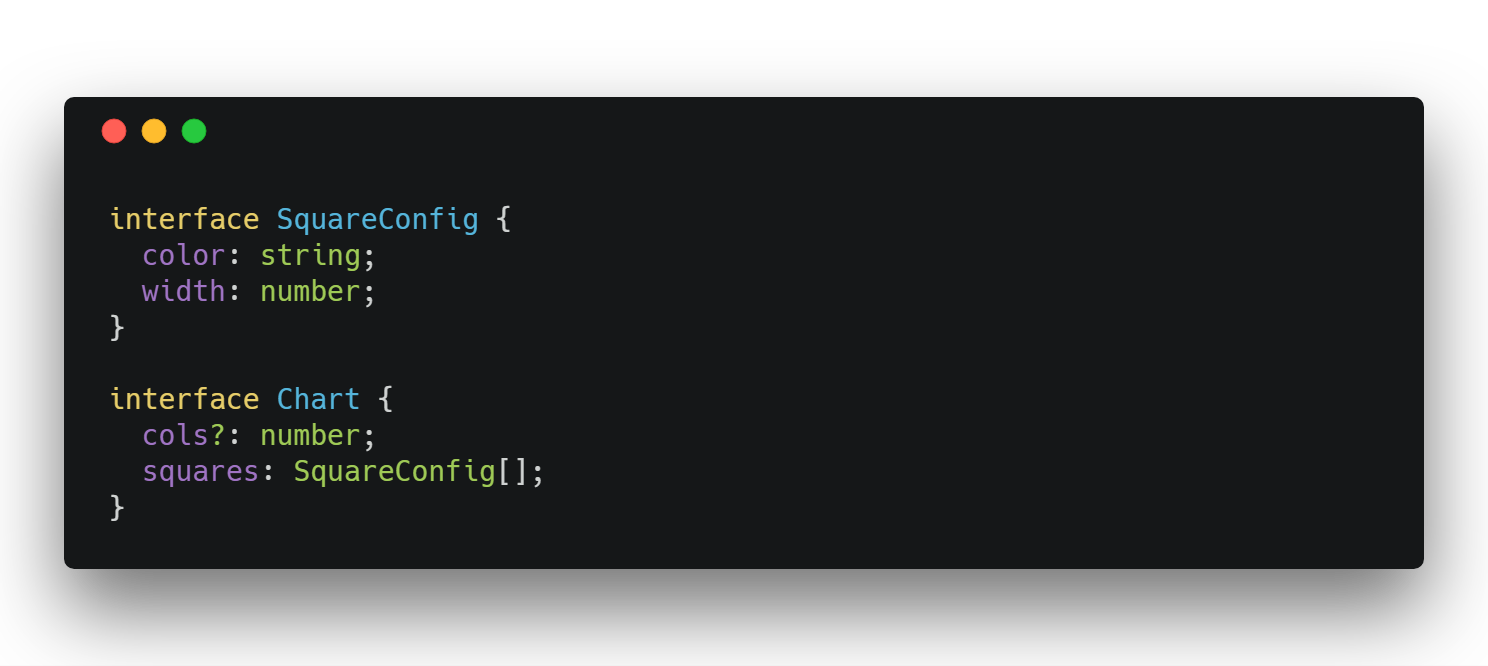


4. RxJs

What is Reactive Extensions?
- Library for working with Async events
- Languages: Java, JavaScript, C#, C++,
Ruby, Python, Swift, and more... - Collaborative Effort between Google, Microsoft, & Netflix
- Open Source
- Works in browser or NodeJS
- Safari 7+, IE9+

- Easier to write, read
- Turn Async events into steams
- Transform streams with Operators
- Streams only become active when subscribed
- 'Lodash for async'
Main Features

Main RxJS players
- Observable - a stream of values that are being pushed over time
- Observer - a consumer of observable values
- Operator – method for value transformation/manipulation



Stream of clicks
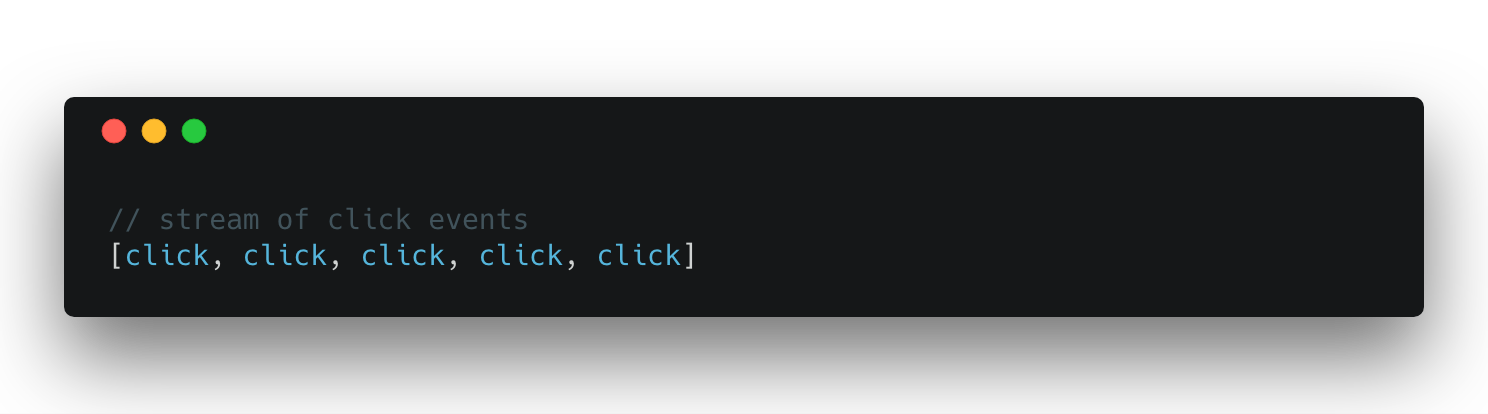





Promises vs. Observable
- Promise is like an async variable
- Observable is like a async array
- Single value
- Cannot be canceled
- Not lazy
- Good for some AJAX calls
- Unless you want to cancel them - Catch, Finally
- Streams
- Can be unsubscribe
- Lazy, until you call .subscribe()
- Better for events, WebSockets
- Animations, AJAX you want to cancel - Can be retried
- Catch, Complete


Observables are lazy
An Observable doesn't start streaming items until it has at least on observer subscribed to it


Subscribe
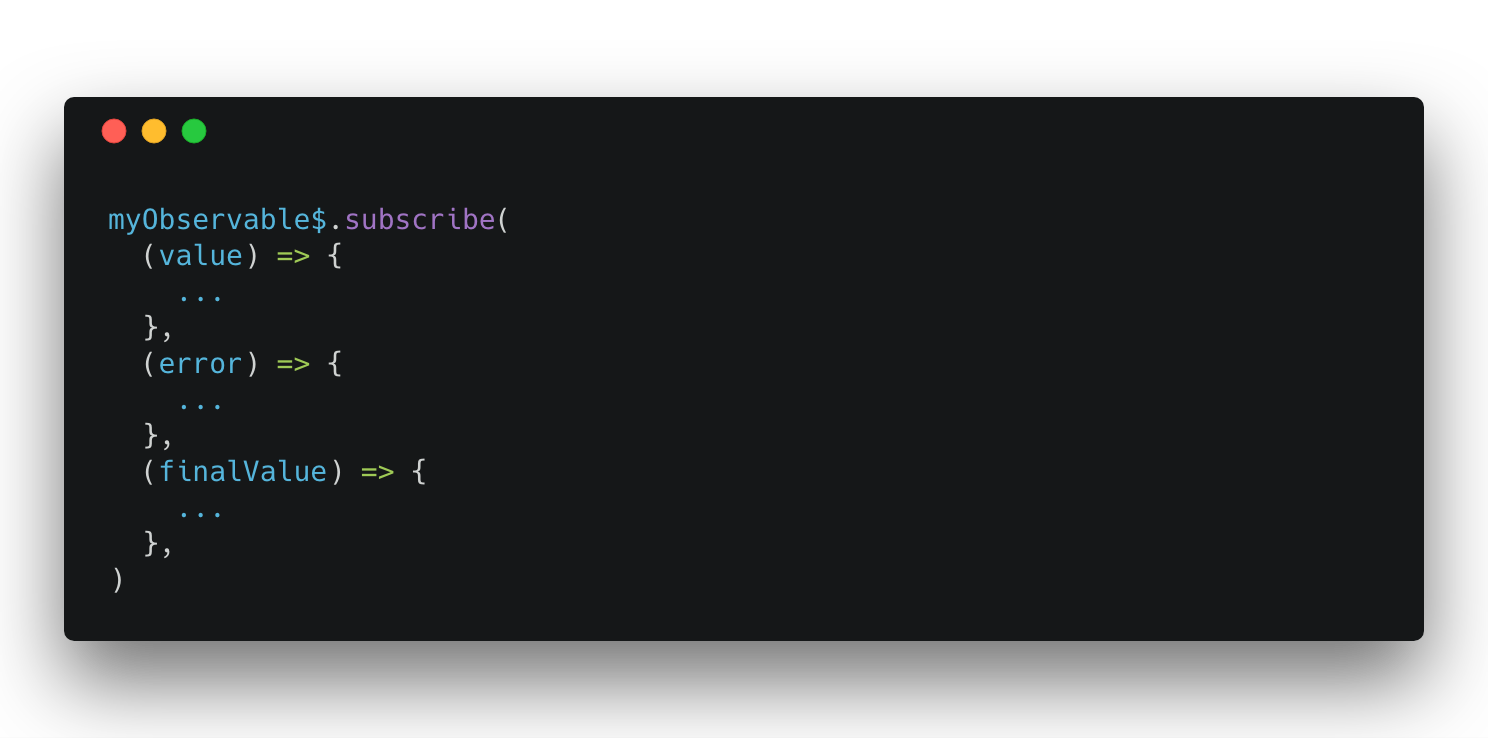
Subscribe Structure

Unsubscription

You must remember to unsubscribe from some observables to prevent memory leaks:
-
From infinitive observables(like mouse events)
-
Any of your custom observables

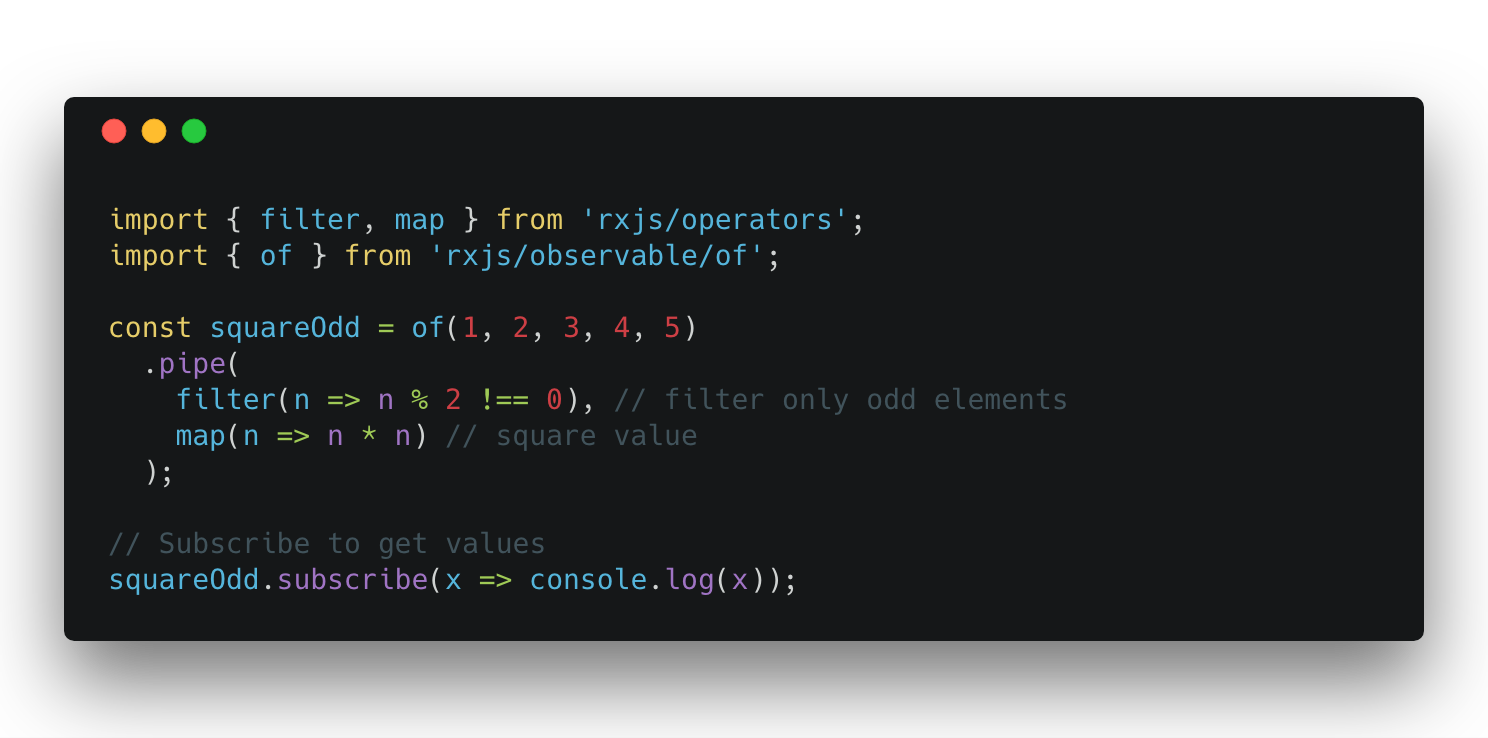
Operators



RxJs Documentation

Switch operator — convert an Observable that emits Observables into a single Observable that emits the items emitted by the most-recently-emitted of those Observables




Observables in Angular
- Forms
- Http
- AsyncPipe
- DOM events
- Change detection

5. Angular Building Blocks


Building Blocks

- Modules
- Components
- Directives
- Pipes
- Forms
- Services


NgModule
- Identified by @NgModule decorator
- Every app has at least one NgModule class, the AppModule
- Provides compilation context for their components

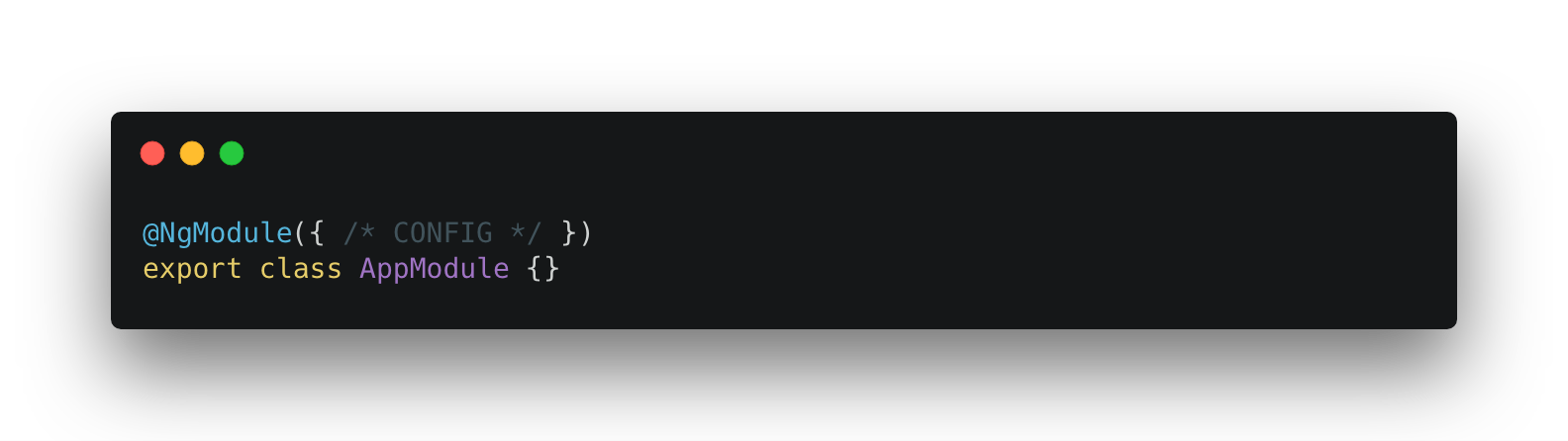

NgModule Metadata

Components/Directives/Pipes
Services
Other Modules
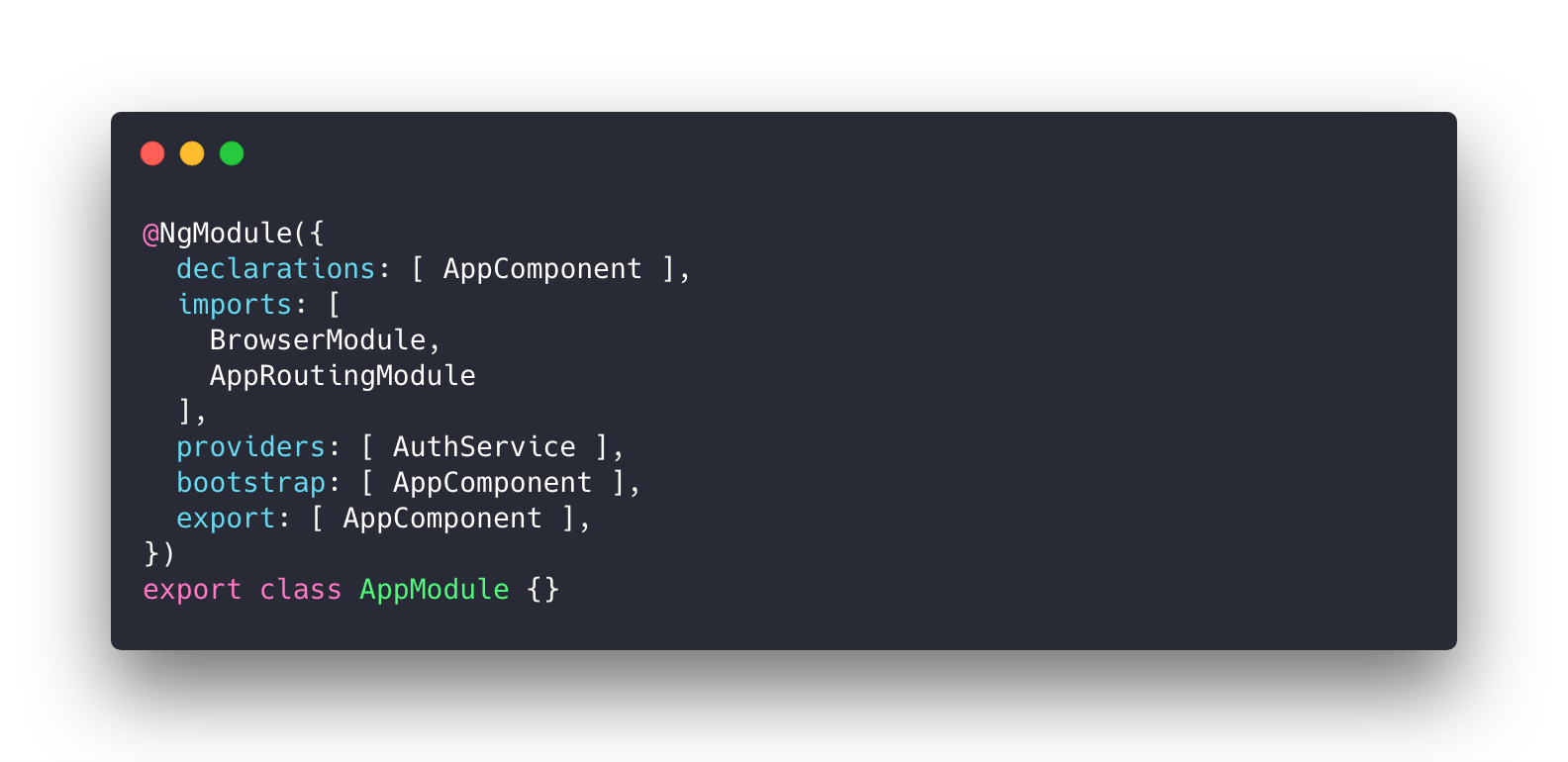
Bootstraped components
Exported members
Every Component/Directive/Service/Pipe should be registered in the Module

Component
- Identified by @Component decorator above component class definition
- Every app has at least one component, the root component



Component metadata


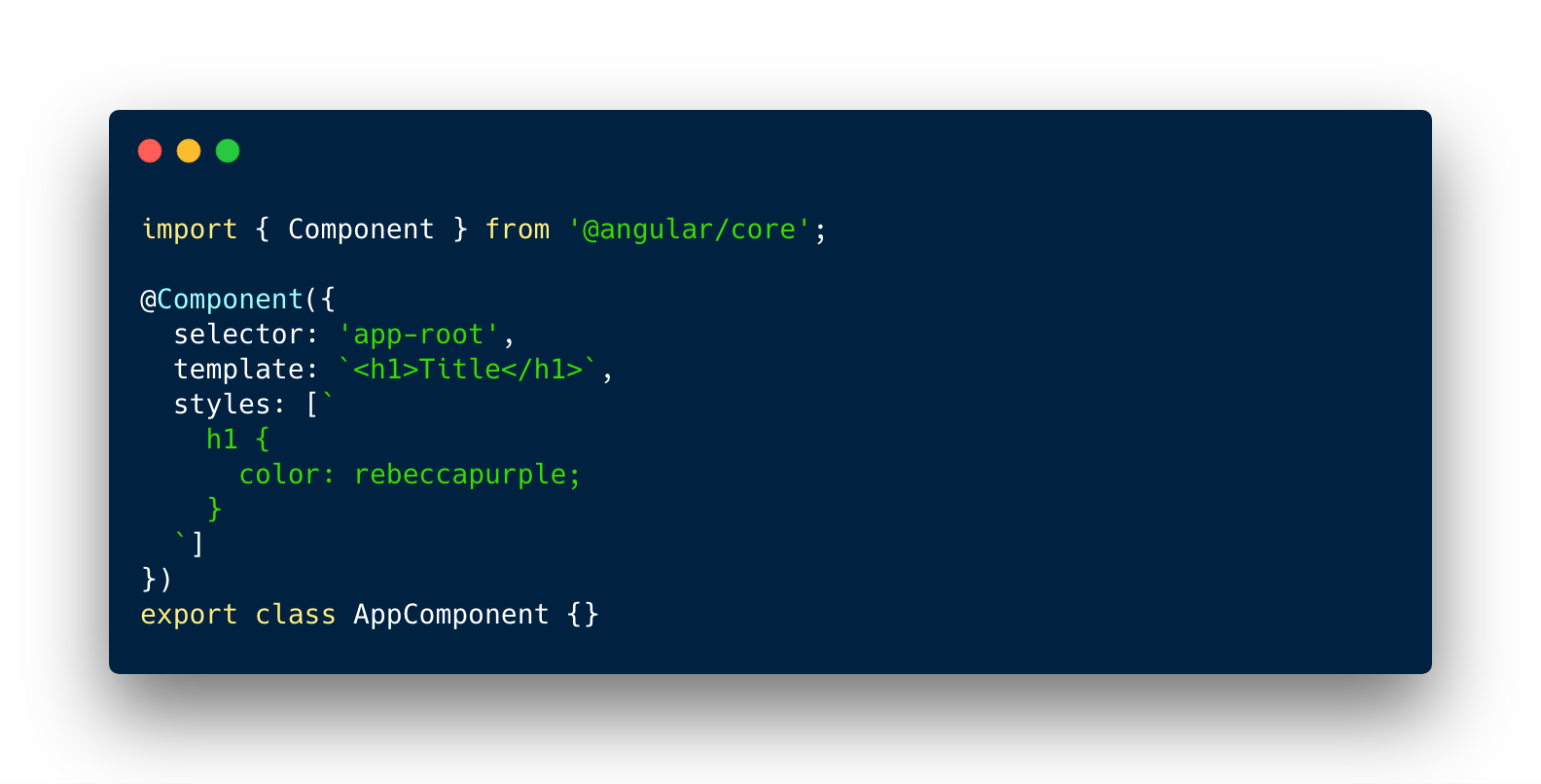
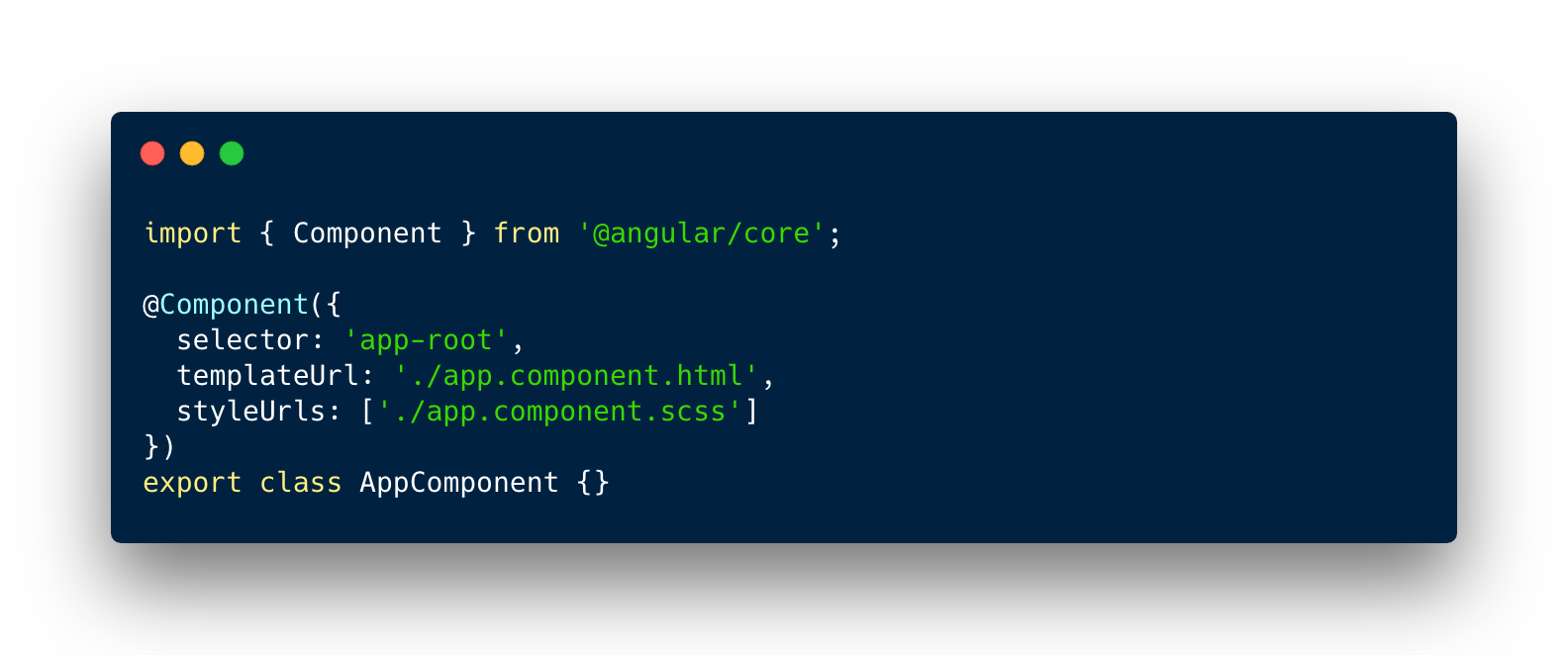
Component tree



Component template(html)



Data binding(a.k.a interpolation)
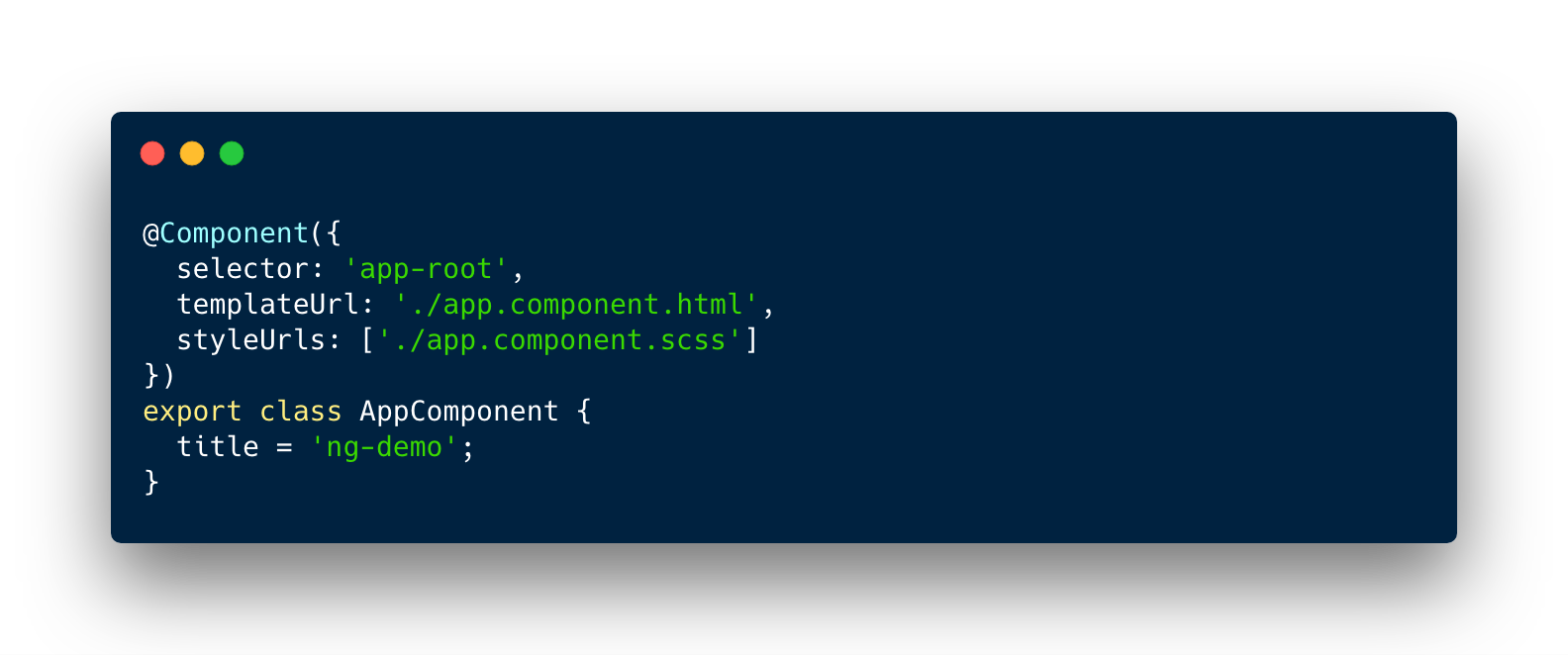
Template syntax


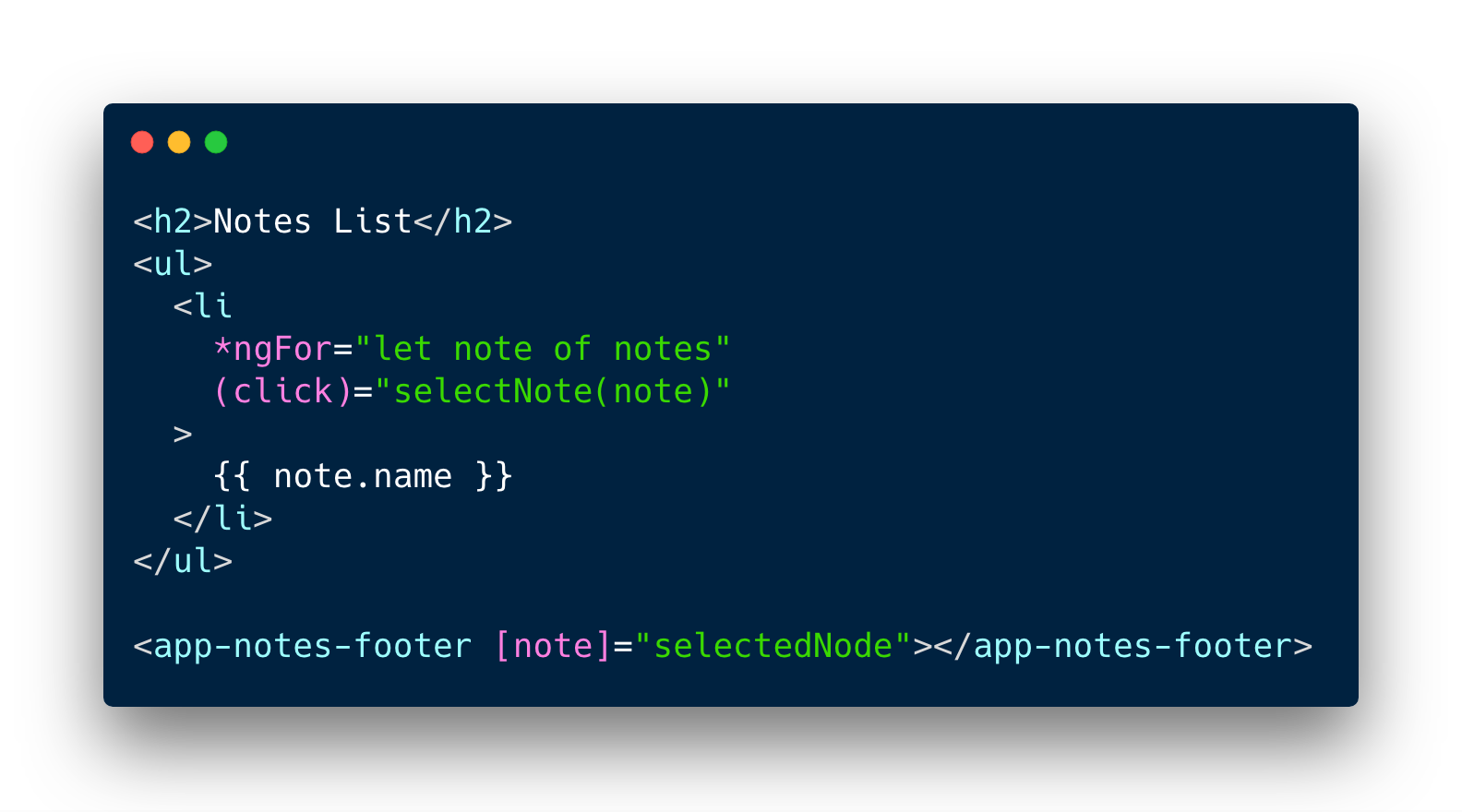
Interpolation
Property binding
Event handler
Child Component
Directive to iterate over collection
Components Communication


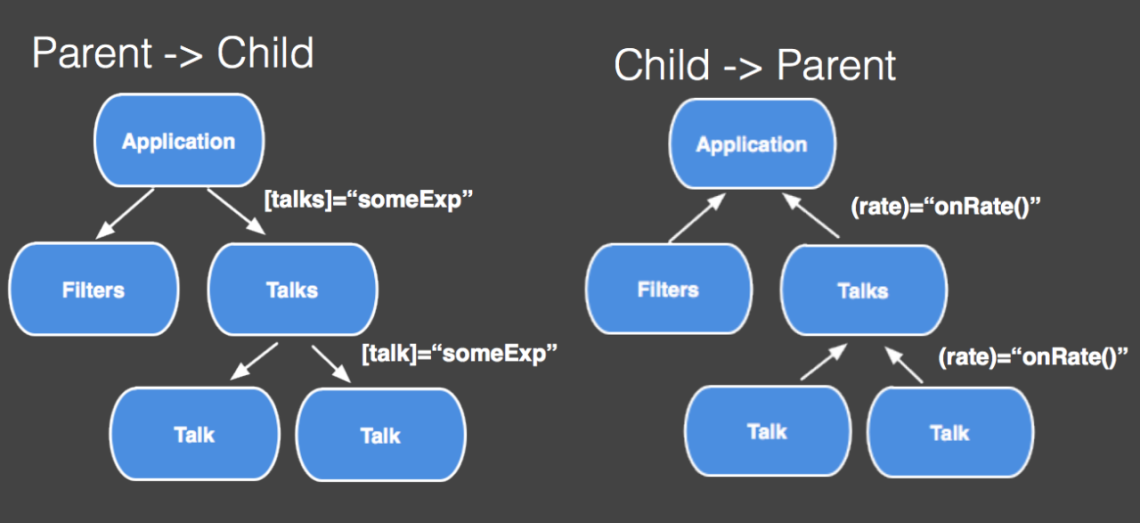
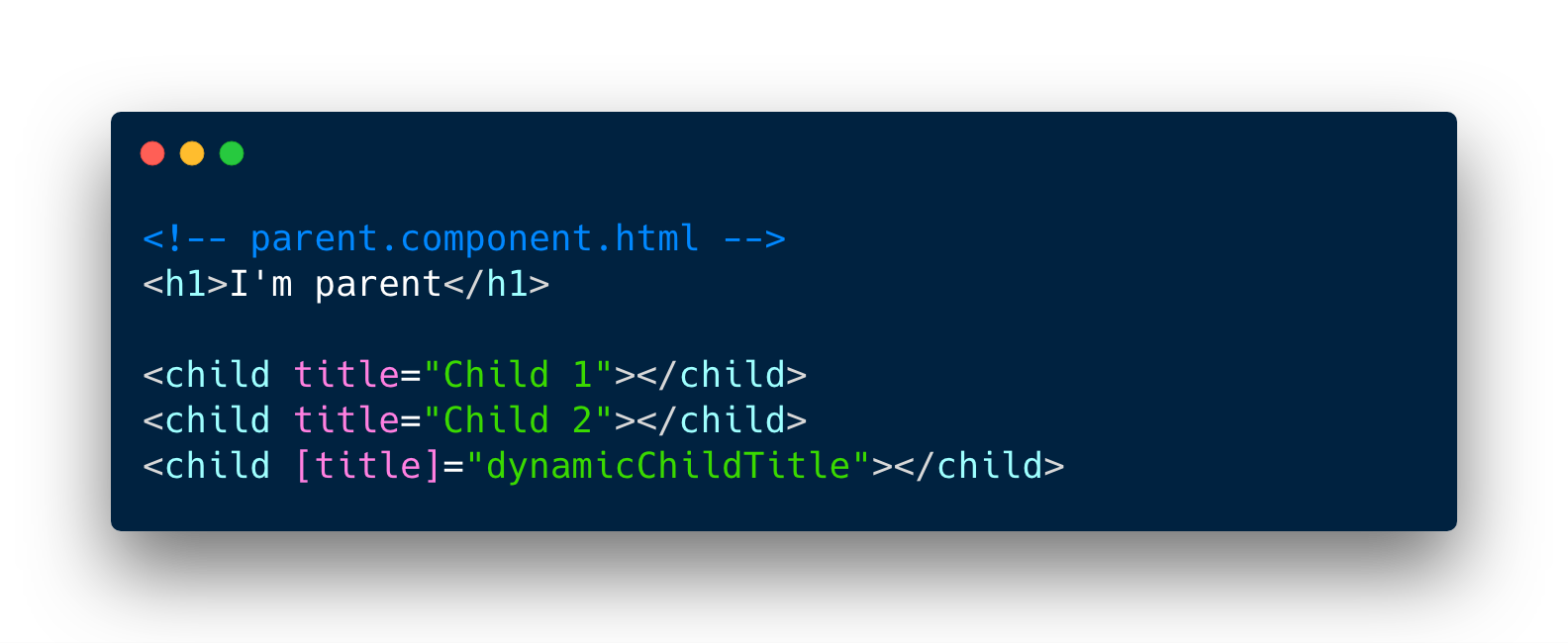
Parent => Child


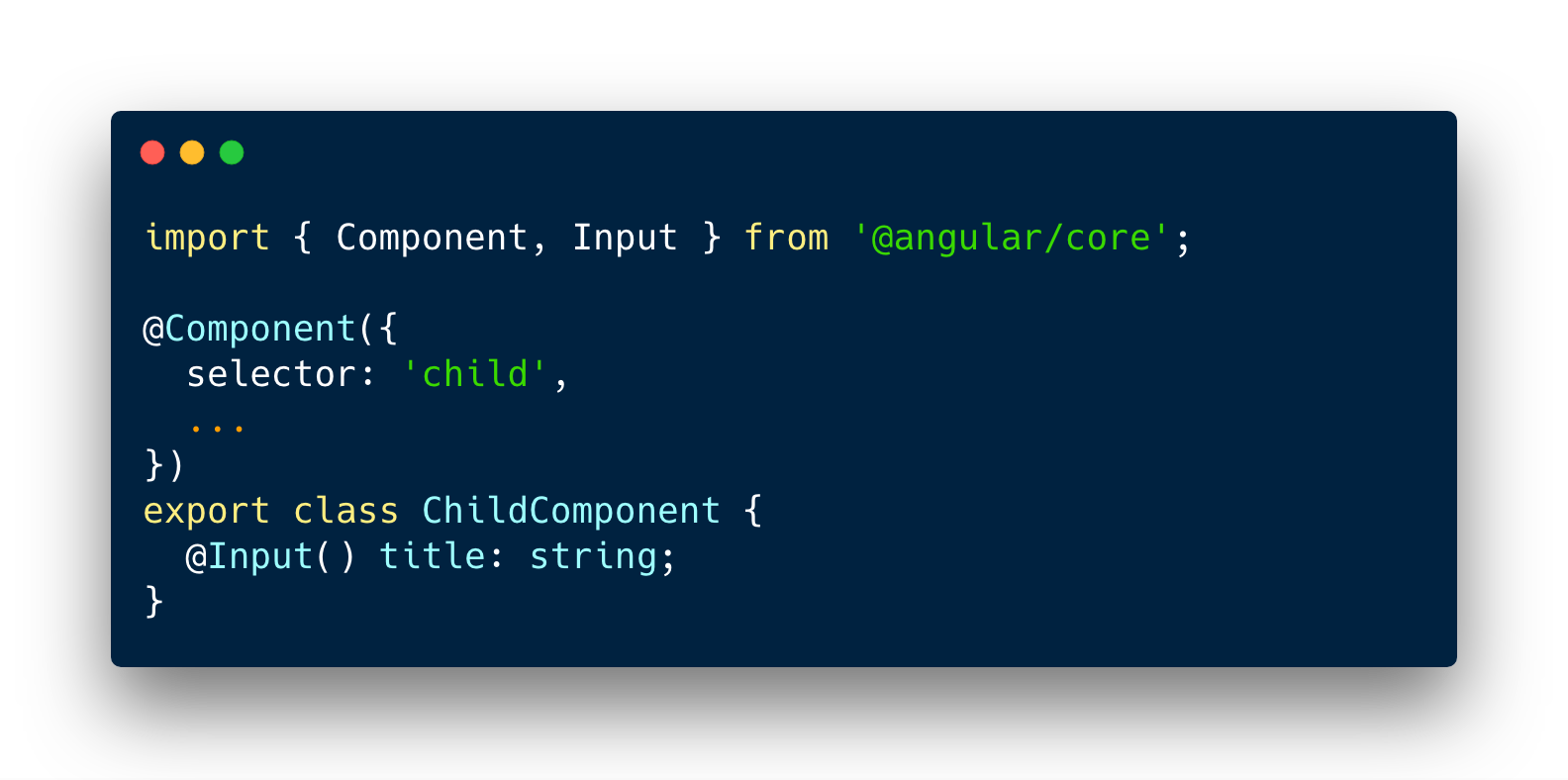
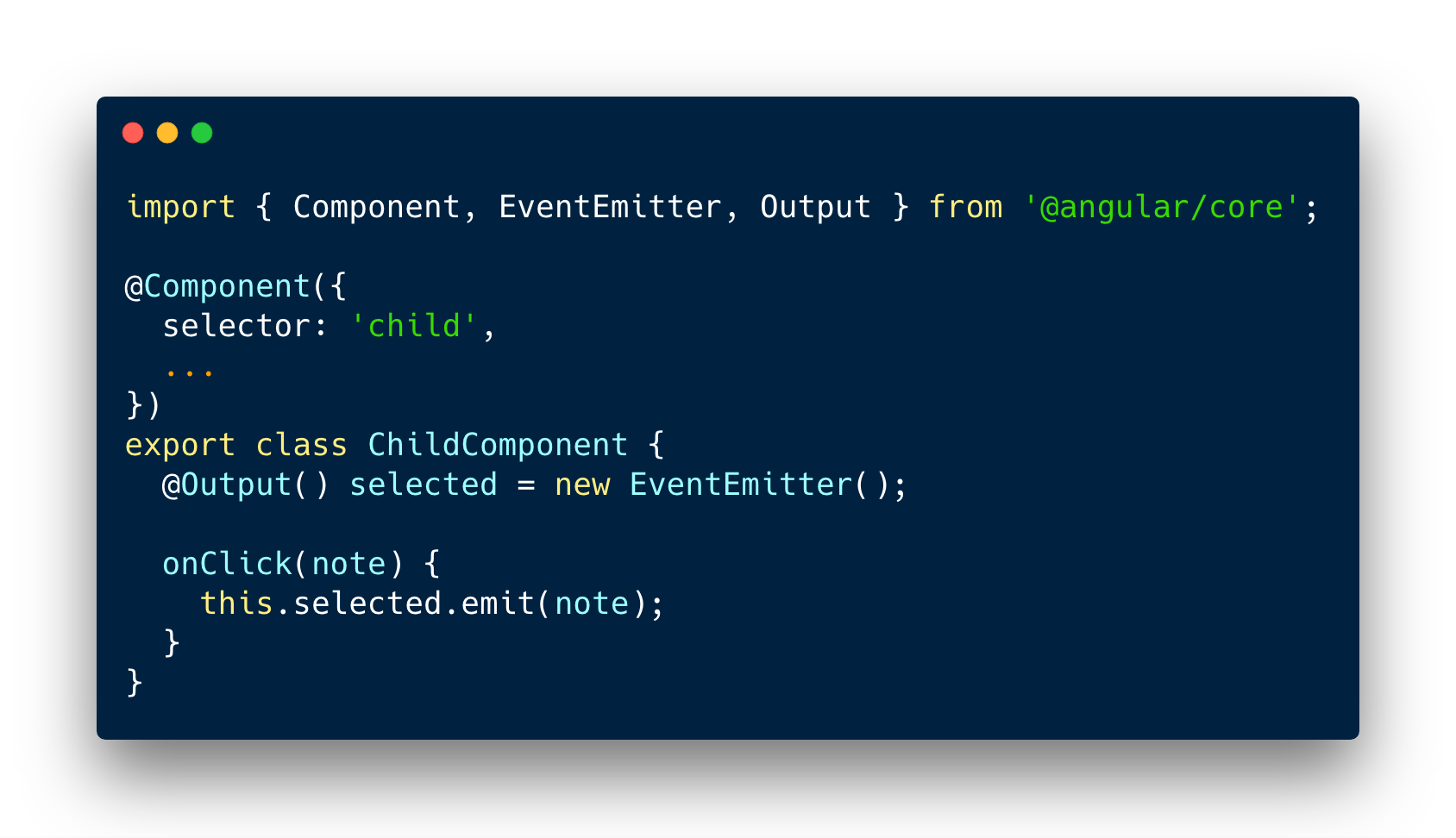
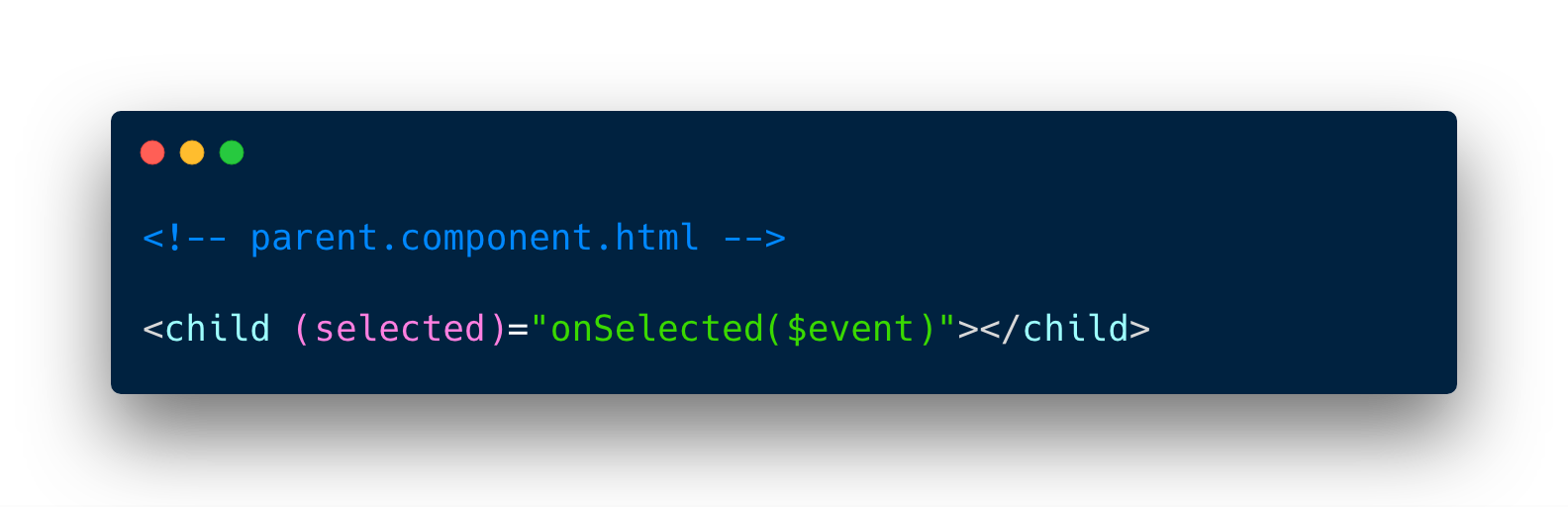
Child => Parent


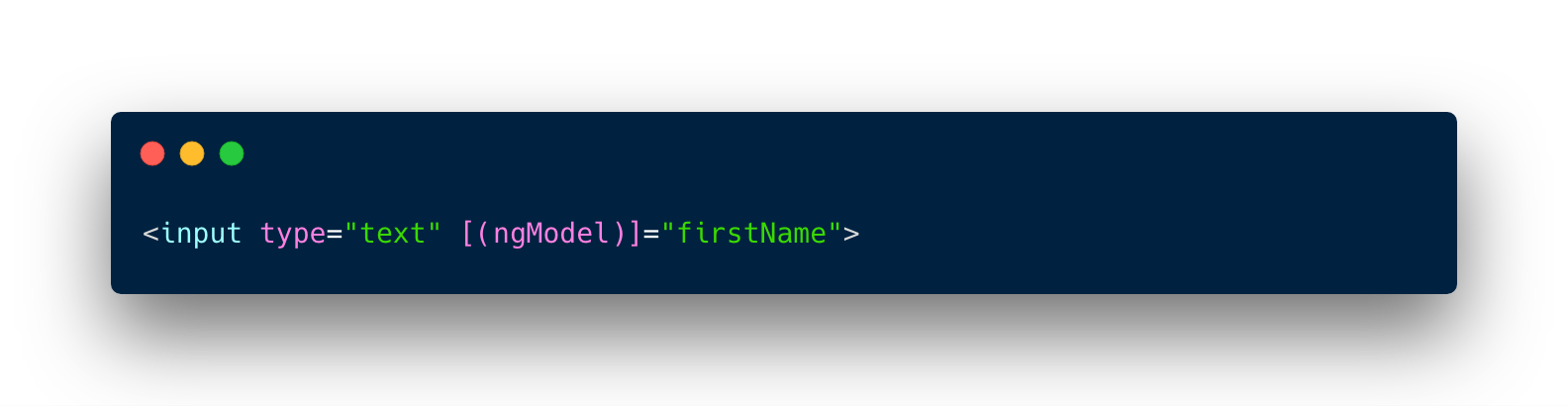
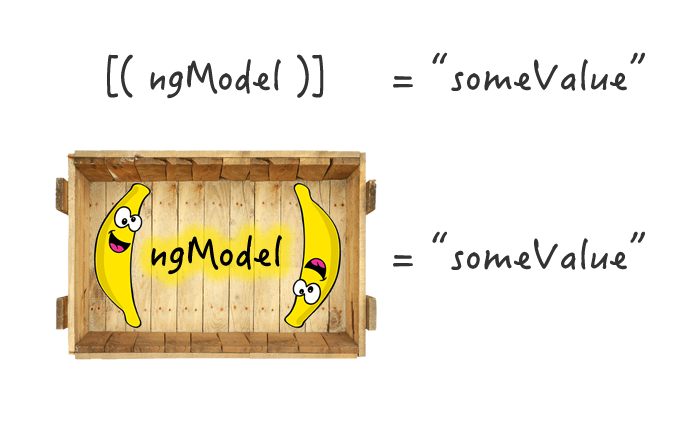
Two-way data binding
- data property value flows to the input box from the component as with property binding
- The user's changes also flow back to the component, resetting the property to the latest value, as with event binding


Lifecycle hooks
Angular:
- creates component
- renders component
- creates and renders component children
- checks component when its data-bound properties change
- destroys component before removing it from the DOM


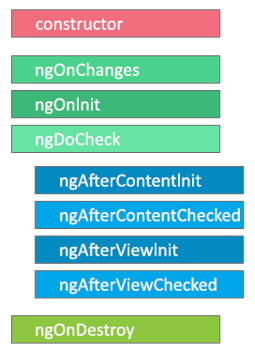
Lifecycle hooks


Pipes
- class with the @Pipe decorator
- transforms input values to output values for display in a view
- examples of Angular defined pipes (complete list at https://angular.io/api?type=pipe):
- date
- currency
- async
- json
- can be chained
- can take arguments
- it is possible to define custom pipes


Pipe examples


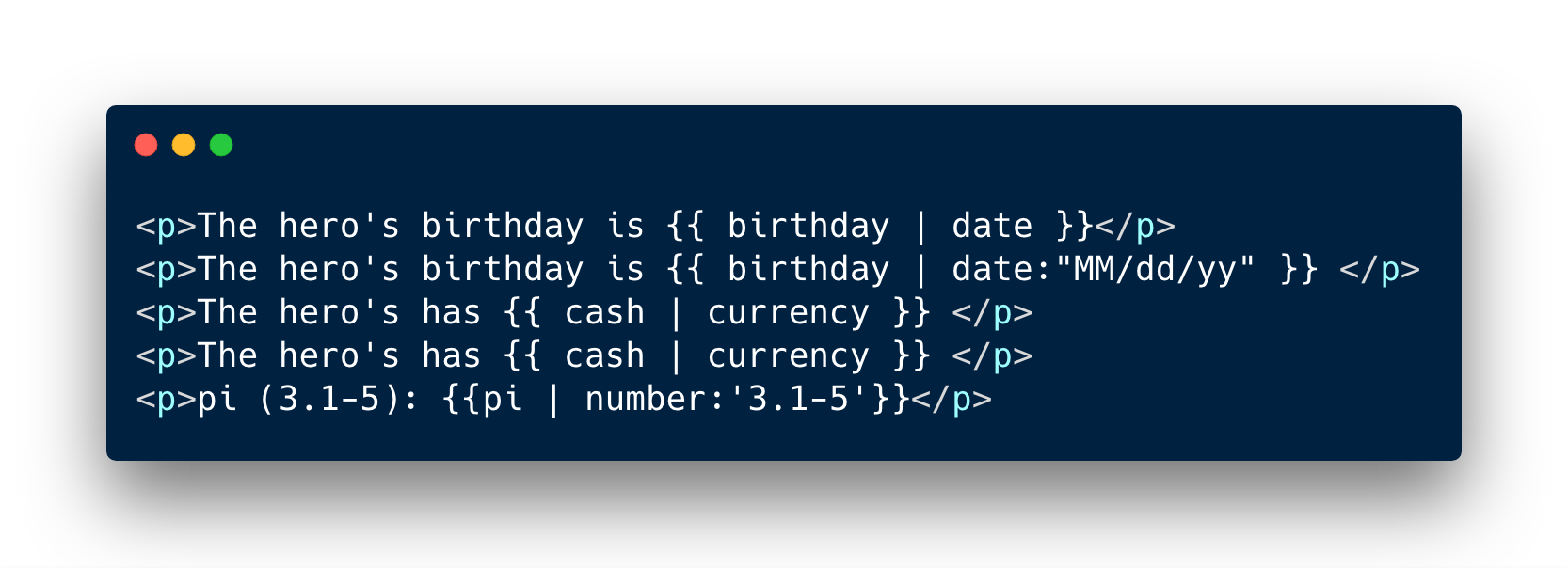
Pipe Name
Pipe Params
Directive
- class with a @Directive decorator
- there are structural and attribute directives
- typically appear within an element tag as attributes
- there are a lot of build in


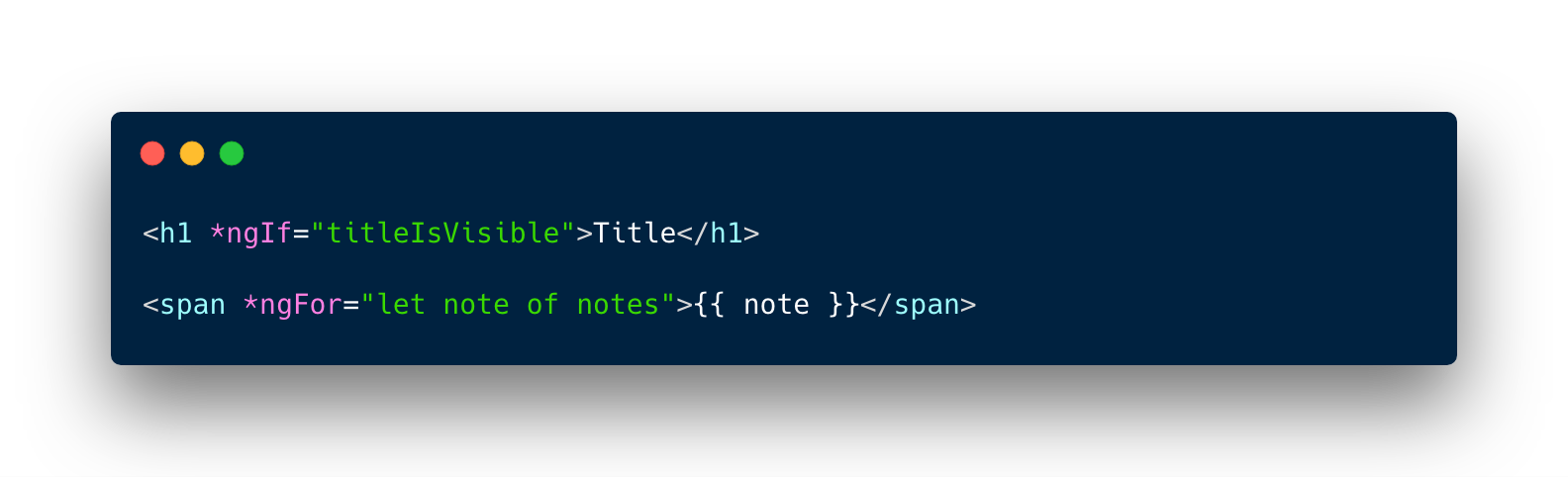
Structural Directives
-
alter layout by adding, removing, and replacing elements in DOM
-
*ngFor is an iterative; it tells Angular to create element for each iteration.
-
*ngIf is a conditional; it includes the element only if a condition is true.


Attribute Directives
Alter the appearance or behavior of an existing element


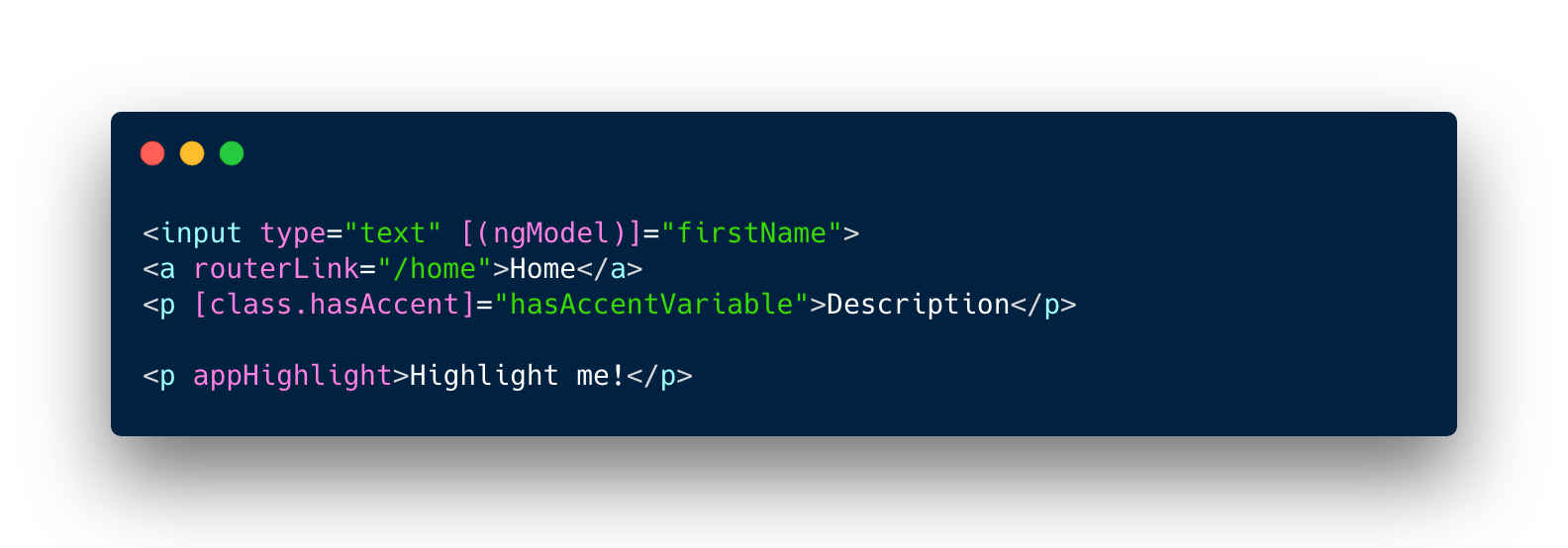
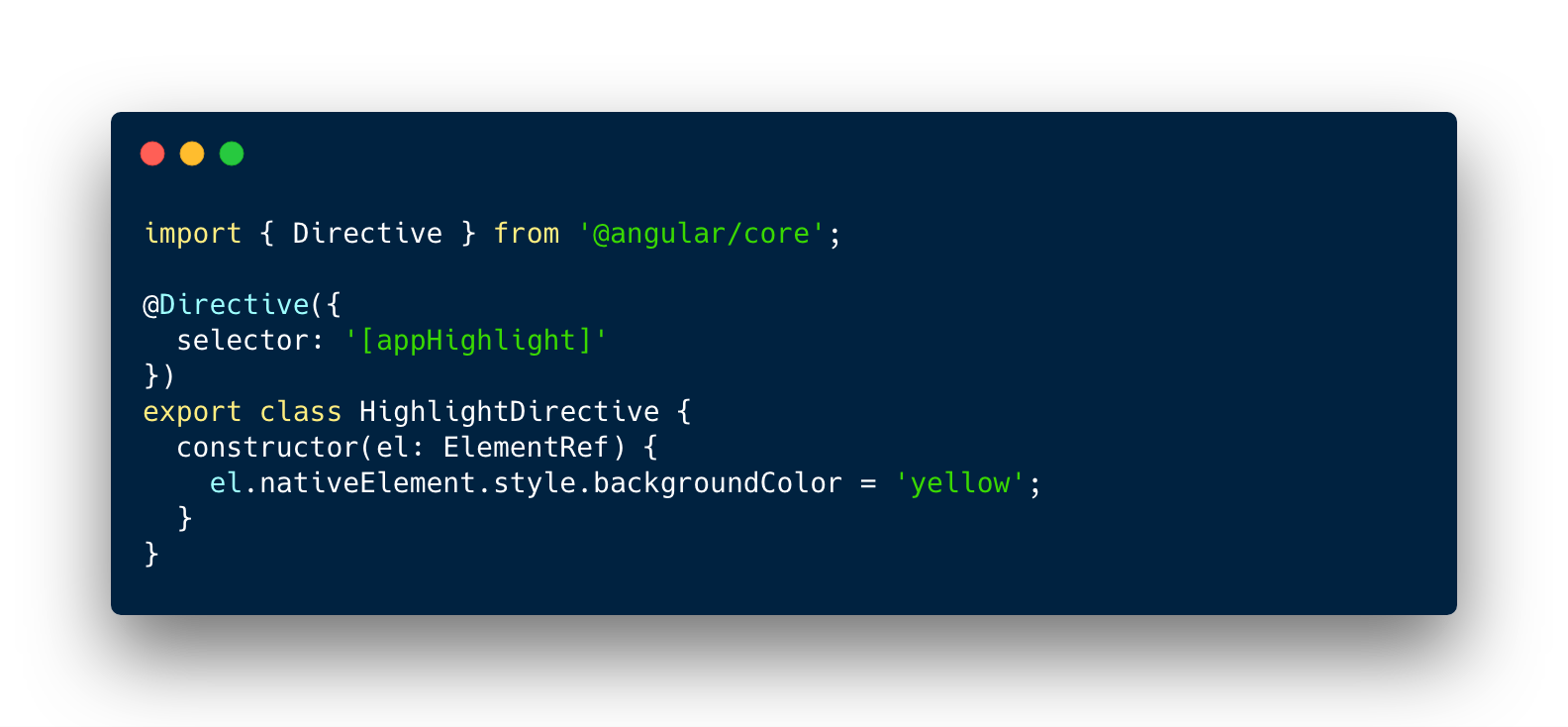
Custom directive
Service
- class with a @Injectable decorator
- typically a class with a narrow, well-defined purpose
- re-usable by any component which could need it
- included using Angular Dependency Injection
- mostly used for server communication or components sharable logic



Registering a services


You can register providers in modules or in components
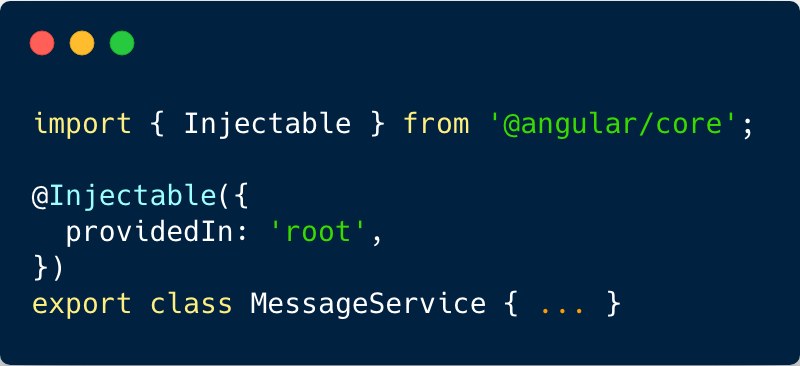

When providers added to the root module, the same instance of a service is available to all components in your app
Registering a services
When providers added at the component level, you get a new instance of the service with each new instance of that component


You can register providers in modules or in components
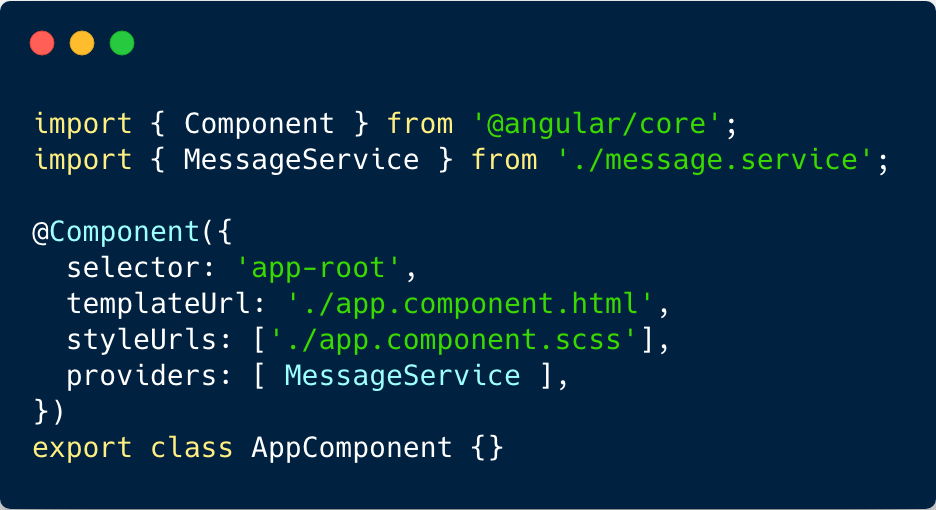
Service usage


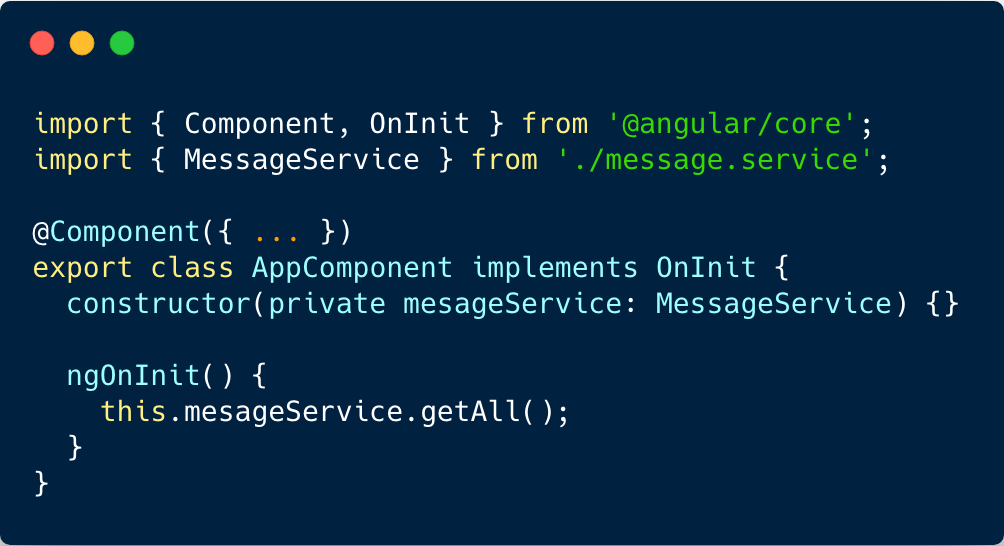
Provide service via DI
Use service
Forms
- Template Driven
- Reactive Forms
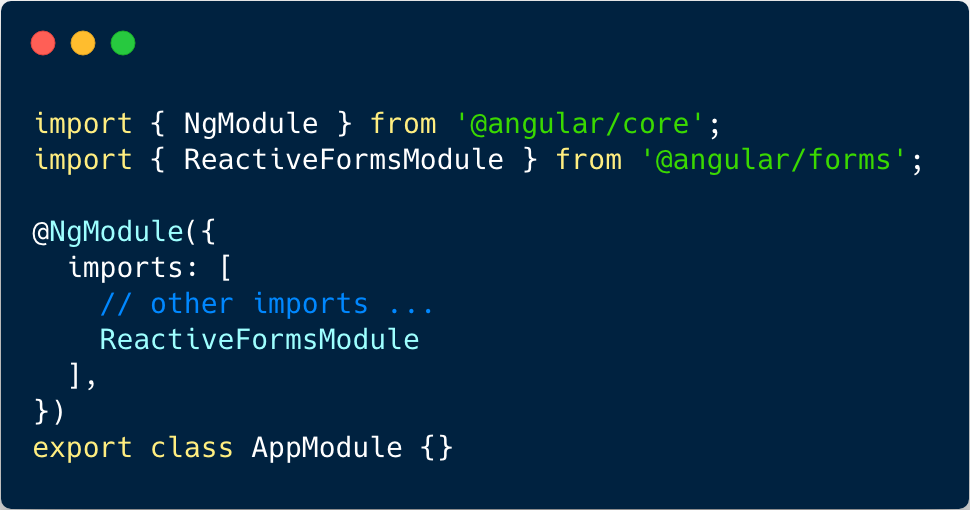
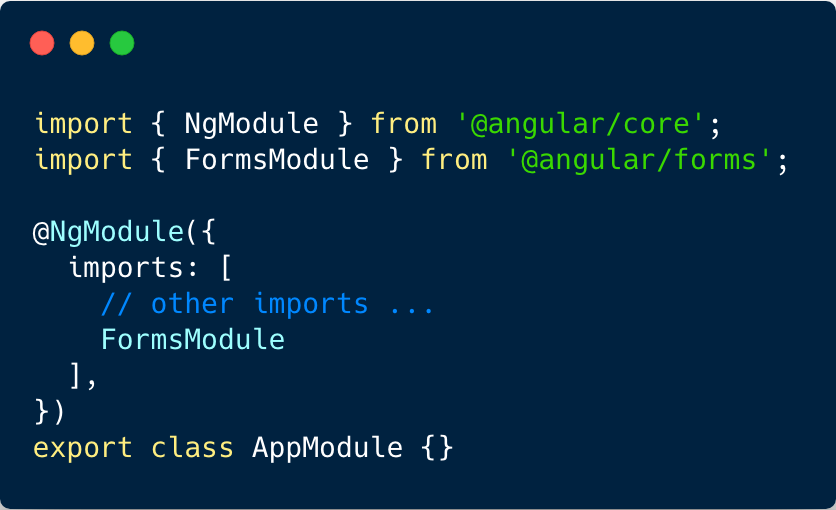

Template-driven forms



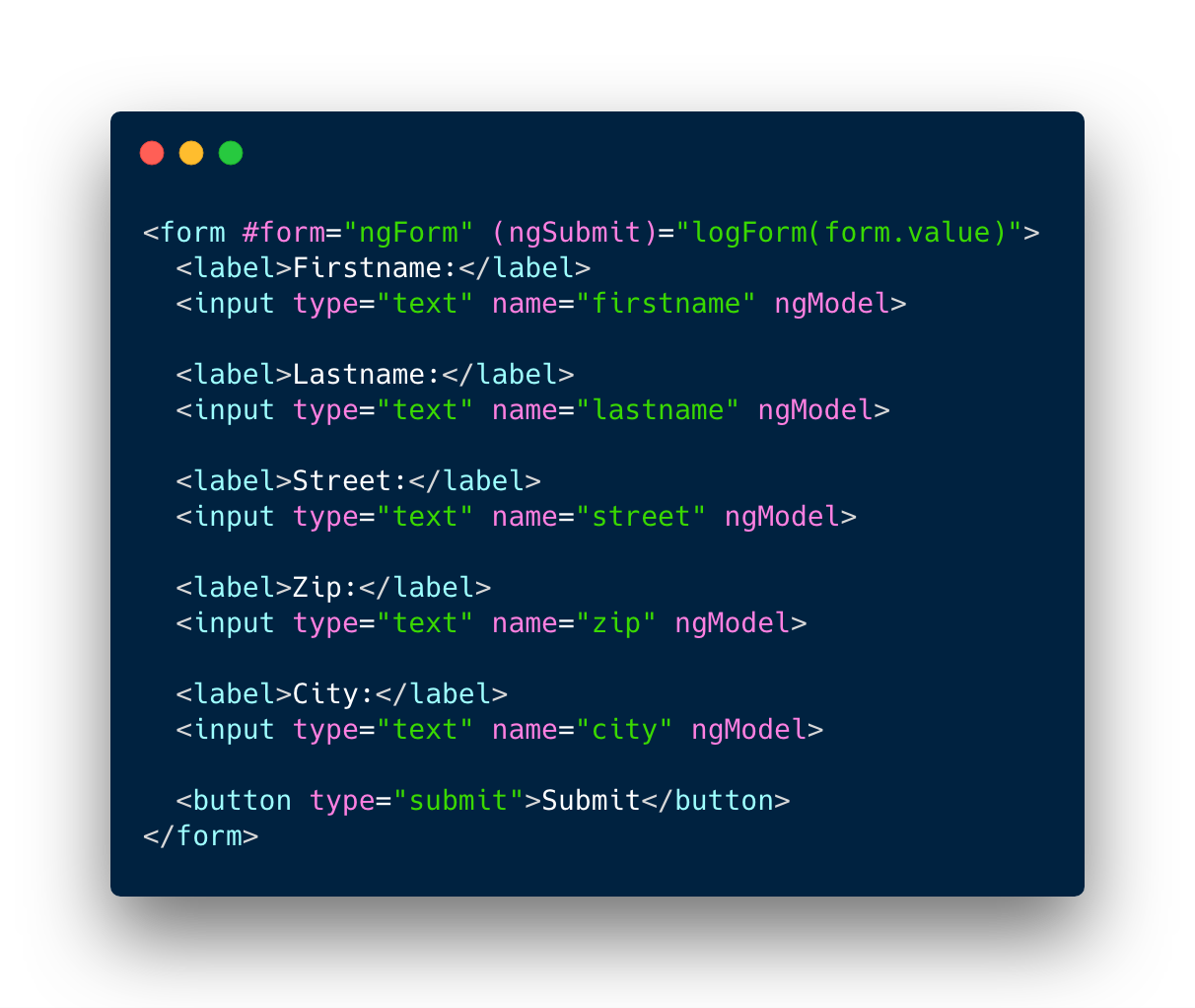
Reactive forms


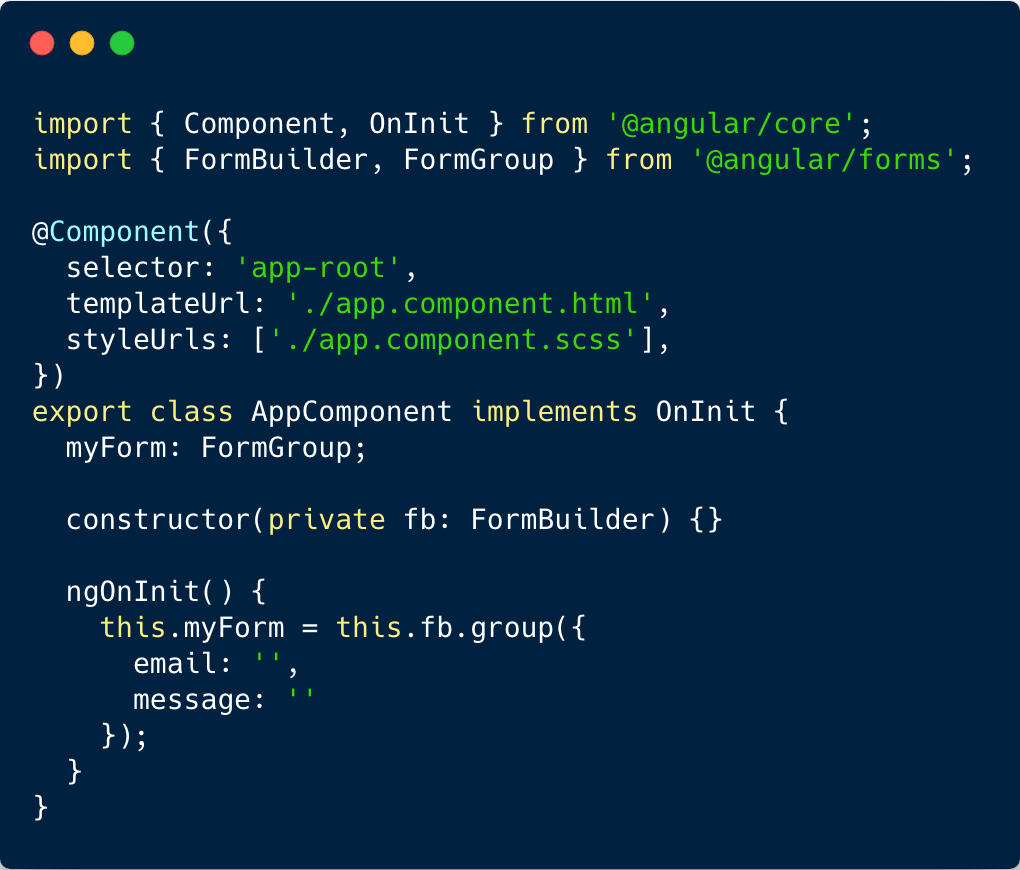
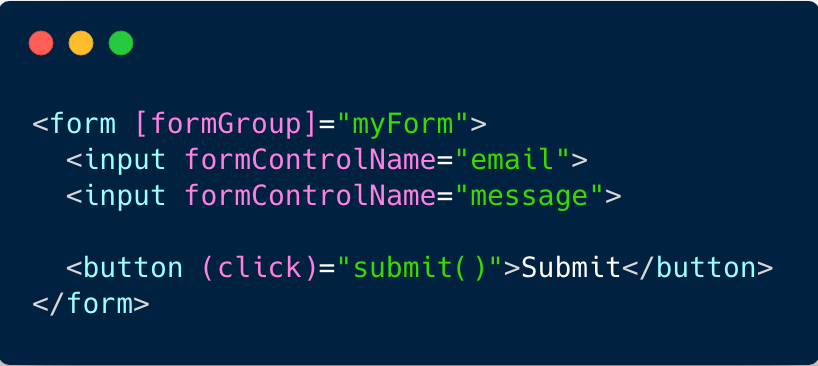
6. Router


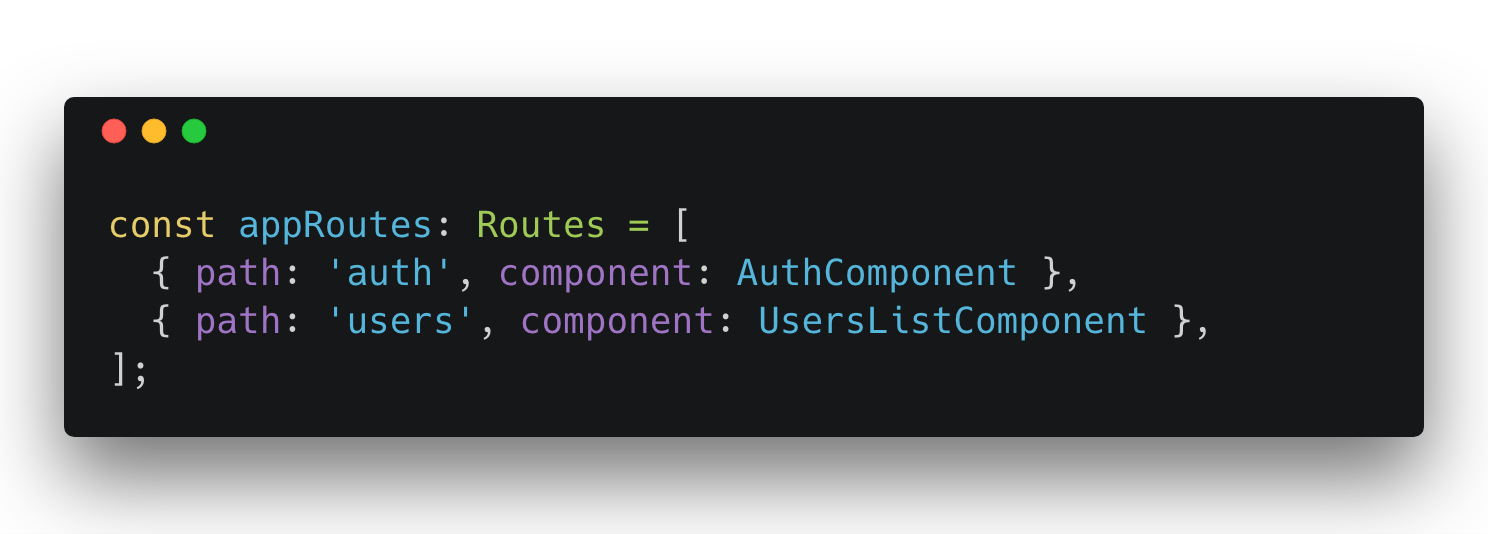
Routes Declaration
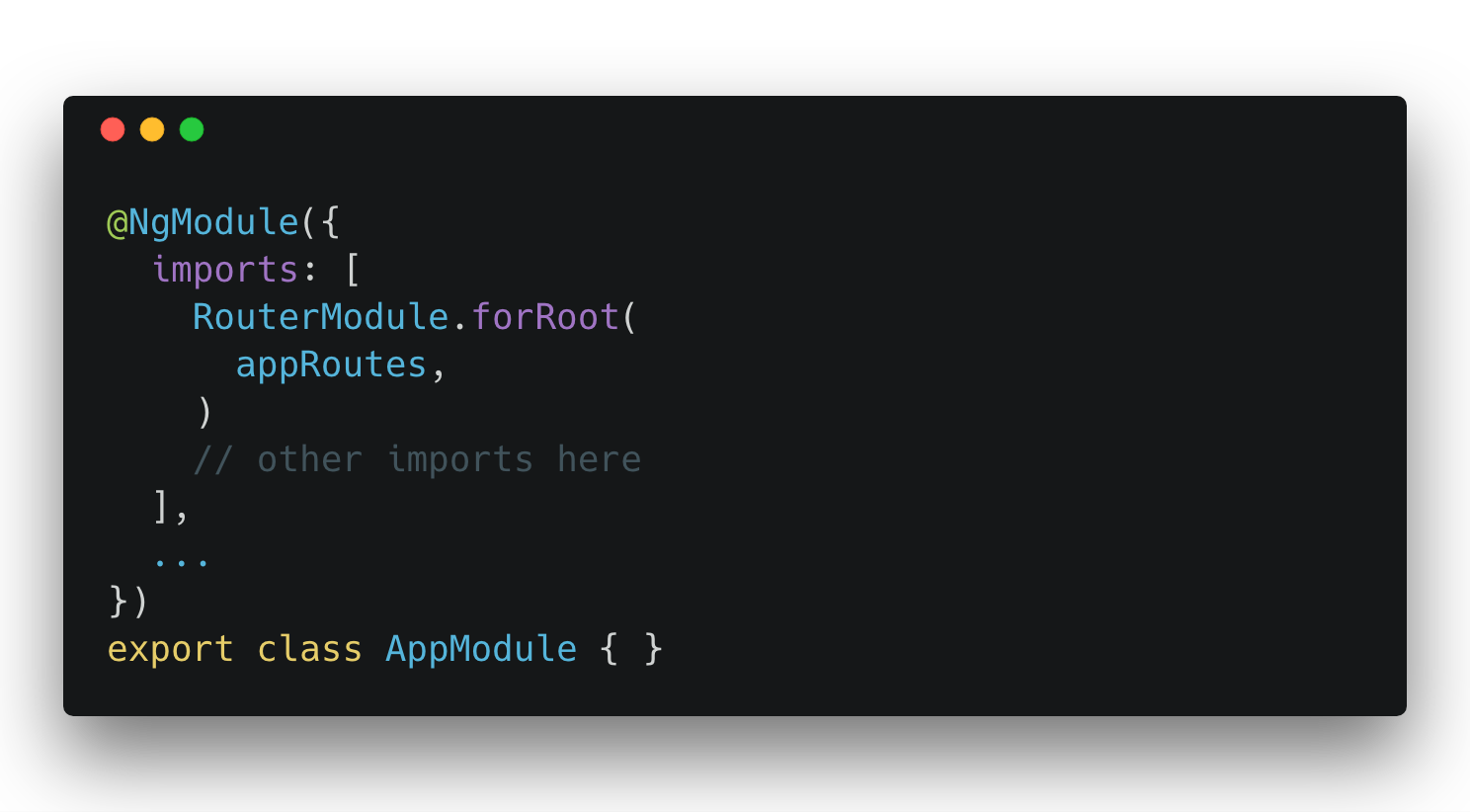


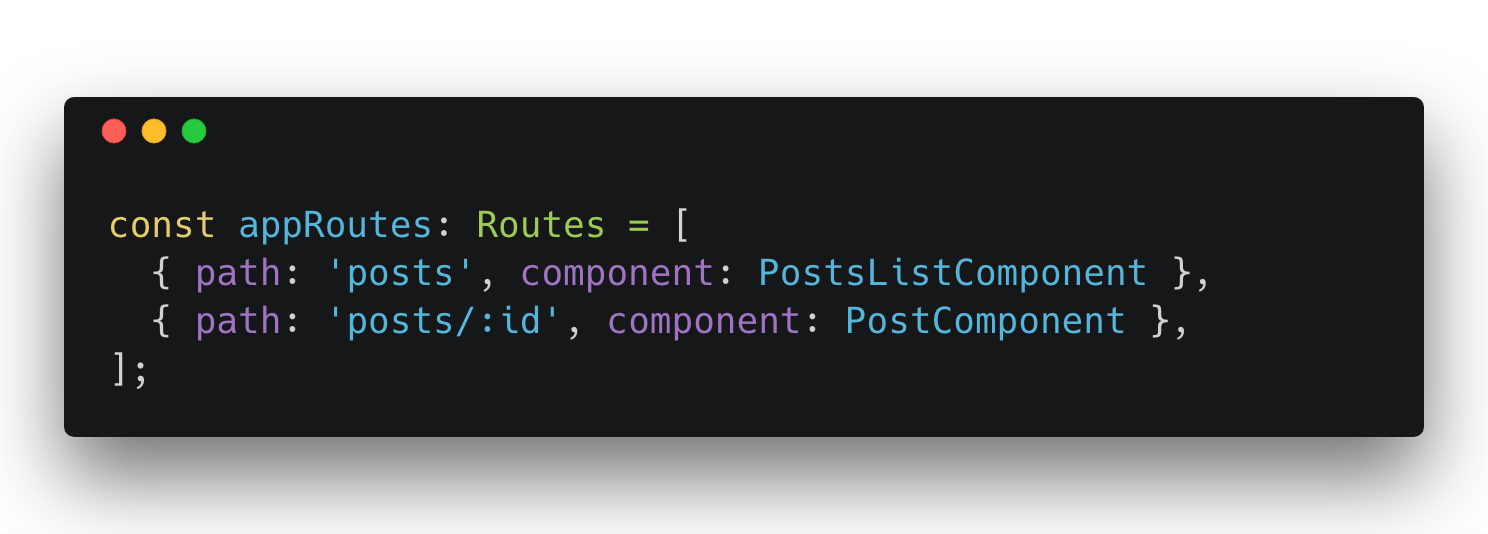
Dynamic Routes




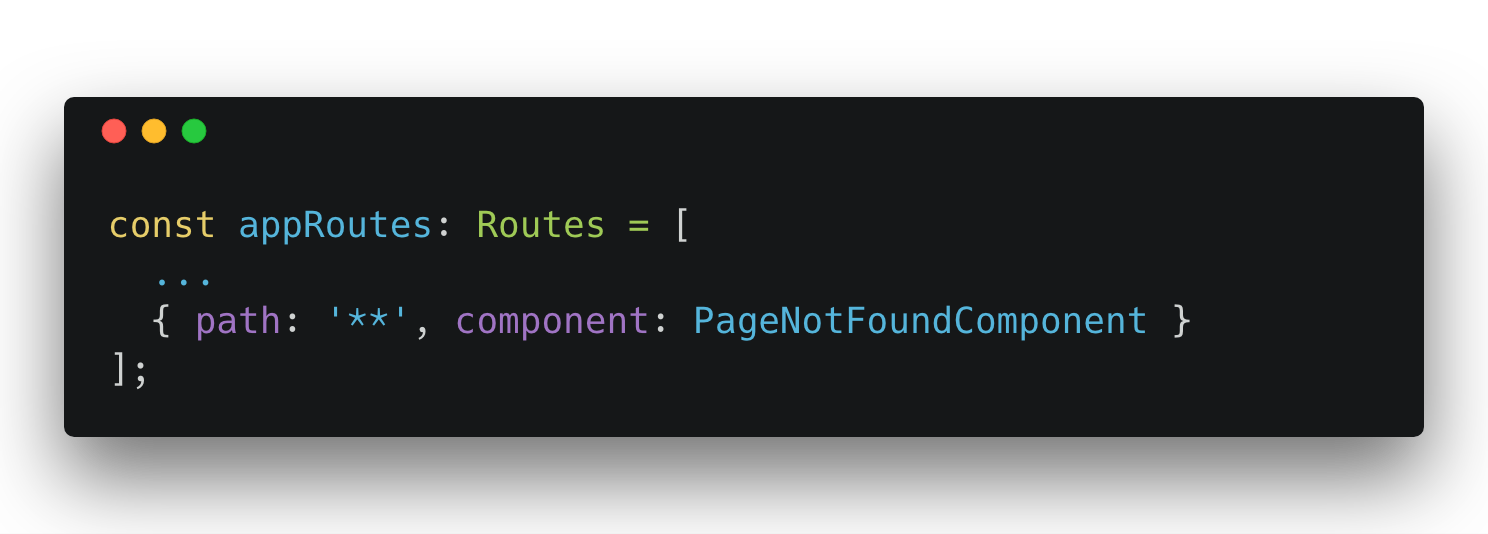
Match Any Route



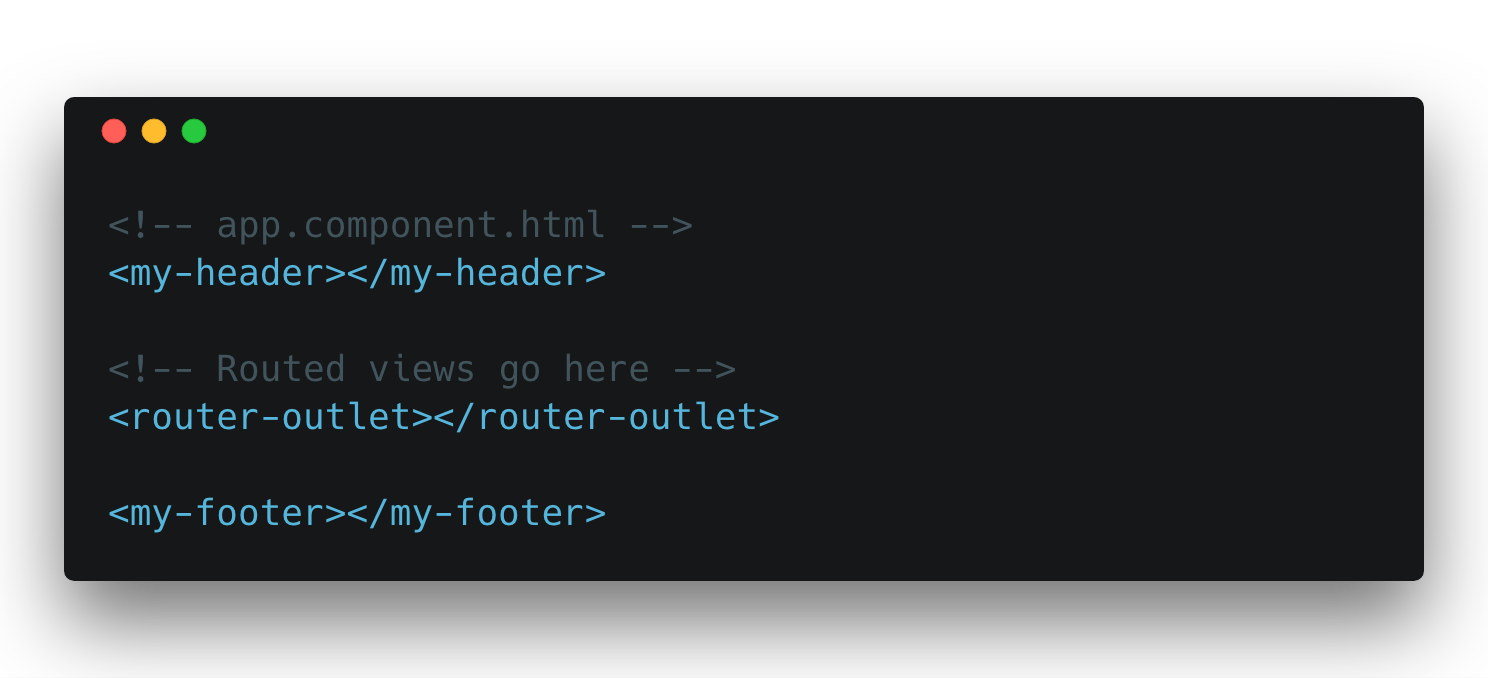
Router Outlet


Navigation Between Routes
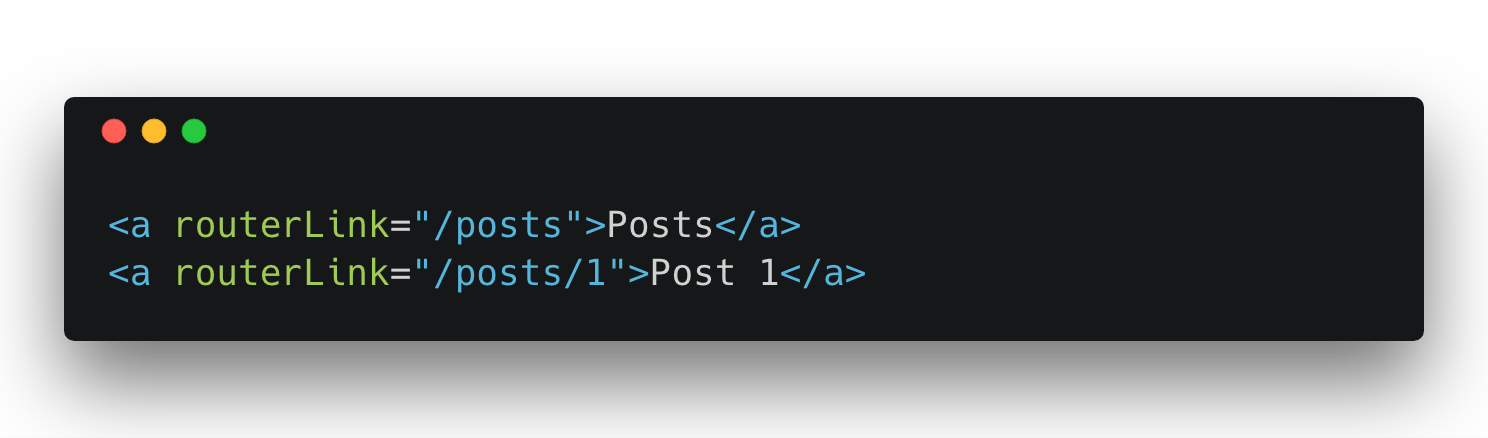
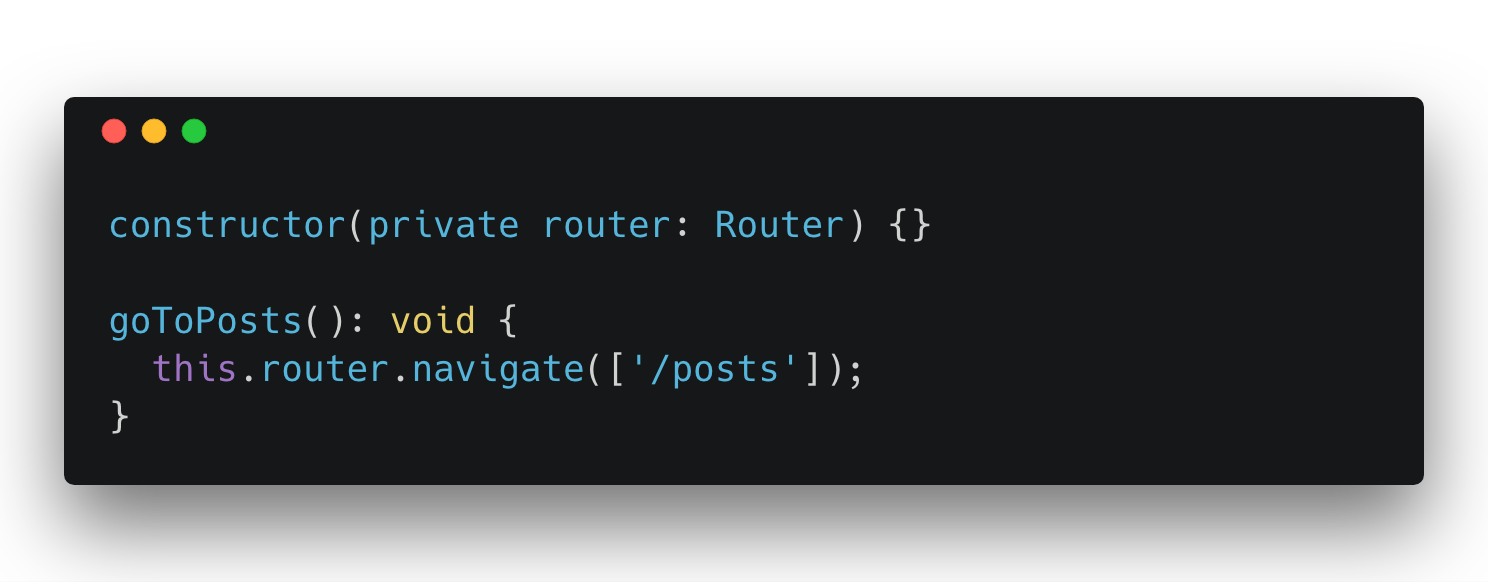


7. Http


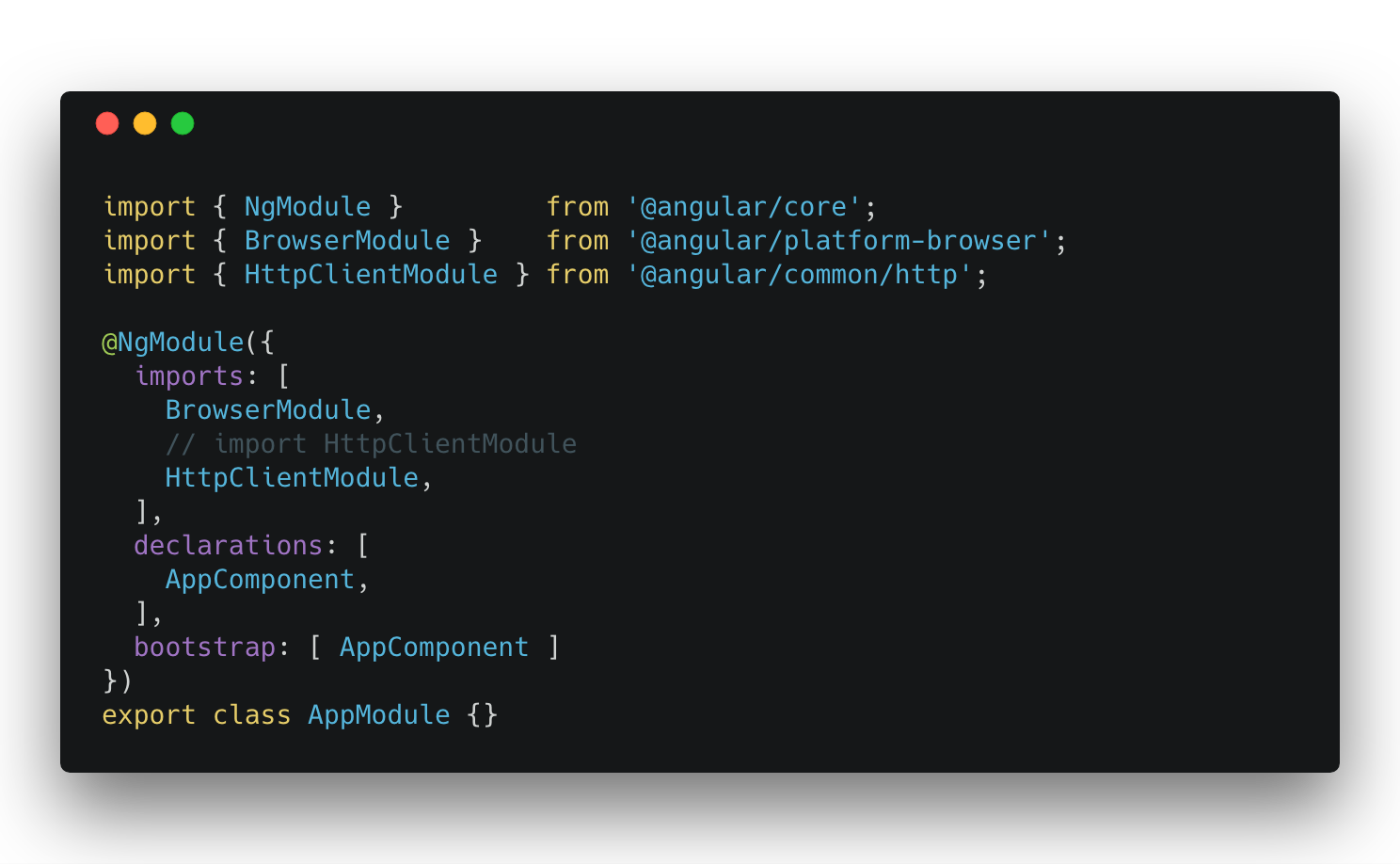
First Step:
Include HttpClientModule into imports array


Second Step:
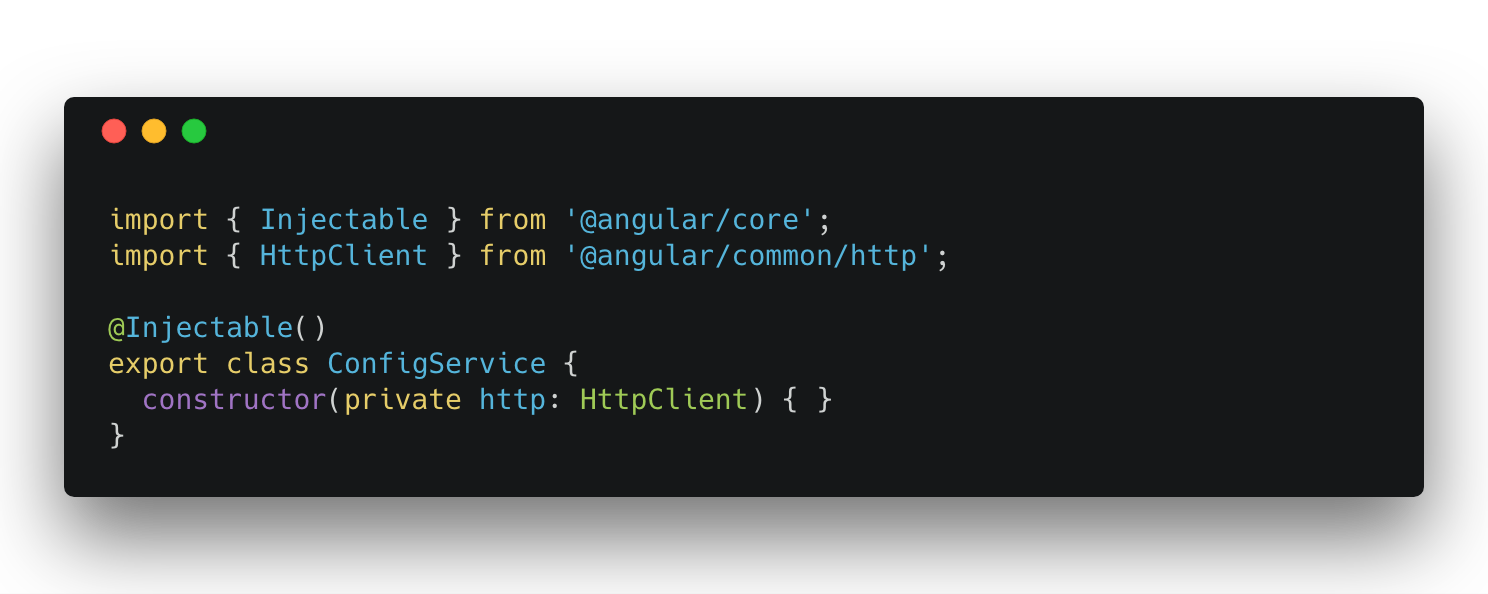
Inject into service


Availabled Methods
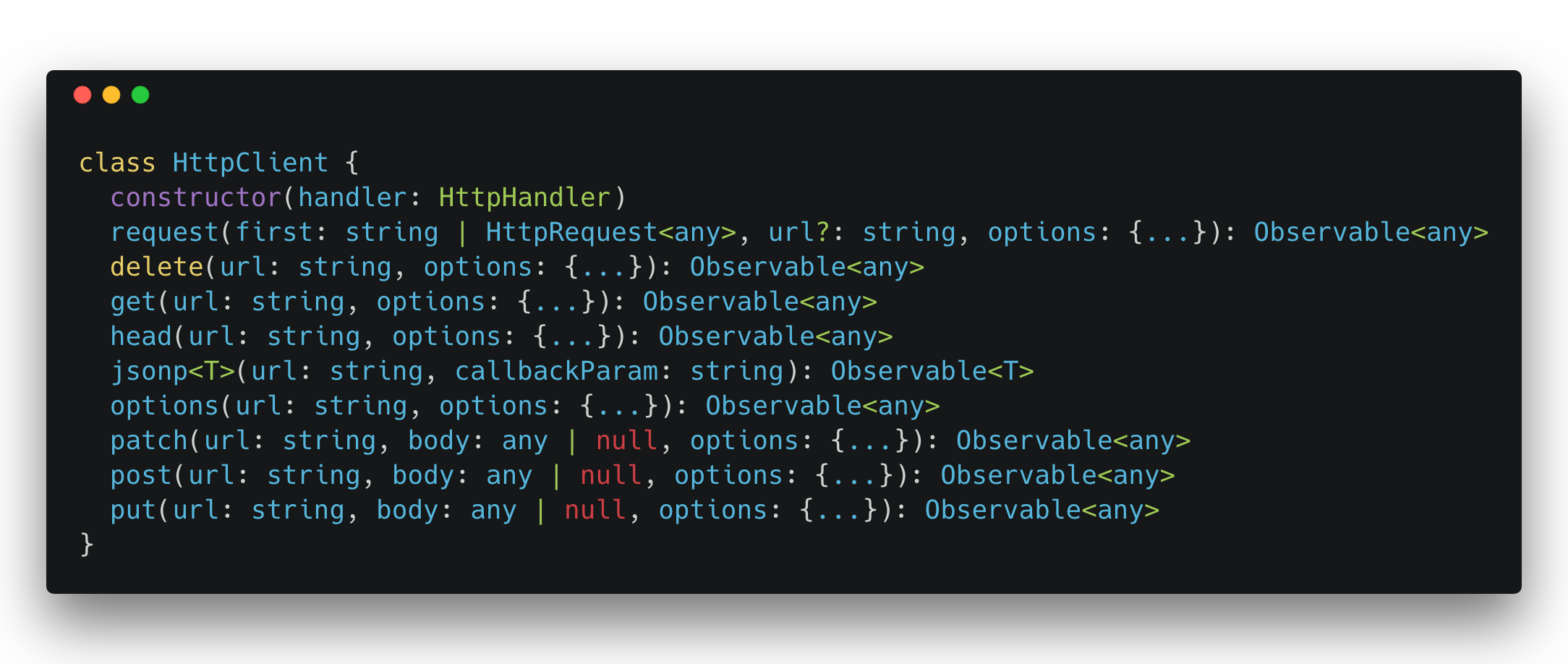


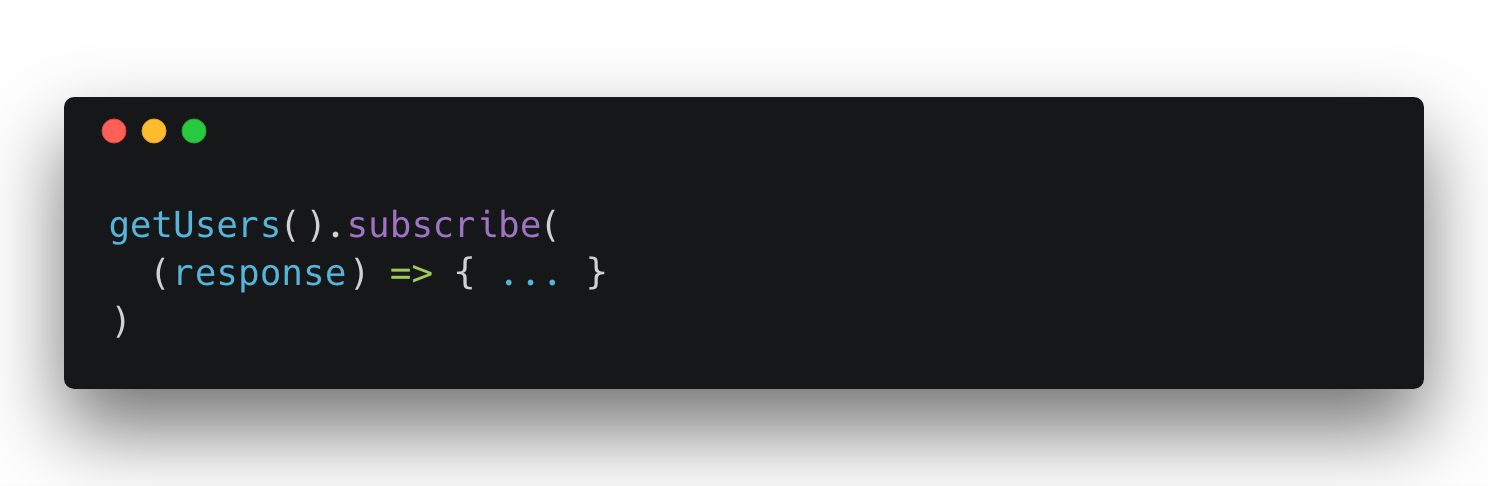
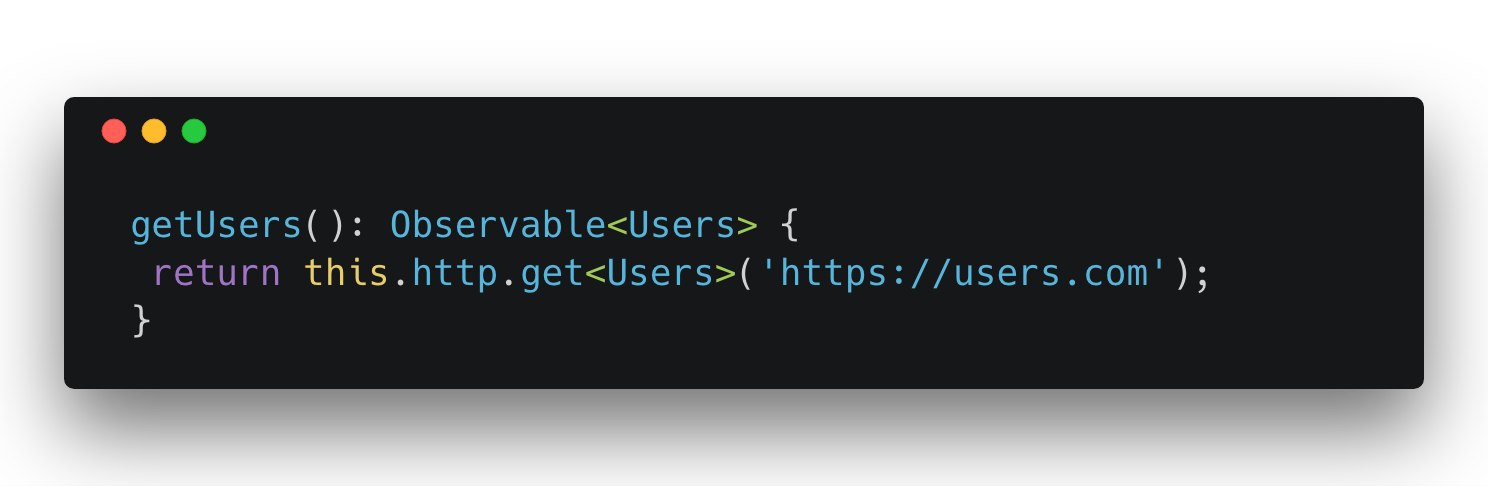
Simple Request


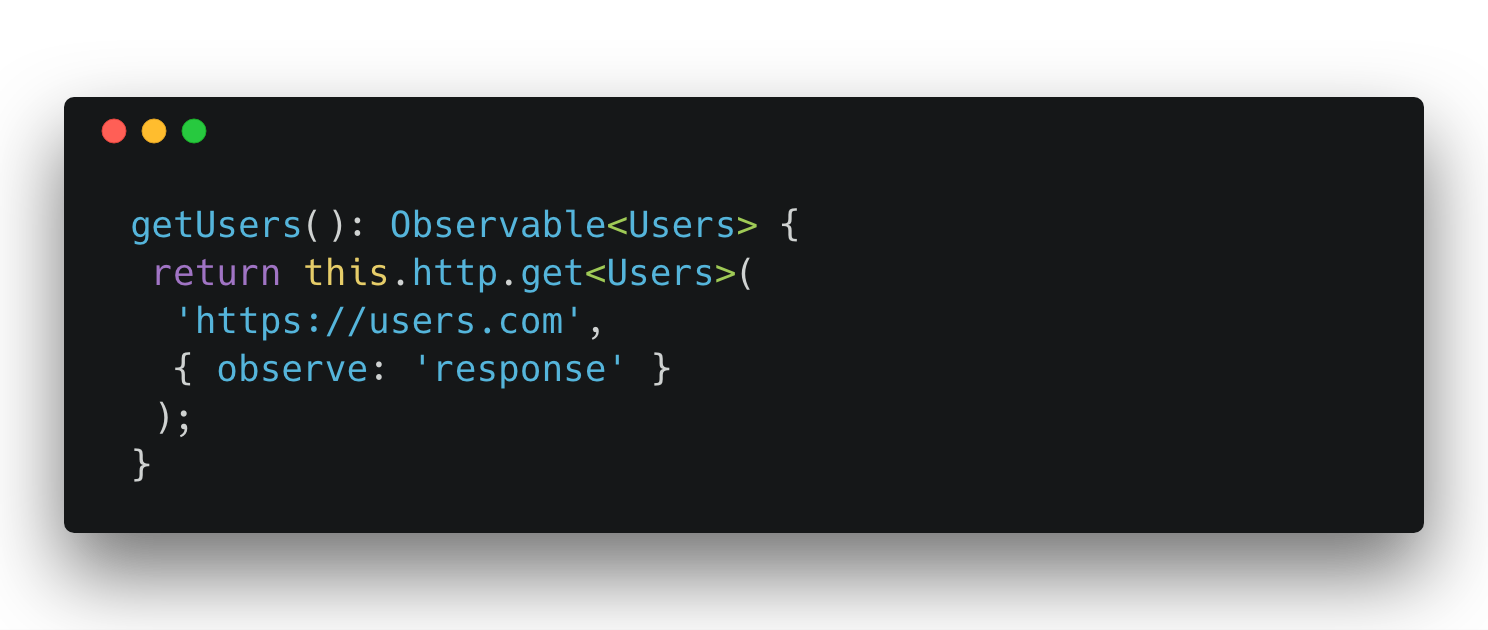
Reading the full response


Error Handling

catchError
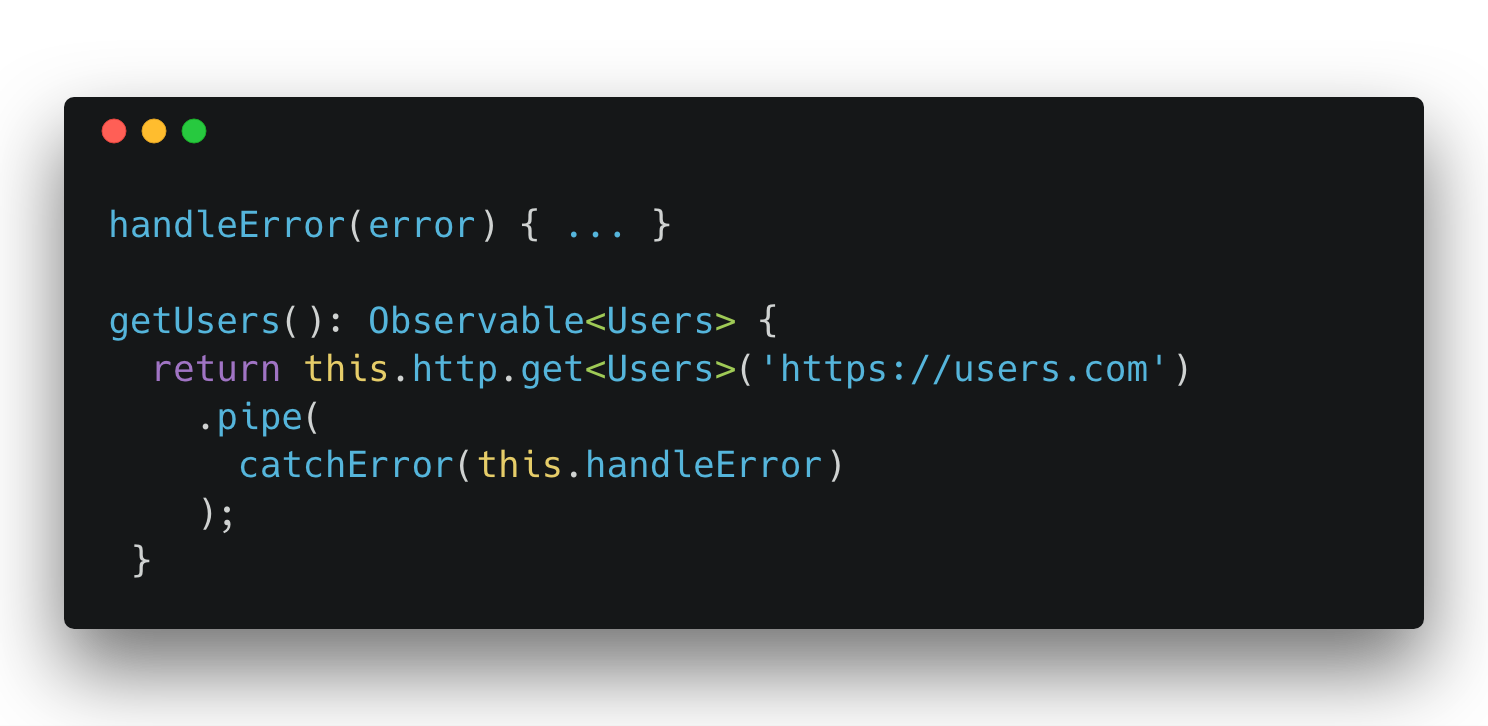

onError


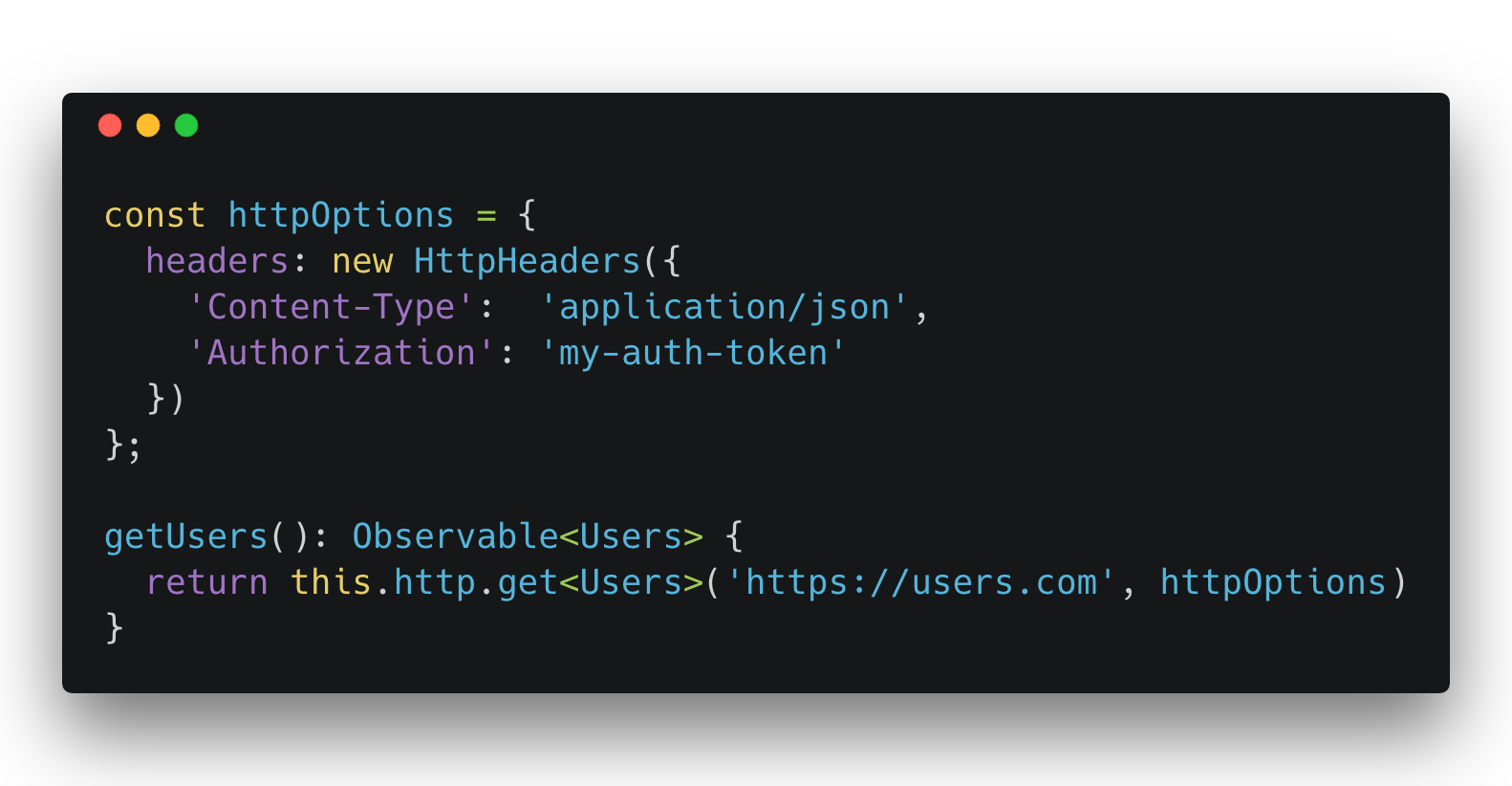
Working With Http Headers


Homework


Do What You Love
&
Love What You Do


Thanks For Attention
Have Any Questions?


Resources/Links


- Architecture - https://angular.io/guide/architecture
- Modules - https://angular.io/guide/architecture-modules
- Components, Templates and ViewsTemplates syntax, Data binding, Pipes, Directives - https://angular.io/guide/architecture-components
- Services and Dependency Injection - https://angular.io/guide/architecture-services
- Template-driven forms - https://angular.io/guide/forms#template-driven-forms
- Reactive forms - https://angular.io/guide/reactive-forms


Resources/Links
Angular. Overview
By Roman Yavoriv
Angular. Overview
Overview of Angular
- 917



