Web 105
Stacks on Stacks
Ronak Raithatha
Software Engineer @ BoomTownROI
Roadmap
Week 1: Web Stack and NodeJS
- What are web stacks?
- NodeJS
- V8
- Call backs
- Async
- Event loop
Roadmap
Week 2: ExpressJS and API
- What are APIs?
- ExpressJS
- Endpoints
- Middleware
Roadmap
Week 3: Frontend and AngularJS
- What does frontend encompass
- AngularJS
- Scope
- Controllers
Roadmap
Week 4: Mongo and Questions
- What is persitant data?
- Mongo
- CRUD
- Q&A
What are the stacks?
At a minimum, a stack refers to a list of technologies/libraries/languages/operating systems required to the get a website up and running.
Examples:
- LAMP
- Javascript + web server
- Ruby on Rails
- MEAN
- etc.
DB
SERVER
CLIENT
Data?
DATA!!!
HTML, Javascript
Backend Logic
Php, ruby, python, Java, Javascript, etc.
Datastore
MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL, etc.
Request
Generally JSON or XML payloads
Response
Generally JSON or XML, but can be pre-rendered HTML, PHTML, etc.
Client
Server
Architechture

MEAN STACK FLOW
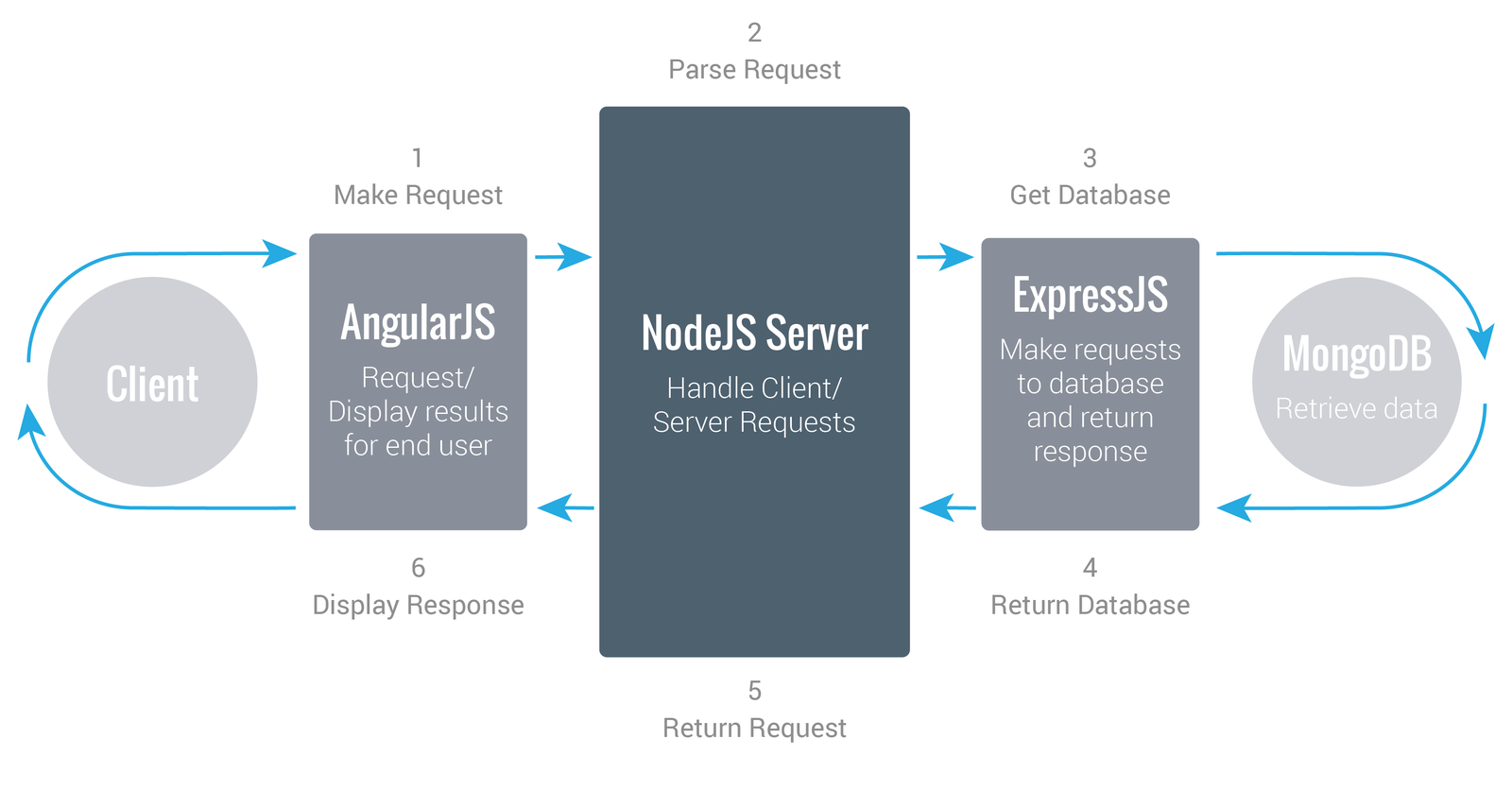
NODE JS
Node.js® is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine. Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model that makes it lightweight and efficient to run as a web server.
Node.js' package ecosystem, npm, is the largest ecosystem of open source libraries in the world.
Source: https://nodejs.org/
Chrome's V8 Engine
V8 is Google's open source high-performance JavaScript engine, written in C++ and used in Google Chrome, the open source browser from Google
V8 compiles and executes JavaScript source code, handles memory allocation for objects, and garbage collects
Source: V8 Website
Other engines are:
Firefox: SpiderMonkey
Safari: Webkit
etc...
Event Driven, Non-Blocking I/O
Event Driven Programming is a programming paradigm in which the flow of the program is determined by events triggered by an action that occur in the application.
Eg. Browser events firing function.
In
This is achieved just like in the browser, through callbacks and the event-loop.
Non-blocking I/O or Asynchronous js is a form of I/O that allows processing to continue without needing each command to complete.
Again, achieved by Javascript's native asynchronous abilities, callbacks and the event loop.
NODE JS
console.log("Hello World");server.js
NODE JS
Async/Non-blocking code
console.log(1);
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(2);
}, 1000);
console.log(3);NODE JS
Callbacks/EventDriven
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(2);
}, 1000);NODE JS
WebServer
var http = require('http');
var server = http.createServer(function(request,response){
console.log("got a request");
response.write("Hi");
response.end();
});
server.listen(3000);NODE JS
WebServer With Endpoints
var http= require('http');
var server = http.createServer(function(request,response){
if(request.url == '/'){
console.log("got a request");
response.write("Hi");
response.end();
return;
}
if(request.url == '/hello'){
console.log("got a request on /hello");
response.write("Hello");
response.end();
return;
}
});
server.listen(3000);
NODE JS
Node Package Manager
package.json
rm -rf node_modules && npm install
ExpressJS
Web Applications
Express is a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for
Source: http://expressjs.com/
ExpressJS
API
With a myriad of HTTP utility methods and middleware at your disposal, creating a robust API is quick and easy.
Source: http://expressjs.com/
What is an API?
API - Application Program Interface
An API expresses a software component in terms of its operations, inputs, outputs, and underlying types.
API - Application Program Interface
An API defines functionalities that are independent of their respective implementations, which allows definitions and implementations to vary without compromising the interface.
API - Application Program Interface
A good API makes it easier to develop a program by providing all the building blocks. A programmer then puts the blocks together.
Types of APIs
Language API - Java Docs
Describing libraries and classes, functions in those libraries
and classes, and the parameters and return types for those functions.
Types of APIs
Library API - UnderscoreJs Docs
Documentation listing and describing each function in the library, the parameters it needs to perform those function and what it should return
Types of APIs
REST API - Twitter
Lists and describes all accessible endpoints for a given Representational State Transfer (REST) protocol implementation. Describes verbs and what body is required with those verbs.
REST Implementation
Endpoints
URIs that execute desired code.
I.E Functions, but on the server. Where the function names are '/something/:id/something'
REST Implementation
REQUEST BODY
If the ENDPOINTS are the function name, the REQUEST BODY are like the parameters that we send to a function.
GET: Generally none, since you get everything.
POST: An object containing necessary information
PUT: An object containing information to be updated, and an id pointing to the object to update.
DELETE: An id to the object to delete.
Popular formats: JSON and XML
REST Implementation
Response status
1XX: Hold on
2XX: Here you go
3XX: Go away
4XX: You messed up
5XX: I messed up
Code Samples
Initial Setup
// Dependency Configuration
var http = require('http');
var express = require('express');
var bodyParser = require('body-parser');
var morgan = require('morgan');
var methodOverride = require('method-override');
// Express Setup
var app = express();
// Middleware Setup
app.use(morgan("dev")); // Logs endpoint hit to console
app.use(bodyParser.json()); // Parses JSON in request body
app.use(methodOverride()); // Makes dealing with PUT and DELETE easier
// Data Setup
// This set is only for us, since we aren't using a database just yet.
var globalId = 2;
var todos = [{
"id":1,
"text": "Need to do this"
}];
//Start Server
app.listen(3000);
console.log("Up and running on port 3000");Code Samples
GET Endpoint
// Data Setup
// ...
// Routes
// GET Endpoint
// This endpoint is triggered by hitting '/api/todos' with the GET verb.
// This endpoint return the array of todos
app.get('/api/todos', function(request, response){
// This function accepts request and response as parameters.
// These are supplied by Express and house important data and functions.
response.send(todos); // Is one way to return a request.
});
// Start Server
// ...Code Samples
POST Endpoint
// GET Endpoint
// ...
// POST Endpoint
// This endpoint is triggered by hitting '/api/todos'
// with the POST verb, and passing data either in JSON or XML format
// This endpoint returns the array of todos with the new todo in it
app.post('/api/todos', function(request, response){
// The request parameter contains the data passed in the HTML request.
// It is accessed with request.body.<name of item passed>
// Create todo object like the todos schema above.
var todo = {
"id": globalId,
"text": request.body.text
};
// Add new todo to todos array
todos.push(todo);
// Increment Global Id in preparation for the next todo
globalId++;
// Send the todos array containing the new todo as the response.
response.send(todos);
});
// Start Server
// ...Code Samples
PUT Endpoint
// POST Endpoint
// ...
// PUT Endpoint
// This endpoint is triggered by hitting '/api/todos/:todo_id'
// with the PUT verb, and passing data either in JSON or XML format
// This endpoint will return a list of todos
// with the text in todos[todo_id] updated to what was passed in
app.put('/api/todos/:todo_id', function(request, response){
// Loop through the todos array to find the todo object being updated
for(var i=0; i<todos.length; i++){
// If the current todo's id matches the query parameter
if(todos[i].id == request.params.todo_id){
// update the text to what was sent in the body
todos[i].text = request.body.text;
// returns the updated list of todos
// The return is in the if statement so that the for loop doesn't
// run for longer than it needs to
response.send(todos);
}
};
});
// Start Server
// ...Code Samples
DELETE Endpoint
// PUT Endpoint
// ...
// DELETE Endpoint
// This endpoint is triggered by hitting '/api/todos/:todo_id' with the DELETE verb
// This endpoint will return a list of todos with the todo at todos[todo_id] deleted
app.delete('/api/todos/:todo_id', function(request, response) {
// Loop through the todos array
for(var i=0; i<todos.length; i++){
// if the current todo's id matches the query parameter's
if(todos[i].id == request.params.todo_id){
// remove it from the array
todos.splice(i, 1);
// return the modified array
response.send(todos);
}
};
});
// Start Server
// ...AngularJS
AngularJS is what HTML would have been, had it been designed for building web-apps.
Declarative templates with data-binding, MVW, MVVM, MVC, dependency injection and great
testability story all implemented with pure client-side JavaScript!
Source: http://angularjs.org
AngularJS
MVC
Model-View-Controller
Models house the data
Views are the compiled HTML Templates
Controllers hold the application logic and drive changes between the view and model.
AngularJS
MVC
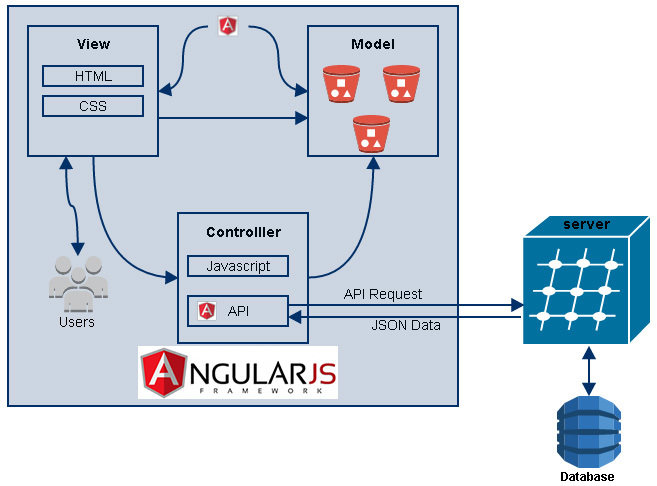
AngularJS
Two-Way Data Binding
Synchronization between Model and View
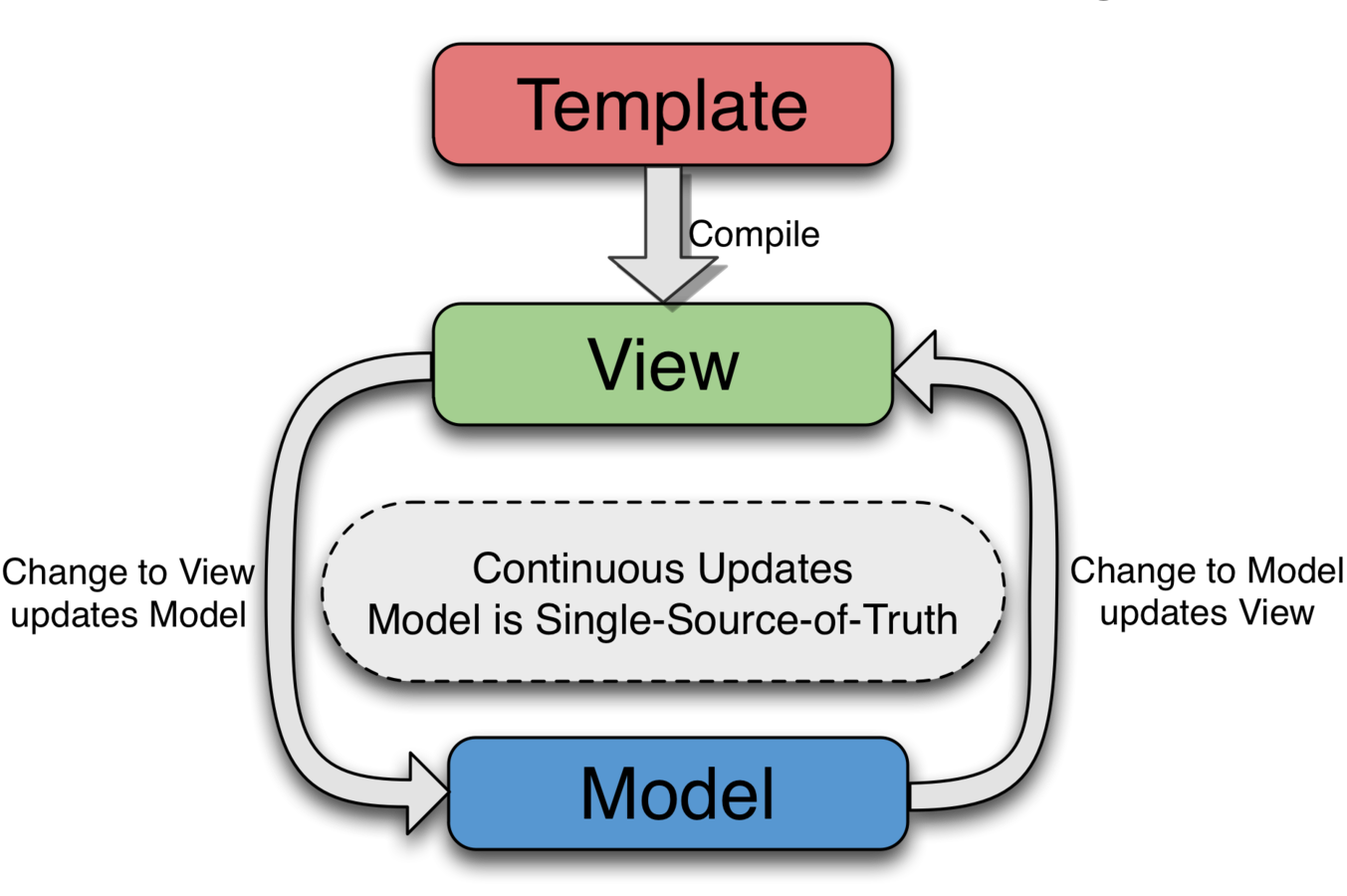
AngularJS
Two-Way Data Binding
Synchronization between Model and View

AngularJS
$scope
$scope:
- sits on the main angular object
- maintains two way data-binding
- bridge between model and view
- bridge between JS and DOM
AngularJS
ng-model
<html>
<head>
<script src="../node_modules/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app>
<div>
<input type="text" ng-model="name" />
<h2>{{name}}</h2>
</div>
</body>
</html>AngularJS
ng-app, ng-controller
<html>
<head>
<script src="../node_modules/angular/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="main.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app="todo">
<div ng-controller="mainCtrl">
<input type="text" ng-model="name" />
<h2>{{name}}</h2>
</div>
</body>
</html>var app = angular.module('todo',[]);
app.controller('mainCtrl', function($scope){
$scope.name = "Default Name";
});HTML
JS
MongoDB
MongoDB (from "humongous") is an open-source document database, and the leading NoSQL database.
MongoDB
Document Database
MongoDB stores all data in documents, which are JSON-style data structures composed of field-and-value pairs

MongoDB
Document Database
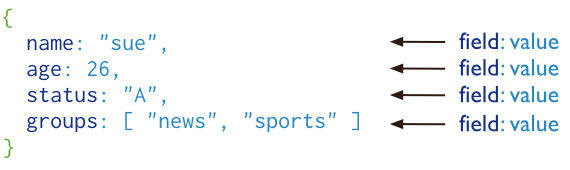
MongoDB
Document Database
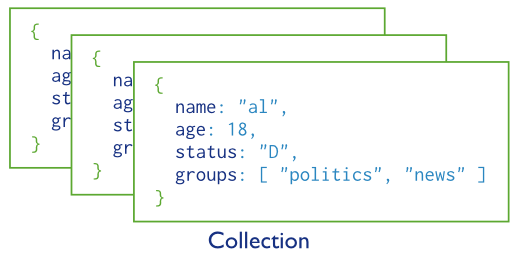
MongoDB
Document Database

MongoDB
Document Database

Web 105
By Ronak Raithatha
Web 105
- 2,120


