Introduction to React



React Library




Why React?
- Declarative
- Component-based
- Suitable for web and mobile
- Small learning curve
Why React?
- Declarative
- you describe the picture and someone else implements it
- we change the state and the UI is updated
- no direct DOM interactions
- web applications runs much faster (VDOM)
Why React?
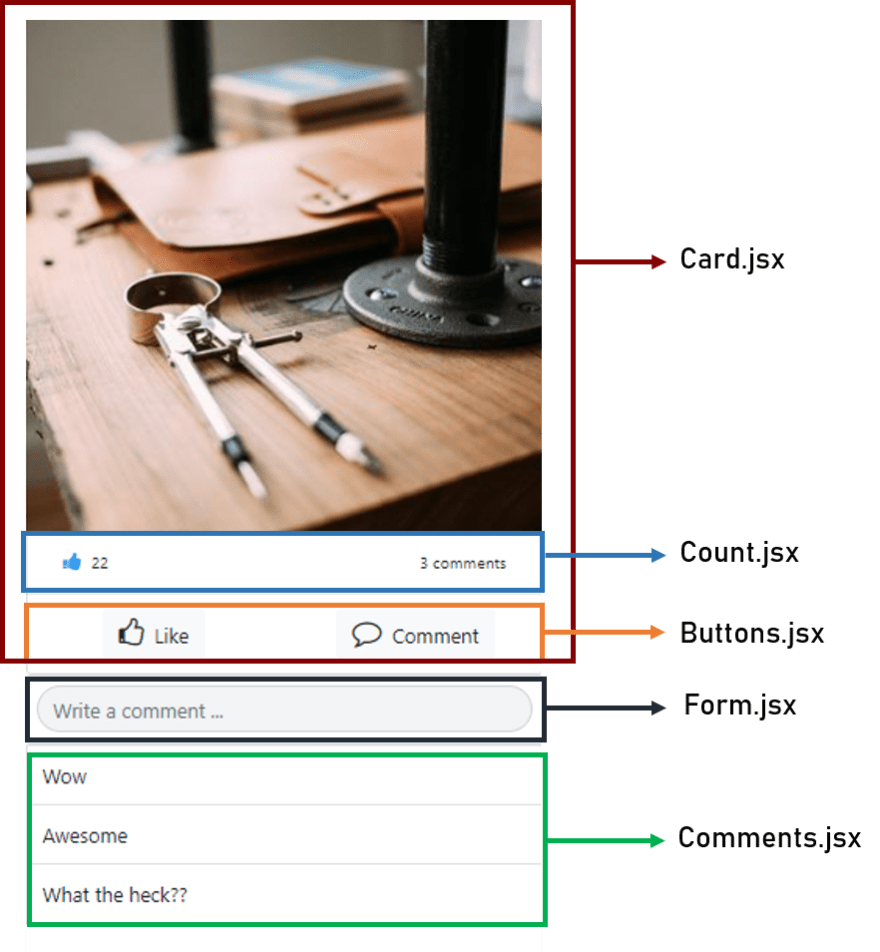
2. Component Based
- each component has its own markup and logic
- reusability, hence DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself)
- less development time
Why React?
2. Component Based
Why React?
3. Suitable for both web and mobile apps
- React Native derived from React for mobile applications
Why React?
4. Small learning curve
- Combines concept of HTML and JavaScript with some benefits
Before we start
Install node (Node >= 10.16 and npm >= 5.6)
https://nodejs.org/en/download/package-manager/
Install yarn
https://classic.yarnpkg.com/en/docs/install
npm install --global yarnCreate React App
npm install -g create-react-app
yarn create-react-app introduction-to-react
npx create-react-app introduction-to-reactRecommended

JSX
(JavaScript Syntax Extension)
JSX
- JavaScript + XML
const name = "Rosy"
const course = "React"
const element =
<div className="introduction">
Ola! I am {name} and I am learning {course} for {5*4} minutes
</div>
JSX
- JavaScript + XML
const name = "Rosy"
const course = "React"
const element =
<div className="introduction">
Ola! I am {name} and I am learning {course} for {5*4} minutes
</div>
must return a single element (alternatively use, <React.Fragment> </React.Fragment> or <> </>)
<>
<h1>blah</h1>
<span>what</span>
<p>ola</p>
</>JSX
- JavaScript + XML
const name = "Rosy"
const course = "React"
const element =
<div className="introduction">
Ola! I am {name} and I am learning {course} for {5*4} minutes
</div>
use className instead of class
camelCase attributes (onClick, onSubmit)
use curly branches for expressionsReact Element
const name = "Rosy";
const course = "React";
const element =
/*#__PURE__*/
React.createElement(
"div",
{
className: "introduction"
},
"Ola! I am ", name, " and I am learning ", course, " for ", 5 * 4, " minutes"
);
//Syntax
React.createElement(component, props, ...children)React Element
const element = {
type: 'div',
props: {
className: 'introduction',
children: "Ola! I am ", name, " and I am learning ", course, " for ", 5 * 4, " minutes"
}
};Render
const name = "Rosy"
const course = "React"
const element =
<div className="introduction">
Ola! I am {name} and I am learning {course} for {5*4} minutes
</div>
//syntax
ReactDOM.render(componentToRender, targetNode)DOM (Document Object Model)
DOM (Document Object Model)
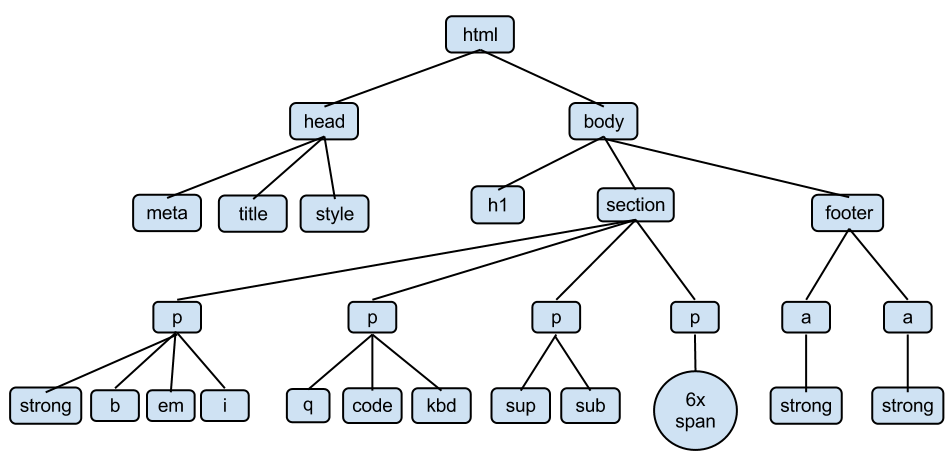
JSX render and Virtual DOM
- VDOM is a simplified copy of the real DOM
- React Element can be inserted into the VDOM, compared and updated fast and easily
State changes
Creates a VDOM with new update
Compares with previous VDOM state
Change in state
Updates only those changes in DOM

- ES6+
- Each child in a list should have a unique "key" prop warning. Why?
- Explore array methods
- Difference between regular and arrow functions
- Create your own stateful and stateless components
Look Into...
Look Into...
React Lifecycle Phases
- Mounting
- Updating
- Unmounting
React Lifecycle Phases
Mounting
when component renders for the first time
- constructor ( )
- render ( )
- componentDidMount ( )
React Lifecycle Phases
- constructor ( )
- initialize local state
- bind event handler to an instance
Mounting
React Lifecycle Phases
- render ( )
- returns single root HTML node element
- handles rendering of component to UI
Mounting
React Lifecycle Phases
-
componentDidMount ( )
- called immediately after component is rendered
- API calls, subscriptions
Mounting
React Lifecycle Phases
Updating
update existing nodes in the DOM
- render ( )
- componentDidUpdate ( )
React Lifecycle Phases
Updating
-
componentDidUpdate ( )
- called after componentDIdMount()
- takes previous props and previous state as arguments
React Lifecycle Phases
Updating
- componentDidUpdate ( prevProps, prevState)
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
const currentProps = this.props
if (currentProps.name !== prevProps.name) {
// do something
}
}React Lifecycle Phases
Unmounting
-
componentWillUnmount ( )
- invoked immediately before a component is unmounted and destroyed
- perform cleanups, cancel network requests
React Lifecycle Phases
Unmounting
-
componentWillUnmount ( )
- DON'T call setState() in this method
React Routers
- allows user to move between your components and different URLs
- Install react-router-dom for routing
npm i react-router-dom
yarn add react-router-dom
React Routers
function Routes(){
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<Switch>
<Route path={'/main'} component={Main}>
<Route path={'/profile'} component={Profile}>
</Switch>
</BrowserRouter>
)
}
Look into:
- Handling asynchronous calls
- JavaScript Promises
- Try out axios library
- Check out airbnb style guides for react
- ES6+ features
Introduction to React
By Rosy Shrestha
Introduction to React
- 290