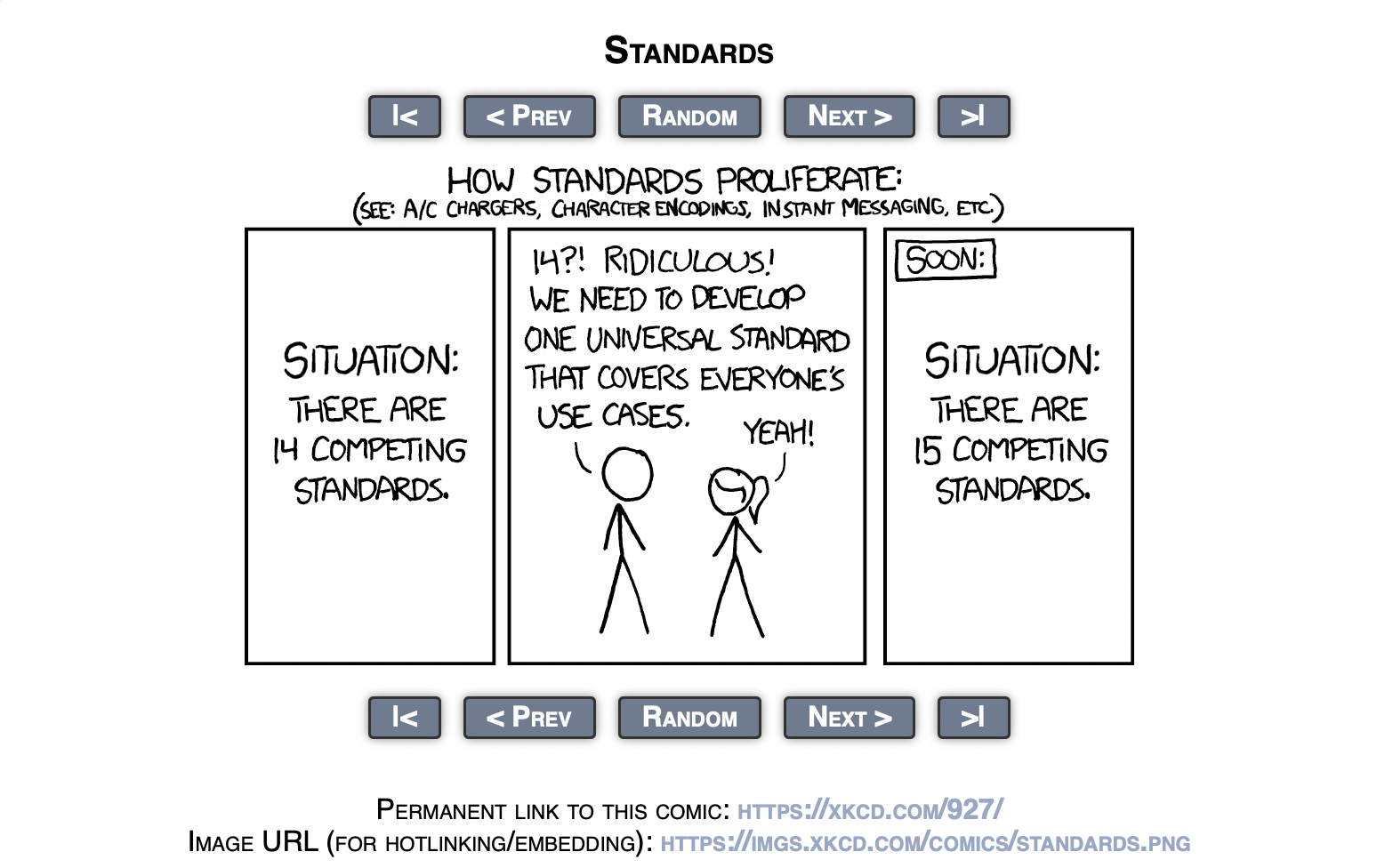
Single Source of Truth and Unidirectional Data Flow
Back End
Data Flows
- Mostly stateless
- Mostly synchronous, with carefully implemented asynchronous elements
- Carefully designed exit points of communication with the outside world: http interfaces, workers, database interactions
- Finite methods for users to interact with software instances

Front End
Data Flows
- Mostly statefull
- Completely asynchronous, with contrived systems to simulate synchronous behaviors
- Multiple exit points of varying levels of design quality
- Infinite methods of users for interacting with software instances


Unidirectional Data Flow
- One Method for data to be transferred between the modules of an application
- Modules are composed in a one-to-many hierarchical fashion - single parent, many children.
- Children subscribe to messages passed from parents, using those messages to process internal logic and pass necessary messages to their children.

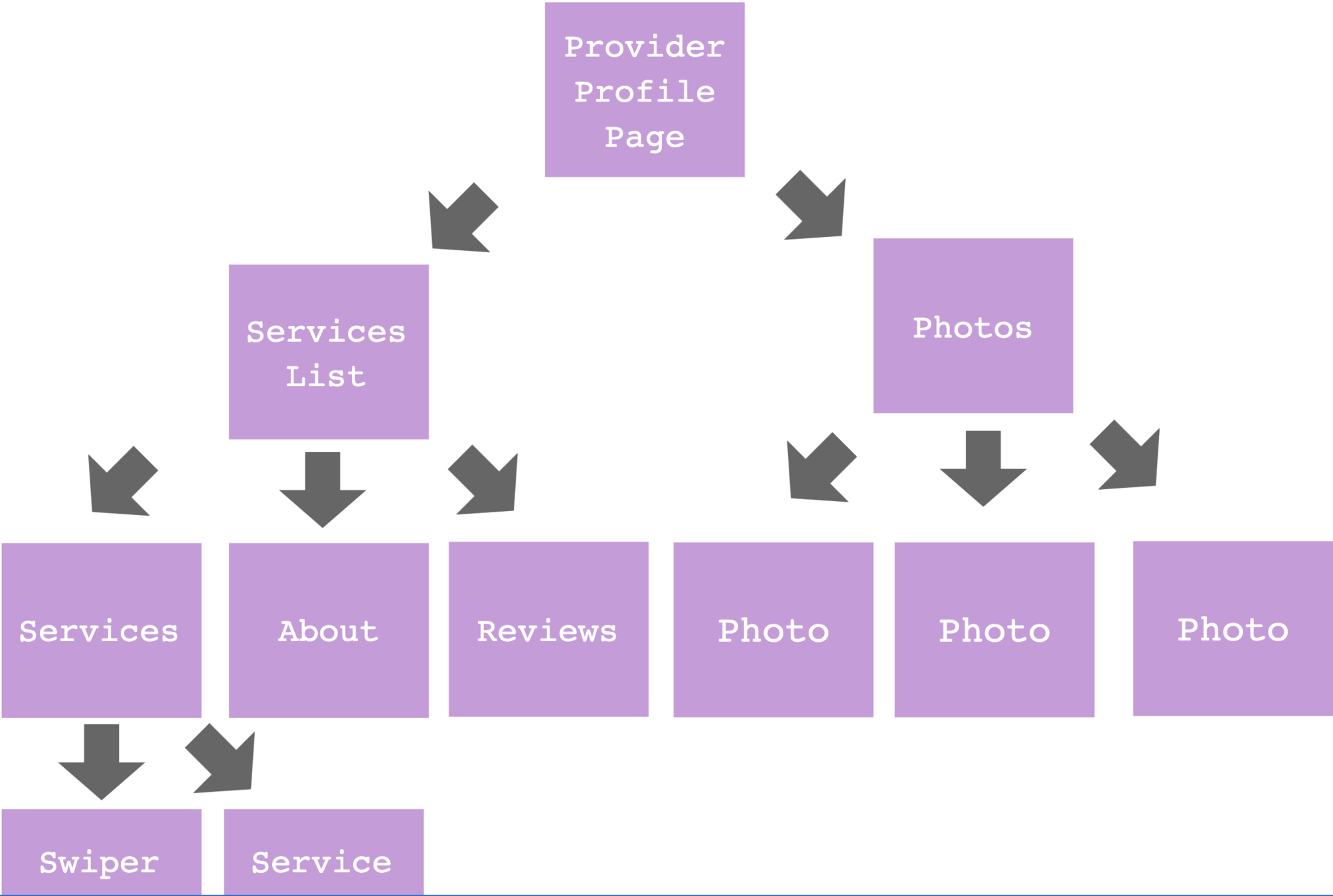
Provider Profile Page
Services
List
About
Reviews
Services
Photos
Photo
Photo
Photo
Swiper
Service
Unidirectional Data Wins
- Page Components can be relied on to fetch and manage data
- Children components can largely focus on presentation and not business logic
- Straightforward paths to debug data issues
- Predictable results from each component


- Data fetching gets large, expensive and slow even when views are fast and responsive
- Lots of code gets exposed to data it doesn't need to know about
- Business logic and view structure tightly coupled
- Difficult to update parent behavior based upon actions made by children
- Difficult to update siblings or cousins etc based upon actions of children
Ruh Rohs:
Actions
Redux Store
Selectors
Redux Wins
- Children receive actions from parents they can call in response to user interactions
- Container components select data their children need
- Data can be wired in anywhere it is needed, regardless of view hierarchy or component hierarchy
- Data only exposed where necessary
- Actions are dispatched synchronously, recorded by redux dev tools


- Actions can trigger renders across multiple siblings cousins, making performance consequences difficult to predict up front
- Data can be wired in anywhere, making it difficult to predict how changes made at the reducer level will impact components across the entire application
- Data logic and view structure uncoupled, but it is difficult to predict what manipulations are business logic and view logic
Ruh Rohs:
Dealing With Ruh Rohs With Design Patterns

-
Encapsulate complex data behind a simple interface - facade pattern.
- Structuring a system into subsystems helps reduce complexity.
Facade Pattern:
- Page Access example of using an action as a facade to prepare data for component tree
-
Rematch selectors allow components to access data regardless of position in hierarchy
- When an action facade stores data in a normalized state, selectors can act as facades to perform complex data manipulations with performance implications independent of view and without impacting sibling or cousins
- The action and selector facades allow us to expose data safely to only the ui pieces that need them
- Page Access example
Facade PAttern Examples:

-
Provide a single interface for incompatible modules
- Can provide reusability to concrete specific or rigid modules
Adapter Pattern:
-
Expose data safely, only where it is needed
-
Predicting actions impacting siblings and cousins by using function composition to wire up groups of components in two different ways - selectors that cleanly grab data as it is stored and transport it to the component it needs used inside an adapter selector that transforms the data for the interface needed
- Separating business and view logic. Get data manipulation out of components! This means that every render you don't have to worry about the performance implications of data manipulation along with presentation issues! Design the component api that you wish the data was presented in, then design an adapter that converts the data to that api!
Adapter Examples:
SuperHeroic model view whatever
A Brief
musical Digression
- You can organize pitches on a keyboard in time
- You can organize pitches on a keyboard in space
- You can do this with all available pitches on the keyboard
- You can do this with a subset of pitches
everything all at once can be confusing
- When you organize pitches around a subset, we call this modality
- "Modern", "Western" music has 7 modes.
- They are named with a super common, modern western terminology
- Ionian, Dorian, Phrygian, Lydian, Myxolydian, Aeolian, Locrian
some Big Stretches
- Mediaeval Christian Scholars started geeking out on greek
- Shoehorned stuff they read about on top of their own systems
- Jazz musicians decided, sure, why the hell not use it too.
Model view Controller
Model
Pure data representation of View.
View
Visual Representation of Model.
Controller
Coordinates, Organizes and lays out Views.
Model view Presenter
Model
Passive data representation of the UI.
Presenter
Retrieves data from the Model and formats it for the View, acts upon events from the View.
View
Passive visual representation of the data, relays events to Presenter.
Model view ViewModel
ViewModel
View
Model
Data and business.
Instantiates appropriate model and view with data binding
Stateless Templated Markup and Styling
Model view whatever
Whatever
View
Model
Data and business.
$scope?
Stateless Templated Markup and Styling
Single Source of Truth and Unidirectional Data Flow
What The Heck Are Modes???
- Ionian
- Dorian
- Phrygian
- Lydian
- Myxolydian
- Aeolian
- Locrian
Miles Davis
John Coltrane


MedieVal Chants

Plato Describing The Hits Of The Day

Shared State in Uniderictional Data Flows
-
identify the core, minimal data representation of your application
-
identify where that data is used in every component
-
lift the state up to a common ancestor, or one component higher than the most common ancestor
-
if you can’t find a component that makes sense, make an arbitrary state-holding component and put it somewhere above the components that need that state.
STORE
STORE
STORE
FLUX
STORE
REDUX
Reducer
Reducer
Reducer
Context/ Provider
REdux Without The Dev Tools
React is The
View
IN
MODEL VIEW CONTROLLER
Model view Controller
Model
Pure data representation of View.
View
Visual Representation of Model.
Controller
Coordinates, Organizes and lays out Views.
Model view Presenter
Model
Passive data representation of the UI.
Presenter
Retrieves data from the Model and formats it for the View, acts upon events from the View.
View
Passive visual representation of the data, relays events to Presenter.
Model view ViewModel
ViewModel
View
Model
Data and business.
Instantiates appropriate model and view with data binding
Stateless Templated Markup and Styling
Model view whatever
Whatever
View
Model
Data and business.
$scope?
Stateless Templated Markup and Styling
SuperHeroic model view whatever
React is STILL The
View
IN
MODEL VIEW CONTROLLER
- Use state sparingly.
- Keep state in a normalized form.
- Perform data transformations through simple functions and prioritize transparency and documentation over colocation.
State Takeaways
- compose state transformation functions, instead of altering existing transformation functions in place.
- Cater data transformation to component APIs, not the other way around.
- Socialize NEVER assuming that state isn’t shared.
State Takeaways
Miles Davis
John Coltrane


Copy of Single Source Of Truth and Unidirectional Data Flow
By Ryan Moore
Copy of Single Source Of Truth and Unidirectional Data Flow
- 149

