Oculo
@sachinkmr_

Sachin Kumar
"Every picture tells a story"
Sarthak Gupta
Shubham Malik


@sarthak32478805
@malikshubham827
Team : GradientDescent
Track DoctorYou
About Us
-
Third year undergrad at NSIT, Delhi University-
B.E. in Information Technology
-
-
Independent study on Deep Learning and its applications.
Outline
-
Intro to Neural Image Captioning(NIC) -
Motivation -
Dataset -
Deep Dive into NIC -
Results -
Your Implementation -
Summary
What is Neural Image Captioning?
Can we create a system, in which feeding an image, we can generate a reasonable caption in plain english ?

Input to the system:
Output :
-
A group of teenage boys on a road jumping joyfully. -
Four boys running and jumping. -
Four kids jumping on the street with a blue car in the back. -
Four young men are running on a street and jumping for joy. -
Several young man jumping down the street.
Let's See, How we can accomplish this!
The Task
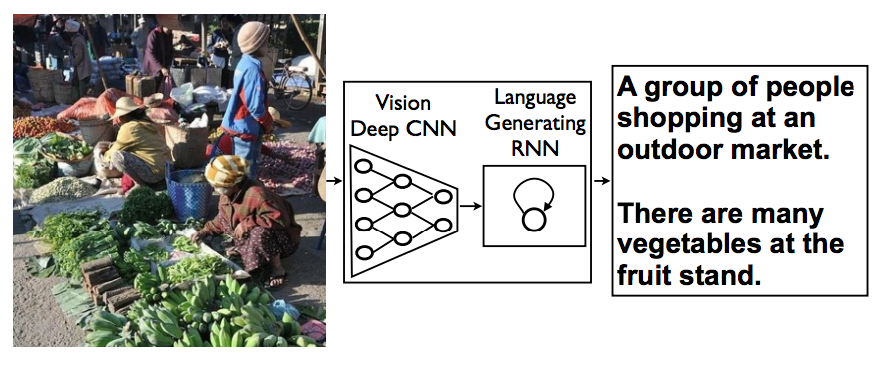
Automatically describe images with words.
Why?
-
Useful for telling stories for album/photo uploads.
-
Gives detailed understanding of an image and an ability to communicate that information via natural language.
-
It's Cool!
Dataset
-
Flickr8k-
8K Images
-
-
MS Coco-
Training Images [80K/13GB] -
Validation Images [40K/6.2GB] -
Testing Images [40K/12.4GB]
-
The Model
We will combine deep convolutional nets for image classification with recurrent networks for sequence modelling, to create a single network that generates descriptions of images.
For image classification, we will use VGG 16 layer model, popularly known as VGG16.
-
Very simple and homogeneous.
-
Better accuracy because of increased depth of the network by adding more convolutional layers.
-
Which is feasible due to the use of very small (3 × 3) convolution filters in all layers.

CNN
For sequence modelling, we use Recurrent Neural Network
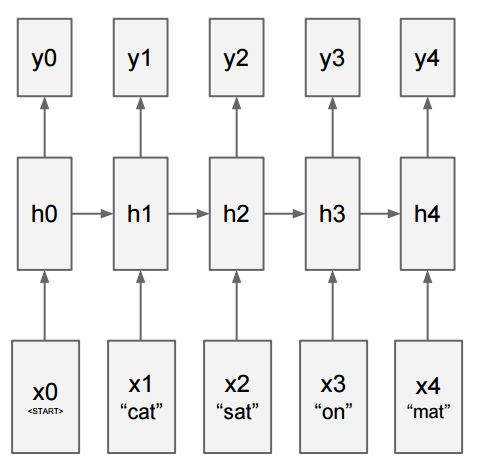
P(next word | previous words)
RNN
Merging CNN with RNN
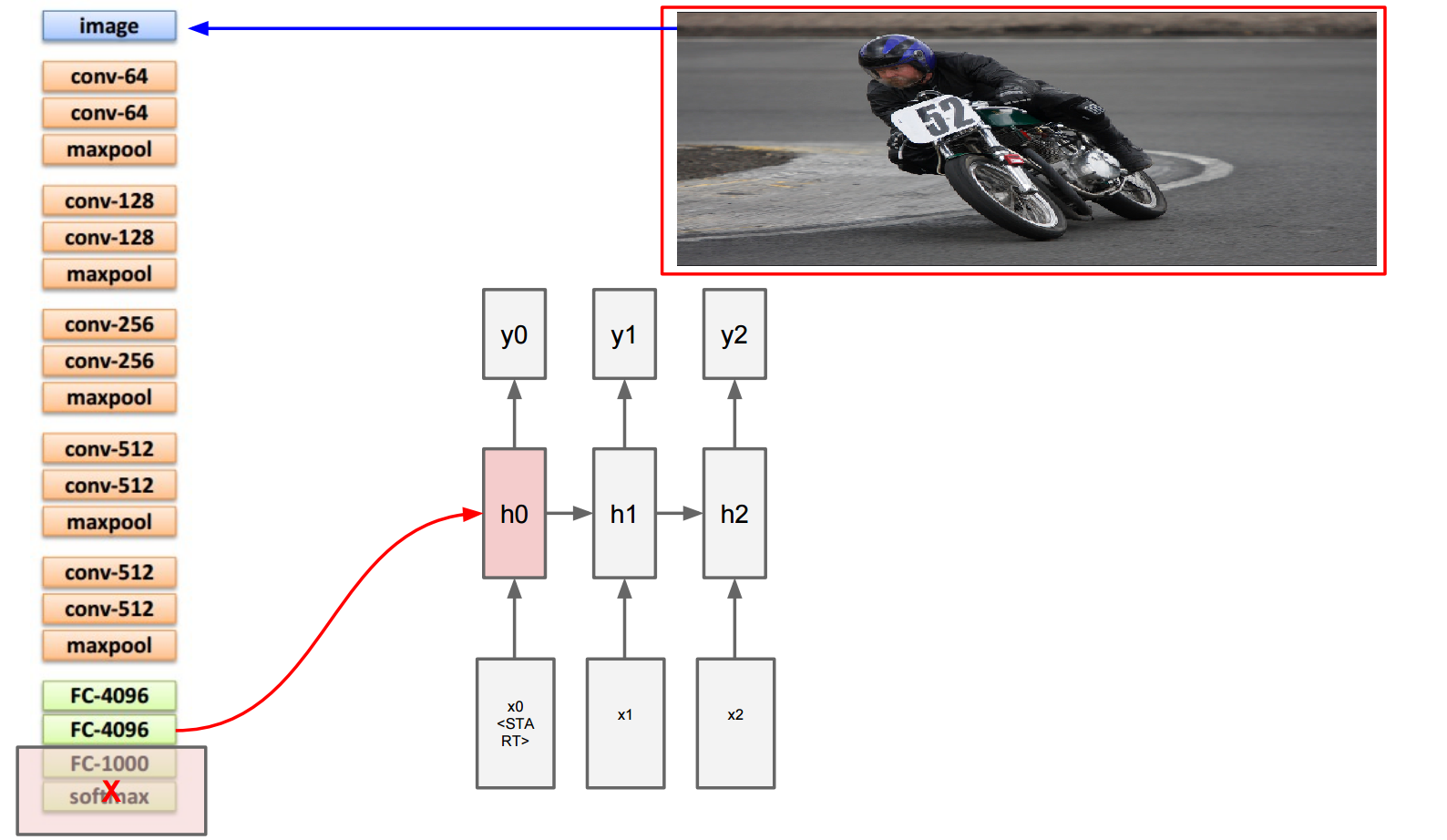
Training Example
Before:
h0 = max(0, Wxh * x0)
Now:
h0 = max(0, Wxh * x0
+ Wih * v)
RNN vs LSTM
-
We will use a Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) net, which has shown state-of-the art performance on sequence tasks such as translation and sequence generation.
-
Also due to its ability to deal with vanishing and exploding gradients, the most common challenge in designing and training RNNs.
RNN vs LSTM (contd.)
LSTM changes the form of the equation such that:
1. More expressive multiplicative interactions rather than transforming interactions.
2. Gradients flow nicer.
3. Network can explicitly decide to reset the hidden state.
-
LSTM model trained to predict word of sentence after it has seen image as well as previous words.

-
Use BPTT (Backprop through time) to train.
-
Loss function used : negative log likelihood as usual.
Model Summary

LSTM model combined with a CNN image embedder and word embeddings. The unrolled connections between the LSTM memories are in blue and they correspond to the recurrent connections. All LSTMs share the same parameters.
How to generate a sentence ?
1. Sampling from Distribution:
We just sample the first word according to probability(p1), then provide the corresponding embedding as input and sample p2, continuing like this until we sample the special end-of-sentence token or some maximum length.
Why the argmax approach might not work ?
-
We are assuming that the best output is always that with highest probability, which is not a valid assumption.
-
It might happen, a better sentence would have been the one that starts with the word that had the 2nd highest probability when we got the output in the first time step of the decoder above.
2. Beam Search:
-
Rather than just considering the highest probable word. -
We iteratively, consider top k best words as input at time t and and get all the prefixes of length 2. So, total k*VocabSize sequences are generated. -
We keep only the resulting top k words. -
The process continues till the end.
Our Web Service

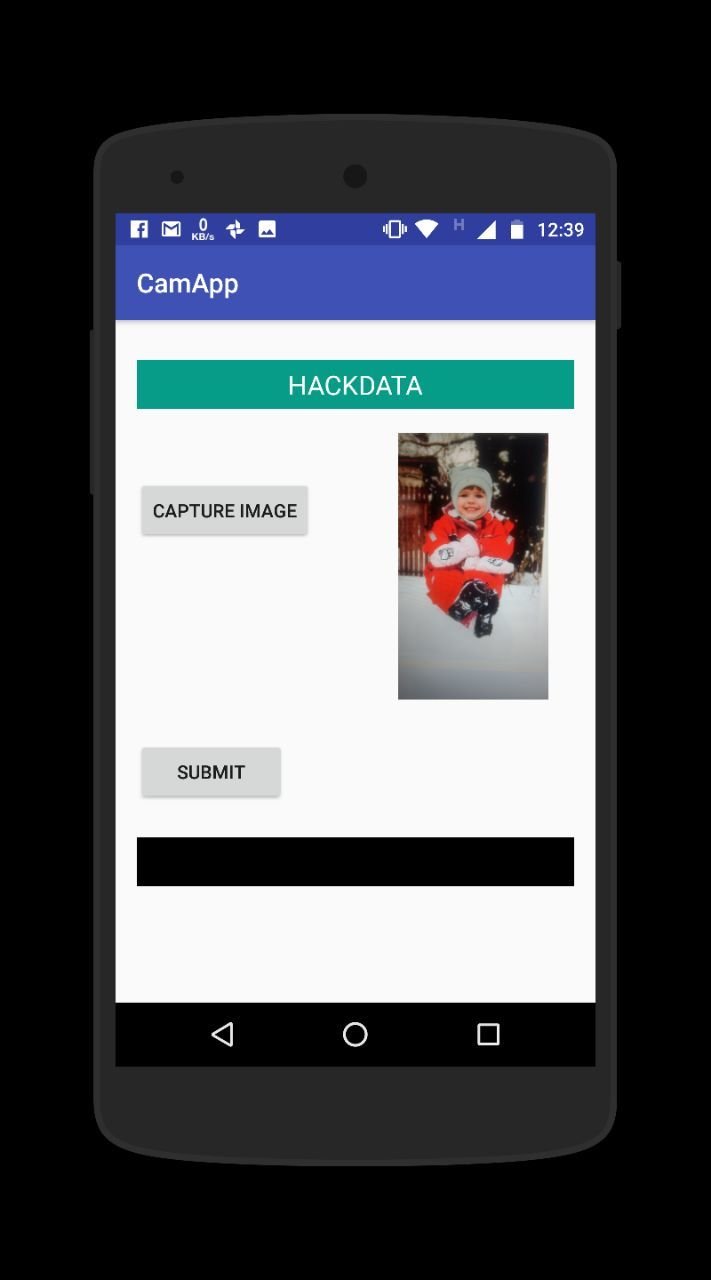
Our Android App
Results
After intial few epochs:

Argmax Search : A boy in in in in in a shirt shirt the the the wall .
Beam Search with k=3 : A boy in in in in in shirt shirt shirt shirt a the the wall .
Beam Search with k=5 : A boy in in in in in shirt shirt shirt shirt a wall wall .
Beam Search with k=7 : A boy in in in in in a shirt a the wall .
Results
After few more training:
Argmax Search : A large brown dog looks at at dog in black dog in in in in black dog in in in in in in in in in in in in in in in in in in in in . . Beam Search with k=3 : A large brown dog looks at the dog .
Beam Search with k=5 : A large brown dog looks at medium dog .
Beam Search with k=7 : A large brown dog looks at medium dog .

After some more training it started making some sense :
Argmax Search : A little girl in a a red coat plays in snow . Beam Search with k=3 : A little girl plays in the snow in a brown jacket and red shorts on a harness .
Beam Search with k=5 : Little girl in red coat going down a hill .
Beam Search with k=7 : Little girl in red coat going down a hill .

Code on GitHub
Summary
Neural Image Captioning (NIC), an end-to-end neural network system that can automatically view an image and generate a reasonable description in plain English. We can say, NIC works as a Machine Translation problem, where


Source : Pixels
Target : English
Thank you!
Team : GradientDescent
Oculo
By Sachin Kumar
Oculo
For HackData 2k17, Held at Shiv Nadar University (SNU)
- 1,255



