EFFECTS OF GLAUCOMA
ON PATH INTEGRATION
IN VIRTUAL REALITY
Safa Andac
Yaxin Hu
Outline
Glaucoma
Damage to the optic nerve
- Visual Loss
- Progressive
https://glaucoma.org.au/
BaCKGROUND
Path Integration
Ability to keep track of a position
- Vestibular system (Wallace et al., 2002)
- Sensory flow (optic-flow) (Wylie et al., 1999)
- Motor efference (Whishaw and Wallace, 2003)
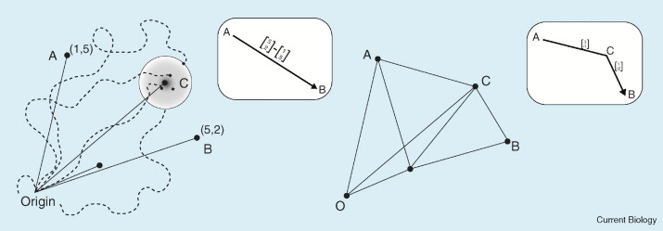
Collett, T. S., & Graham, P. (2004)
Daga et al. (2017) -Wayfinding and Glaucoma
BaCKGROUND
Optic Flow
The pattern of apparent motion of objects
- Relative motion between an observer and a scene
https://www.bi.mpg.de/opticflow

BaCKGROUND
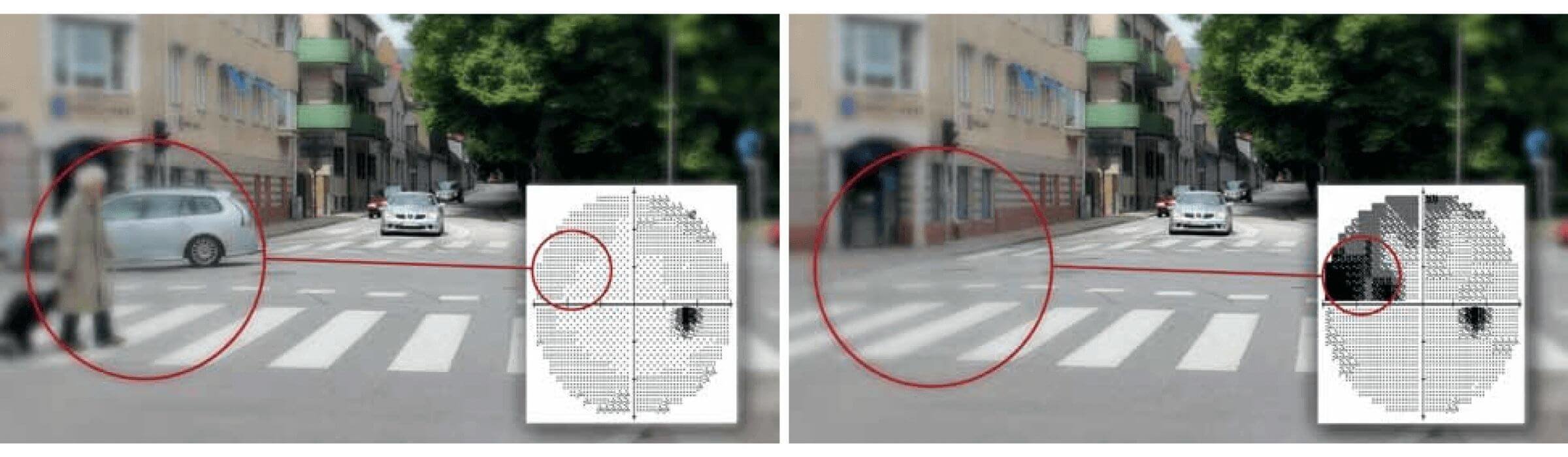
- 29 participants (15 control, 14 glaucoma)
- 12 different triangular paths (3 angle x 4 path length)
- Environment with/out optic flow (w OF // w/o OF)
- 48 trials in total

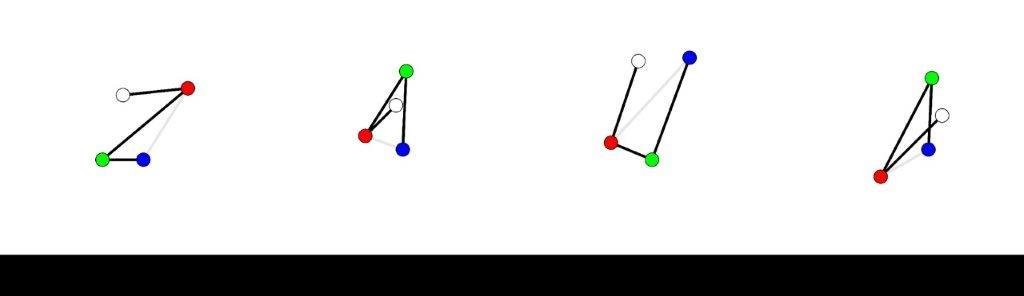

METHODS


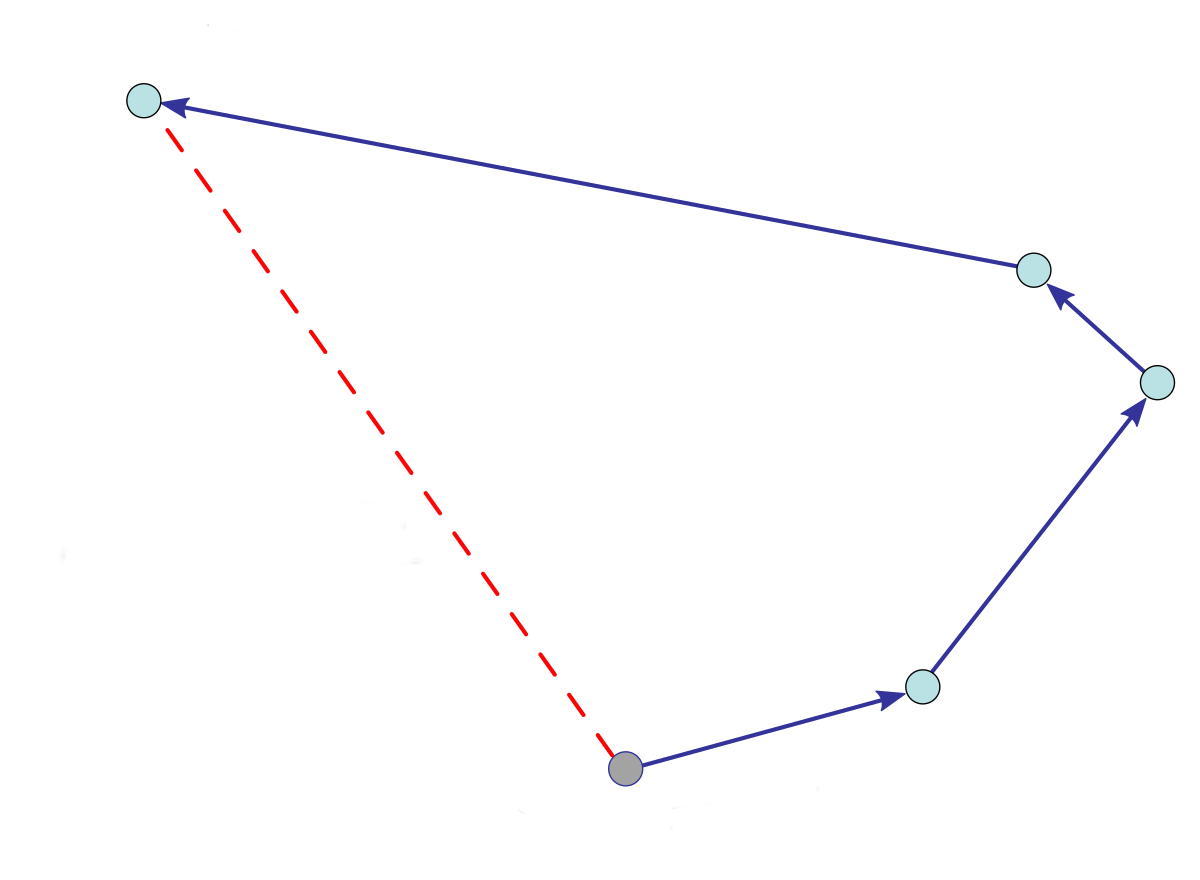
- Start from Point 0
- Move to Point 1
- Remember the position
- Move to Point 2 (second waypoint)
- Move to Point 3 (final waypoint)
- Point the position to be remembered
1
2
3
0
METHODS
DATASET
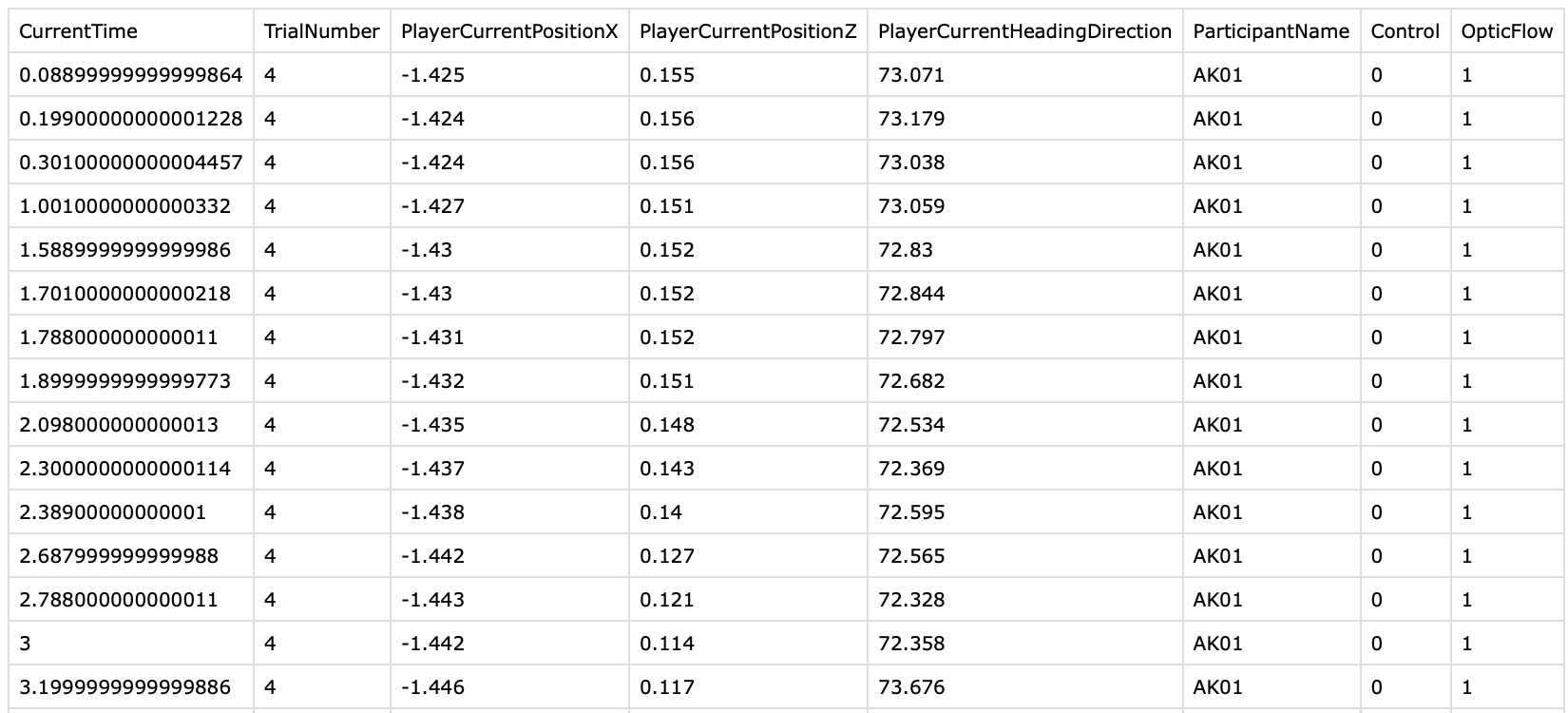
Time Series Data
- Position of the Participant
- Heading Direction
- Time
- Group
- Optic Flow
DATASET
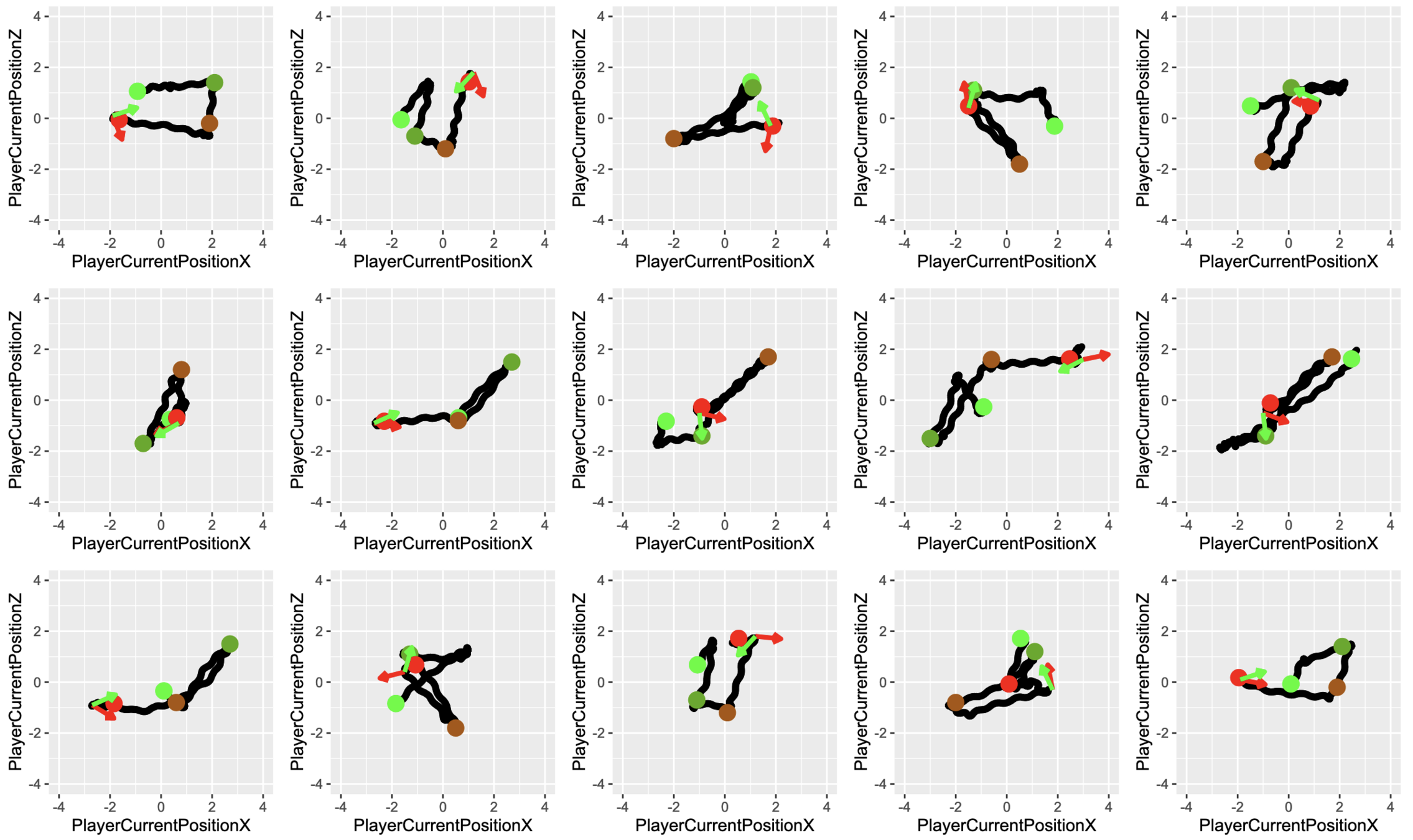
Glaucoma
Control
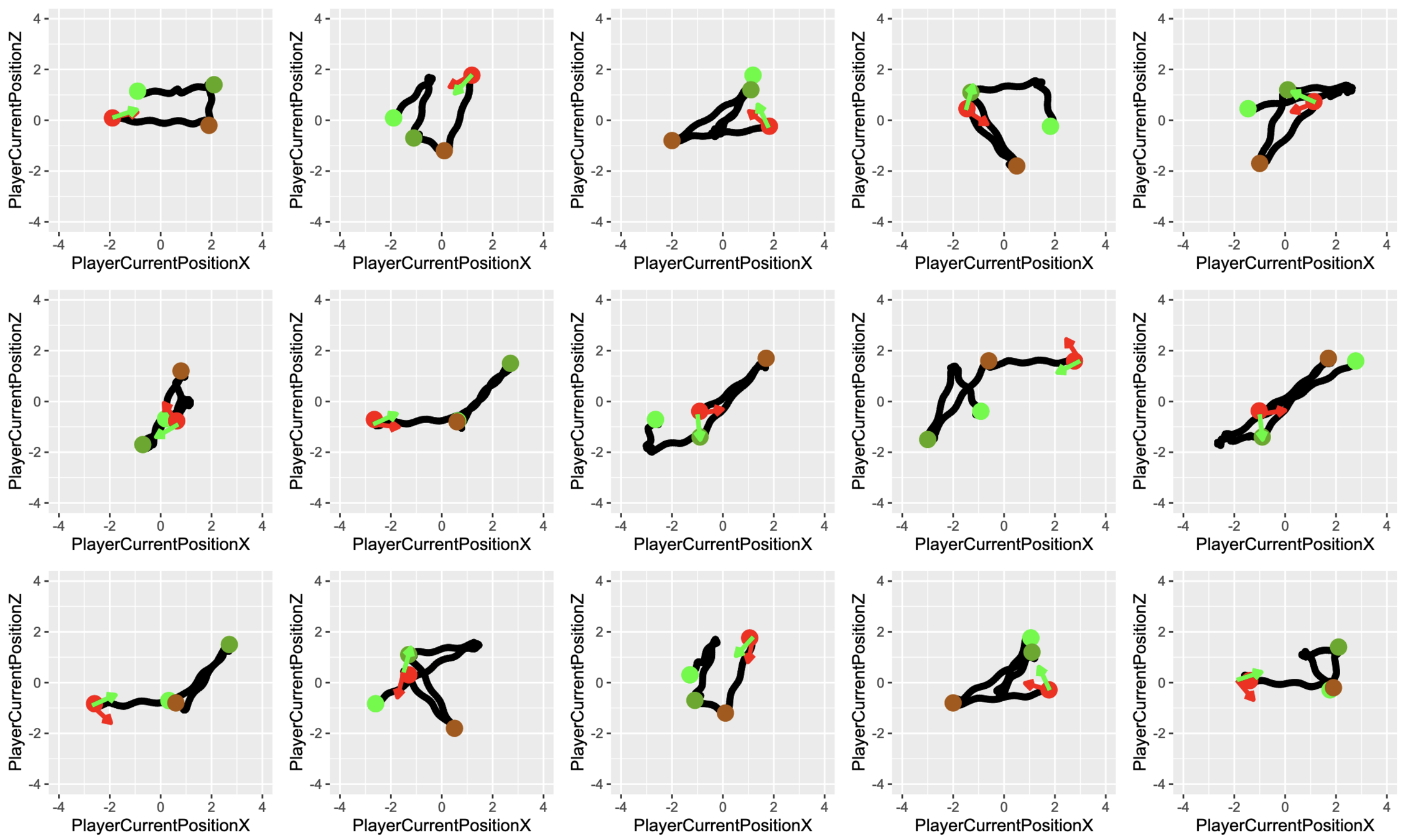
DATASET
Model Concerns
- Time to complete one trajectory is different across participants.
- Trajectory is similar but the way participants walk is different.
- Different trajectories
- Each trajectory consists of 4 trials for each participant
- Classification of participants using navigation data
PRELIMINARY RESULTS
200 data points sampled from each trials
1392 trials in total (29 participants * 48 trials)
Model : ResNet 18
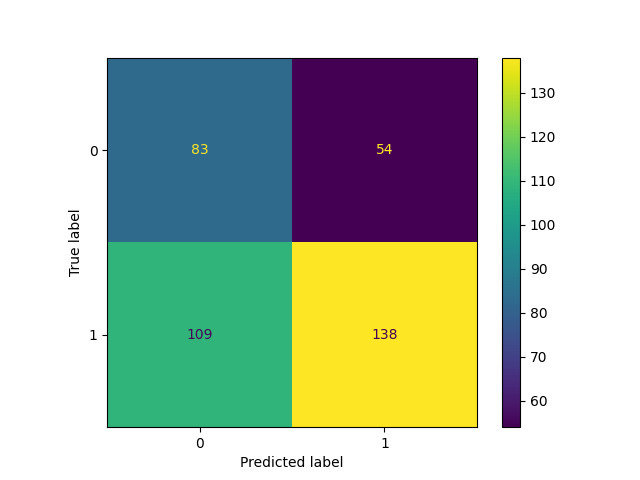
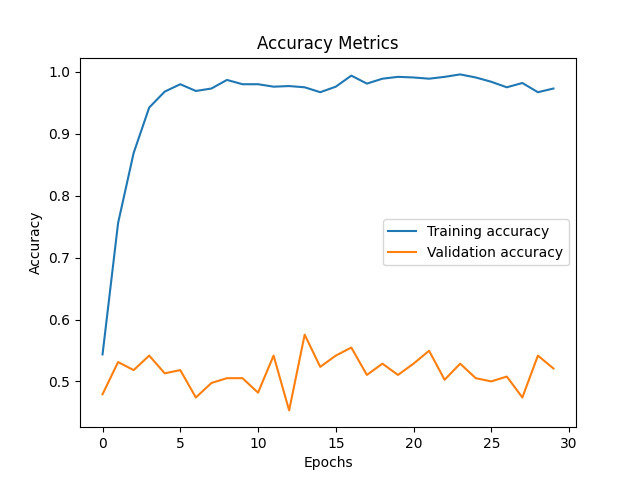
Predictors : Location X, Location Y and Heading Direction
dataset-presentation
By Safa Andac
dataset-presentation
- 123



