Effects of Glaucoma
on path integration
in virtual reality
M.A. Safa Andac
M.Sc. Francie Kramer
Advisor: Prof. Dr. Michael Hoffmann
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No 955590.


Outline


Glaucoma
Damage to the optic nerve
- Visual Loss
- Progressive
https://glaucoma.org.au/
BaCKGROUND


Path Integration
Ability to keep track of a position
- Vestibular system (Wallace et al., 2002)
- Sensory flow (optic-flow) (Wylie et al., 1999)
- Motor efference (Whishaw and Wallace, 2003)
Collett, T. S., & Graham, P. (2004)
Daga et al. (2017) -Wayfinding and Glaucoma
BaCKGROUND


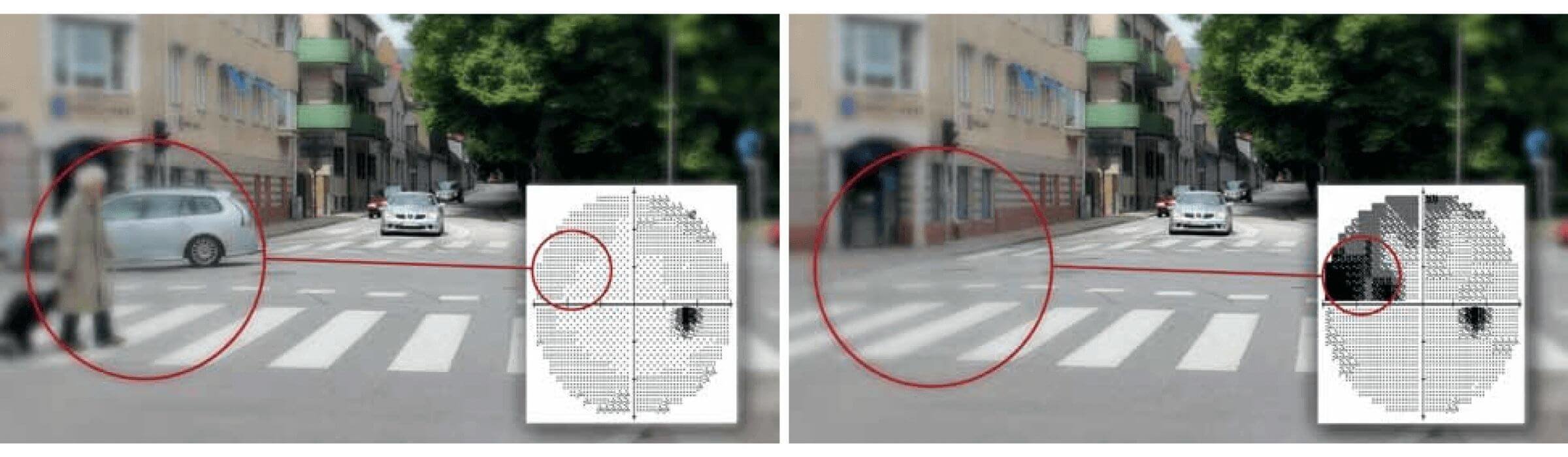
Optic Flow
The pattern of apparent motion of objects
- Relative motion between an observer and a scene
https://www.bi.mpg.de/opticflow

BaCKGROUND


Virtual Reality
Safer

Manipulable

Immersive

BaCKGROUND


- [H1] Glaucoma patients are slower than control group in path following.
- [H2] Participants move slower in an environment without optic flow than the one with optic flow.
- [H3] The effect of optic flow increases the performance of control group better than glaucoma group on path integration task.
HYPOTHESES


- 29 participants (15 control, 14 glaucoma)
- 12 different triangular paths (3 angle x 4 path length)
- Environment with/out optic flow (w OF // w/o OF)
- 48 trials in total


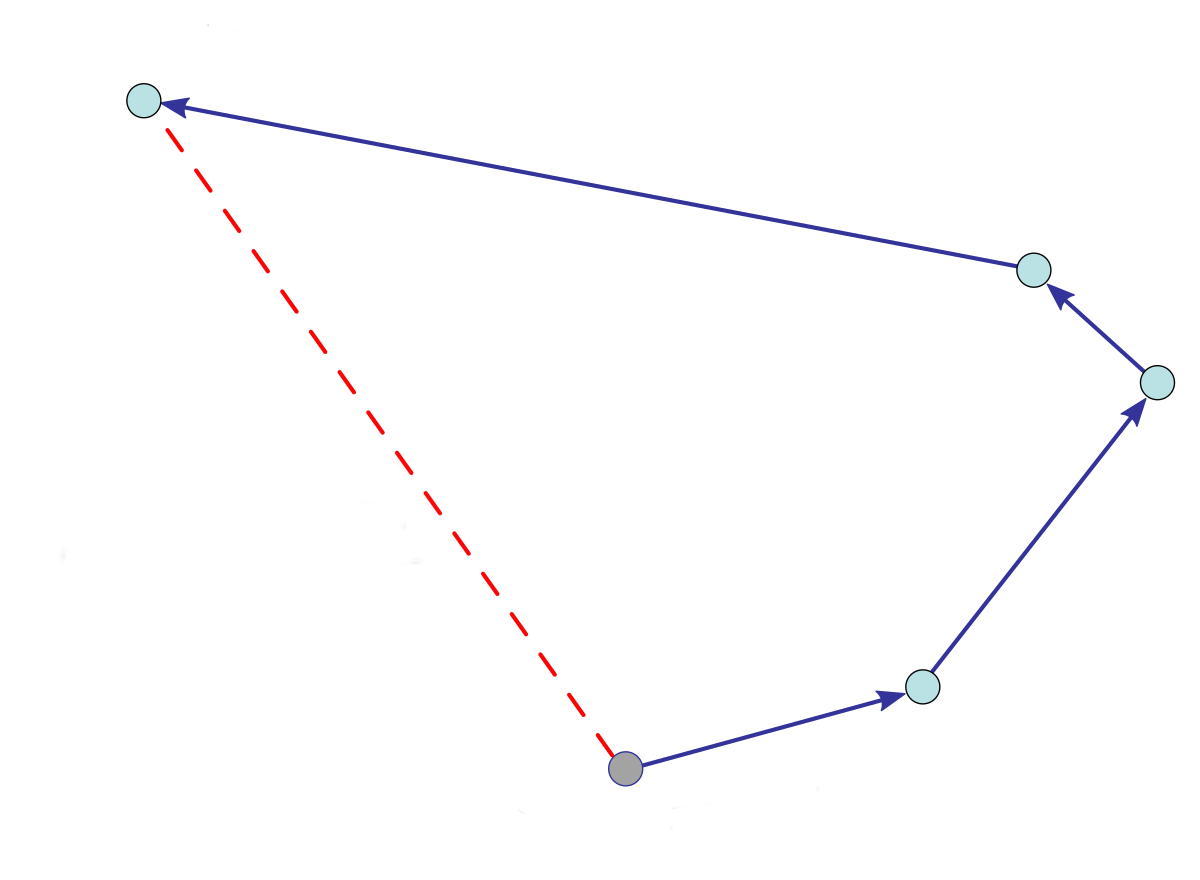
METHODS


- Start from Point 0
- Move to Point 1
- Remember the position
- Move to Point 2 (second waypoint)
- Move to Point 3 (final waypoint)
- Point the position to be remembered
1
2
3
0
Measures
- Travel Time
- Pointing Task Duration
- Error distance btw expected location - response location
- Angle Error
METHODS
Statistics
Mixed-ANOVA with factors
- Group
- Optic Flow
- Group x Optic Flow


RESULTS
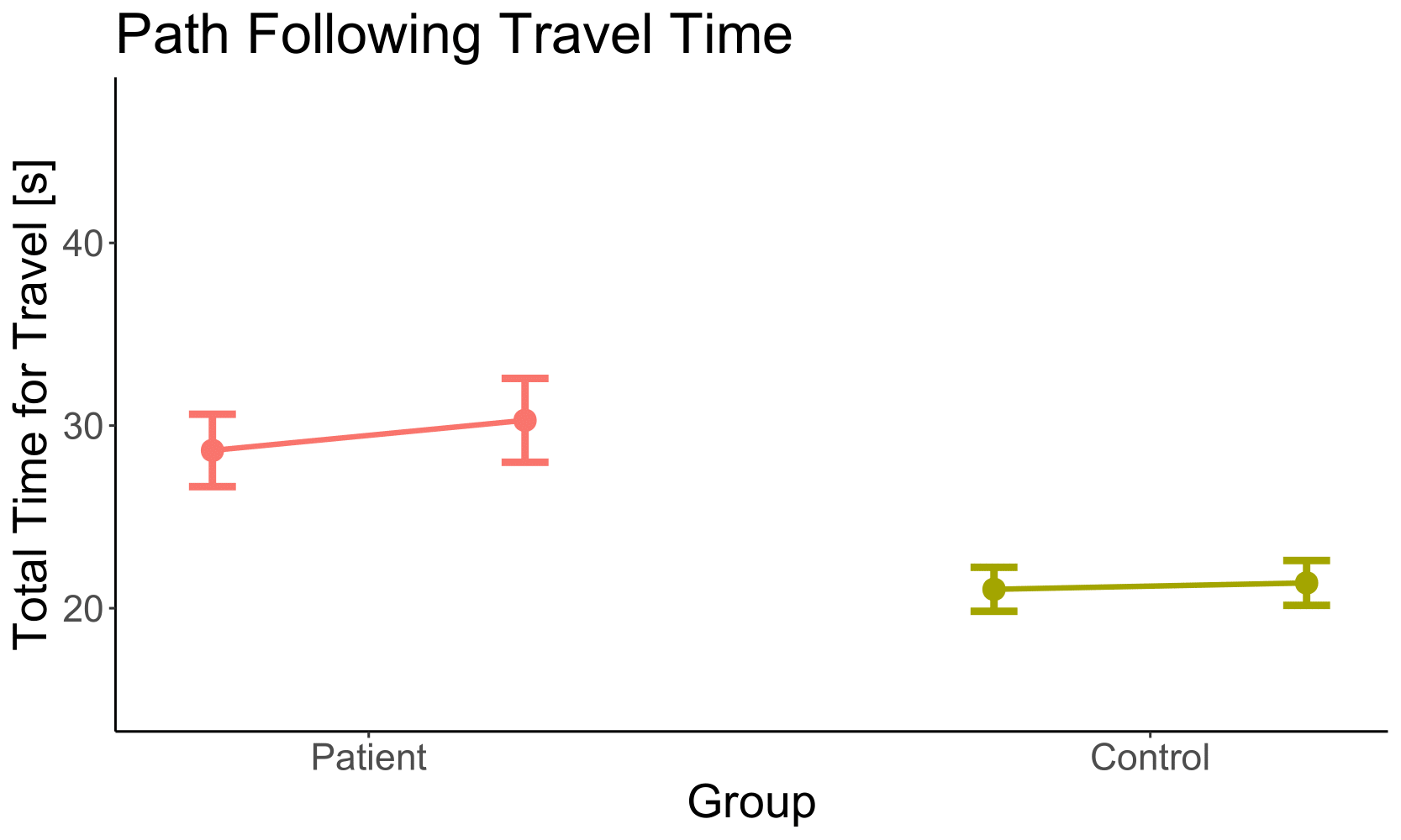
w/o OF
OF
w/o OF
OF
| Factor | p |
|---|---|
| Group | < 0.01 |
| Optic Flow | 0.03 |
| Group x Optic Flow | 0.14 |


RESULTS
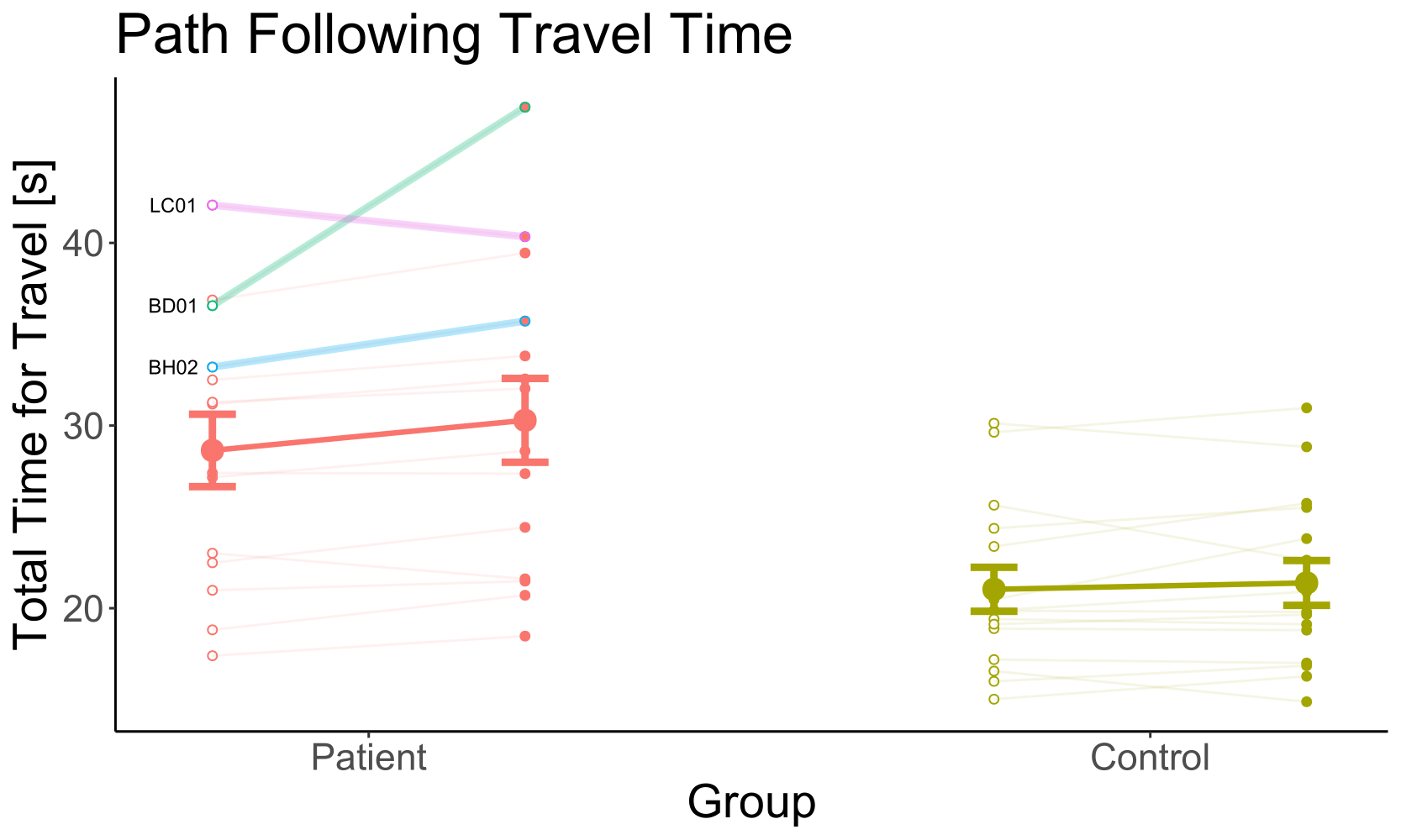
w/o OF
OF
w/o OF
OF
| Factor | p |
|---|---|
| Group | < 0.01 |
| Optic Flow | 0.03 |
| Group x Optic Flow | 0.14 |


| Factor | p |
|---|---|
| Group | 0.02 |
| Optic Flow | < 0.01 |
| Group x Optic Flow | 0.58 |
RESULTS
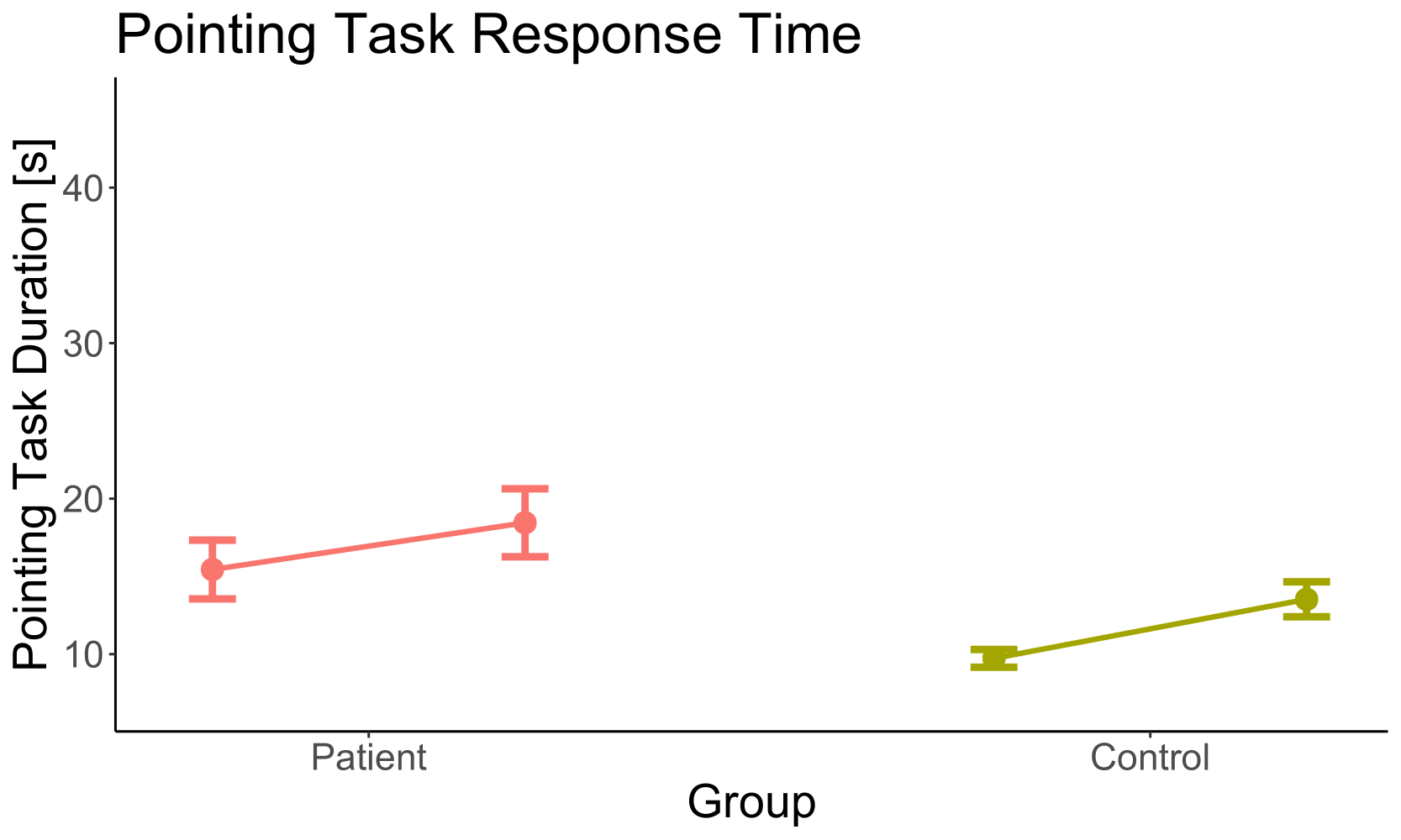
w/o OF
OF
w/o OF
OF


RESULTS
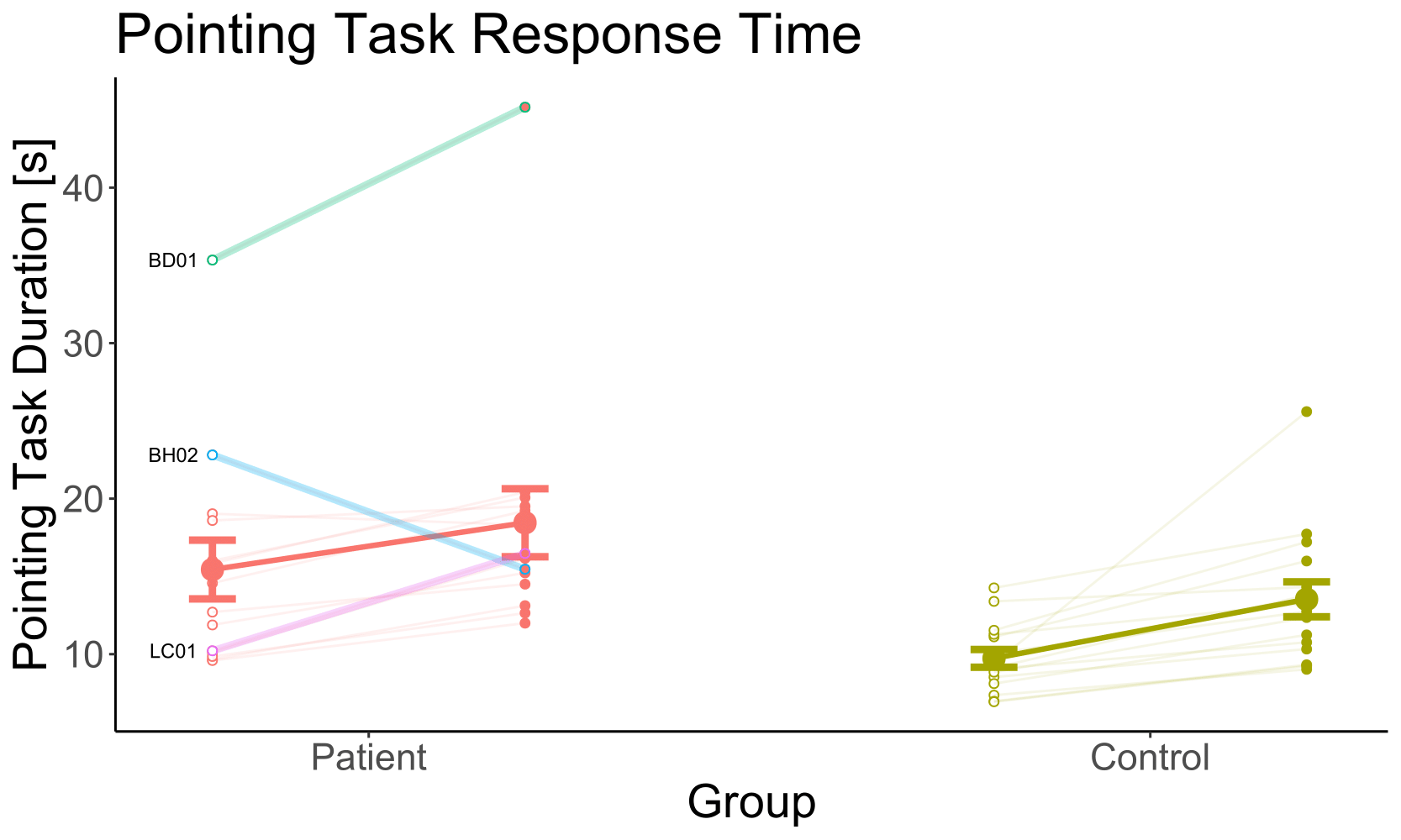
w/o OF
OF
w/o OF
OF
| Factor | p |
|---|---|
| Group | 0.02 |
| Optic Flow | < 0.01 |
| Group x Optic Flow | 0.58 |


| Factor | p |
|---|---|
| Group | 0.19 |
| Optic Flow | 0.02 |
| Group x Optic Flow | 0.04 |
RESULTS
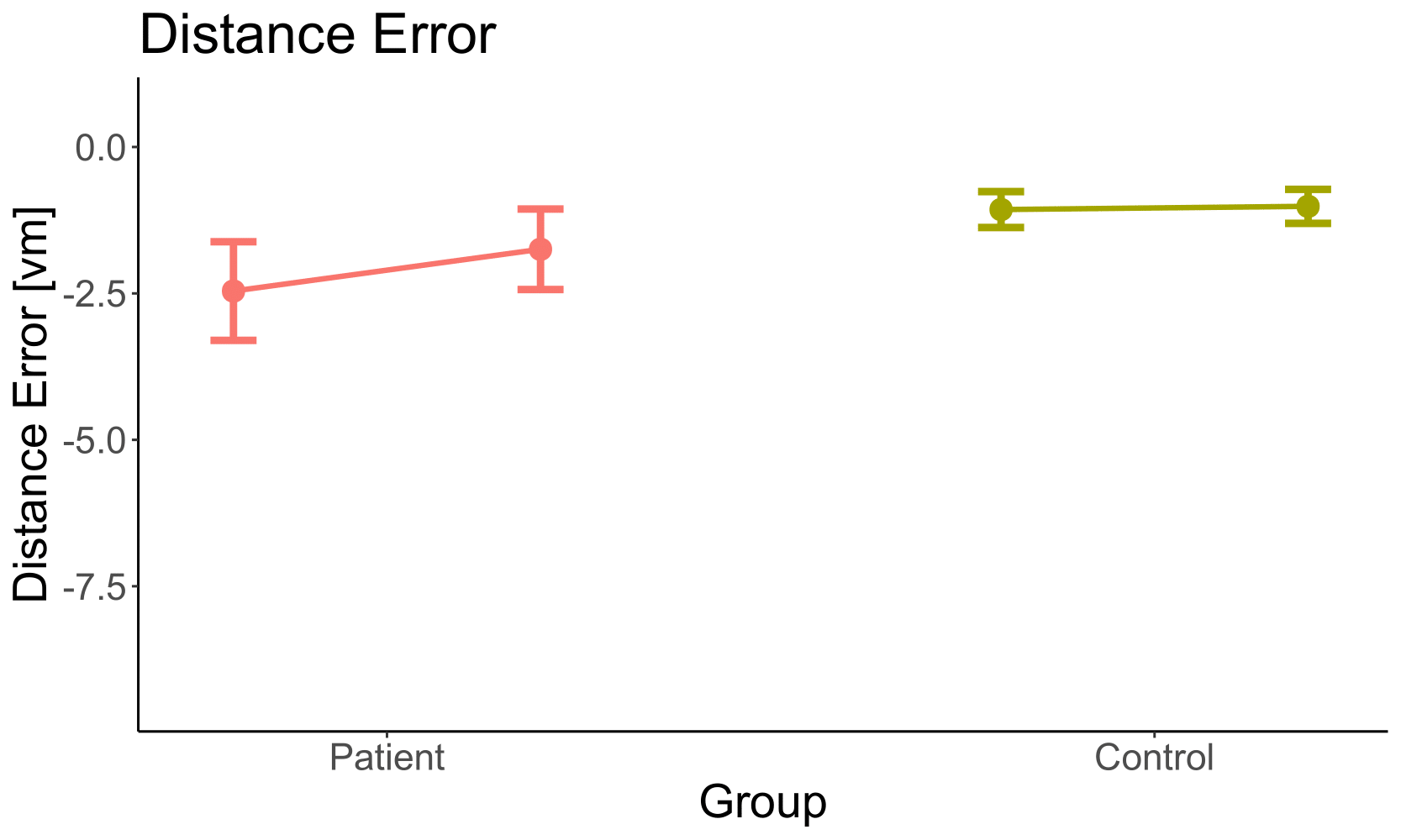
w/o OF
OF
w/o OF
OF
Undershoot
Overshoot


RESULTS
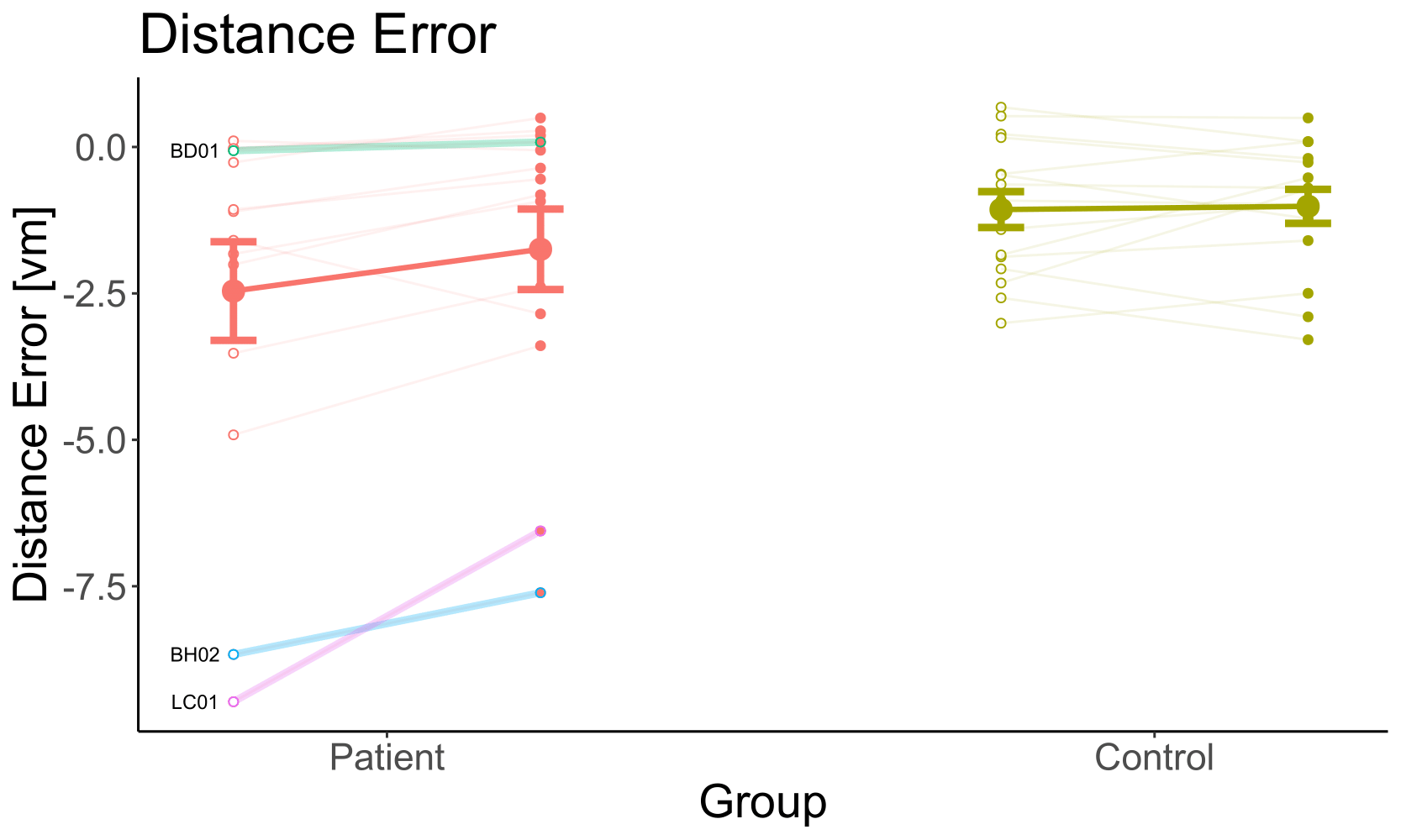
w/o OF
OF
w/o OF
OF
Undershoot
Overshoot
| Factor | p |
|---|---|
| Group | 0.19 |
| Optic Flow | 0.02 |
| Group x Optic Flow | 0.04 |


| Factor | p |
|---|---|
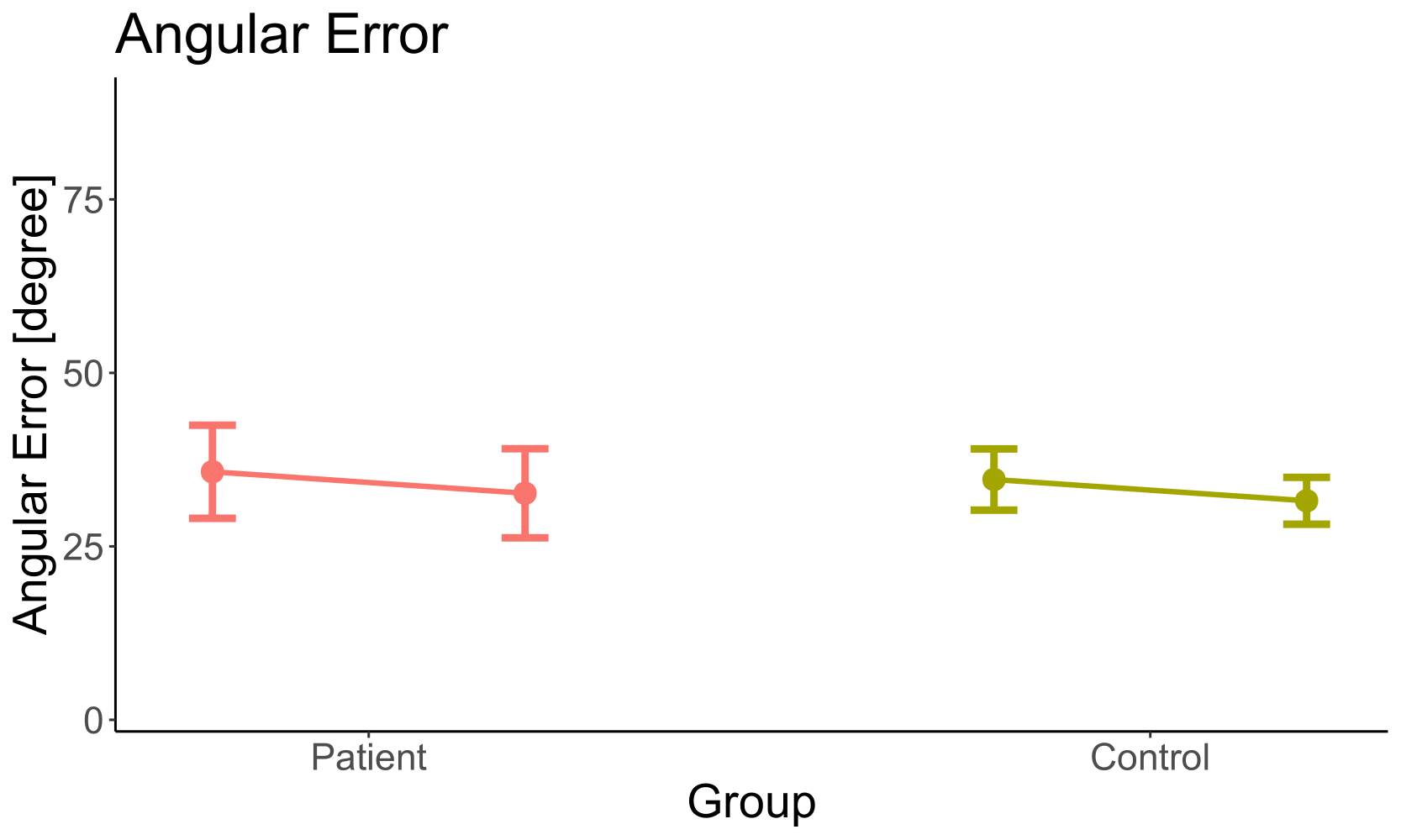
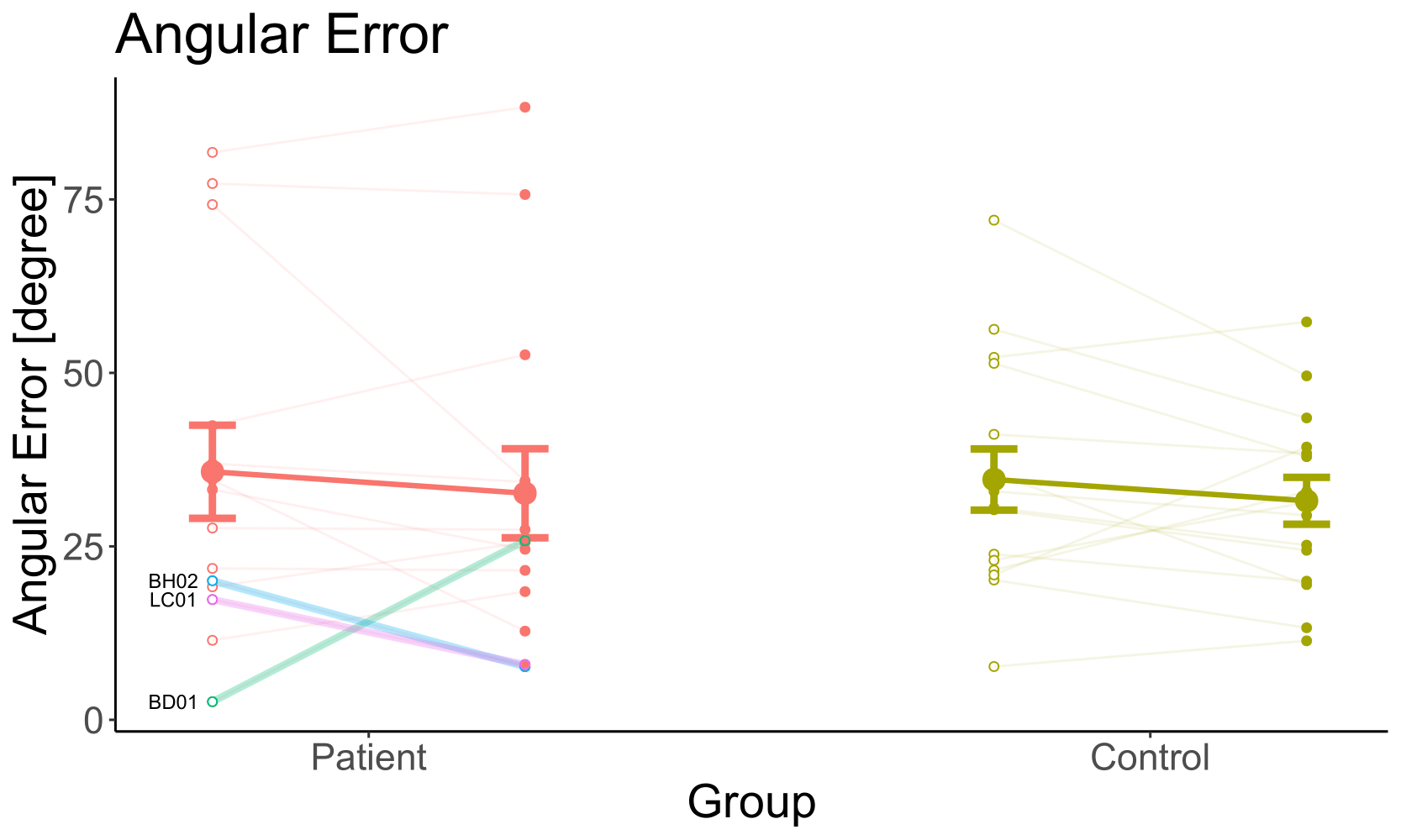
| Group | 0.88 |
| Optic Flow | 0.22 |
| Group x Optic Flow | 0.99 |
RESULTS
w/o OF
OF
w/o OF
OF
Undershoot
Overshoot


RESULTS
w/o OF
OF
w/o OF
OF
Undershoot
Overshoot
| Factor | p |
|---|---|
| Group | 0.88 |
| Optic Flow | 0.22 |
| Group x Optic Flow | 0.99 |


- [H1] Glaucoma patients are slower than control group in path following.
- [H2] Participants move slower in an environment without optic flow than the one with optic flow.
- [H3] The effect of optic flow increases the performance of control group better than glaucoma group on path integration task.
SUMMARY


- Insecurity in glaucoma patients
- Accuracy improvement in glaucoma patients in the environment with optic flow than control group
- Ceiling effect on control group, improvement in glaucoma
- No effect on angle error
- Effect of severity of the visual loss on performance
DISCUSSIOn


- Equiluminant Environment / Glaring Effect
- Broader Range Cohort
- Time Limit for Pointing Task
- Different Paths
OUTLOOK


ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Wolbers Lab
- Thomas Wolbers
- Vladislava Segen
- Matthieu Bernard
VPL
- Khaldoon Al-Nosairy
- Gokulraj Prabhakaran
THANKS!
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No 955590.


VR-Presentation
By Safa Andac
VR-Presentation
- 144



