Intro to JavaScript
Java script
Brendan Eich
JavaScript was invented by Brendan Eich in 1995. It was developed for Netscape 2, and became the ECMA-262 standard in 1997. After Netscape handed JavaScript over to ECMA, the Mozilla foundation continued to develop JavaScript for the Firefox browser.
What is Javascript
- JavaScript is a lightweight programming language that web developers commonly use to create more dynamic interactions when developing web pages, applications, servers, and or even games.
- Developers generally use JavaScript alongside HTML and CSS The scripting language works well with CSS in formatting HTML elements. However, JavaScript still maintains user interaction, something that CSS cannot do by itself.
What makes JavaScript unique?
There are at least three great things about JavaScript:
- Full integration with HTML/CSS.
- Simple things are done simply.
- Supported by all major browsers and enabled by default.
Today, JavaScript can execute not only in the browser, but also on the server, or actually on any device that has a special program called the JavaScript engine.
The browser has an embedded engine sometimes called a “JavaScript virtual machine”.
Different engines have different “codenames”. For example:
- V8 – in Chrome, Opera and Edge.
- SpiderMonkey – in Firefox.
- …There are other codenames like “Chakra” for IE, “JavaScriptCore”, “Nitro” and “SquirrelFish” for Safari, etc.
Javascript used for
Front-end (Client side)
- React Js
- Angular
- Vue Js
- React-native
Back-end (Server-side)
- Node js
The “script” tag
JavaScript programs can be inserted almost anywhere into an HTML document using the <script> tag
<script> alert( 'Hello, world!' ); </script>
We can write 2 types of Js
- Internal Js
- External Js
Naming convetions
- Snake case - python
- ex: user_name
- Camel case - Js
- ex : userName
- Pascal case - Java
- ex: UserName
- Kebab case
- CSS, JS
Browser Interaction: alert, prompt, confirm
As we’ll be using the browser as our demo environment, let’s see a couple of functions to interact with the user: alert, prompt and confirm.
Javascript Variables
A variable is a “named storage” for data. We can use variables to store goodies, visitors, and other data.
- var
- let
- const
We have use these variable name to initialise a variable with value.
- var name = 'Javascript'
- let city = 'Hyderabad'
- const rank = 1;
There are 8 basic data types in JavaScript.
There are 7 Primitive data types
- number
- bigint
- string
- boolean
- null
- undefined
One non-primitive data type:
-
objectfor more complex data structures.
Type conversions
1. Implicit conversion
2. Explicit conversion
We can convert data types from one data type to another data type is called to type convertion
Operators In Javascript
- Addition
+, - Subtraction
-, - Multiplication
*, - Division
/, - Remainder
%, - Exponentiation
**.
Js supports this math operators
Comparisons
- Greater/less than:
a > b,a < b. - Greater/less than or equals:
a >= b,a <= b. - Equals:
a == b, please note the double equality sign==means the equality test, while a single onea = bmeans an assignment. - Not equals: In maths the notation is
≠, but in JavaScript it’s written asa != b.
Even we can perform the string comparisons:
- There string comparison works based on its unicode value.
- Every letter has their own unicode value
Conditional branching: if, '?'
- Sometimes, we need to perform different actions based on different conditions.
- To do that, we can use the
ifstatement and the conditional operator?, that’s also called a “question mark” operator.
if(condition){console.log(true)}
if(condition){
} else{
}
if(){
}else if(){
}
'?' This is question mark is called Ternary operator works like if condition
Variables scopes
Scope determines the accessibility (visibility) of variables.
JavaScript has 3 types of scope:
- Block scope
- Function scope
- Global scope
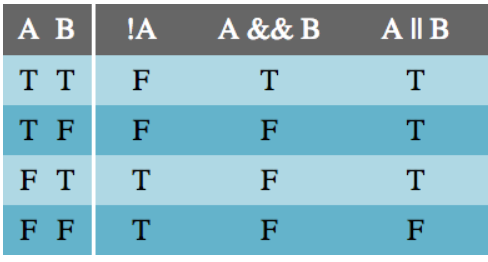
There are 3 logical operators in JavaScript:
- || (OR)
-
&&(AND) -
!(NOT),
Logical operators
Loops in Javascript
We have 3 types of loops :
- forloop
- while
- do-while
Functions
We have 3 types of function declarations in JS
- Function Declaration
- Function expressions
- Arrow functions
Objects
Object is a combination of key value pairs
Ex: const user = {
name: 'R15',
company: 'Yamaha'
}
Object Notations
For accessing the values from the Object we have 2 types of notations
- Dot notation
- Bracket notation
We have a loop for access the object key in JS. That loop is called "for..in" loop
Object methods, "this"
Object.keys()
Object.values()
Object.entries()
' this ' keywords refers to the current object to access the keys.
Constructor, operator "new"
function User(name) {
this.name = name;
this.isAdmin = false;
}
let user = new User("Jack");
We can create an objects with ' new ' keyword constructor
\n |
New line |
\r |
In Windows text files a combination of two characters \r\n represents a new break, while on non-Windows OS it’s just \n. That’s for historical reasons, most Windows software also understands \n. |
\', \", \` |
Quotes |
\\ |
Backslash |
\t |
Tab |
\b, \f, \v |
Backspace, Form Feed, Vertical Tab – mentioned for completeness, coming from old times, not used nowadays (you can forget them right now). |
Arrays
Array is collection of similar data types
Array methods
arr.push(...items)– adds items to the end,arr.pop()– extracts an item from the end,arr.shift()– extracts an item from the beginning,arr.unshift(...items)– adds items to the beginning.
Destructuring assignment
The two most used data structures in JavaScript are Object and Array.
- Objects allow us to create a single entity that stores data items by key.
- Arrays allow us to gather data items into an ordered list.
let arr = ["John", "Smith"]
let [firstName, surname] = arr;
alert(firstName);
Destructuring assignment is a special syntax that allows us to “unpack” arrays or objects into a bunch of variables, as sometimes that’s more convenient.
let options = {
title: "Menu",
width: 100,
height: 200
};
let {title, width, height} = options;
OBJECT-DESTRUCTURING
String methods
String length
String slice()
String substring()
String substr()
String replace()
String replaceAll()
String toUpperCase()
String toLowerCase()
String concat()
String trim()
String charAt()
String charCodeAt()
String split()
String startsWith()
String EndsWith()
Array methods
Adding and removing elements from an array

Array methods

Finding the elements in the array
High-order array methods

High-order array methods are accepts the call back function.
Array methods
Some other array methods
Scheduling: setTimeout and setInterval
We may decide to execute a function not right now, but at a certain time later. That’s called “scheduling a call”.
There are two methods for it:
setTimeoutallows us to run a function once after the interval of time.setIntervalallows us to run a function repeatedly, starting after the interval of time, then repeating continuously at that interval.
Many functions are provided by JavaScript host environments that allow you to schedule asynchronous actions. In other words, actions that we initiate now, but they finish later.
For instance, one such function is the setTimeout function.
new Date() Object in js
getFullYear()
getMonth()
getDate()
getDay()
getHours()
getMinutes()
getTime()
getMilliseconds()
OOPS IN JS
- ECMAScript 2015, also known as ES6, introduced JavaScript Classes.
- JavaScript Classes are templates for JavaScript Objects
Use the keyword class to create a class.
Always add a method named constructor():
class Car {
constructor(name, year) {
this.name = name;
this.year = year;
}
}
IMPORTS AND EXPORTS IN JS
JavaScript modules allow you to break up your code into separate files.
This makes it easier to maintain a code-base.
Modules are imported from external files with the import statement.
Modules also rely on type="module" in the <script> tag.
Ex: import { name, age } from "./person.js";
Intro DOM (DOCUMENT OBJECT MODEL)
- The HTML DOM can be accessed with JavaScript (and with other programming languages).
- In the DOM, all HTML elements are defined as objects.
- The programming interface is the properties and methods of each object.
- A property is a value that you can get or set (like changing the content of an HTML element).
- A method is an action you can do (like add or deleting an HTML element)
Javascript
By Saikumar Gadde
Javascript
- 20


