GIT OVERVIEW

The book

Overview
- The basics
- Workflows
- Good practices
GIT BASICS
Version Control System
Tool that allows to manage the changes of computer programs and allows multiple people to work on the same project
Primitives
Repository: A database of changes
Working copy (checkout): Personal copy of all the files
Local VCS
Centralized VCS
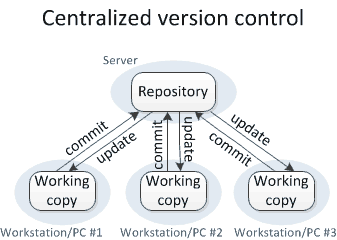
e.g. Subversion
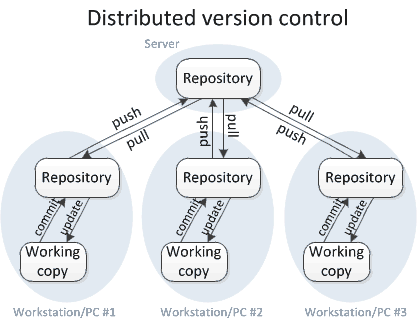
Distributed VCS
e.g. Git, Mercurial
History



2002
2005
Features
- Fast
- Simple design
- Strong support for non-linear development
- Fully distributed
- Able to handle large progects (like Linux)
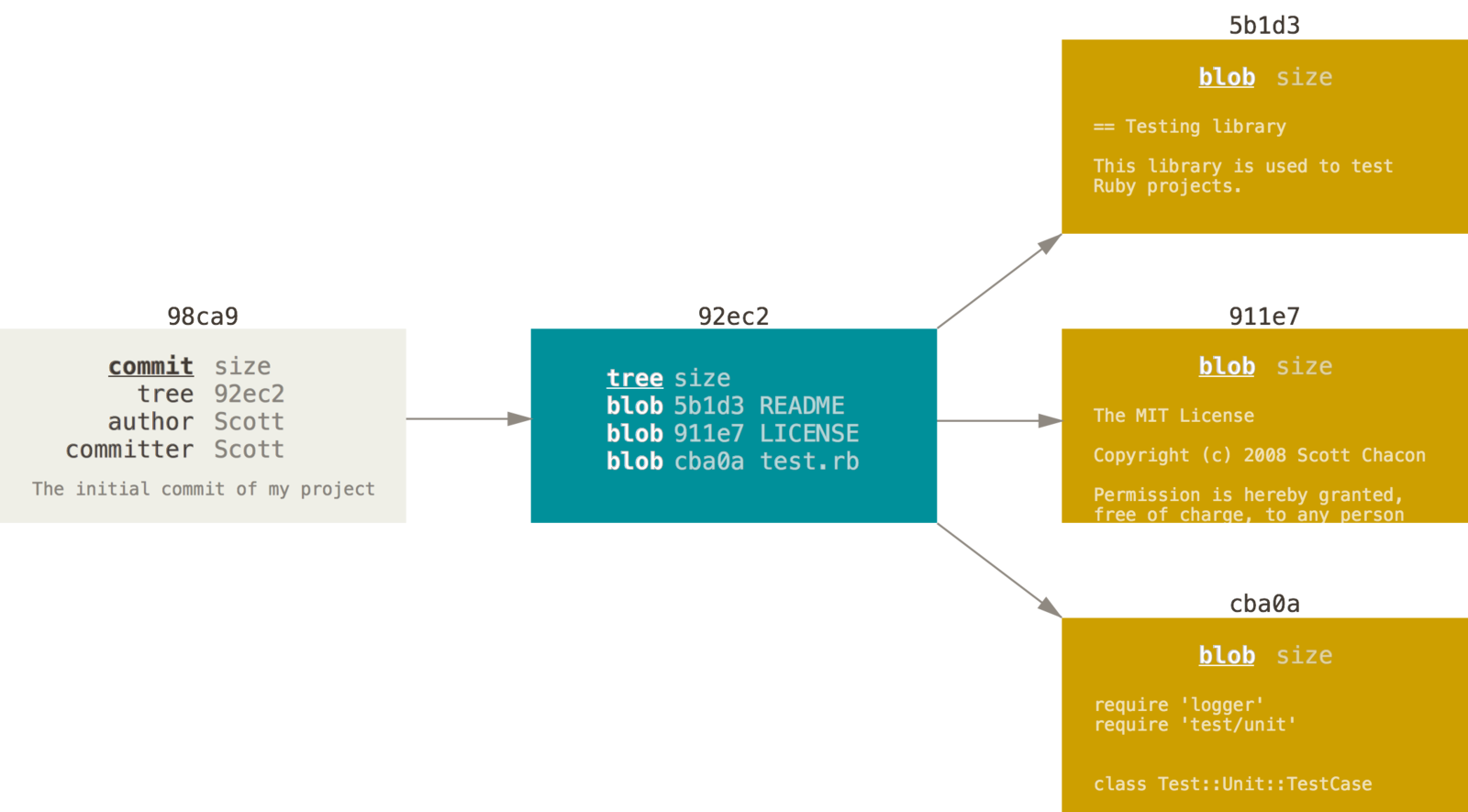
Snapshots, not differences
Almost all the operations are local
Integrity
Everything is SHA-1 checksummed
fcfb90bb310742df5a745b406bebfa718fbecea4
Git generally only adds data
The tree states
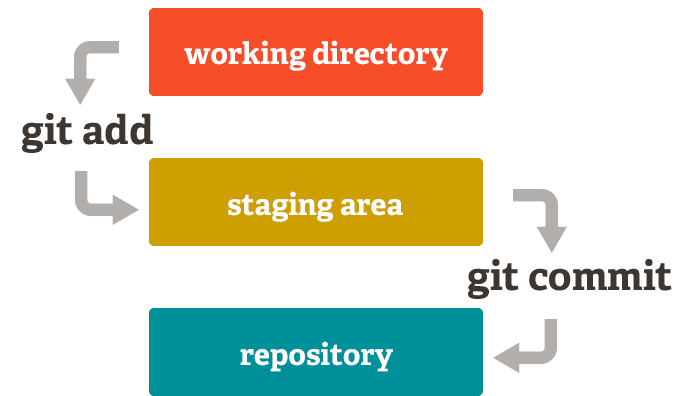
The command line
Tags
Specify a point in history as being important
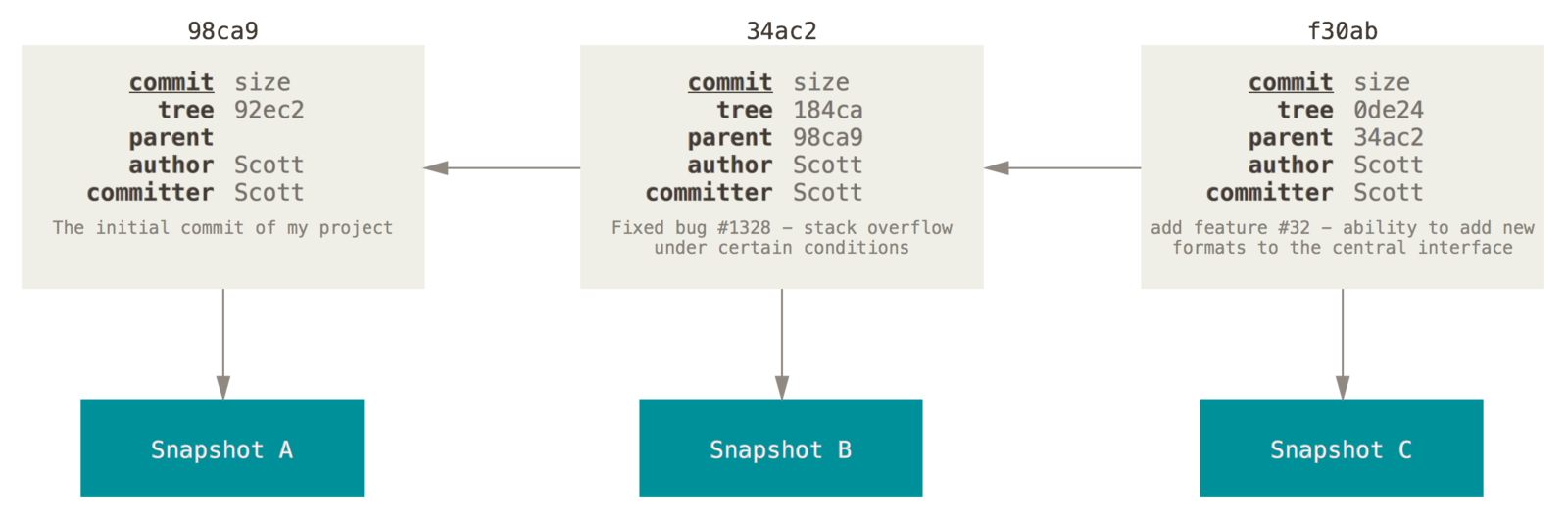
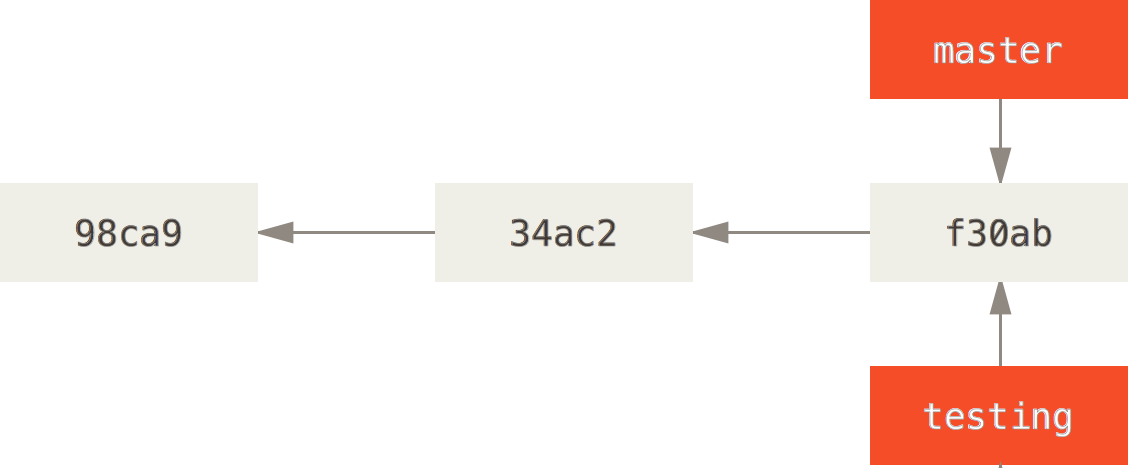
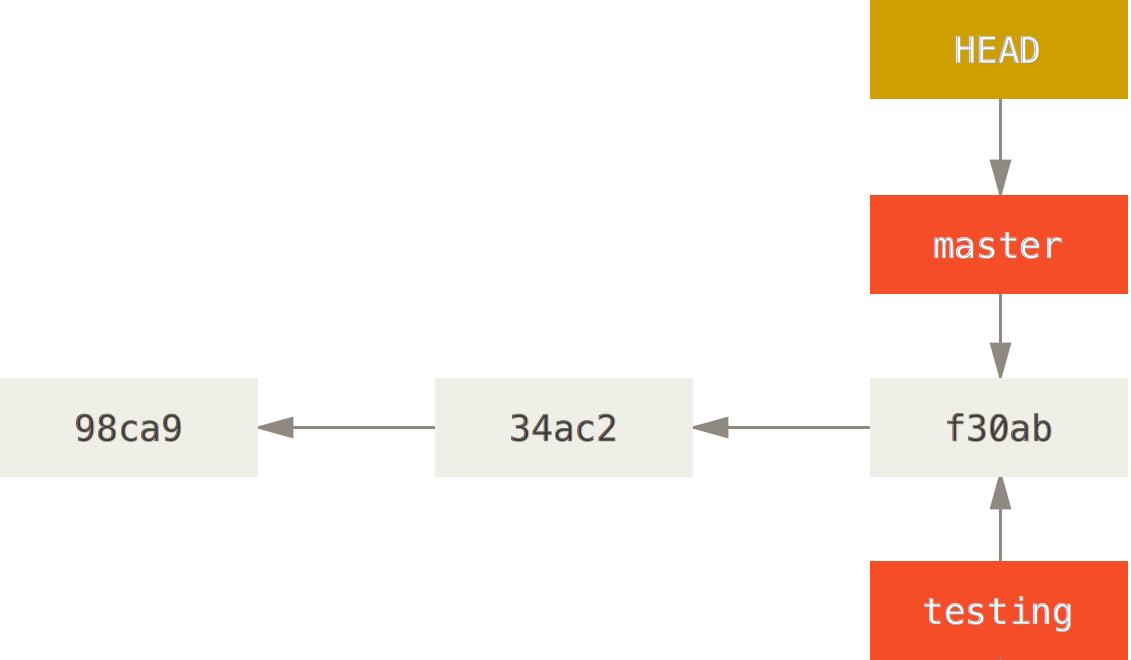
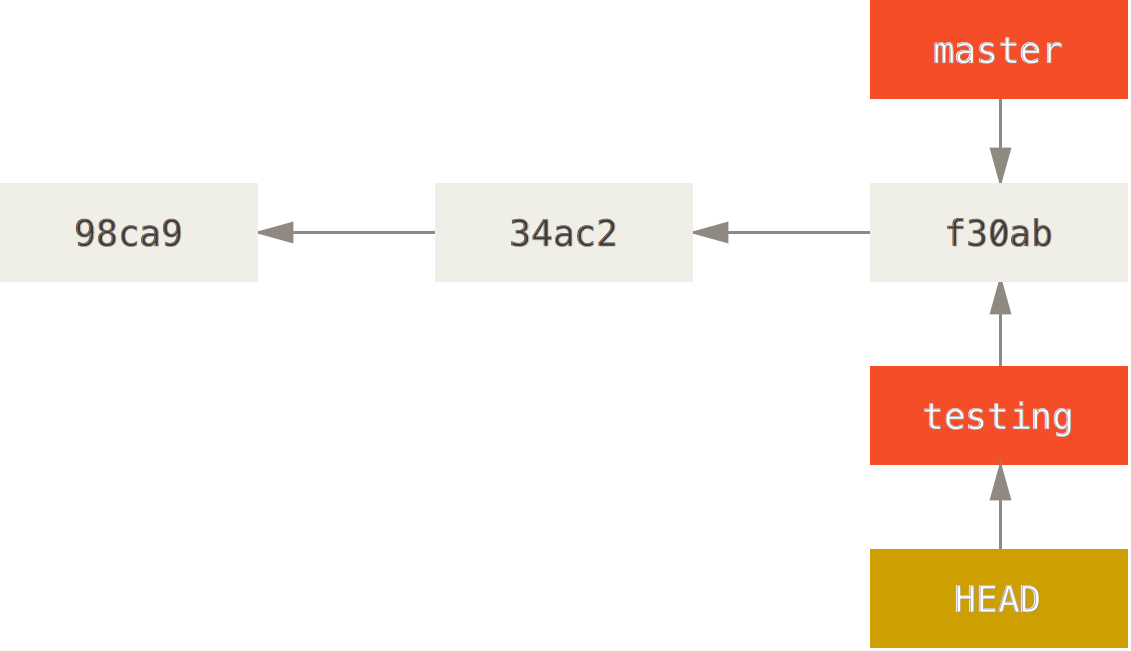
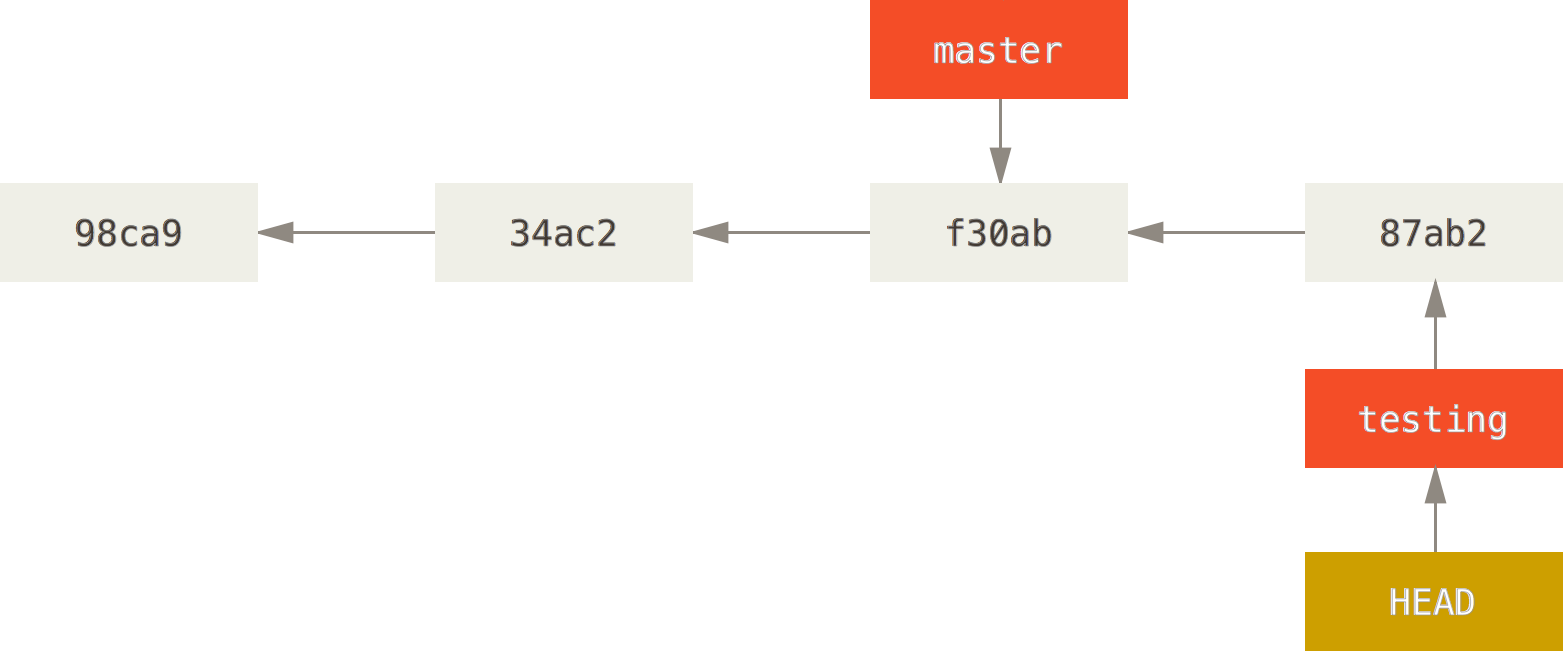
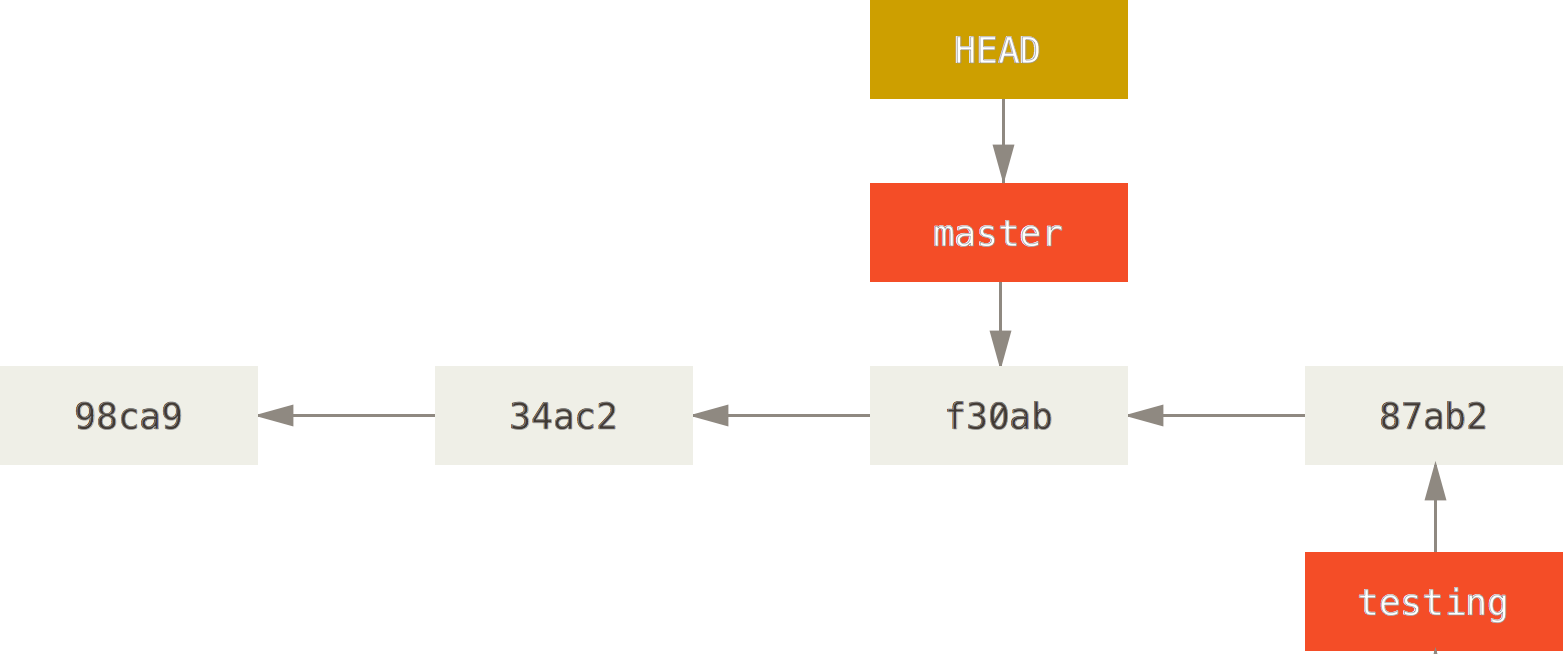
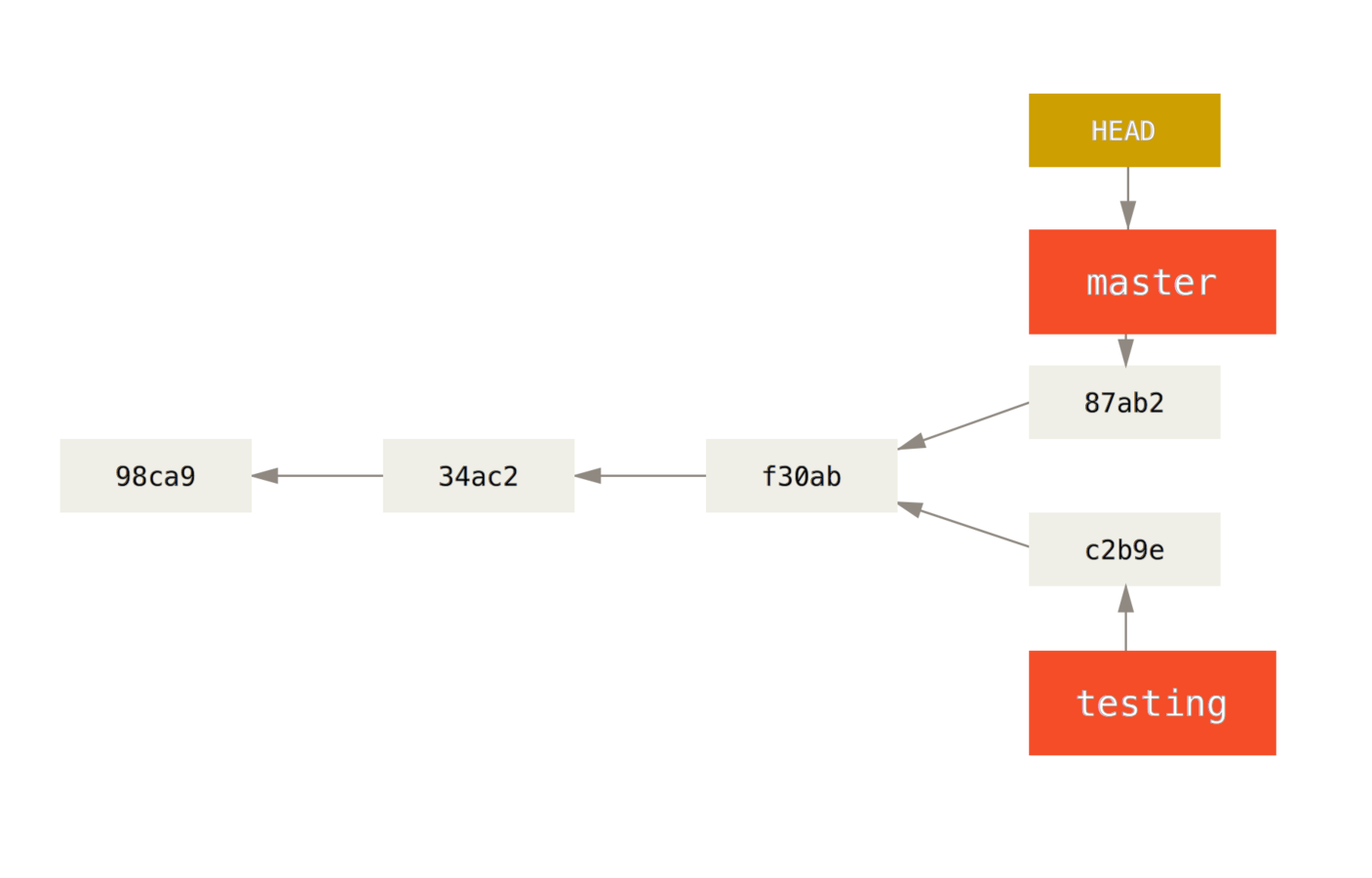
Branches
With braches you can diverge from the main line of development and continue to do work without messing with that main line
WORKFLOWS
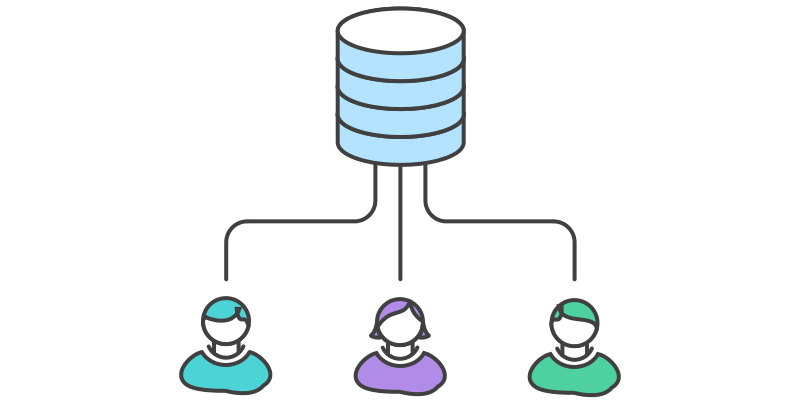
Centralized
Everybody clones and work on the same branch (usually called master)
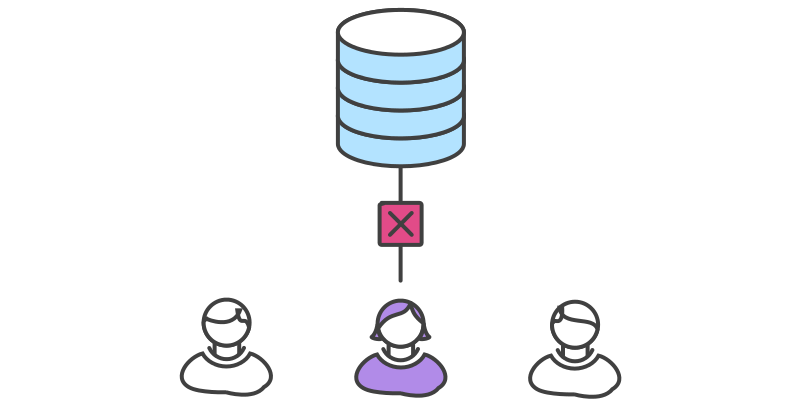
+ Easy (less conflicts)
+ Encourages small changes
- Can get messy
- Difficult to have a stable version
- Not friendly to hotfixes and CI
Feature Branch
Every feature has its own branch

!
master
new menu
+ Better structured workflow
+ Friendly to hotfixes
- Harder to enforce
- On long branches can be hard to merge
- Requires more discipline
+ Less fear to deploy
Hybrid approach
Use branches for complex freatures
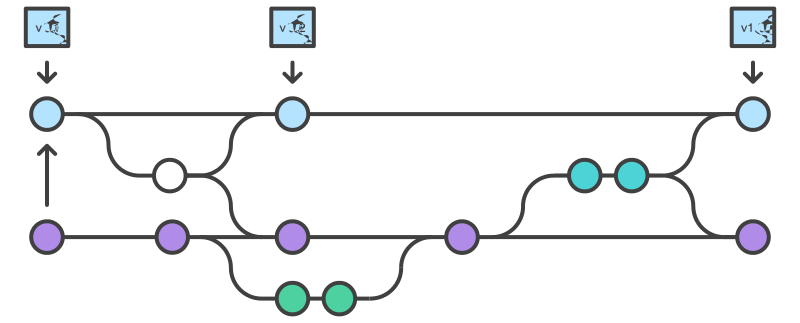
Gitflow
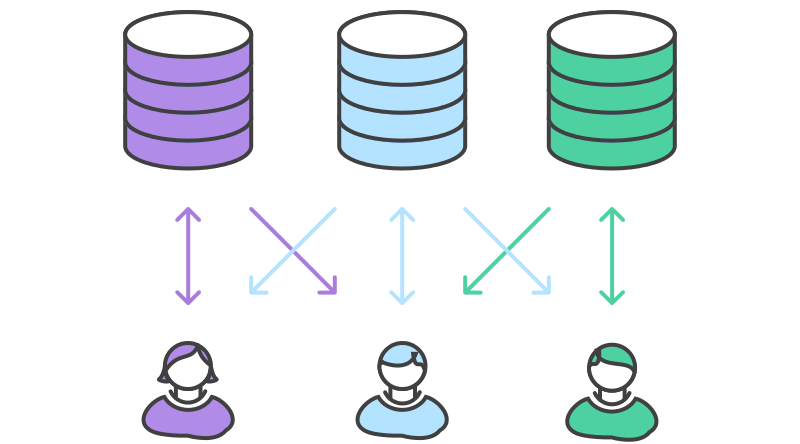
Forking workflow
BEST PRACTICES
aka: commit often, perfect later
https://sethrobertson.github.io/GitBestPractices/
Read about git

Commit early and often

Don't panic

Don't change published history
Do choose a workflow
Write useful commit messages

Git overview
By salvozappa
Git overview
Introduction to Git history, how it works and main workflows
- 609


