Introduction to Functional Programming
Sébastien BESNIER
What's Functional Programming?
→ Limit Mutations as most a possible







F# (.NET)
Java Virtual Machine
Haskell
PureScript
Elm
ReScript
Byte code
Native
(+to JS)
To JS
(this is ML-family languages,
there's also the LISP family)


Helpful
Compiler
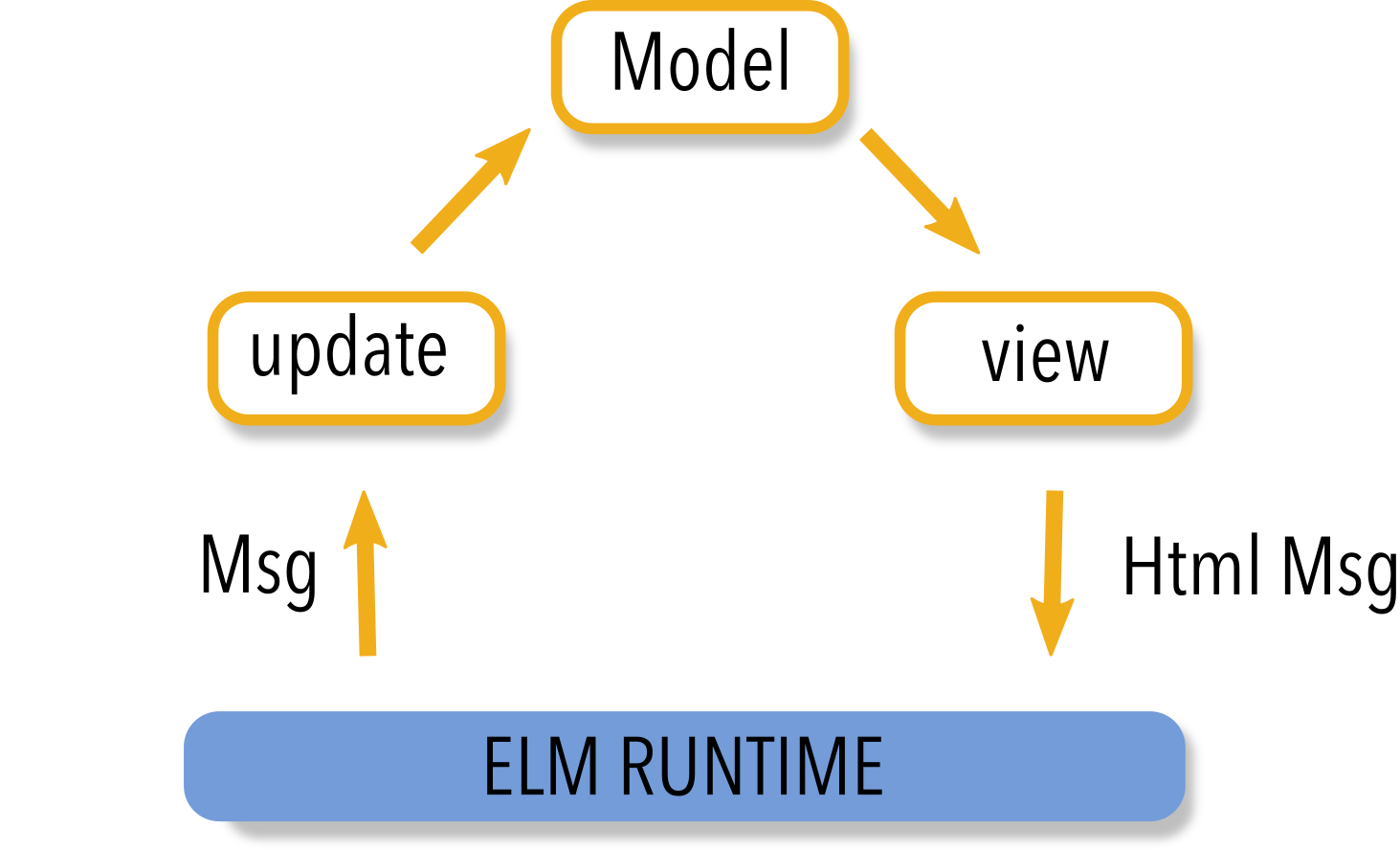
initialModel =
{ count = 0 }
type Msg
= Increment
| Decrement
update msg model =
case msg of
Increment ->
{ model | count = model.count + 1 }
Decrement ->
{ model | count = model.count - 1 }
view model =
div [style "font-size" "200%"]
[ button [ onClick Increment ] [ text "+1" ]
, div [ style "color" "red" ] [ text <| String.fromInt model.count ]
, button [ onClick Decrement ] [ text "-1" ]
]https://ellie-app.com/fDyHsFVJCska1
Challenge: Reset to 0
Implement a Nim game
https://ellie-app.com/g8qBmxW99x4a1
Rules:
- 10 lucifers at the beginning
- 2 players
- at his turn, the player can take 1,2 or 3 matches
- the player taking the last lucifer lost
No mutation! Only values and pure functions
No mutation! Only values and pure functions
Do you know impure functions?
eight = 5 + 3Affectation
Try it online
eight = round 8.3Function call
add a b = a + bFunction definition
add a b = a + b
-- call that function:
eight = add 7 1Function definition
Challenge
Compute length of \(\texttt{"hello world"}\) and add 5 to it using the \(\texttt{add}\) function (in 1 expresion!)
String.length "abc" -- returns 3eight = add 7 1
add a b = a + b
Order of declarations does not matter
add : Int -> Int -> Int
add a b = a + b
Types
String.length : ???
What is the type of String.length ?
String.length : String -> Int
What is the type of String.length ?
add3 a b c = a + b + c
What is the type of add3?
add3:
Int
-> Int
-> Int
-> Int
add3 a b c = a + b + c
Good practice:
add type anotation!
String.append "hello " "world"
-- returns "hello world"
What is the type of String.append ?
String.append "hello " "world"
-- returns "hello world"
String.append : String -> String -> StringWhat is the type of String.append ?
t = add 5 String.append "hey" "hoy"
f a b =
String.length (String.append a b)
g a b =
add (String.append a a) b
h a b =
add (String.append a b) bWhat is the type of the following expressions?
user =
{ name = "Seb"
, score = 42
, city = "Paris"
}Records
user : User
user =
{ name = "Seb"
, score = 42
, city = "Paris"
}Records
type alias User =
{ name : String
, score : Int
, city : String
}Records
newUser =
{ user | score = 43 }
newUserBis =
{ user | score = user.score + 1 }Record updates
newUser : User
newUser =
{ user | score = 43 }
newUserBis : User
newUserBis =
{ user | score = user.score + 1 }Record updates
rewardUser : User -> User
-- increase the score by oneRecord updates
rewardUser : User -> User
rewardUser user =
{ user | score = user.score + 1 }Record updates
Challenge: add type definition for the model in the counter example
Custom types
Records to store multiple data
(name, score, city....)
Custom types
Records to store multiple data
(name, score, city....)
What about data following various patterns ?
Modeling a shape
Point Circle Float Rectangle Float Float
Radius
Length
Width
What is the type of a shape?
Reminder: counter
type Msg
= Increment
| DecrementFirst variant
Second variant
Modeling a shape
Point Circle Float Rectangle Float Float
Radius
Length
Width
Modeling a shape
Point Circle Float Rectangle Float Float
Modeling a shape
type Shape =
Point | Circle Float | Rectangle Float FloatUse a custom type
myRect = Rectangle 10 20
bigCircle = Circle 420000
describe : ???
describe shape =
case shape of
Point ->
"A lonely point"
Circle radius ->
"A circle of radius "
++ String.fromFloat radius
Rectangle width height ->
"A rectangle of area "
++ String.fromFloat (width*height)
Use a custom type
myRect = Rectangle 10 20
bigCircle = Circle 420000
describe : Shape -> String
describe shape =
case shape of
Point ->
"A lonely point"
Circle radius ->
"A circle of radius "
++ String.fromFloat radius
Rectangle width height ->
"A rectangle of area "
++ String.fromFloat (width*height)
Boolean
Defined by the language
-- Defined by Elm
type Bool = True | False
-- our code:
myBool = True
res =
case myBool of
True -> 42
False -> 18
Boolean
Defined by the language
-- Defined by Elm
type Bool = True | False
-- our code:
myBool = True
res =
case myBool of
True -> 42
False -> 18
res =
if myBool then
42
else
18Preferred way:
if(condition) {
myVar = 42;
} else {
myVar = 18;
}myVar = condition ? 42 : 18;VS
Conditionals
in imperative language (Java, C, Python...)
Conditionals
in imperative language (Java, C, Python...)
myVar = condition ? 42 : 18;VS
INSTRUCTION:
changes the state
EXPRESSION:
compute a new value
This is what Elm (and other FP languages does!)
if(condition) {
myVar = 42;
} else {
myVar = 18;
}Implement highlight on hover
https://ellie-app.com/fF4BSNrDVK4a1
1st step: define Model & Msg and implement update
[] -- empty list
[1, 2, 6] : List number
["Hello", "world"] : List String
Lists
[] -- empty list
[1, 2, 6] : List number
["Hello", "world"] : List String
["Hello", 42] -- impossible!Lists are homogeneous
ages : List Int
ages = [ 18, 14, 35, 10, 51 ]
agesInFiveYears : List Int
agesInFiveYears =
-- add five to each elementNo for-loops!
addFive : Int -> Int
addFive x = 5 + x
ages : List Int
ages = [ 18, 14, 35, 10, 51 ]
agesInFiveYears : List Int
agesInFiveYears =
List.map addFive agesNo for-loops!
List.map :
(a -> b)
-> List a
-> List b
agesInFiveYears =
List.map addFive agesMap signature
ages : List Int
ages = [ 18, 14, 35, 10, 51 ]
-- transform into :
-- [ "18 ans", "14 ans", ... ]
-- Hint:
-- String.fromInt : Int -> StrMap challenge
ages : List Int
ages = [ 18, 14, 35, 10, 51 ]
displayAge : Int -> String
displayAge age =
String.fromInt age ++ " ans"
agesDisplayed =
List.map displayAge agesMap challenge
{-| Compute the total number of chars in the
list of strings given in argument. Example:
totalLength ["hey!", "I am", "Hungry!!"]
returns 16
-}
totalLength : List String -> Int
totalLength strings = ...
-- HINT: List.sum : List Int -> IntMap challenge 2
{-| Compute the total number of chars in the
list of strings given in argument. Example:
totalLength ["hey!", "I am", "Hungry!!"]
returns 16
-}
totalLength : List String -> Int
totalLength strings =
List.sum (List.map String.length strings)Map challenge 2
Copy of Introduction to Functional Programming
By sebbes
Copy of Introduction to Functional Programming
- 743



