SQL Server: Manage your Database Better


Seiji Villafranca
Seiji Villafranca
github.com/SeijiV13


Senior Developer, Wypoon Technologies Netherlands
Microsoft MVP
Auth0 Ambassador
Community Lead, AngularPH,
Author
seijivillafranca.com


Seiji Villafranca
Talks















What will we learn
Basic SQL statements
Database Keys and Table Relationships
SQL Server Management Studio Introduction
Azure SQL Introduction

SQL
structured query language
standardized programming language that is used to manage relational databases and perform various operations
Add data - INSERT
Get data - SELECT
Remove data - DELETE
Update data - UPDATE
"deals with data in database"



Select * from
Transactions where ID = 'SEIJI'
return transaction list
call query
display transaction list
call api
Real world
What will you see
Tables with Data and Relationships
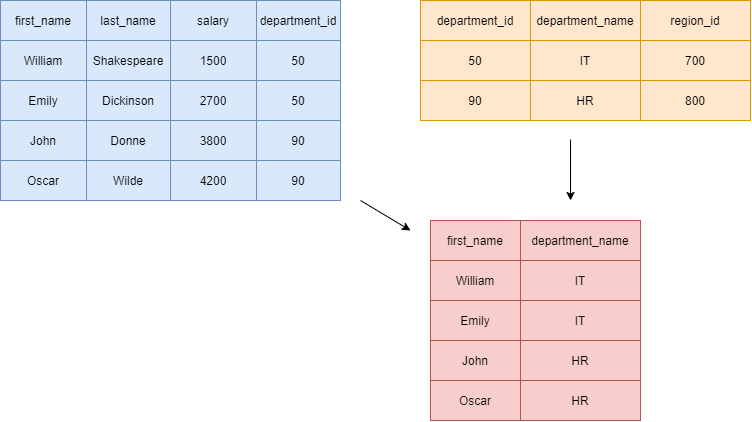
Where will you use SQL
Relational Databases
| SQL Databases | No SQL Databases |
|---|---|
| Databases are categorized as Relational Database Management System (RDBMS). | NoSQL databases are categorized as Non-relational or distributed database system. |
| MySQL, Oracle, Sqlite, PostgreSQL and MS-SQL etc. are the example of SQL database | MongoDB, BigTable, Redis, RavenDB, Cassandra, Hbase, Neo4j, CouchDB etc. are the example of nosql database |
What will you be

Want to start SQL?
"Learn the syntax"
remember there are different SQL Dialects
Command types
Data Definition Language - defines the tables
Data Manipulation Language - alters the data in the tables
Data Query Language - get data from the table
Data Control Language - grant or revoke user accesss
Transaction Control Language - grant or revoke user accesss
Data Definition Language
Create, Alter, Drop
CREATE DATABASE databasename;CREATE DATABASE databasename;Create Database
CREATE DATABASE databasename;DROP DATABASE databasename;Drop Database

CREATE DATABASE databasename;CREATE TABLE tablename (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
....
);Create Table
DROP TABLE tablenameDrop Table
Data Query Language
Select
SELECT * from Users
all columns
table to select
Data Manipulation Language
Insert, Update, Delete

INSERT INTO tablename (column1, column2, column3, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);Insert Data
Update Data
Delete Data
UPDATE tablename
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ...
WHERE condition;DELETE FROM tablename WHERE condition;
Select Cheat Sheet
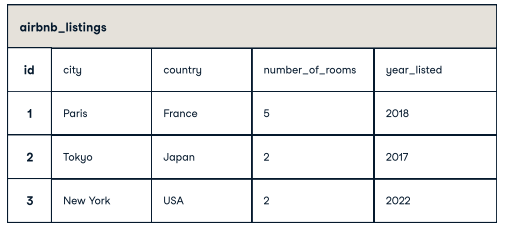
Get all the columns
Return country column
Get the listing id, city, ordered by the number_of_rooms in ascending order
QUERYING TABLES
SELECT * FROM airbnb_listings
SELECT country FROM airbnb_listings
Get the listing id, city, ordered by the number_of_rooms in ascending order
SELECT id, city from airbnb_listings ORDERED BY number_of_rooms ASC

number of rooms equals to 2
number of rooms equals or greater than 2
Filtering Data - Numeric
SELECT * FROM airbnb_listings WHERE number_of_rooms = 2
SELECT * FROM airbnb_listings WHERE number_of_rooms >= 2

country is France
country is USA or FRANCE
Filtering Data - Text Columns
SELECT * FROM airbnb_listings WHERE country = 'France'
SELECT * FROM airbnb_listings WHERE country IN('USA', 'FRANCE')
country starts with J
SELECT * FROM airbnb_listings WHERE country LIKE 'J%'

country is France AND year listed is rooms greater than 3
country is USA or year_listed is on 2018
Filtering Data - Multiple Columns
SELECT * FROM airbnb_listings WHERE country = 'France' AND number_of_rooms = 3
SELECT * FROM airbnb_listings WHERE country = 'USA' OR year_listed = 2012
Primary Key
Table Keys
Unique Key
Unique identifier
Does not allow null values
allow null values
Unique identifier
table supports only one
Table supports only one
Foreign Key
constraint is used to prevent actions that would destroy links between tables

CREATE TABLE Customers (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);Customer
CREATE TABLE Orders (
ID int NOT NULL,
CustomerID int,
OrderNumber varchar(255) NOT NULL,
Total int NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);Order
| ID | Last Name | First Name | Age |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Doe | John | 30 |
| 2 | Doe | Jane | 26 |
| ID | CustomerID | Order Number | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 11 | 200 |
| 2 | 2 | 22 | 300 |
primary key
foreign key
unique key
primary key
Importance of keys
maintains the integrity of the data
prevents destroying of links
"keys are the most important features of relational databases"
Other things you should learn
Normalization
Joins
Stored Procedures
Aggregate and Server Functions
You have the knowledge...,
Tools
managing your database
Tools for SQL
SSMS
Azure


A Short Demo


Hey I'm a Mentor!
github.com/SeijiV13

seijivillafranca.com
fb.com/seiji.villafranca



Thank you
and happy learning!

SQL Server: Manage your database better
By Seiji Ralph Villafranca
SQL Server: Manage your database better
- 200



