Introduction to RxJs


and
Seiji Villafranca
Functional Reactive Programming
Seiji Villafranca
github.com/SeijiV13


Senior Developer, CoDev
Microsoft MVP
Auth0 Ambassador
Community Lead, AngularPH,
seijivillafranca.com


Talks















What is RxJS?


RxJS
Reactive Extensions for JavaScript
JavaScript Library that uses Observables for reactive programming
Library that deals with callbacks, asynchronous implementations and event-based programs
ReactiveX is not just for JavaScript




can be used in browser or even on Node.JS Backend

RxJS
Reactive Extensions for JavaScript
Core Features
Observable
Observer
Subscription
Subject
Operator
Scheduler

Functional Programming
2
1
3
X Reactive Programming
= FRP
What is Functional Programming?
Present in programming for many years
focused on writing more compounded and pure functions
can be used in JavaScript since it is a multi-paradigm language
Several Concepts we need to know
First-Class Objects
Pure functions
Higher Order functions
Composition
Immutability
pure use of functions
Functional Programming is
First-Class Objects
First-class variables, functions can be used as variables
const product = (a, b) => a * b;
//use function directly to a variable
const result = product(2, 2);
//use function as a parameter
const anotherResult = (a, b, product) => product(a, b)pure use of functions
Functional Programming is
Pure Functions
will always return the same output, does not maintain any state which is reliable for testing ann debugging
const displayName = (name) => `${name}`;
myName("Seiji Villafranca") // Should always return the namepromotes reusability of code ad it can be used anywhere
pure use of functions
Functional Programming is
Higher-Order Functions
Concept used for writing better code
const person = "" // value to find
const names = ["Seiji", "Shey", "John", "Jame"];
const findPerson = names.find(name => name === person);used for a function receiving another function as a parameter
.find, .filter, map are example of Higher-Order Functions
pure use of functions
Functional Programming is
Composition
Combination of multiple functions to create a new a new function or process
const findPerson = (names) => names.find((data) => name === person);
const returnFirstName = (name) => name ?? name.split(" ")[0] : "";
const result =
returnFirstName(
findPerson(["Seiji Villafranca", "Shey Cadavero", "John Doe", "Jane Doe"])
);
console.log(result); // returns the first name of the searched personpassing inputs from one function to another function
pure use of functions
Functional Programming is
Immutability
object is an object that can’t be modified after its creation
const game = {
name: 'Zelda',
price: 2000
}
const newgame = Object.assign({}, game, {
name: 'Super Smash'
})Object.assign is used to create a new copy for the data
Reactive Programming
"It is a programming of event streams that happens in time"
also a programming paradigm that deals wit Asynchronous data streams
Asynchronous means not existing or happening at the same time
Reactive Programming
also a programming paradigm that deals wit Asynchronous data streams
Streams, Streams everywhere!
sequence of ongoing events ordered in time
events such as inputs button and keyboard clicks
emits a value, error, and complete signal
Reactive Programming
Promises and Observables - to handle async callbacks
Streams, Streams everywhere!
Dom Events
AJAX
WebSockets
Server-Sent Events

Reactive Programming
Let's have an example
Imperative Programming
var x = 4;
var y = 6;
let sum = x + y;
console.log(sum);
x = 1;
y = 2;
console.log(sum);
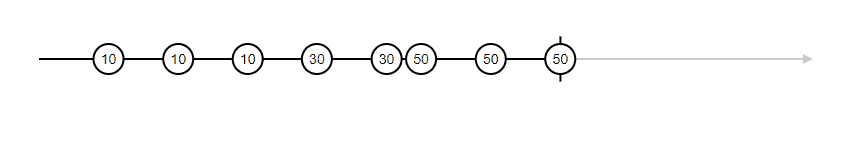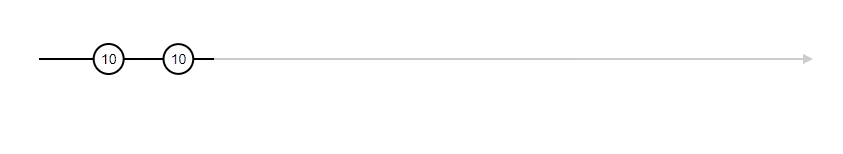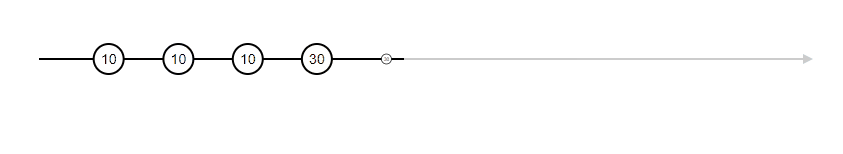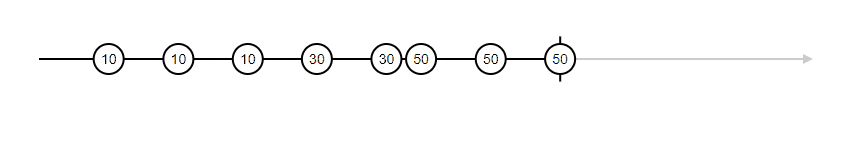
Ouput -->
10
10variable x, and y does not affect the sum upon changes (no dynamic change)
Reactive Programming
Moving to Dynamic Behavior
import { from, interval, of } from "rxjs";
import { map, mapTo } from "rxjs/operators";
let x = of(3, 4).pipe(map((x) => x * 3));
x.subscribe((data) => console.log(data));
// Output
--> 9
--> 12of is an observable that sends values and receives at subscription at a particular time
Use of Observables
Reactive Programming
Moving to Dynamic Behavior
import { from, interval, of } from "rxjs";
import { map, mapTo, take } from "rxjs/operators";
let x = interval(1000).pipe(
take(6),
map(i => [1,2,3,4,5,6][i]));
x.subscribe((data) => console.log(data));
--> outputs each values every one secondStream is sending data one by base on the interval
Use of Observables with interval
Reactive Programming
everything is Streams Streams and Streams!
Stream of values
use for depicting streams, values and their output

Functional Reactive Programming

RxJs
Diving Deep
Reactive programming is programming with asynchronous data streams.
Reactive Programming should be used as one to construct a Reactive System.
Reactive Systems.
Responsive
Resilient
Elastic
Message Driven
Functional Reactive Programming

RxJs
Diving Deep
Streams can emit three things, value, error and termination/complete
Defining the Stream (Comparing it to real life)
faucet
Observable (water stream)
values (water)
Subscriber
Received values


Functional Reactive Programming

RxJs
Diving Deep
Observable (water stream)
values (water)


Subscriber
Received values
It emits values asynchronously and we need to capture it
On value emission
On error emission.
termination:
Capturing the water
Functional Reactive Programming

RxJs
Diving Deep
Observable (water stream)
values (water)


Filter
Received values

Filtering the water
Subscriber
filtered values (water)
Operators (map, filter, reduce etc.)
Used for transforming emitted values in the stream, this is depicted as the filter in our faucet
Functional Reactive Programming

RxJs
Observable (water stream)
values (water)


Filter
Received values

The whole concept
Subscriber
filtered values (water)
Water Stream = Observable: A structure representing a stream of values over time.
Tap = Subscriber: the code that calls the subscription process on an observable
Opening the tap = Subscription: opens the stream for the observer.
Closing the tap = Completing: marking the stream as completed meaning it is terminated.
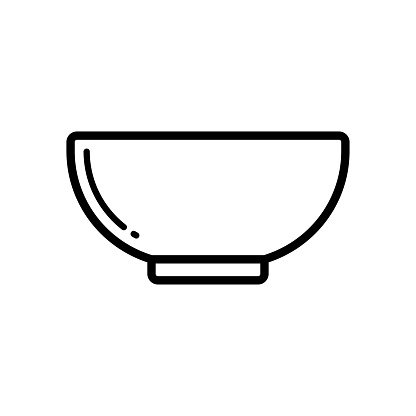
Bowl = Observer: The structure that captures the values
Appliances = Operators: Functions that transform the stream.
Converting terms
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
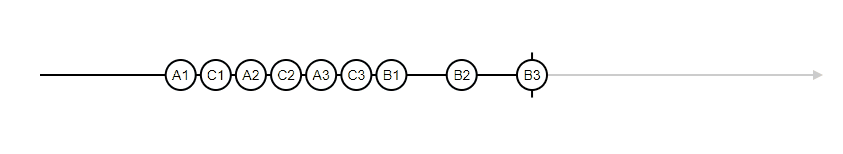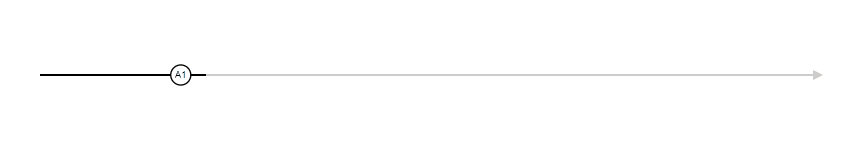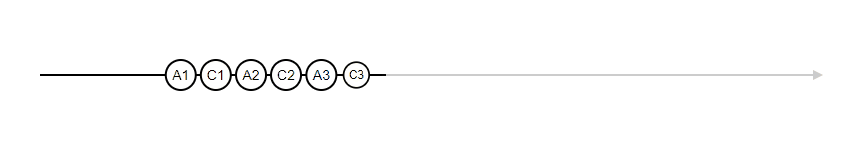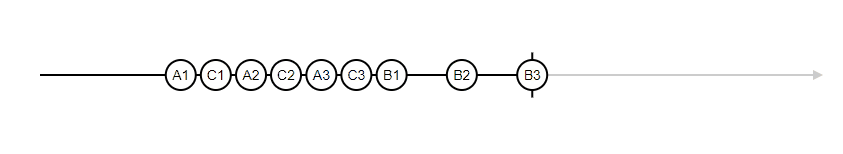
Marble Diagrams (you will see this every time you deal with RxJS
3
5
S
6
execution of the Input Observable
Values emitted
Complete Notification
addByFive
10
8
Operator to be applied in the input Observable
Output Observable produced by the Operator
Error emitted by the Output Observable
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
Filtering Operators
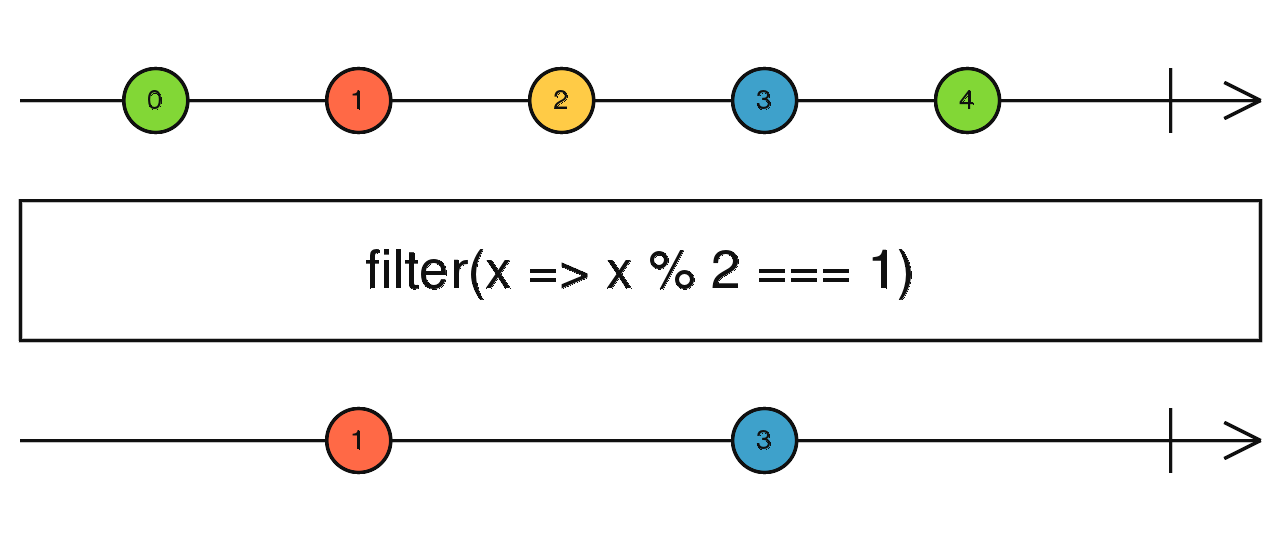
filter()
const filtered = of(0,1,2,3,4).pipe(
filter((x) => (x % 2) === 1)
);
filtered.subscribe(data => console.log(data))Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
Filtering Operators
first()
const filtered = of(0,1,2,3,4).pipe(
first()
);
const filtered = of(0,1,2,3,4).pipe(
first(x => x % 2 === 0)
);
filtered.subscribe(data => console.log(data))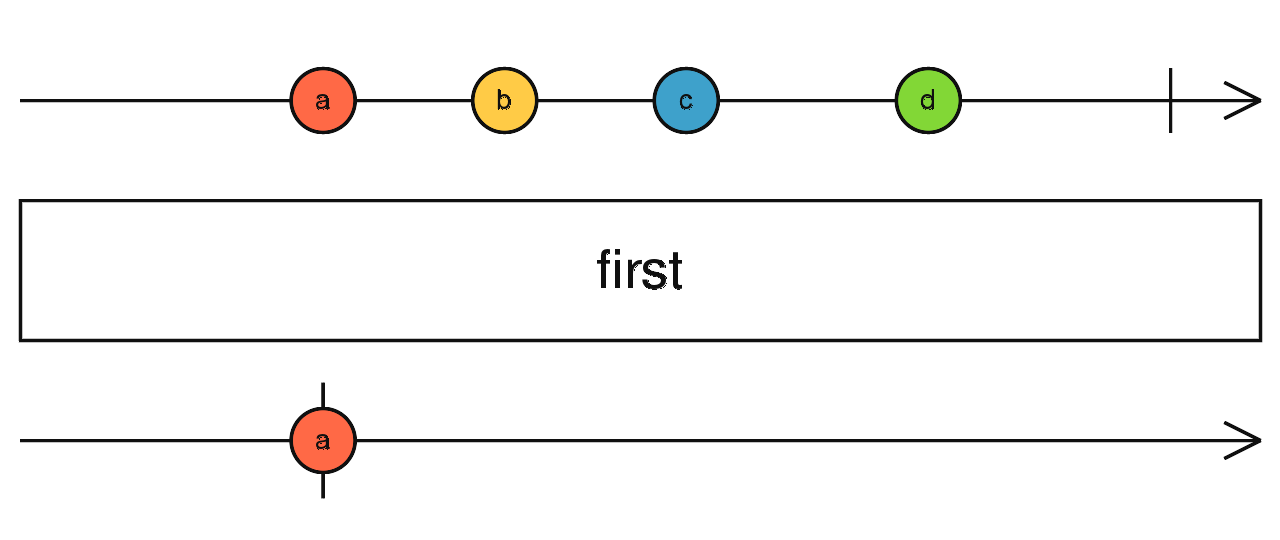
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
Filtering Operators
skipWhile()
const filtered = of(2, 3, 4, 5 ,6).pipe(
skipWhile(x => x < 4)
);
filtered.subscribe(data => console.log(data))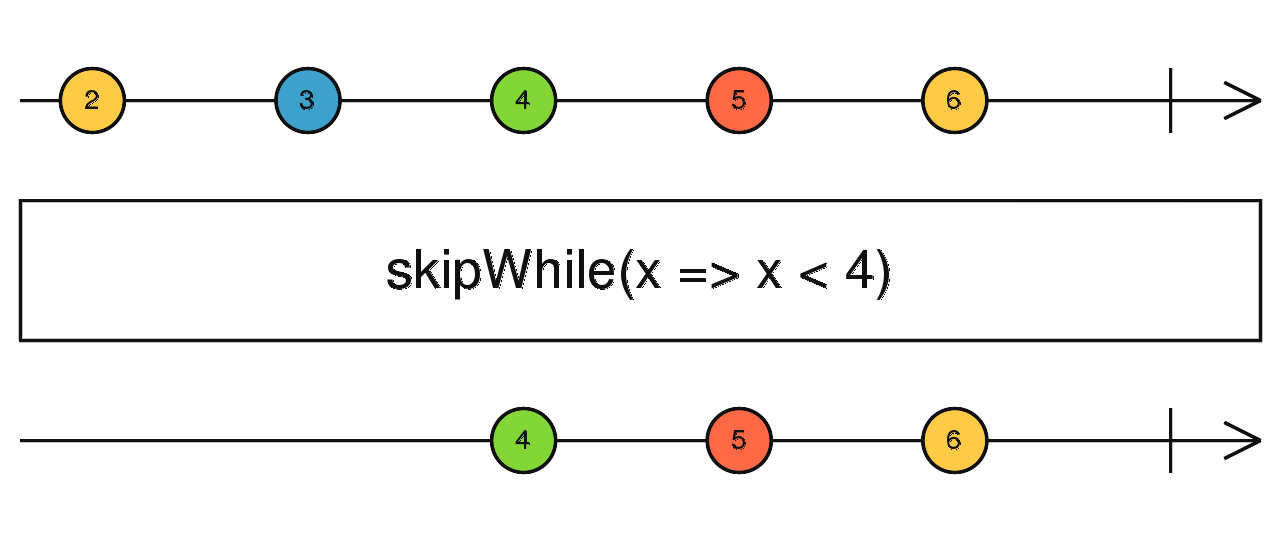
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
Filtering Operators
skipUntil()
const click = fromEvent(document, 'click');
const filtered = interval(1000).pipe(
skipUntil(click)
);
filtered.subscribe(data => console.log(data))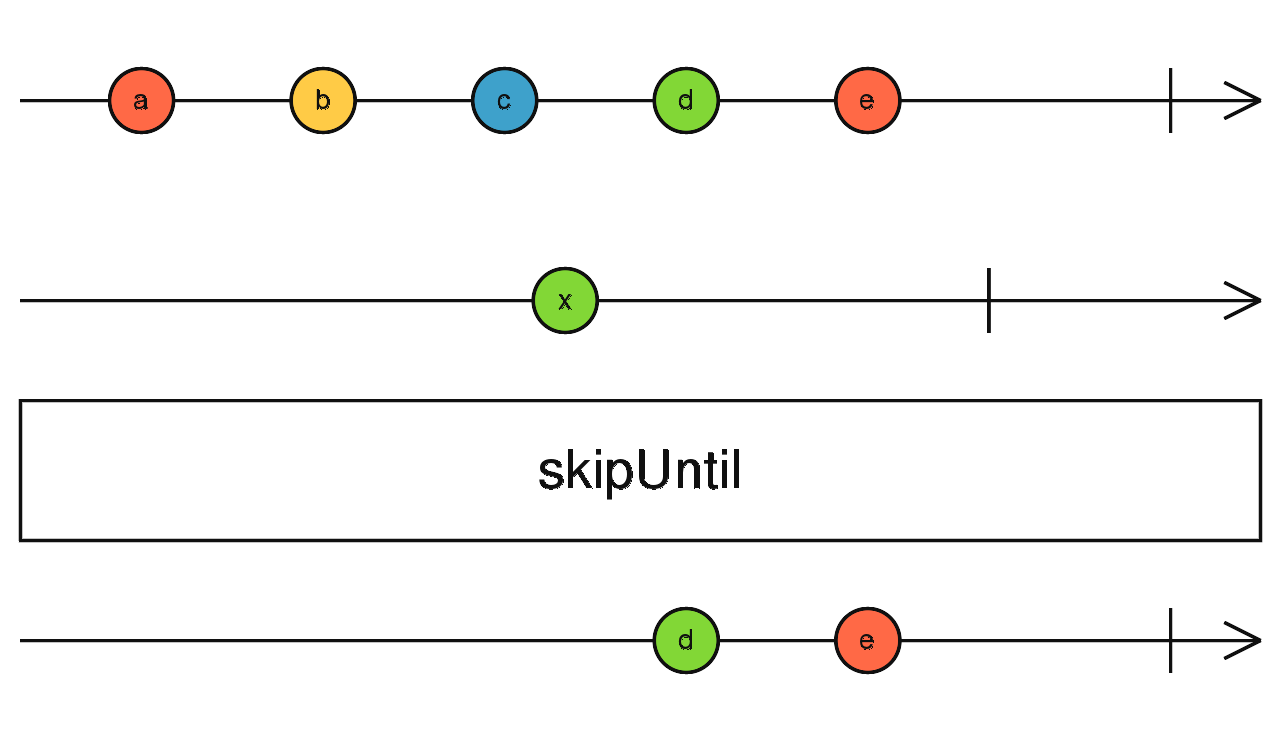
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
Filtering Operators
take()
const filtered = of(2, 3, 4, 5 ,6).pipe(
take(2)
);
filtered.subscribe(data => console.log(data))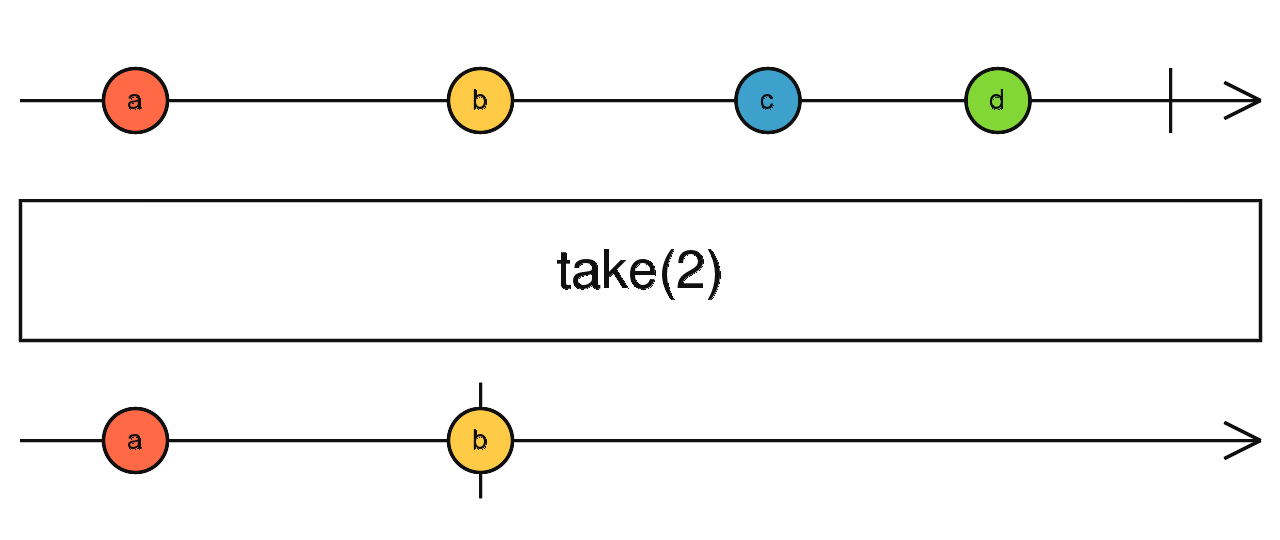
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
Filtering Operators
takeUntil()
const click = fromEvent(document, 'click');
const filtered = interval(1000).pipe(
takeUntil(click)
);
filtered.subscribe(data => console.log(data))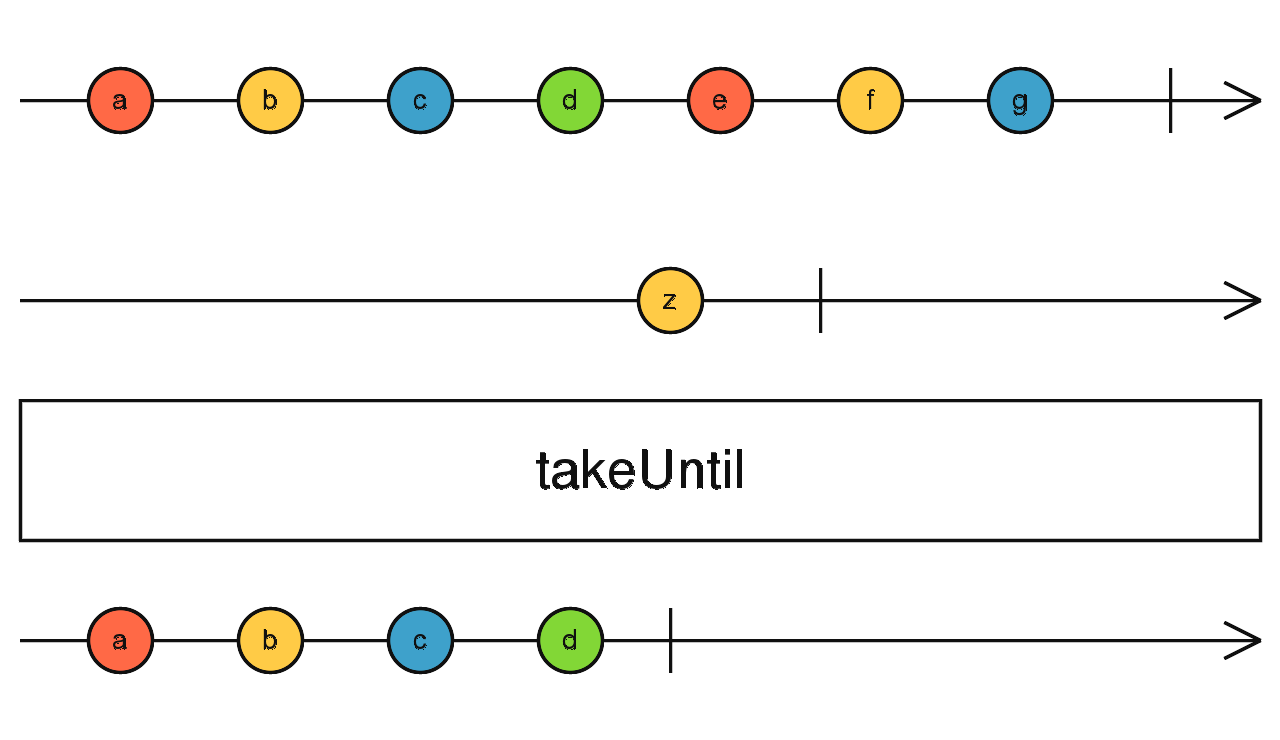
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
transformation Operators
map()
const filtered = of(2, 3, 4, 5 ,6).pipe(
map(x => x * 2)
);
filtered.subscribe(data => console.log(data))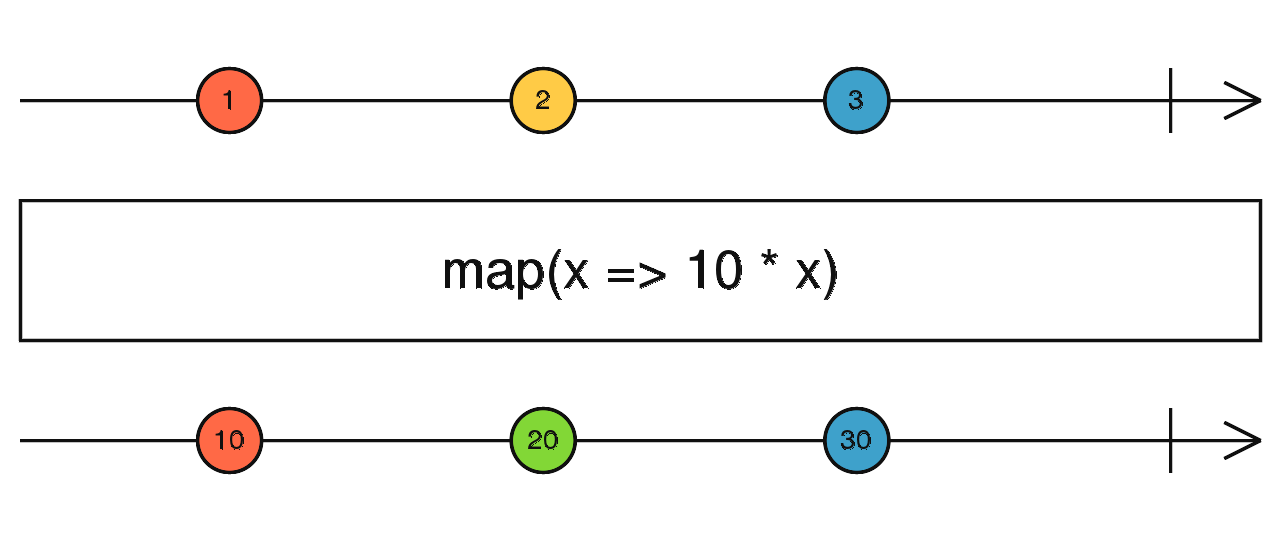
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
transformation Operators
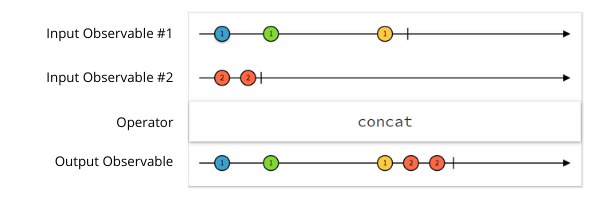
concatMap() - Each new inner Observable is concatenated with the previous inner Observable using concatAll
const sub1 = of(0, 1, 2, 3, 4);
const sub2 = of(5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
sub1.pipe(concatMap((d) => sub2.pipe(
map((x) => x * d)
))).subscribe((data) => console.log(data));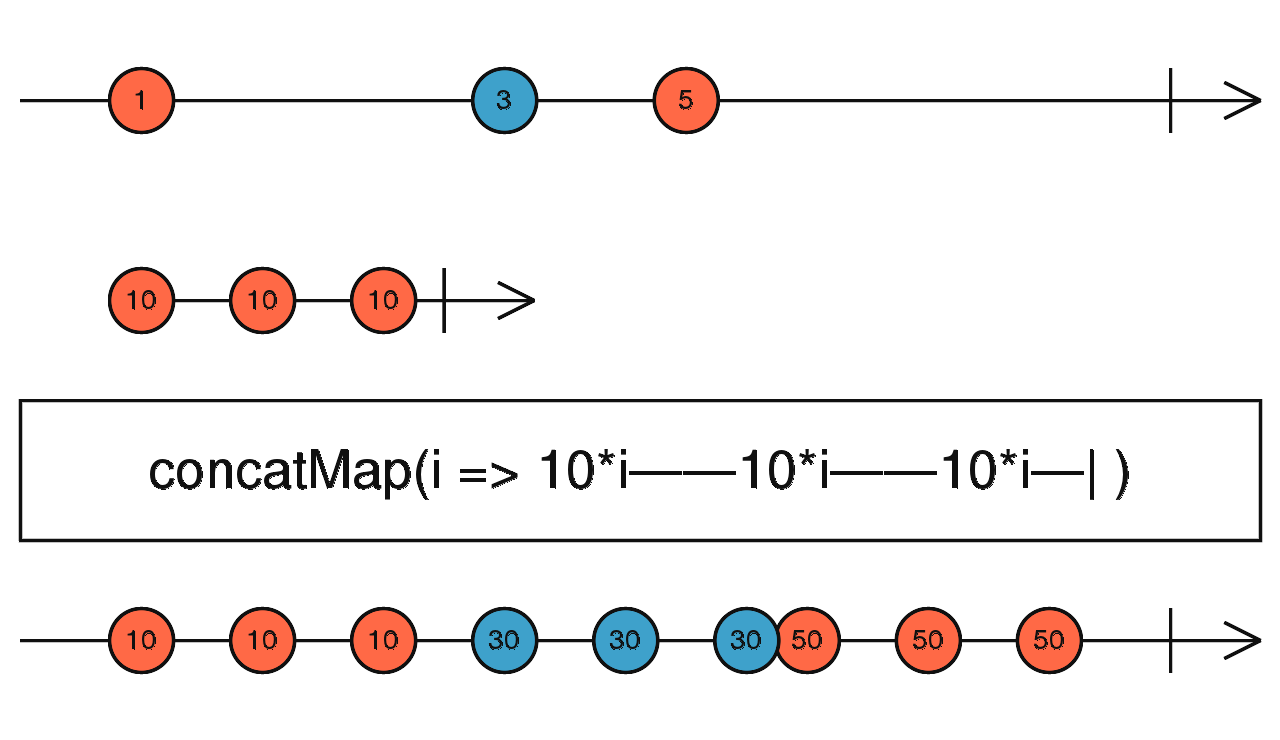
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
transformation Operators
exhaustMap() - Each new inner Observable is concatenated with the previous inner Observable using exhaust
const sub1 = of(0, 1, 2, 3, 4);
const sub2 = of(5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
sub1.pipe(exhaustMap((d) => sub2.pipe(
map((x) => x * d)
))).subscribe((data) => console.log(data));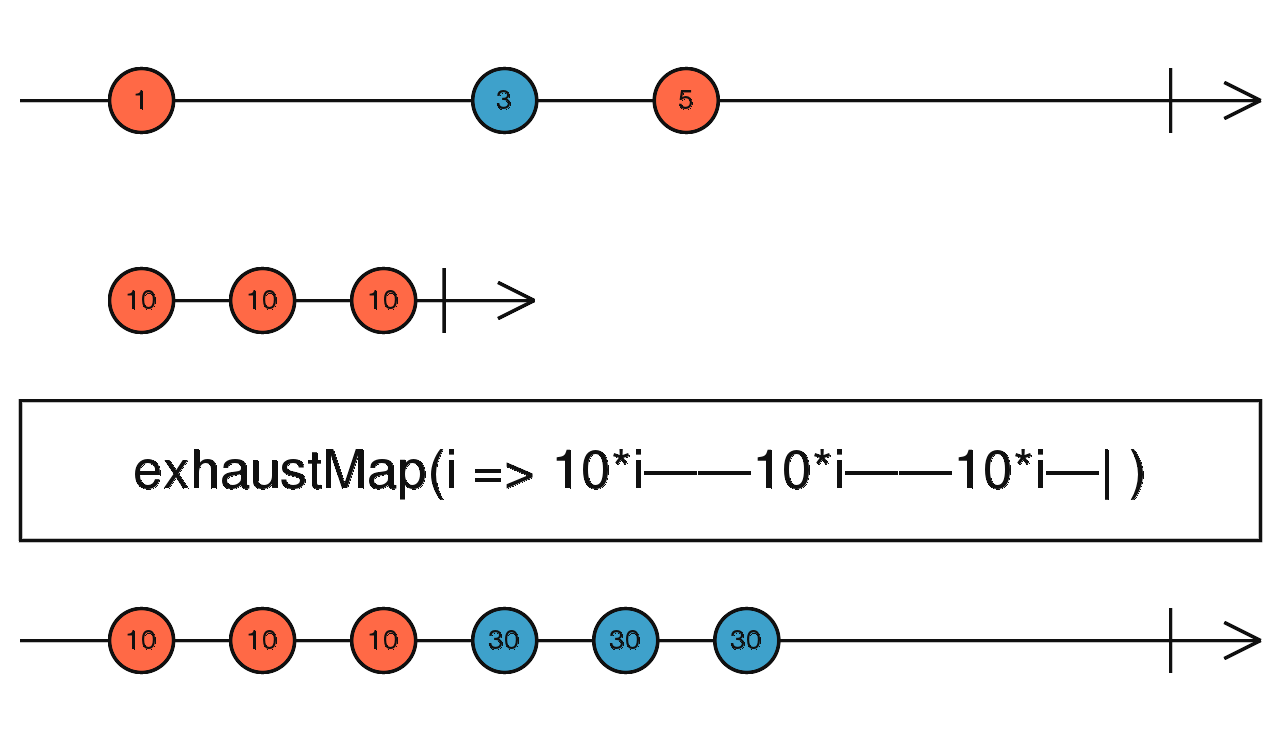
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
transformation Operators
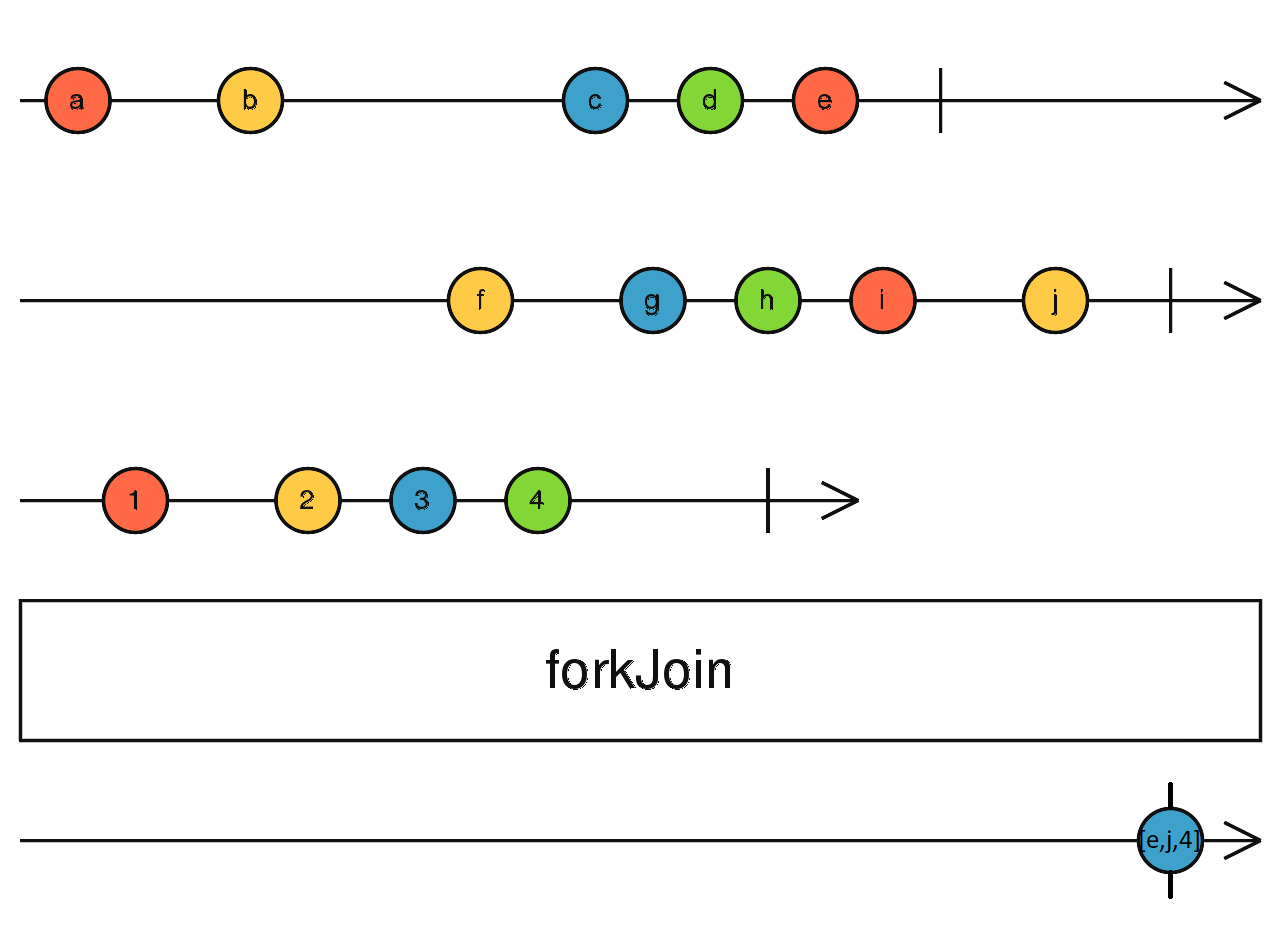
forkJoin() - emitting either an array of last values emitted by passed Observables
const sub1 = of(0, 1, 2, 3, 4);
const sub2 = of(5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
const sub3 = of(10, 12, 3);
forkJoin(sub1, sub2, sub3)
.subscribe(data => {
console.log(data)
})
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
- Used for transforming data in Observable
transformation Operators
switchMap() - Each new inner Observable is concatenated with the previous inner Observable
const sub1 = of(0, 1, 2, 3, 4);
const sub2 = of(5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
sub1.pipe(switchMap((d) => sub2.pipe(
map((x) => x * d)
))).subscribe((data) => console.log(data));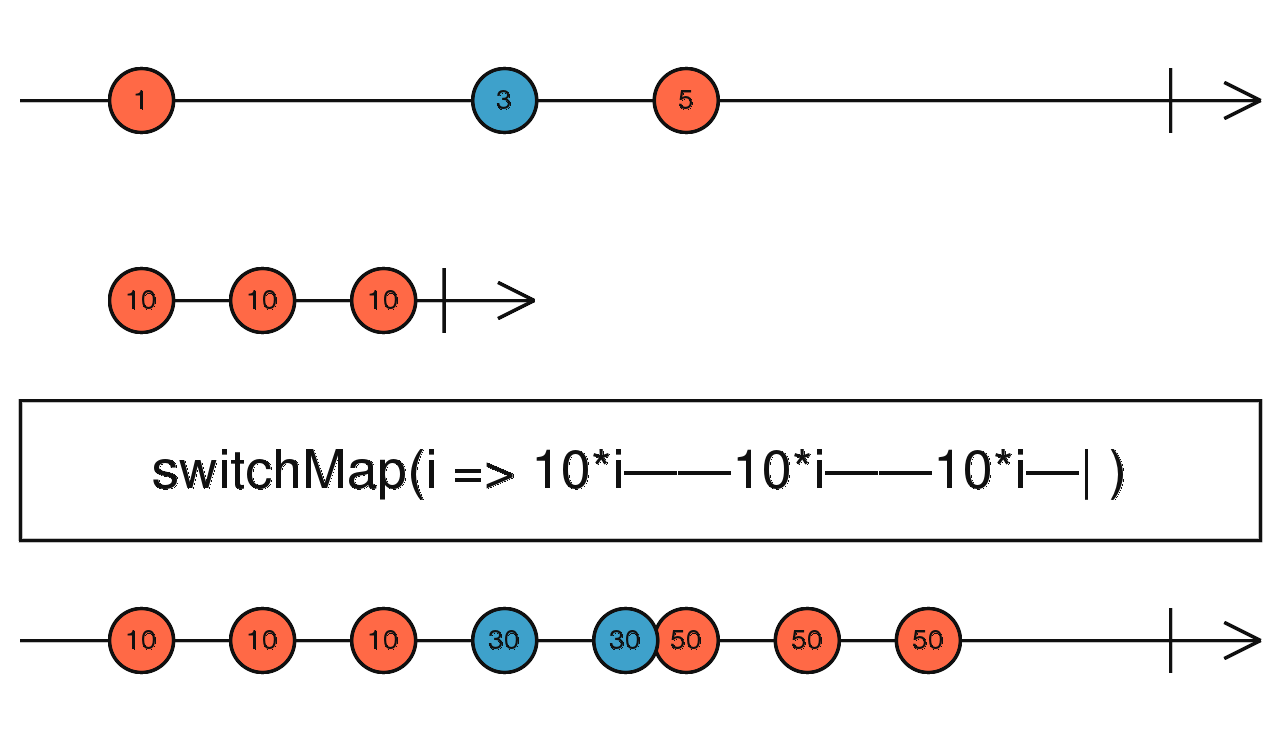
Concepts we need to know

RxJs
Operators (https://rxjs.dev/guide/operators)
Other Operators
min - emits item with the smallest value.
Mathematical and Aggregate Operators
max - emits item with the largest value.
count - returns howany values were emitted, when the source completes
Conditional and Boolean Operators
find - searches for the first item in the source Observable that matches the specified conditio
findIndex - searches for the first item in the source Observable that matches the specified condition and returns the index
isEmpty - Tells whether any values are emitted by an Observable.
Other Observable Concepts

RxJs
Hot
const observable = Observable
.create((observer) => {
observer.next(3);
observer.next(10);
});
// Subscription 1
observable.subscribe((data) => {
console.log(data);
});import { Observable } from "rxjs";
const observable = Observable
.fromEvent(document, 'click');
// Subscription 1
observable.subscribe((event) => {
console.log(event);
});
Cold
Let's Wrap up!

RxJs
RxJs is a Functional Reactive Programming Library that is flexible to use
offers an easy way of handling asynchronous data, call backs and event-based programs
wide range of operators that makes programming easier and simple expecially together with reactive programming

References
https://dev.to/gitpaulo/reactive-programming-demystified-using-rxjs-53g5
https://rxjs.dev/
https://blog.angular-university.io/functional-reactive-programming-for-angular-2-developers-rxjs-and-observables/
Hey I'm a Mentor!
github.com/SeijiV13

seijivillafranca.com
fb.com/seiji.villafranca




Introduction to RxJs and Functional Reactive Programming
By Seiji Ralph Villafranca
Introduction to RxJs and Functional Reactive Programming
- 307



