




Fusion neutronics workshop
with OpenMC
Dr Jonathan Shimwell.
Jonathan.Shimwell@ukaea.uk
This work was funded by the RCUK Energy Programme
[Grant number EP/P012450/1]
Neutron birth
(n,n')
(n,f)
(n,n')
(γ,γ')
(n,nγ')
(n,pn')
(n,f)
(n,2n)
(n,α)
(n,γ)
this presentation has moved to
Neutronics analysis has a role in assessing the functionality and viability of nuclear reactor designs, particle accelerators, radiation shielding, medical treatment devices, etc
Neutronics analysis also has uses in fusion reactor design and can ascertain:
- The tritium breeding ratio (TBR)
- Activation of material and resulting radioactivity
- Biological dose rates
- Deposited heat within components
- Material damage (e.g DPA or Helium production)


How can neutronics help
Cross section data is key to the neutronics workflow and provide us with the likelihood of a particular interaction.


Interaction cross sections
Availability of experimental data varies.
Typically the experimental data is then interpreted to create evaluation libraries, such as ENDF, JEFF, JENDL, CENDL.
Cross sections can be measured experimentally with monoenergetic neutrons.


Interaction cross sections
Cross section evaluations exist for different isotopes and different interactions.


Interaction cross sections
A list of interactions is available online
MT numbers using in this workshop include:
- DPA 444
- n,Xt 205
Making materials
import openmc
mat1 = openmc.Material(name='natural Li2O')
mat1.add_element('Li', 2)
mat1.add_element('O', 1)
mat1.set_density('g/cm3', 2.01)
mat2 = openmc.Material(name='enriched Li20')
mat2.add_nuclide('Li6', 0.6*2)
mat2.add_nuclide('Li7', 0.4*2)
mat2.add_nuclide('O16', 0.9976206)
mat2.add_nuclide('O17', 0.000379)
mat2.add_nuclide('O18', 0.0020004)
mat2.set_density('g/cm3', 2.01)
Making materials
import openmc
mat1 = openmc.Material(name='natural Li2O')
mat1.add_element('Li', 2)
mat1.add_element('O', 1)
mat1.set_density('g/cm3', 2.01)
mat2 = openmc.Material(name='enriched Li20')
mat2.add_nuclide('Li6', 0.6*2)
mat2.add_nuclide('Li7', 0.4*2)
mat2.add_nuclide('O16', 0.9976206)
mat2.add_nuclide('O17', 0.000379)
mat2.add_nuclide('O18', 0.0020004)
mat2.set_density('g/cm3', 2.01)
Making materials
import openmc
mat1 = openmc.Material(name='natural L2O')
mat1.add_element('Li', 2)
mat1.add_element('O', 1)
mat.density = 2.01
mat2 = openmc.Material(name='enriched Li20')
mat2.add_nuclide('Li6', 0.6*2)
mat2.add_nuclide('Li7', 0.4*2)
mat2.add_nuclide('O16', 0.9976206)
mat2.add_nuclide('O17', 0.000379)
mat2.add_nuclide('O18', 0.0020004)
Making geometry
Making surfaces
surface_xp = openmc.XPlane(x0=0)
surface_yp = openmc.YPlane(y0=0)
surface_zp = openmc.ZPlane(z0=0)
surface_p = openmc.Plane(A=1.0, B=0.0, C=0.0, D=0.0)
surface_xcy = openmc.XCylinder(y0=0.0, z0=0.0, R=1.0)
surface_ycy = openmc.YCylinder(x0=0.0, z0=0.0, R=1.0)
surface_zcy = openmc.ZCylinder(x0=0.0, z0=0.0, R=1.0)
surface_s = openmc.Sphere(x0=0.0, y0=0.0, z0=0.0, R=1.0)
surface_xco = openmc.XCone(x0=0.0, y0=0.0, z0=0.0, R2=1.0)
surface_yco = openmc.YCone(x0=0.0, y0=0.0, z0=0.0, R2=1.0)
surface_zco = openmc.ZCone( x0=0.0, y0=0.0, z0=0.0, R2=1.0)
surface_quad = openmc.Quadric(a=0.0, b=0.0, c=0.0, d=0.0, e=0.0, f=0.0, g=0.0, h=0.0, j=0.0, k=0.0)
The geometry of a model in OpenMC is defined using constructive solid geometry (CSG) although CAD is supported via DAGMC
Making geometry
Making volumes
surface_sphere = openmc.Sphere(r=10.0) region_inside_sphere = -surface_sphere cell_sphere = openmc.Cell(region=region_inside_sphere)
cell_sphere.fill = steel
surf_sphere1 = openmc.Sphere(r=10.0)
surf_sphere2 = openmc.Sphere(r=20.0)
region_inside_sphere = +surf_sphere1 & -surf_sphere2
cell = openmc.Cell(region= region_inside_sphere)
cell_sphere.fill = steel
Making geometry
Making volumes | (union)
surf_sphere1 = openmc.Sphere(r=10.0)
surf_sphere2 = openmc.Sphere(r=20.0)
surf_cy = openmc.ZCylinder(r=5) surf_up_zp = openmc.ZPlane(z0=30)
surf_low_zp = openmc.ZPlane(z0=-30)
hollow_sph = ( +surf_sphere1 & -surf_sphere2)
capped_cy = ( -surf_cy & -surf_up_zp & +surf_low_zp)
cell = openmc.Cell(region = hollow_sph | capped_cy)
cell_sphere.fill = steel
Making geometry
Making volumes & (intersection)
surf_sphere1 = openmc.Sphere(r=10.0)
surf_sphere2 = openmc.Sphere(r=20.0)
surf_cy = openmc.ZCylinder(r=5) surf_up_zp = openmc.ZPlane(z0=30)
surf_low_zp = openmc.ZPlane(z0=-30)
hollow_sph = ( +surf_sphere1 & -surf_sphere2)
capped_cy = ( -surf_cy & -surf_up_zp & +surf_low_zp)
cell = openmc.Cell(region = hollow_sph & capped_cy)
cell_sphere.fill = steel
Making geometry
Making volumes ~ (complement)
surf_sphere1 = openmc.Sphere(r=10.0)
surf_sphere2 = openmc.Sphere(r=20.0)
surf_cy = openmc.ZCylinder(r=5) surf_up_zp = openmc.ZPlane(z0=30)
surf_low_zp = openmc.ZPlane(z0=-30)
hollow_sph = ( +surf_sphere1 & -surf_sphere2)
capped_cy = ( -surf_cy & -surf_up_zp & +surf_low_zp)
cell = openmc.Cell(region = hollow_sph ~ capped_cy)
cell_sphere.fill = steel


Task 1
Cross section plotting
Plot reactions for isotopes, elements or materials


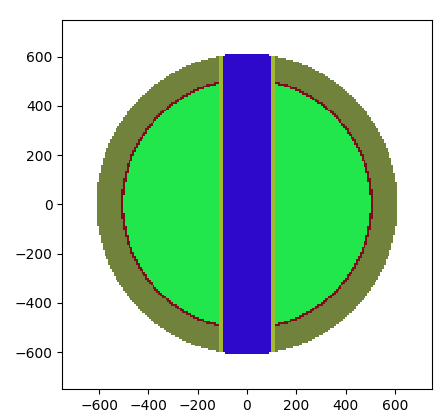
Task 2
Building and visualizing the model geometry
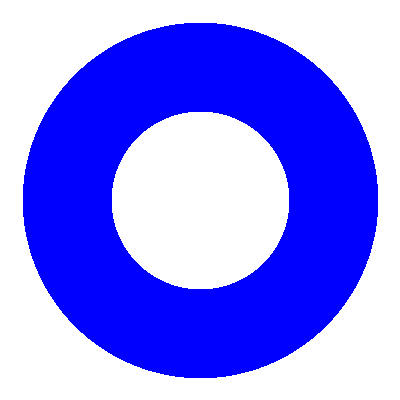
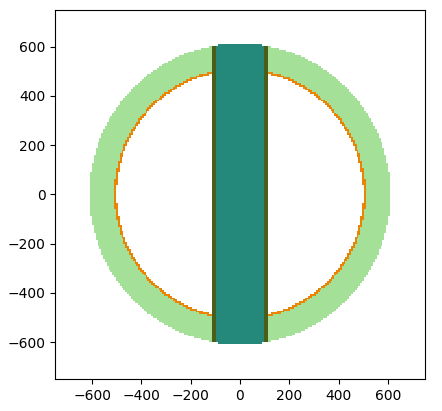
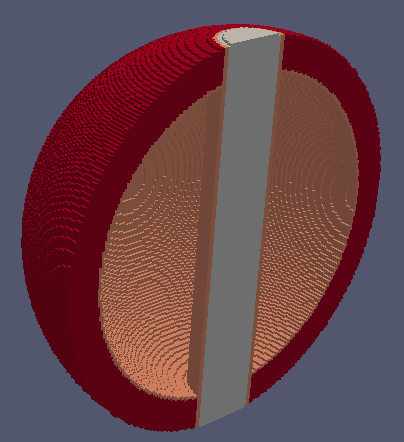
Construct geometry and view it in 2D or 3D


Task 3
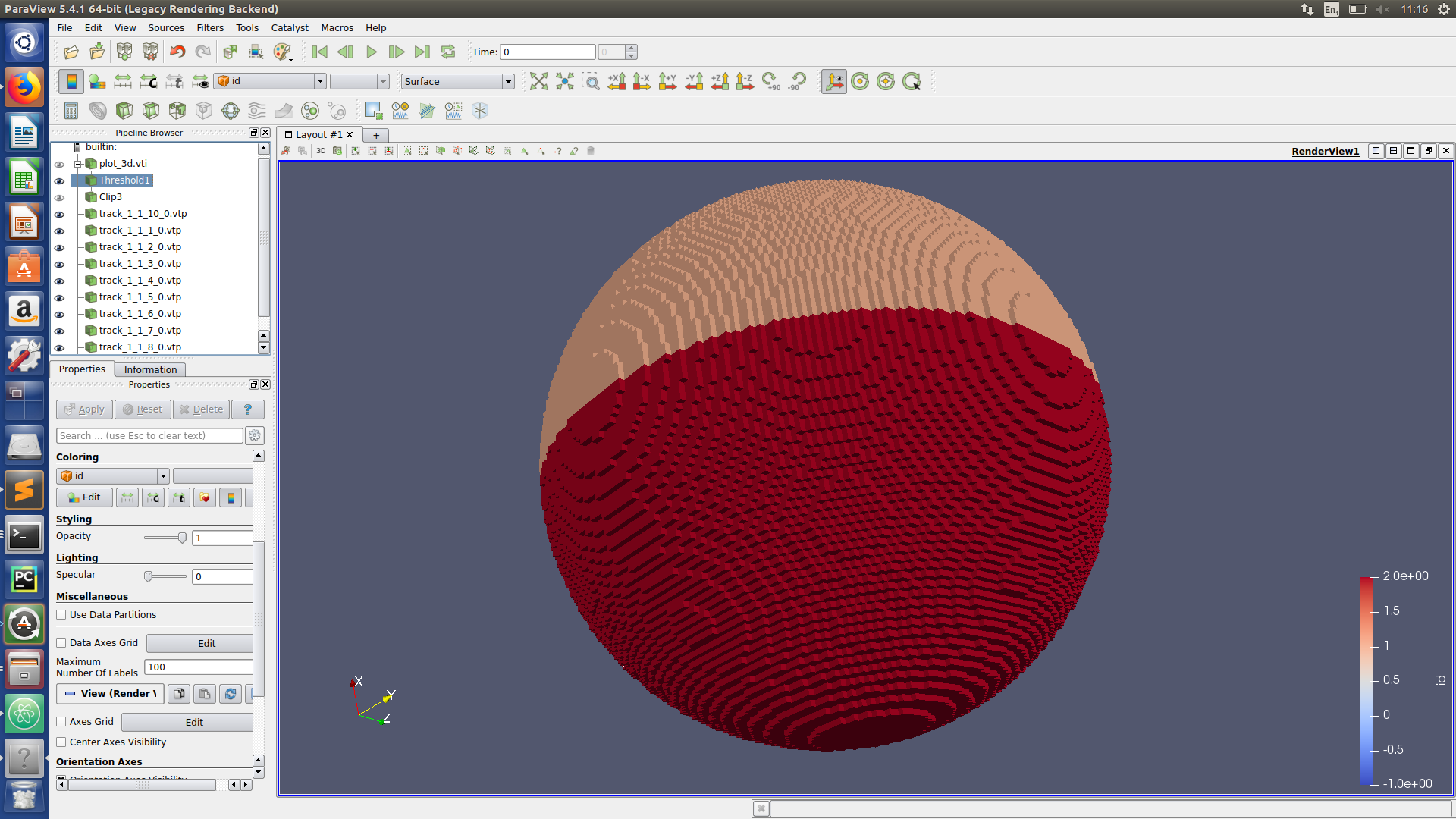
Visualizing neutron tracks
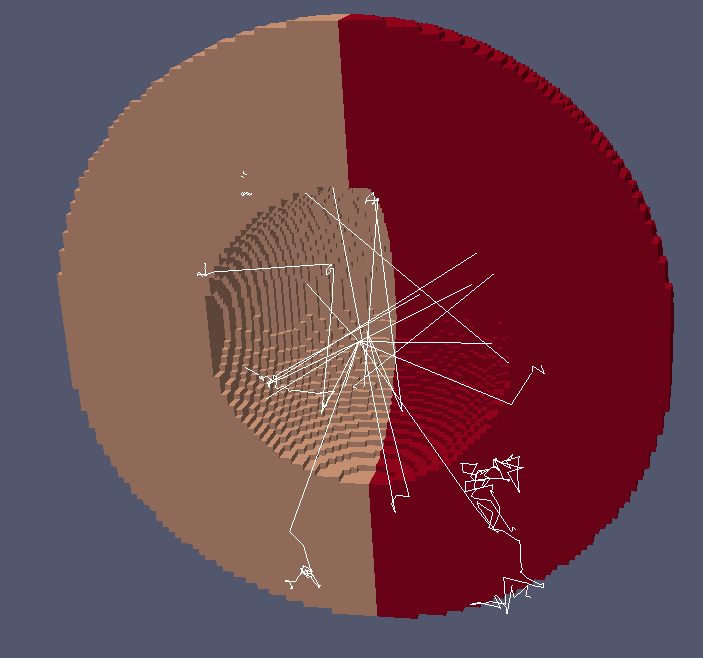
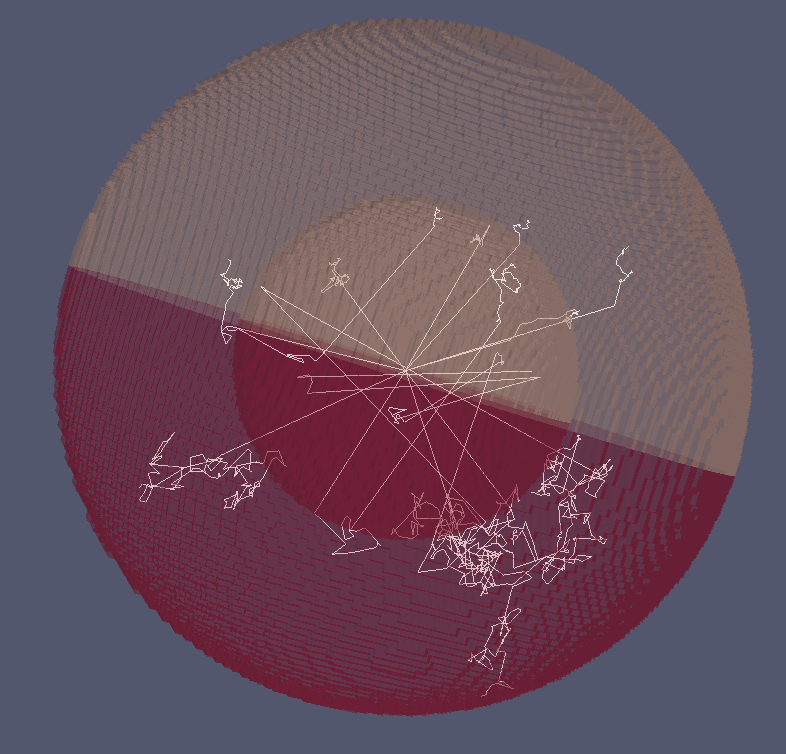


Paraview hints




Paraview hints
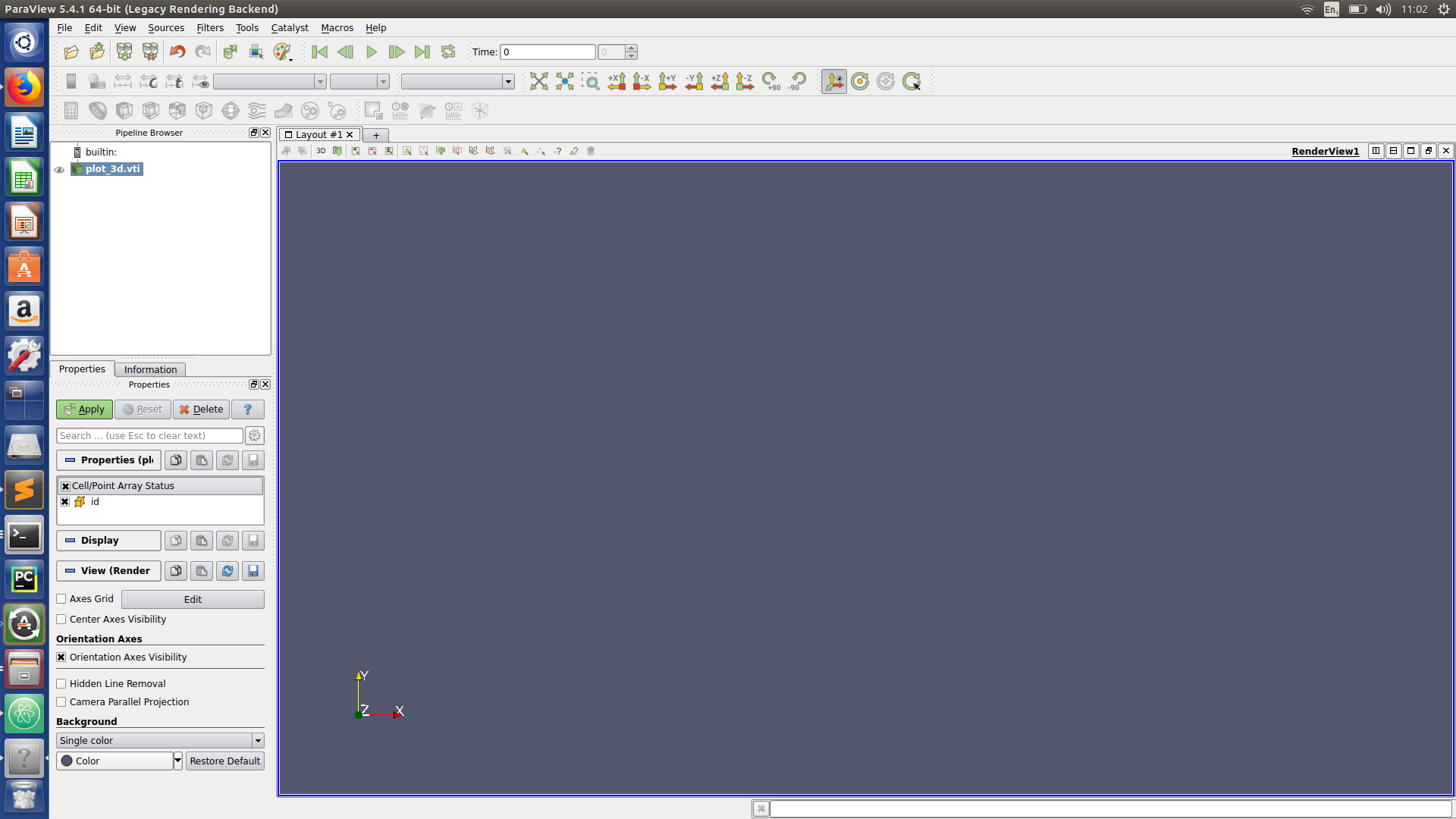


Paraview hints
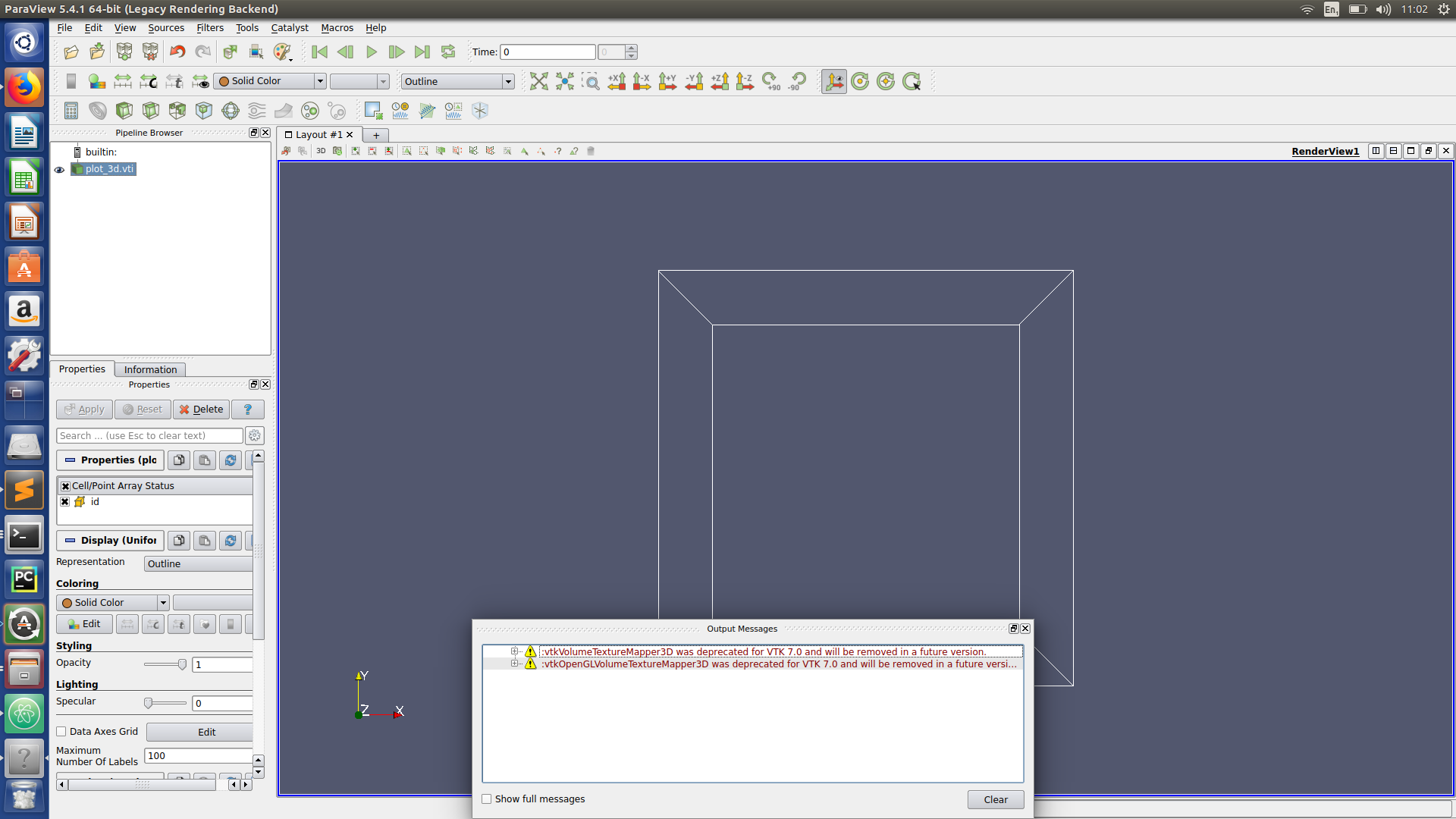


Paraview hints
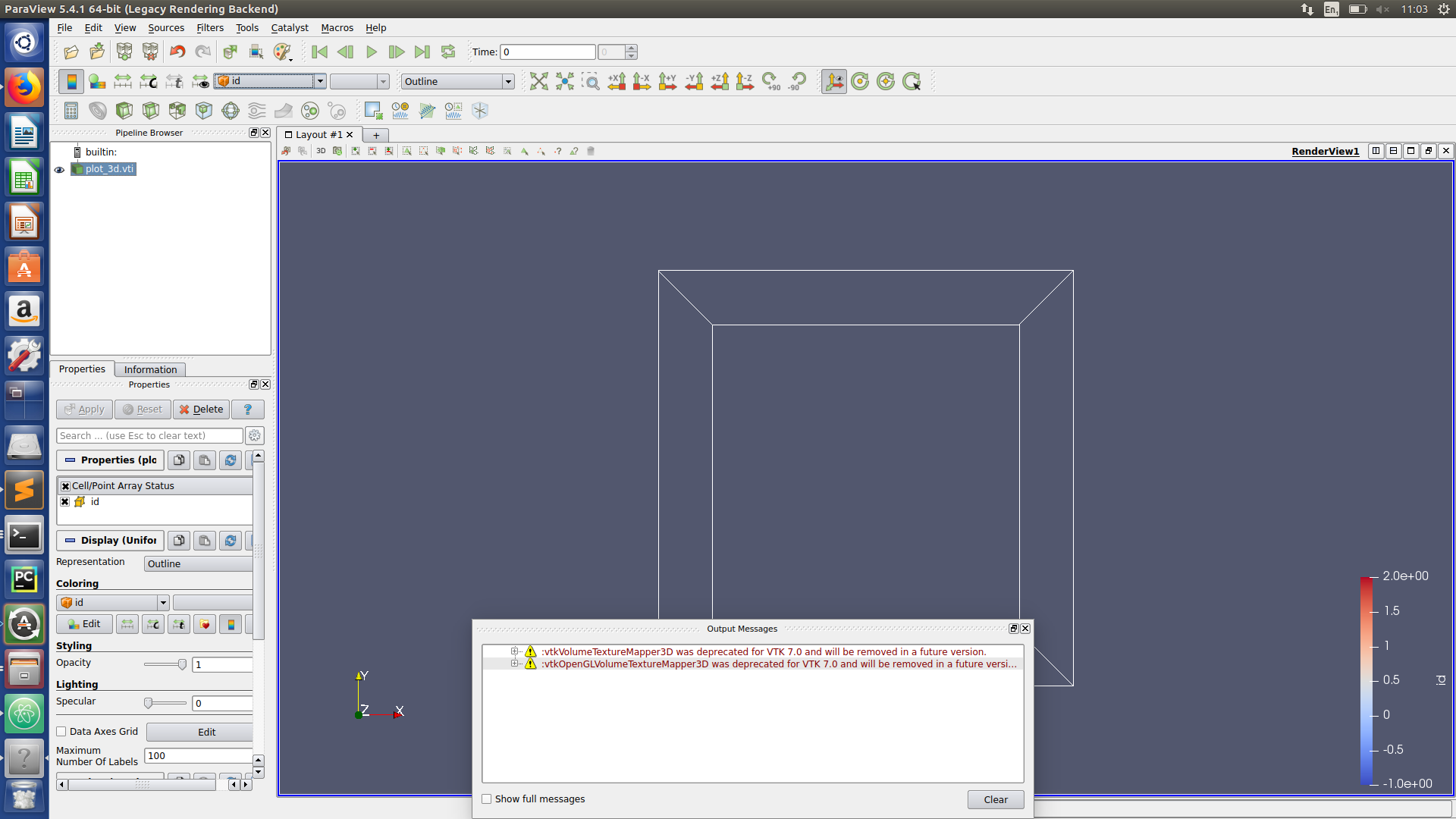


Paraview hints
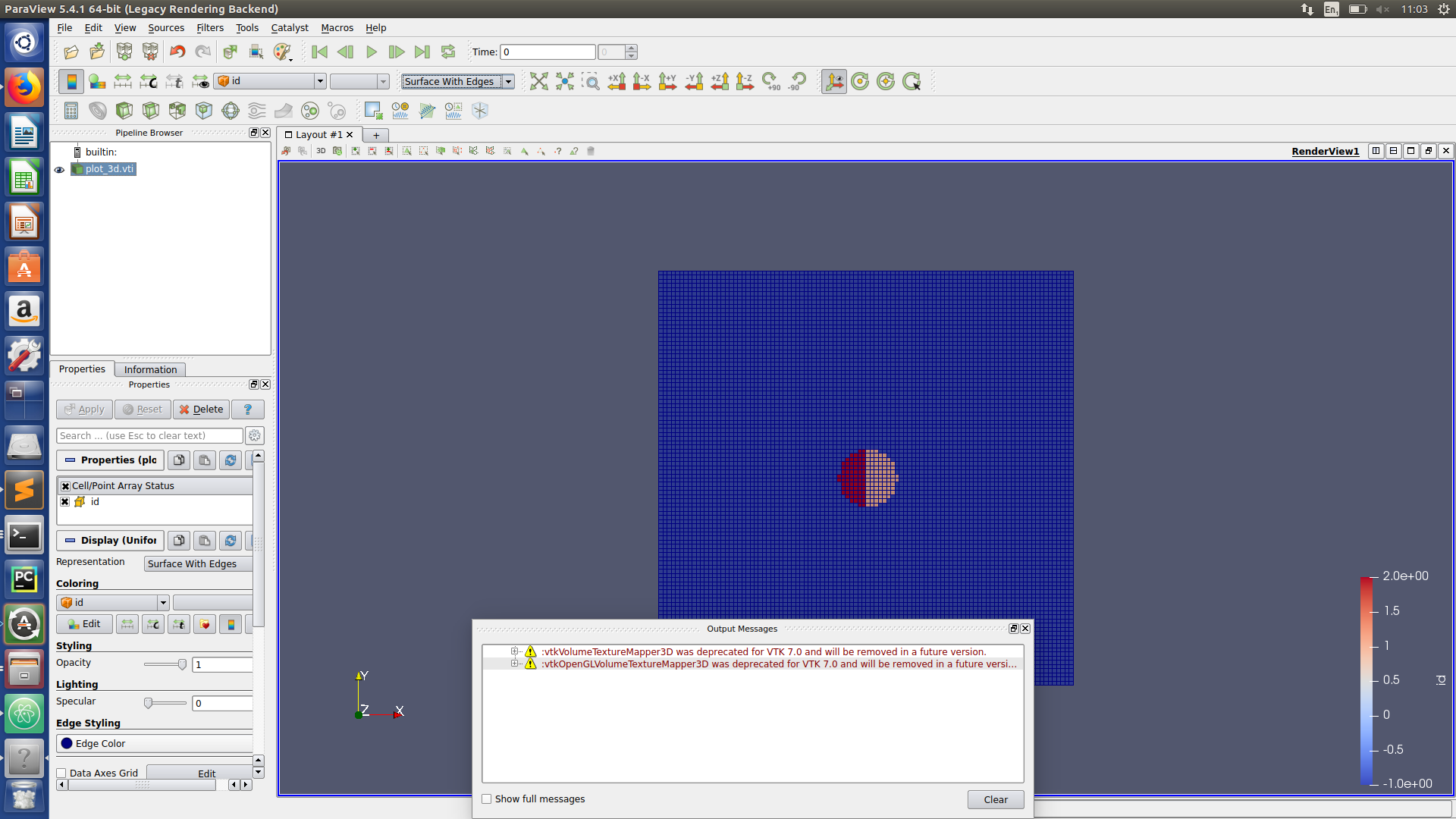


Paraview hints
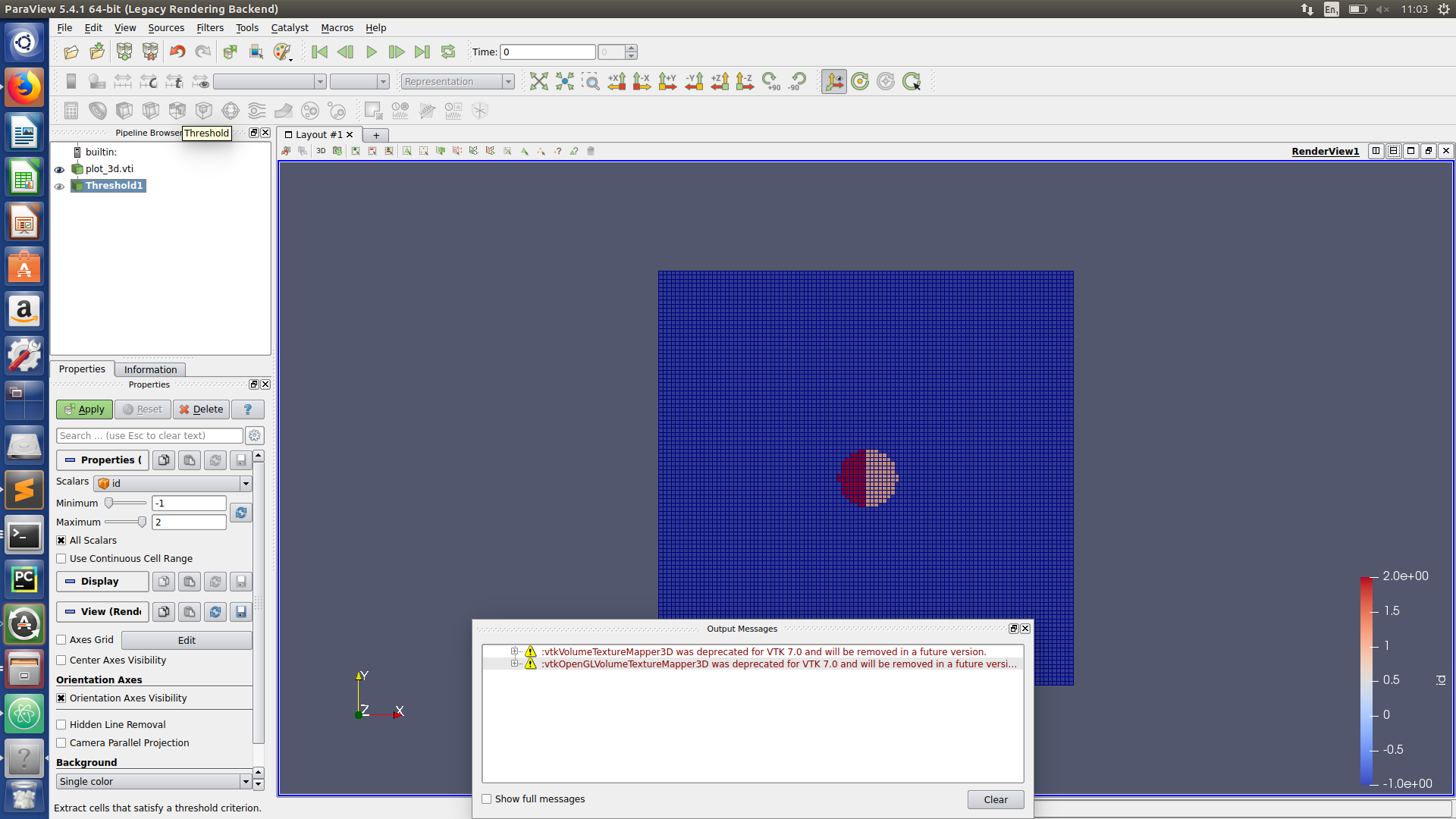


Paraview hints
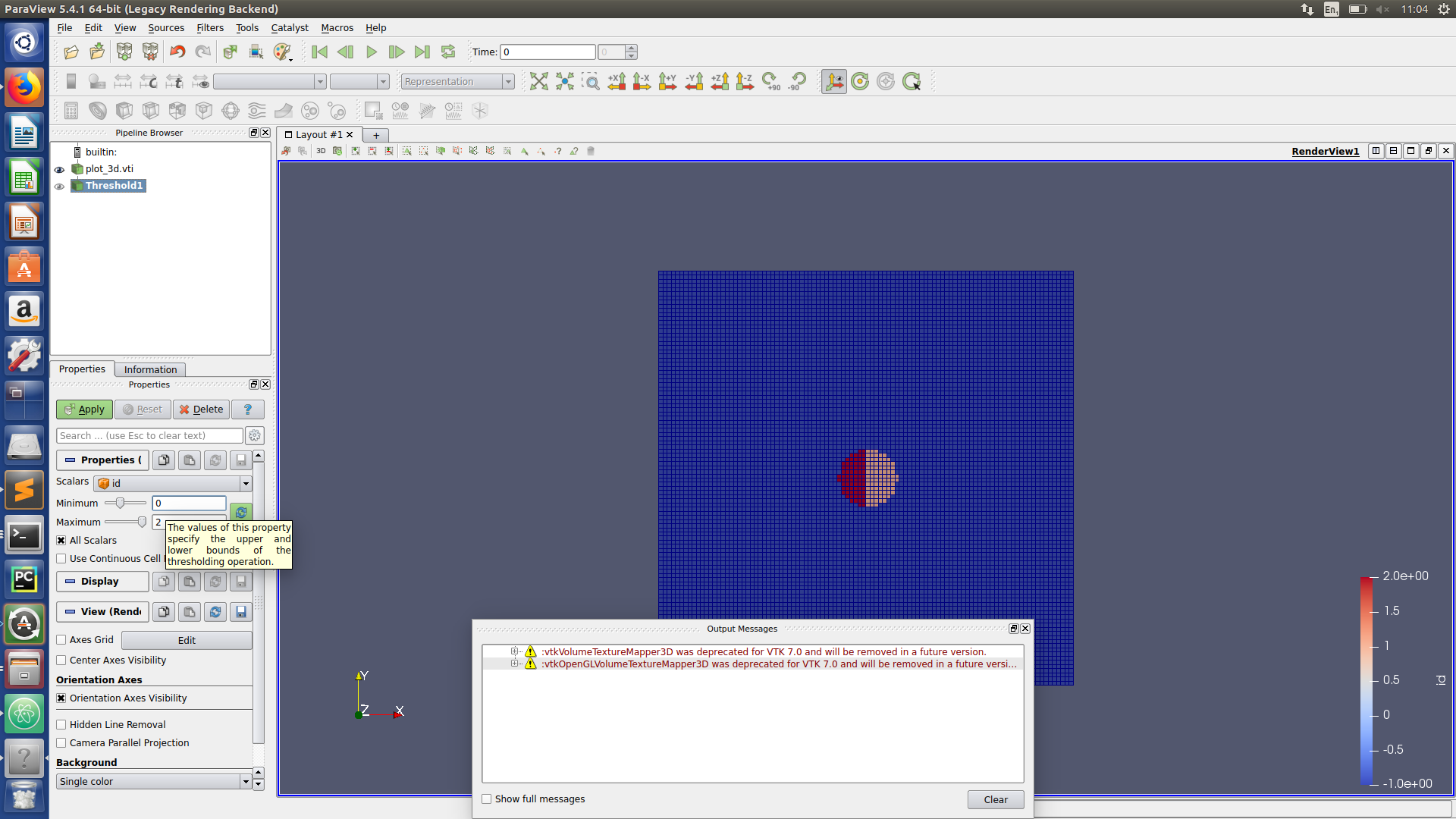


Paraview hints


Paraview hints


Paraview hints


Paraview hints


Paraview hints
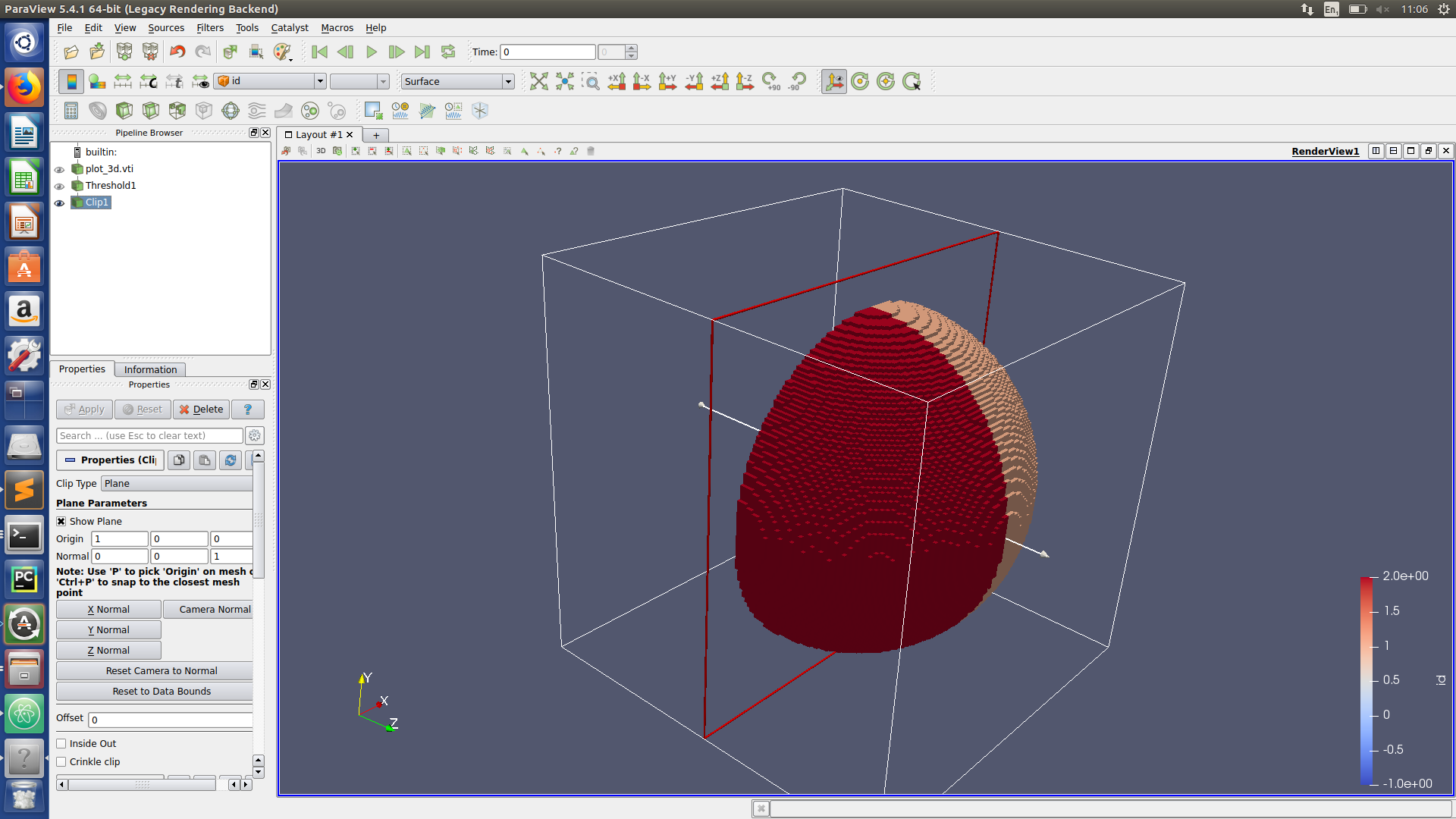


Paraview hints
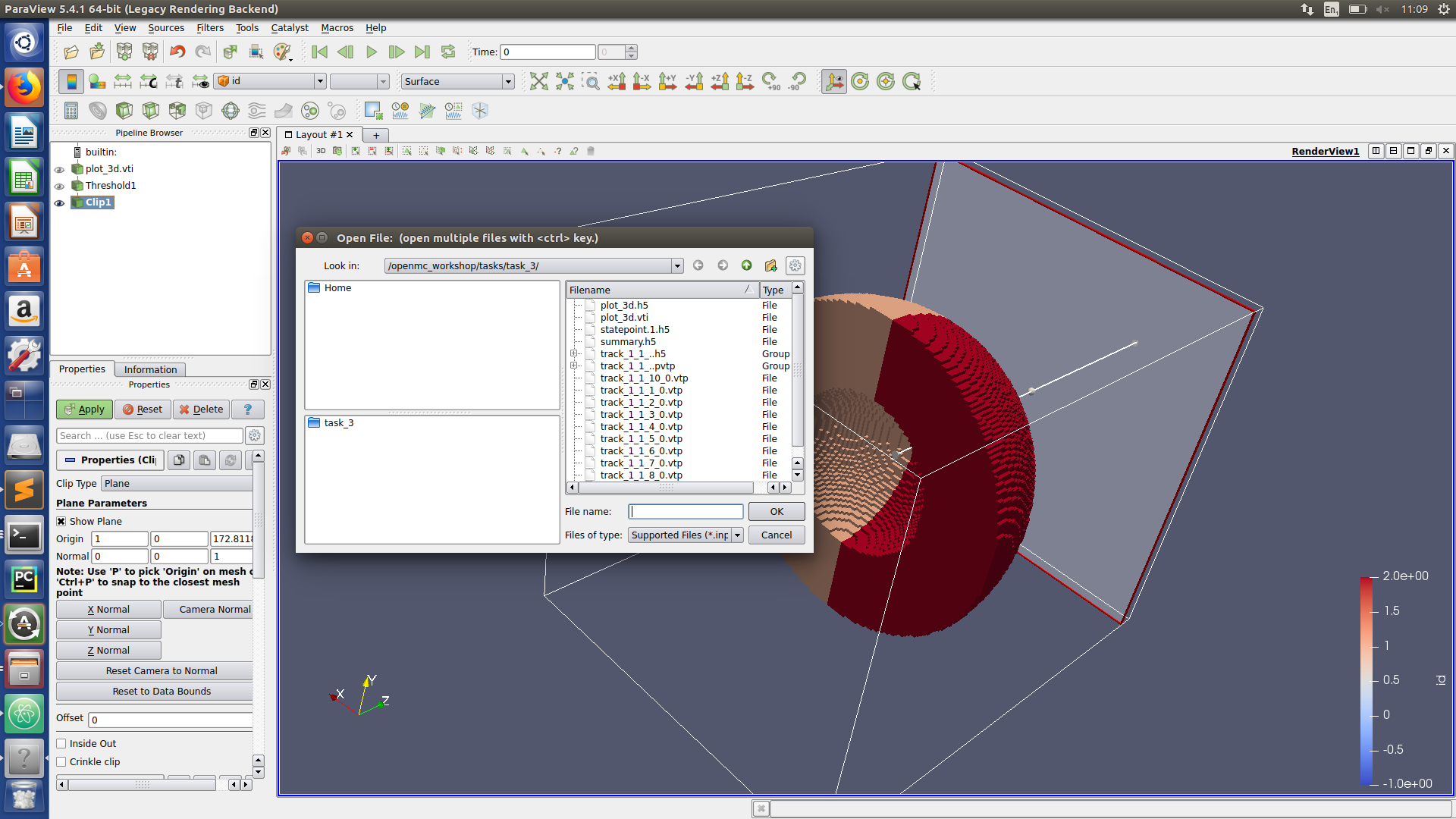


Paraview hints
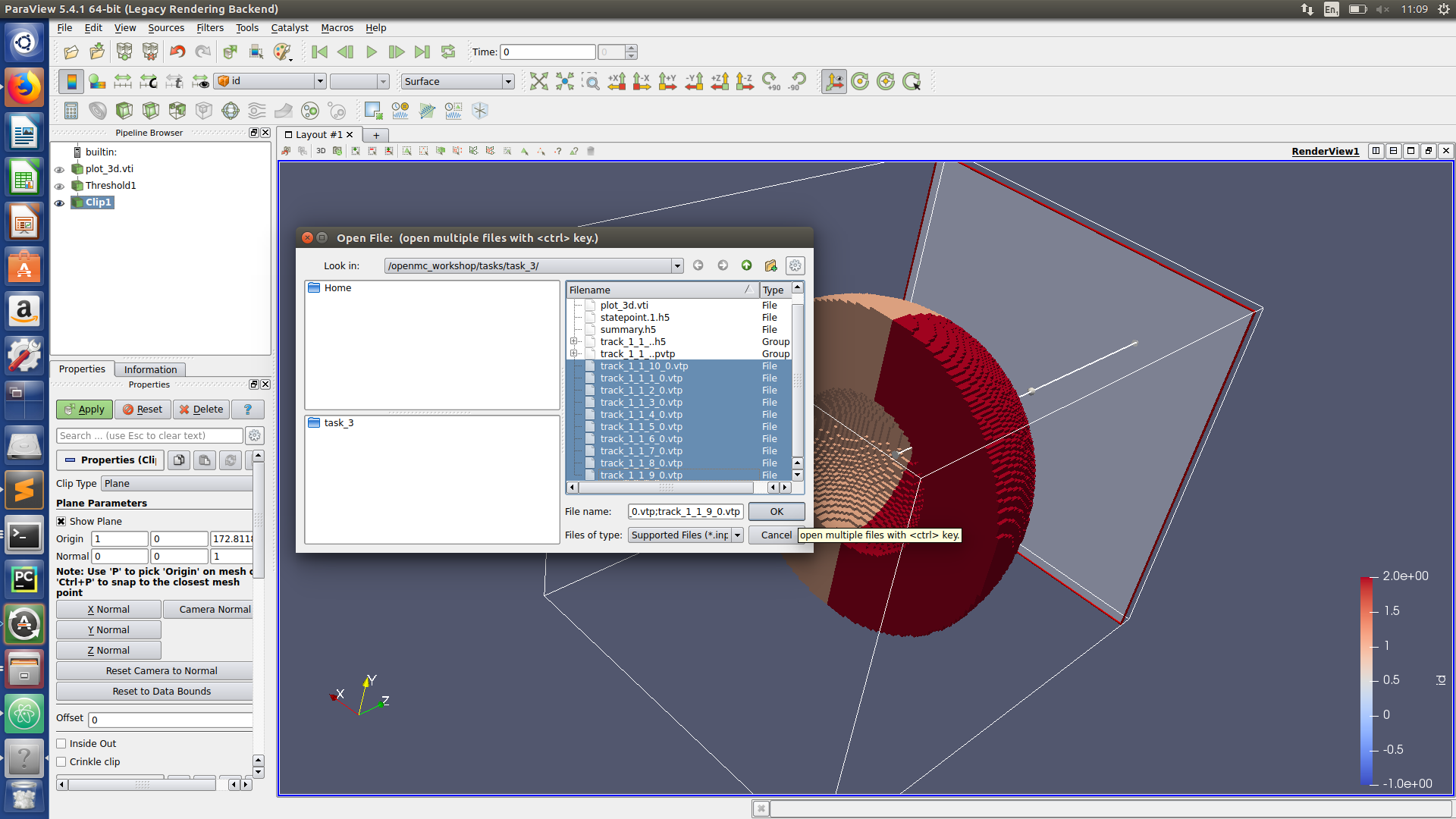


Paraview hints
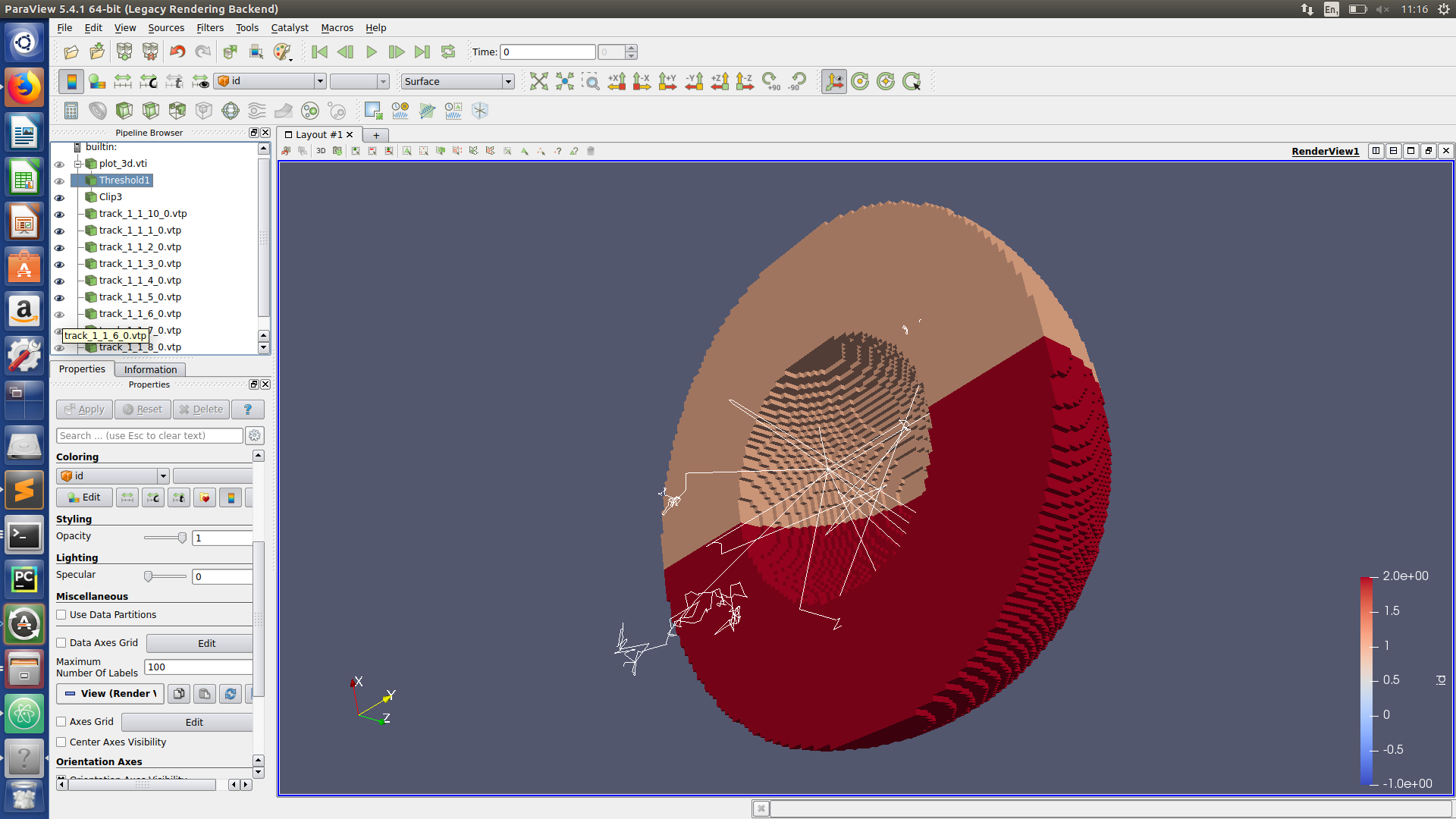


Paraview hints


Paraview hints
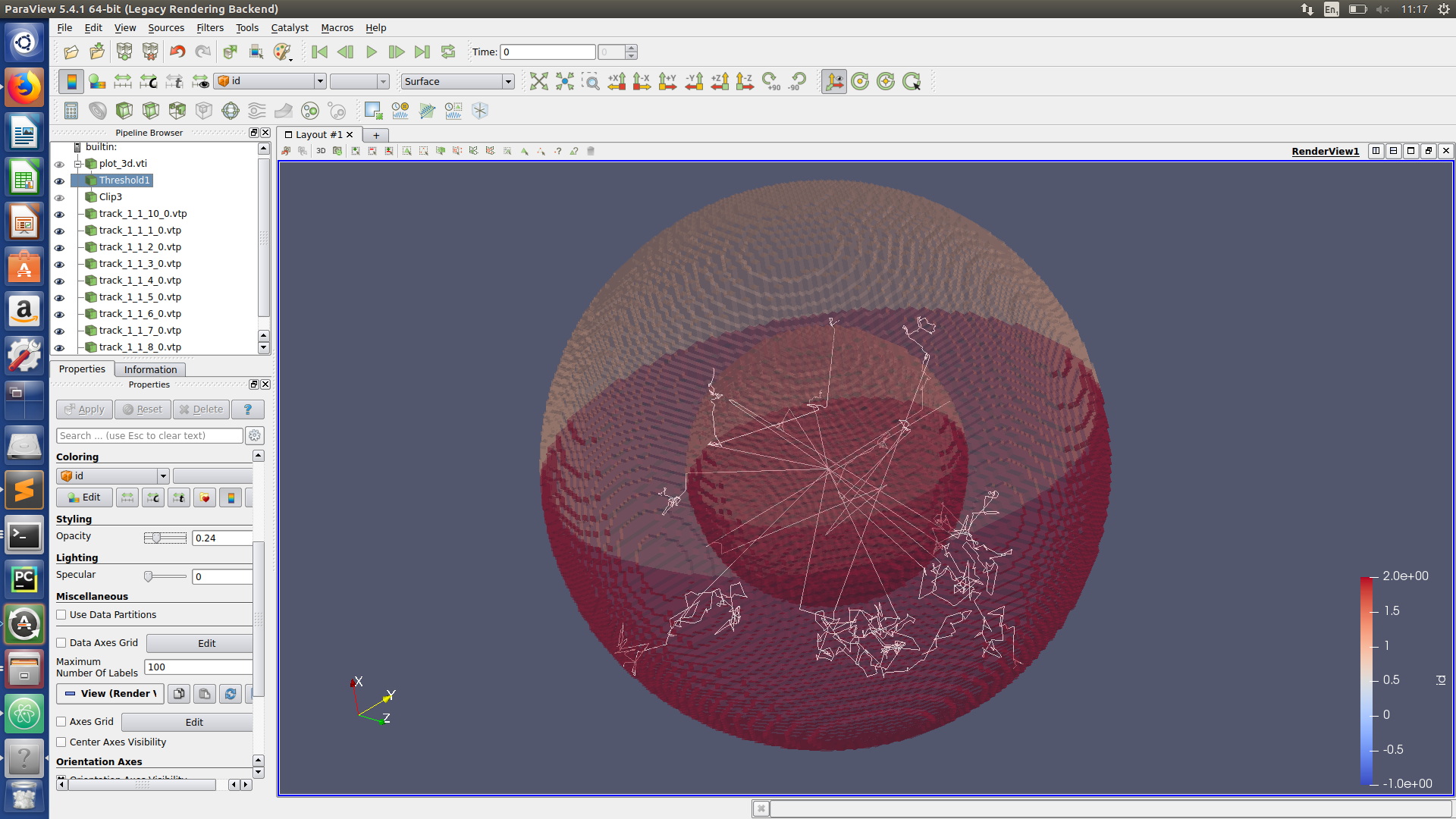


Task 3
Visualizing neutron tracks




Task 4
Finding the neutron flux
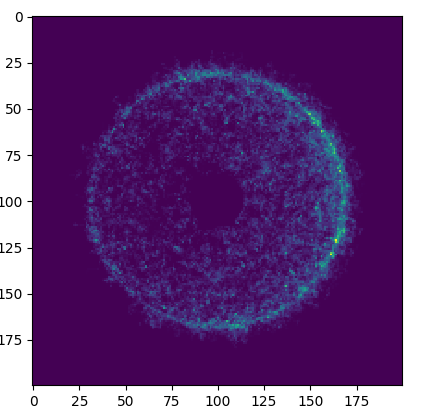
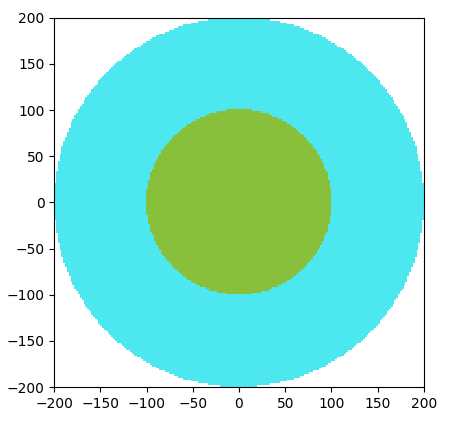
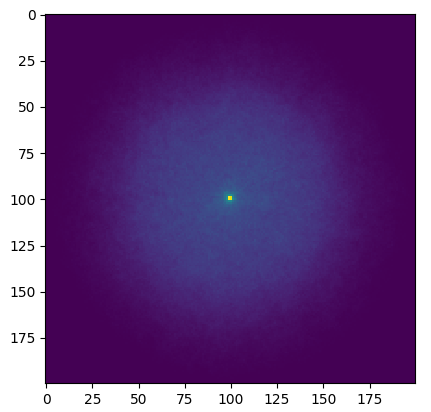
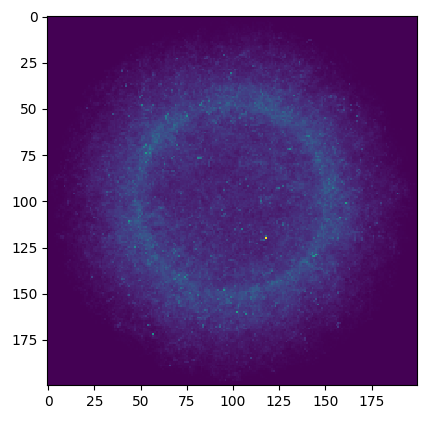








Task 5
Finding the neutron spectra


Task 6
Finding the tritium production


Task 7
Finding the neutron damage
The DPA tally will just produce a single number


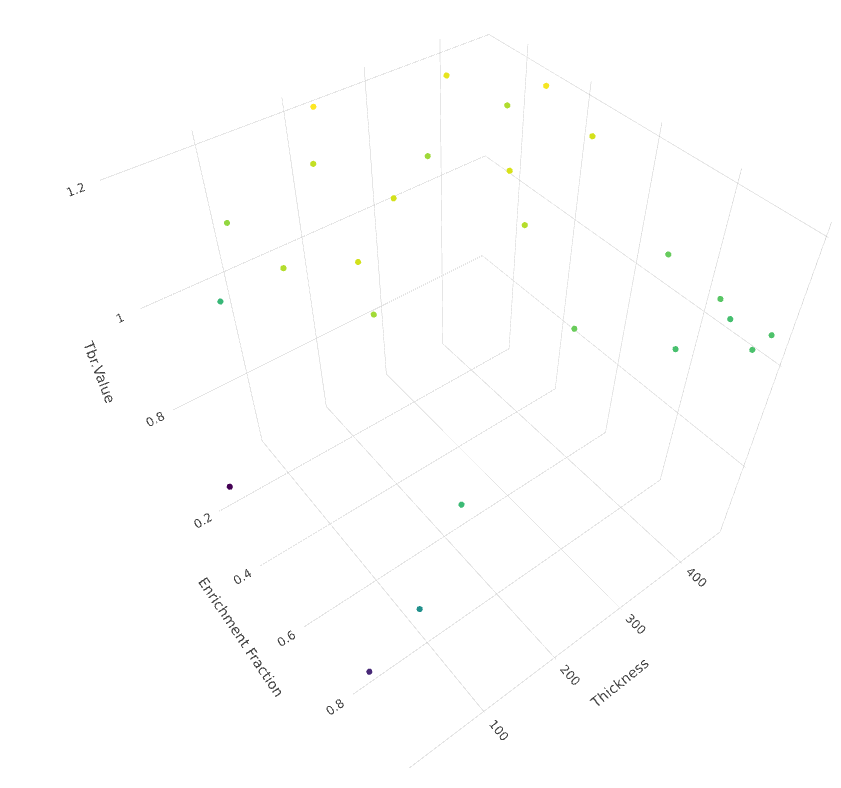
Task 8
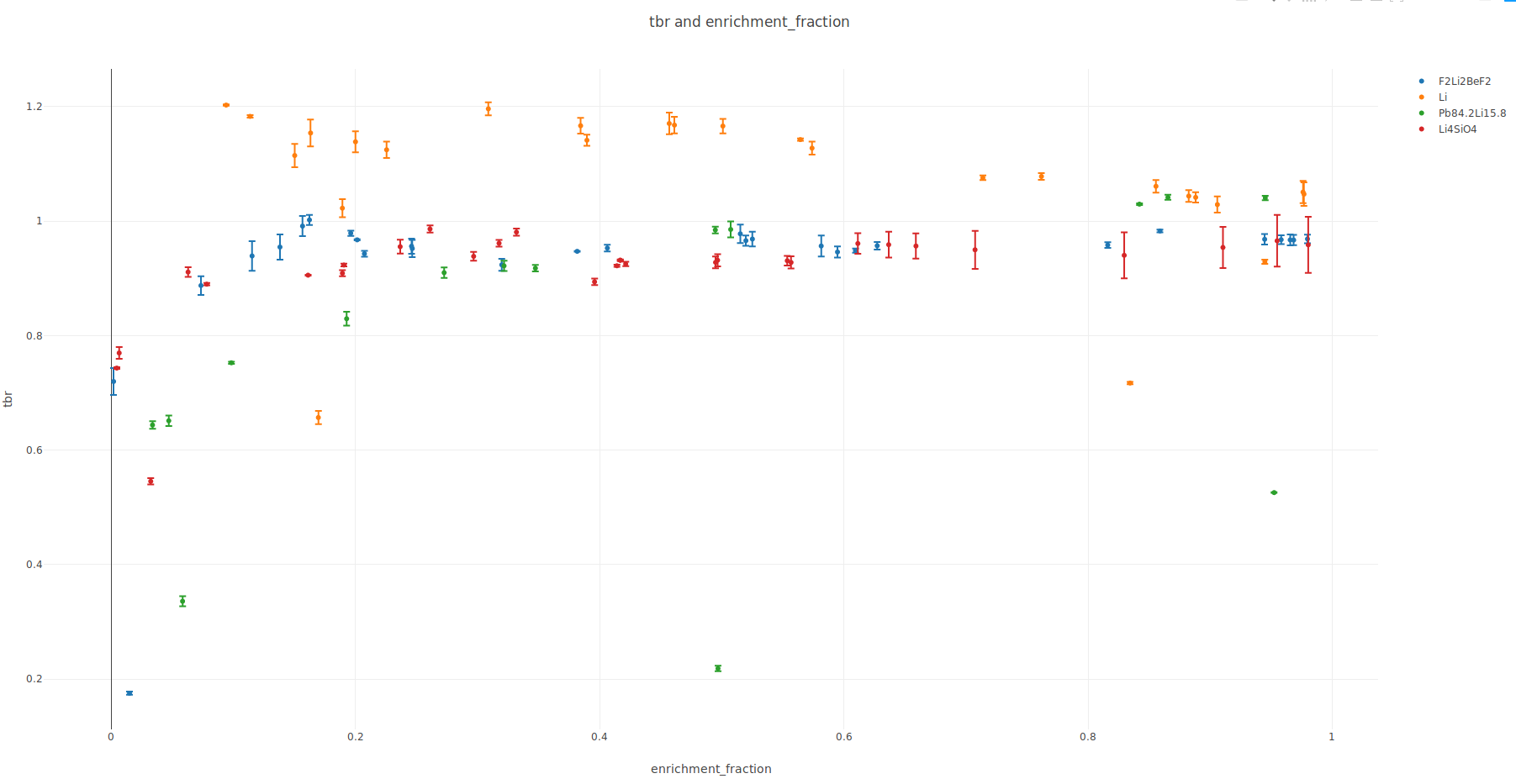
Optimize a breeder blanket
for tritium production
Neutronics workshop
By Jonathan Shimwell
Neutronics workshop
Fusion relevant with OpenMc
- 2,108


