State management with Vuex
Divya Tagtachian
Developer Experience Engineer

@shortdiv
Before we begin
Repo:
Code Tools:
Vue Dev Tools
Code Sandbox
Codepen
VS Code
github.com/shortdiv/frontend-masters-vuex
What we'll cover
-
The Fundamentals of Vuex
-
Vuex + Vue (SFCs)
-
Vuex + Vue Router
-
Composing Vuex
-
Vuex Modules
-
Vuex Plugins
-
Normalizing State
Principles of State Management
What is State?
State is a condition of an object stored as data.



Get items from vending machine
x 100


Stock items in a vending machine


Bag of Cookies
Inventory
Vending Machine
Supplier
emit
emit
emit
props
props
Passing State in Vue
-
Props
-
Events
Props are custom attributes you can register on a component. When a value is passed to a prop attribute, it becomes a property on that component instance.
Events are used for communication between components as opposed to communication between DOM nodes.


























Events












Props


Fix vending machine




















Events
repair
restock





















Separation of Concerns






Enter: Vuex

Centralized data store for shared data, logic, and methods, with rules ensuring that the state can only be mutated in a predictable fashion.
What is Vuex?
Vue Components
Actions
State
Mutations
Backend API
Devtools
Dispatch
Commit
Mutate
Render
Vuex
single source of truth for store state
State
Actions
Mutations
Getters
similar to mutations but it commits mutations
the only way to change store state
to compute derived state based on store state.
(is cached)
(can only be sync)
(can be async)
Vending Machine Stock Counter
Vending Machine Stock Counter
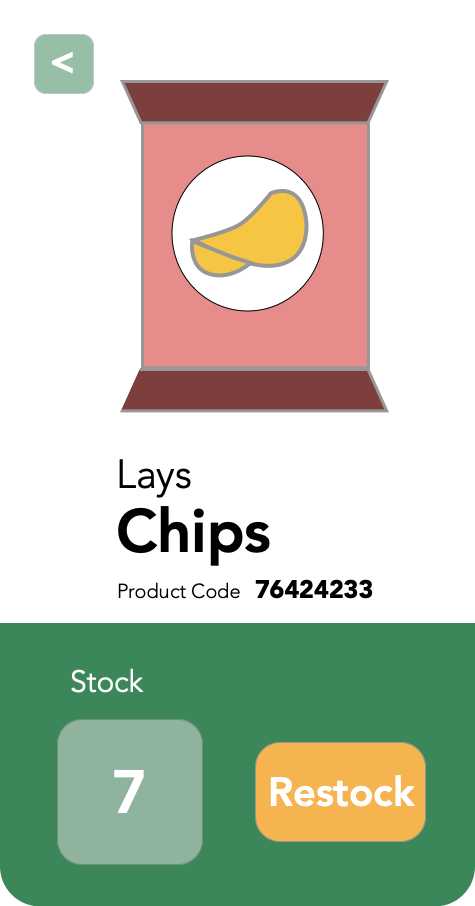
State
Action +
Mutation
new Vue({
el: "#vue",
data() {
return {
supply: 40
}
},
methods: {
dispense() {
this.supply--
},
restock() {
this.supply = 40
}
},
template: `
<div>
<p class="supply">{{ supply }}</p>
<div class="actions">
<button @click="dispense">+</button>
<button @click="restock">-</button>
</div>
</div>
`,
})Methods
Vuex Store
State
Vuex Store
Let's add Vuex!
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
actions: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {}
})
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
actions: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {}
})
new Vue({
el: "#vue",
store: store,
data() {
return {
supply: 40
}
},
methods: {
dispense() {
this.supply--
},
restock() {
this.supply = 40
}
},
template: `
<div>
<p class="supply">{{ supply }}</p>
<div class="actions">
<button @click="dispense">+</button>
<button @click="restock">-</button>
</div>
</div>
`,
})const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
actions: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {}
})
new Vue({
el: "#vue",
store: store,
data() {
return {
supply: 40
}
},
methods: {
dispense() {
this.supply--
},
restock() {
this.supply = 40
}
},
template: `
<div>
<p class="supply">{{ supply }}</p>
<div class="actions">
<button @click="dispense">+</button>
<button @click="restock">-</button>
</div>
</div>
`,
})// Convert to Vuex Store //
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
supply: 40
},
actions: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {}
})
new Vue({
el: "#vue",
store: store,
computed: {
supply() {
return this.$store.state.supply
}
},
data() {
return {
supply: 40
}
},
methods: {
dispense() {
this.supply--
},
restock() {
this.supply = 40
}
},
template: `
<div>
<p class="supply">{{ supply }}</p>
<div class="actions">
<button @click="dispense">+</button>
<button @click="restock">-</button>
</div>
</div>
`,
})1
2
3
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
supply: 40
},
actions: {
dispense(context) {
return context.commit('dispense')
}
},
getters: {},
mutations: {
dispense(state) {
state.supply--
}
}
})
new Vue({
el: "#vue",
store: store,
computed: {
supply() {
return this.$store.state.supply
}
},
methods: {
dispense() {
this.supply--
this.$store.dispatch('dispense')
},
restock() {
this.supply = 40
}
},
template: `
<div>
<p class="stock">{{ stock }}</p>
<div class="actions">
<button @click="dispense">+</button>
<button @click="restock">-</button>
</div>
</div>
`,
})1
2
3
4
Exercise Time!
Convert the dispense method to using state and actions in a vuex store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
supply: 40
},
actions: {
...
restock(context) {
return context.commit('restock')
}
},
getters: {},
mutations: {
...
restock(state) {
state.supply = 40
}
}
})
new Vue({
el: "#vue",
methods: {
...
restock() {
this.supply++
this.$store.dispatch('restock')
}
},
template: `
<div>
<p class="supply">{{ supply }}</p>
<div class="actions">
<button @click="dispense">+</button>
<button @click="restock">-</button>
</div>
</div>
`,
})1
2
3
4
Exercise Time!
https://codepen.io/shortdiv/pen/rNVjzoe
Convert the restock method to using state and actions in a vuex store
Vuex Part 1
By shortdiv
Vuex Part 1
- 1,560



