Java part 2
Java - Interfaces
- Reference type
- Collection of methods
- Contains only behaviour of object not attributes
- Countless methods
- .java .class files similar to Class
- Follows package flow
- Cannot be instantiated
- No constructors
- Abstract methods
- No instance fields
- Class implements it. not extends
- Can extend multiple Instances
Java - Collections
What is Collection?
- A group of objects collected in single unit
- Provides readymade architecture.
- Represents a set of classes and interfaces.
- optional.
- Has Interfaces and its implementations, i.e., classes
- Has Algorithms
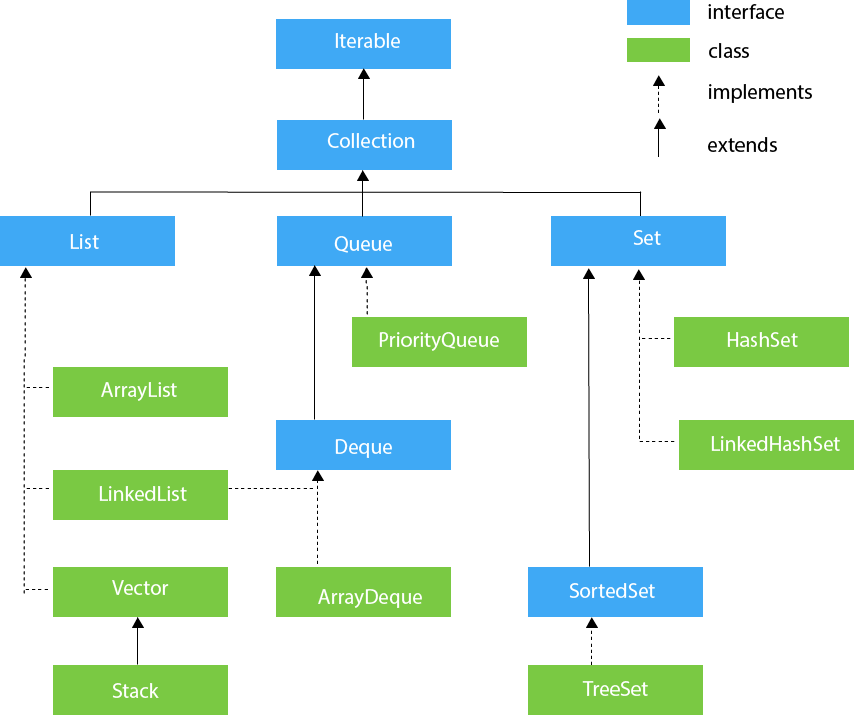
Java - Collections
| No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | public boolean add(E e) | It is used to insert an element in this collection. |
| 2 | public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | It is used to insert the specified collection elements in the invoking collection. |
| 3 | public boolean remove(Object element) | It is used to delete an element from the collection. |
| 4 | public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) | It is used to delete all the elements of the specified collection from the invoking collection. |
| 5 | default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) | It is used to delete all the elements of the collection that satisfy the specified predicate. |
| 6 | public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) | It is used to delete all the elements of invoking collection except the specified collection. |
| 7 | public int size() | It returns the total number of elements in the collection. |
| 8 | public void clear() | It removes the total number of elements from the collection. |
| 9 | public boolean contains(Object element) | It is used to search an element. |
| 10 | public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) | It is used to search the specified collection in the collection. |
| 11 | public Iterator iterator() | It returns an iterator. |
| 12 | public Object[] toArray() | It converts collection into array. |
| 13 | public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) | It converts collection into array. Here, the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
| 14 | public boolean isEmpty() | It checks if collection is empty. |
| 15 | default Stream<E> parallelStream() | It returns a possibly parallel Stream with the collection as its source. |
| 16 | default Stream<E> stream() | It returns a sequential Stream with the collection as its source. |
| 17 | default Spliterator<E> spliterator() | It generates a Spliterator over the specified elements in the collection. |
Java - Generics
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new Integer(2));
list.add("a String");Integer integer = (Integer) list.get(0);
String string = (String) list.get(1);List<String> strings = new ArrayList<String>();
strings.add("a String");
String aString = strings.get(0);List<String> strings = new ArrayList<String>();
//... add String instances to the strings list
for(String aString : strings)
System.out.println(aString);Java - Exceptions
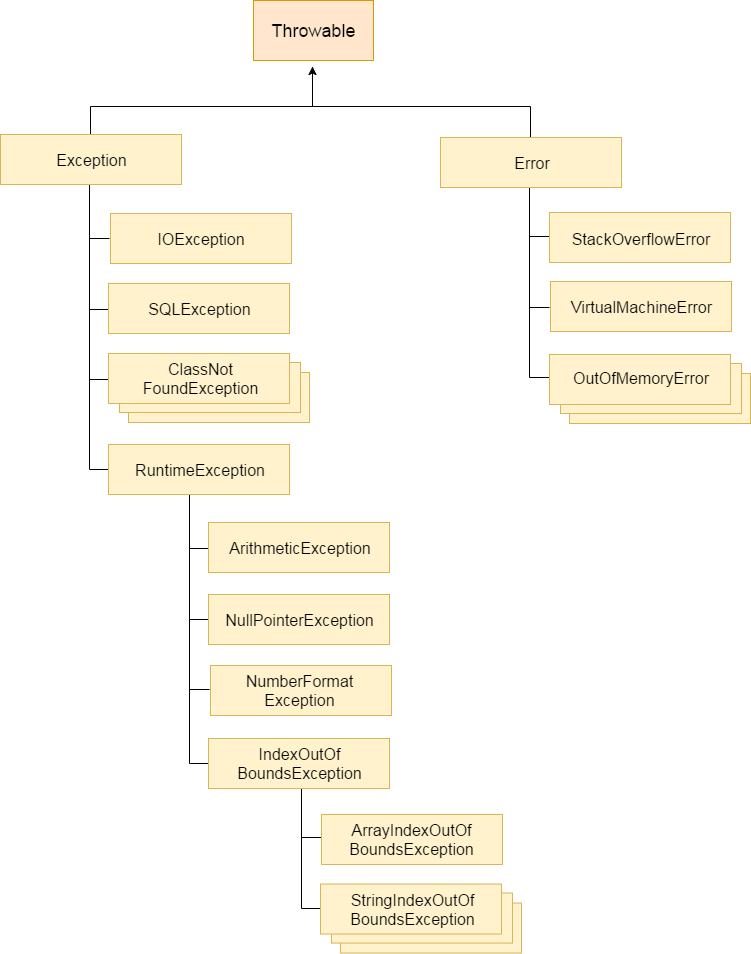
- try
- catch
- finally
- throw
- throws
Java - File I/O



Java - Date Time

Java - Multi Threading




multitasking
multithreading

Life cycle of a thread
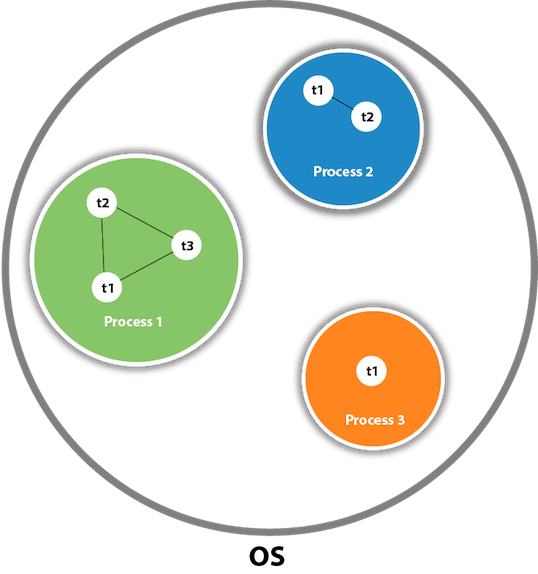
Java - Multi Threading

Life cycle of a thread

JDBC

Components of JDBC
- Driver Manager
- Driver
- Connection
- Statement
- Result Set
- SQL Exception
Java - Localization (L10N)
Create an application that adapts to a specific language and region by adding locale-specific text and component.
Information differing locale-wise:
- Messages
- Dates
- Times
- Numbers
- Currencies
- Measurements
- Phone Numbers
- Postal Addresses
- Labels on GUI components etc.
Day 2 Java
By shraddheya shrivastava
Day 2 Java
Interfaces, Collections, Generics, Exceptions, Deployment, Date/Time API, I/O, Concurrency, Parallelism, The JDBC API and Localization
- 172



