Phylodynamics
How pathogens
evolve and spread
CZI journal club 2019-03-28




Metagenomics, intrahost evolution
Phylodynamics,
genomic epidemiology











car

cat
Reconstructing evolution is a lot like "telephone"
zebra



....
car
cat
Reconstructing evolution is a lot like "telephone"
zebra




Reconstructing evolution is a lot like "telephone"






ACG
AGG
AGT
Evolution provides context
to viral outbreaks
Where did this virus come from?
When did interesting traits change?




ACG
AGG
AGT
A note about sampling




ACG
AGG
AGT
Most models make strong assumptions about sampling (e.g., sparse, equal sampling or complete sampling)
A note about sampling
Context is everything.
Tree clustering is NOT necessarily direct transmission.

-
Evolve quickly
-
Small, simple genomes
-
Some classes: only vertical gene transfer
-
Analytical models,
prediction and epidemiological inference


-
Evolve more slowly
-
Larger, complex genomes
-
Horizontal gene transfer (reticulate evolutionary history)
-
Descriptive models, retrospective
Sidebar:
"Erm, did you forget all the other pathogens?"
Core concepts
& types of questions
Molecular Clock
Ancestral state reconstruction
Demographic history
Molecular clocks
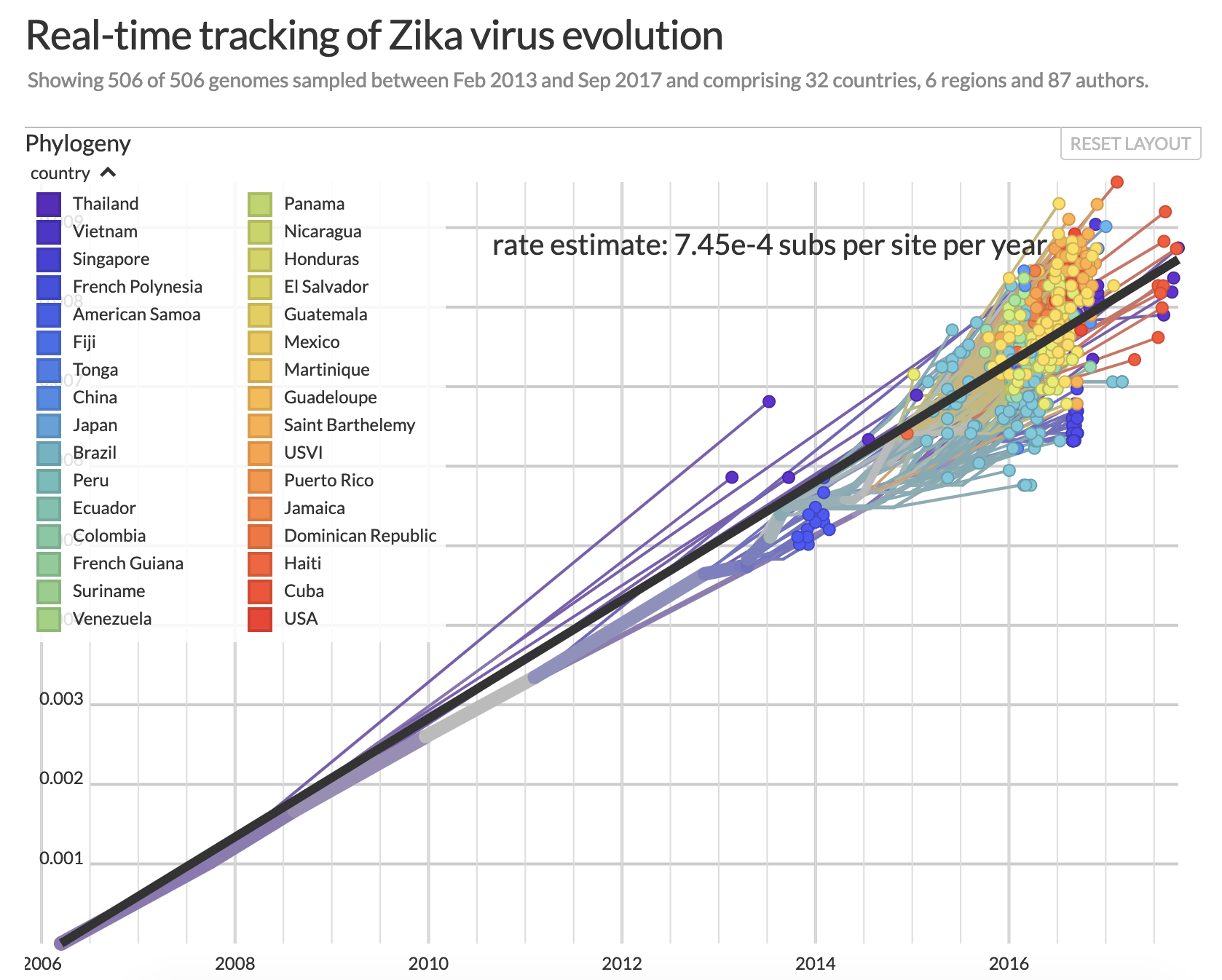
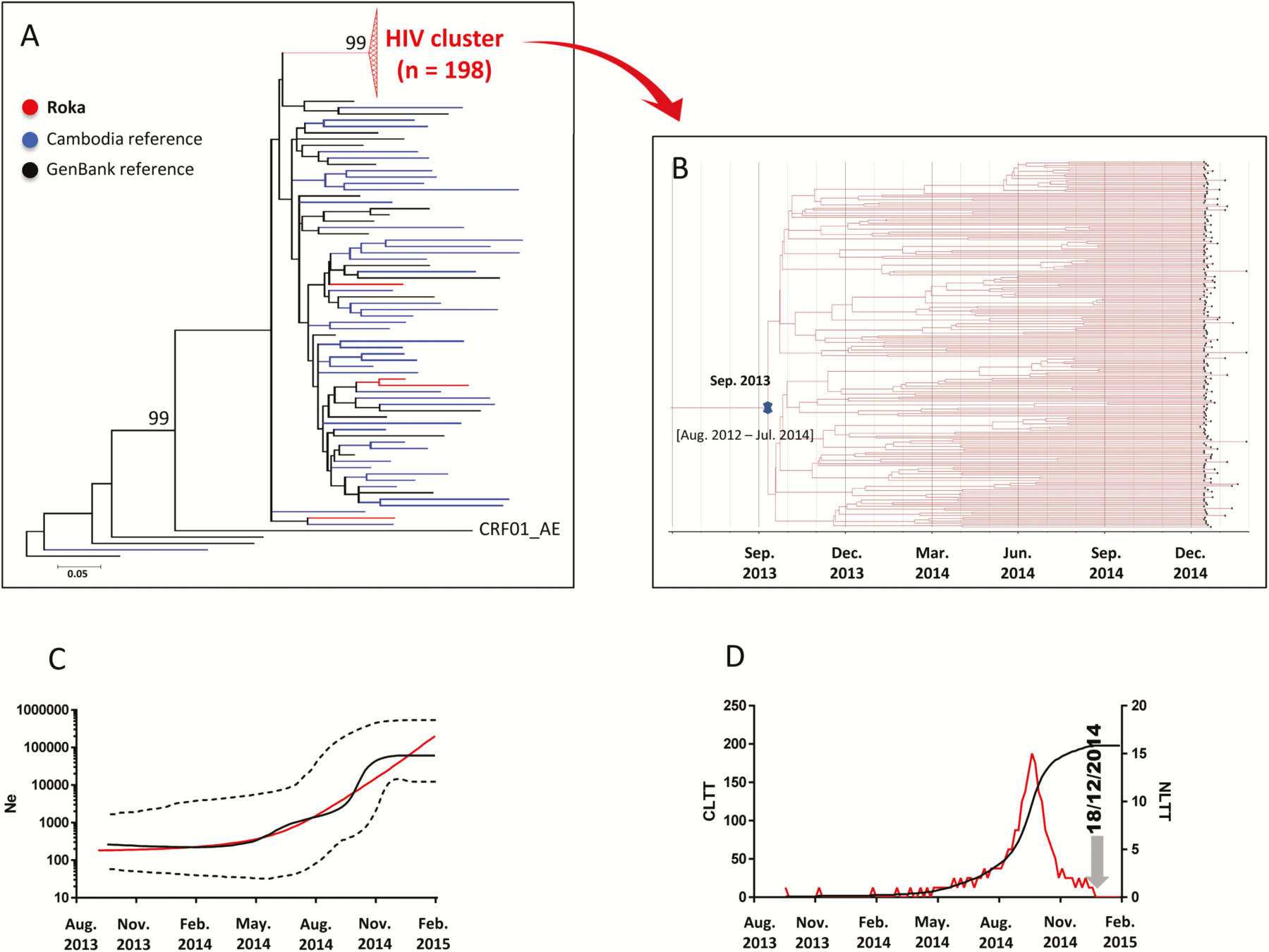
Example: dating epidemiological events
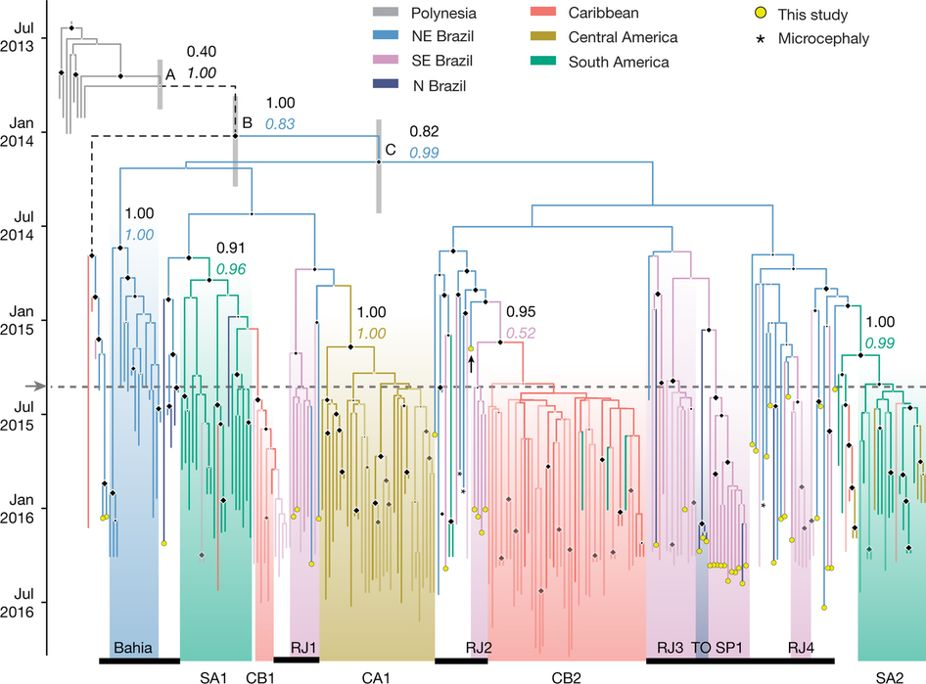
Ancestral state reconstruction
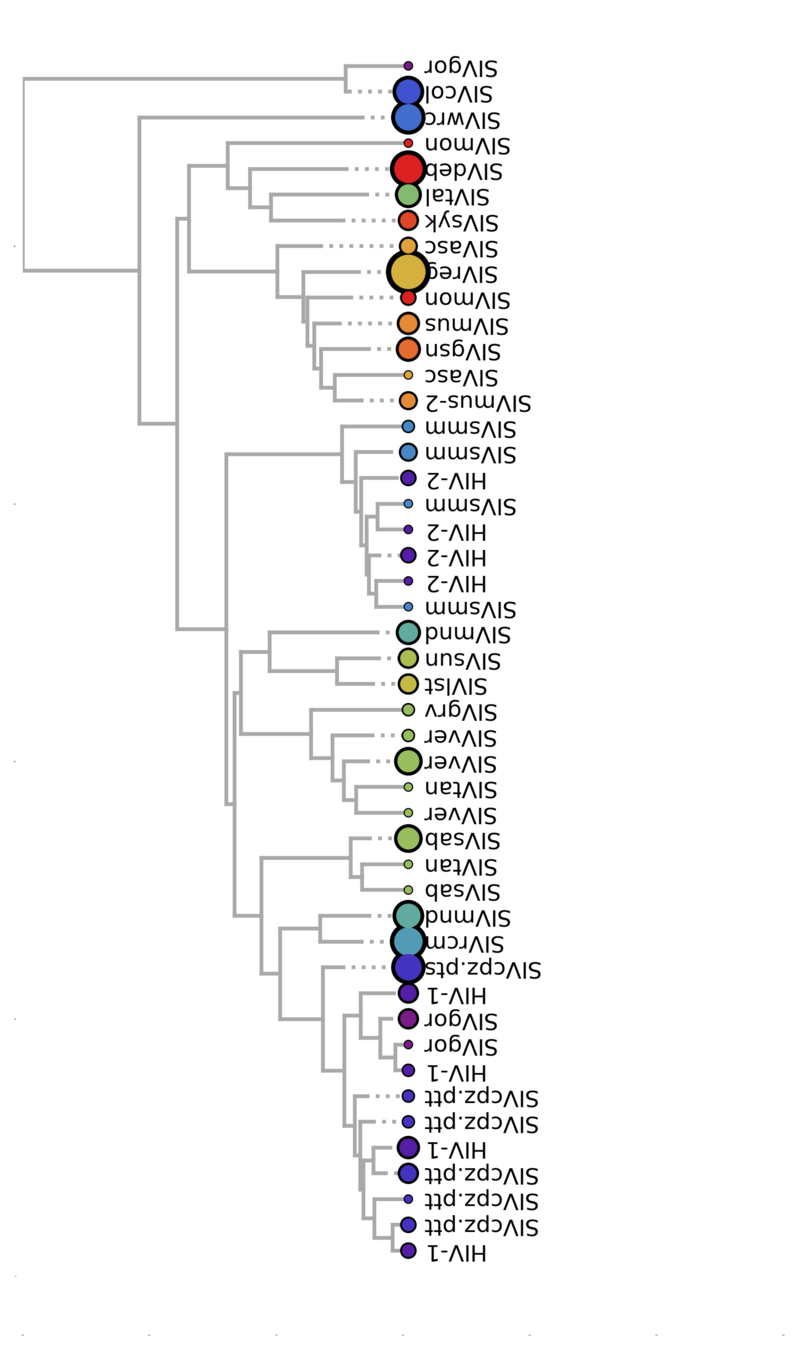
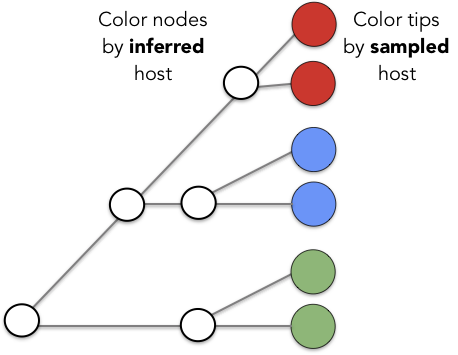
Model trait as an evolving site
Model trait as an evolving site
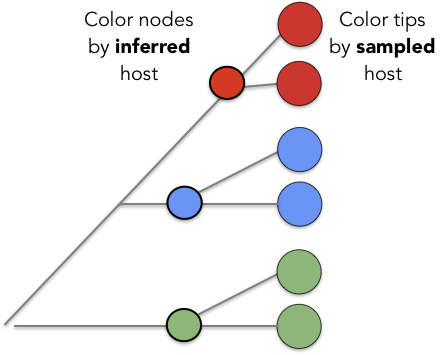
Model trait as an evolving site
Use continuous time markov chain (CTMC) to estimate pairwise rate of transition between states



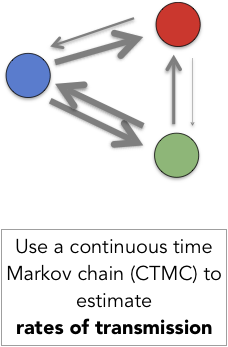
Example: phylogeography
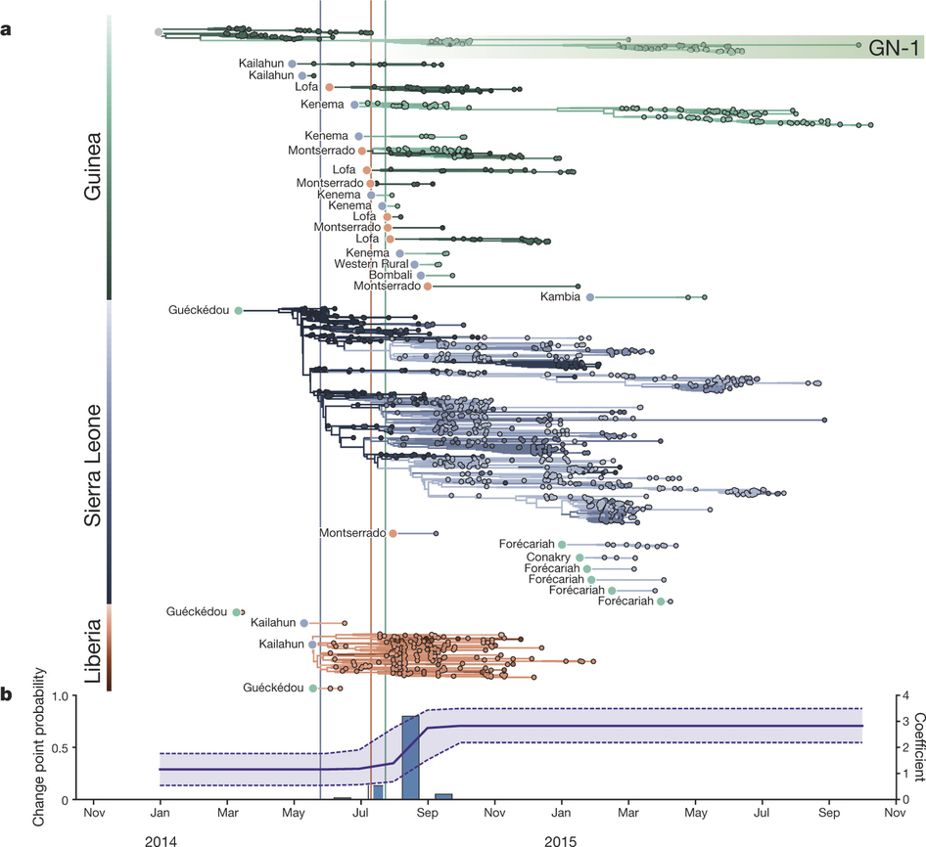
Example: phylogeography
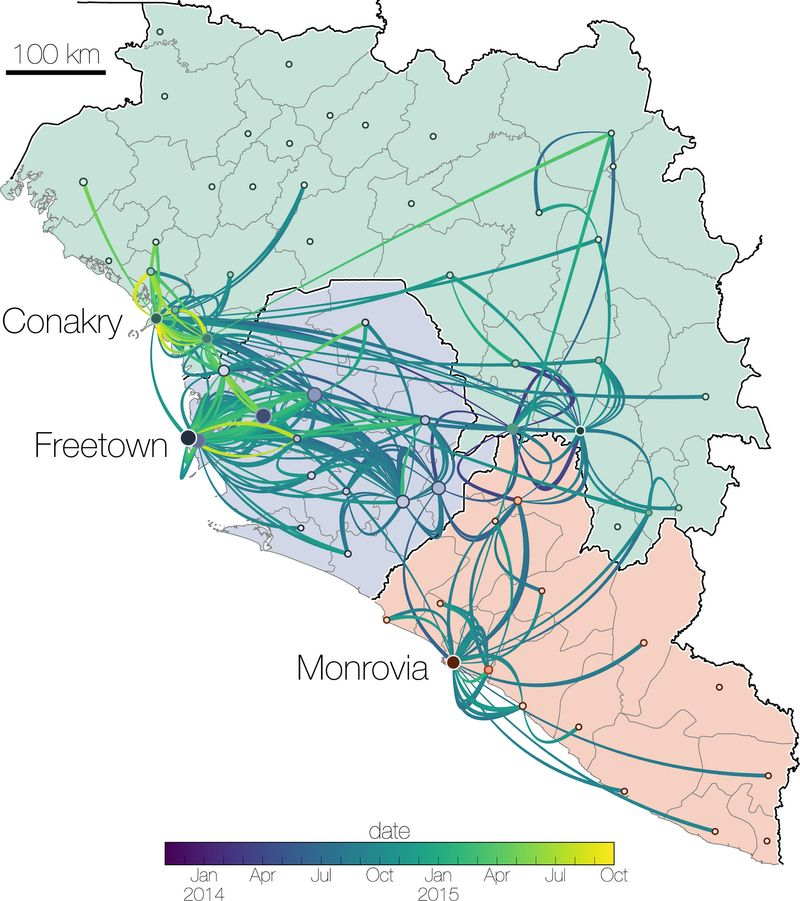
Example: epidemiological inference
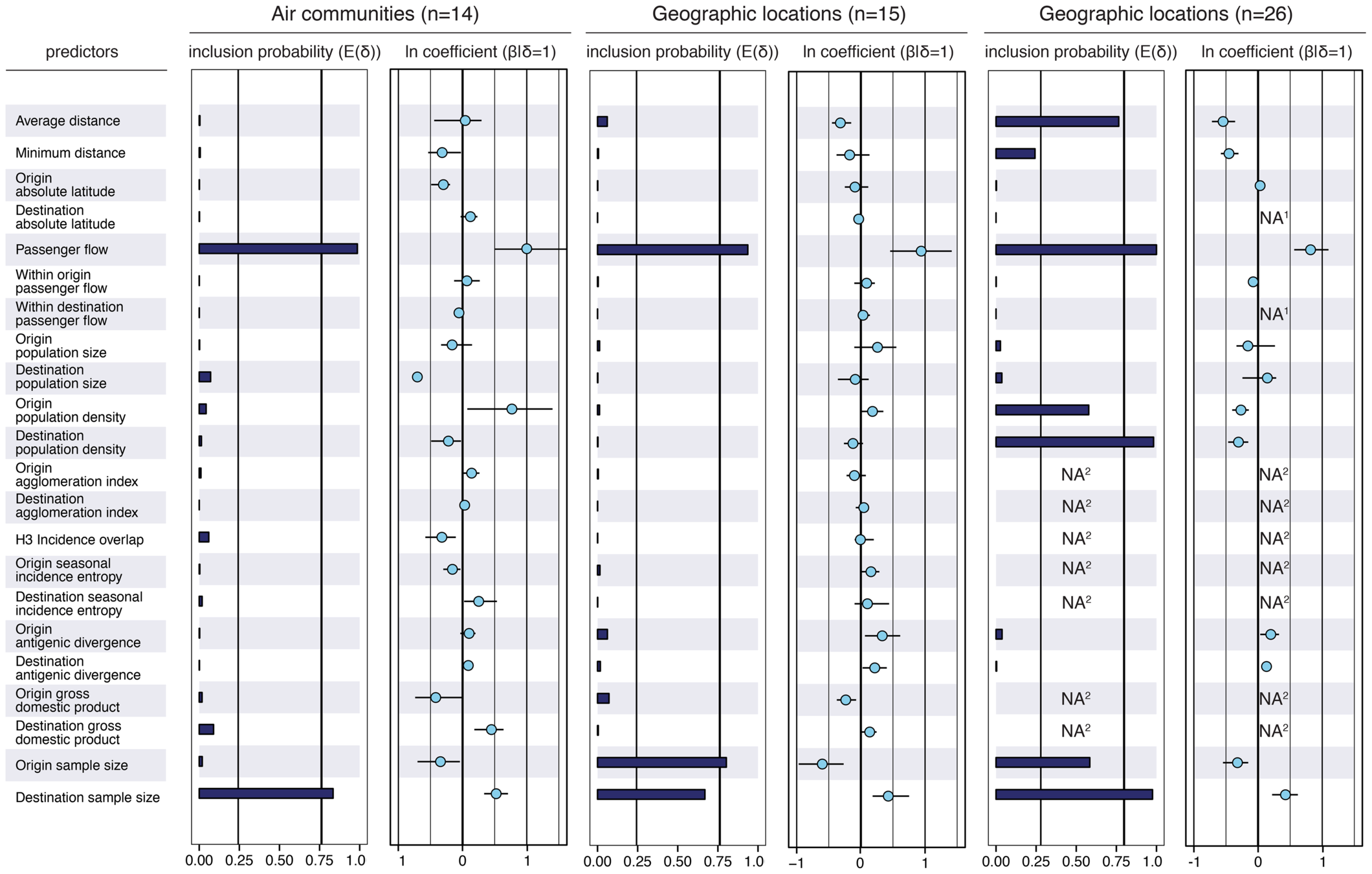
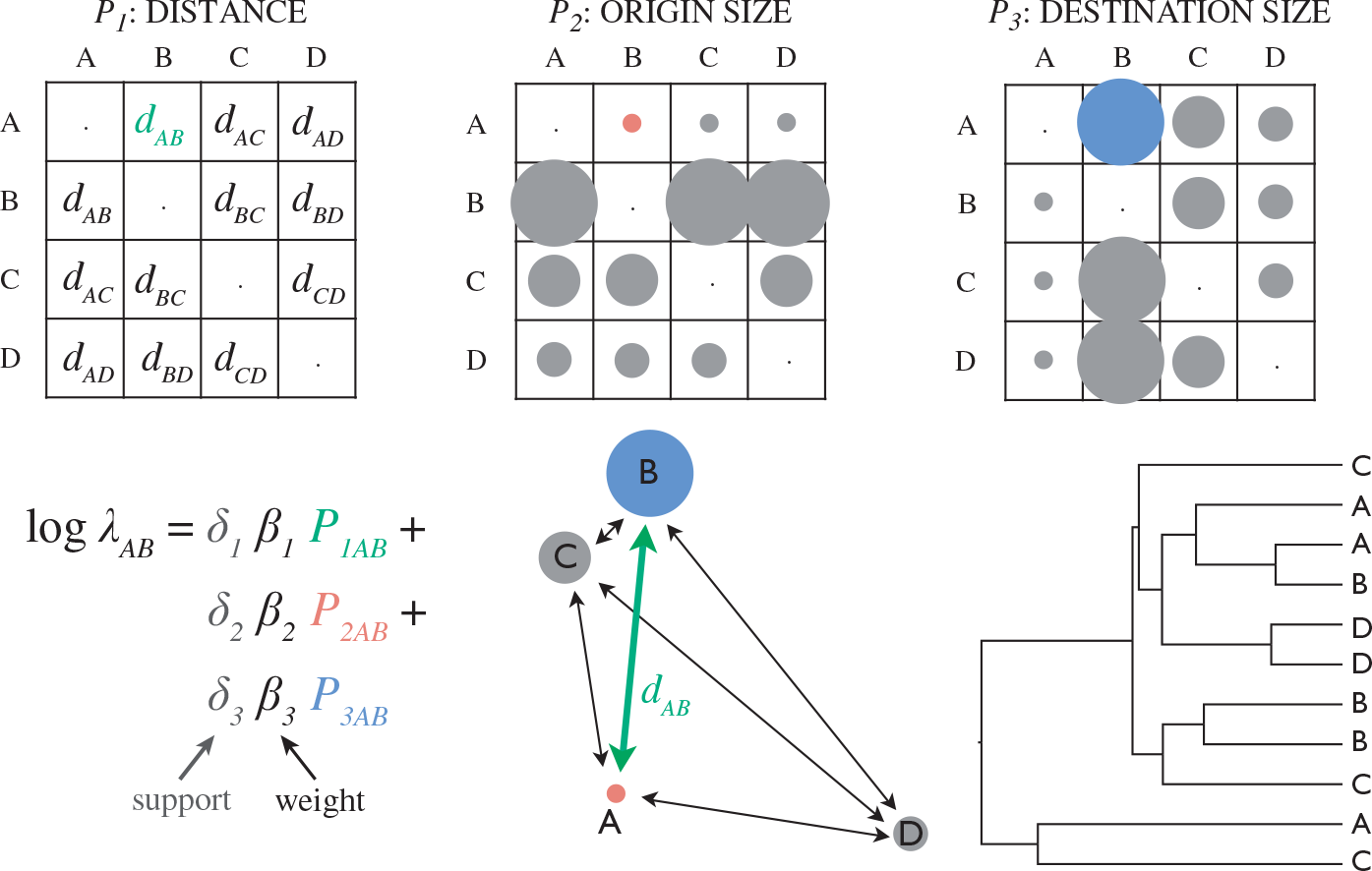
Example: inferring
cross-species transmission
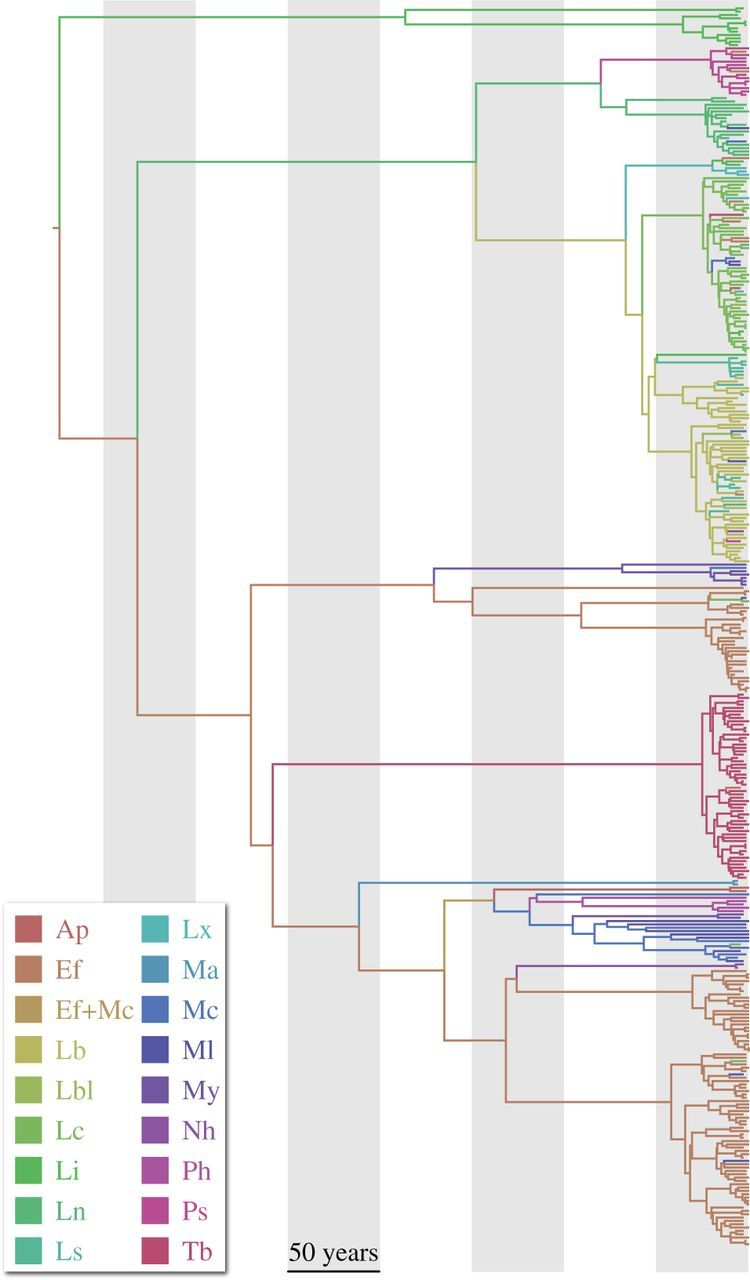
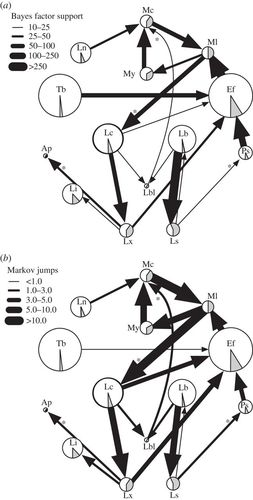
Demographic history


'Skyline' demographic models estimate population size in windows of time
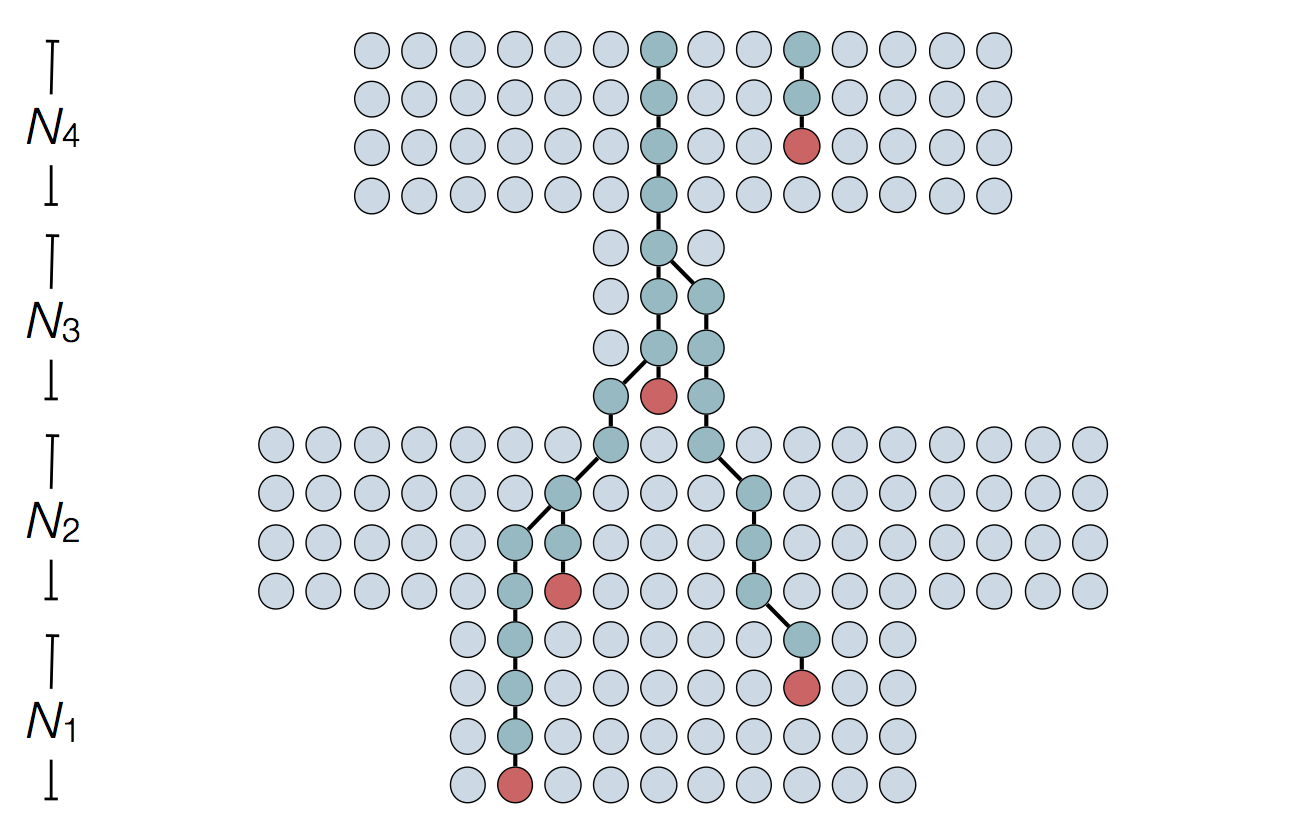
Example: inferring epidemiological dynamics
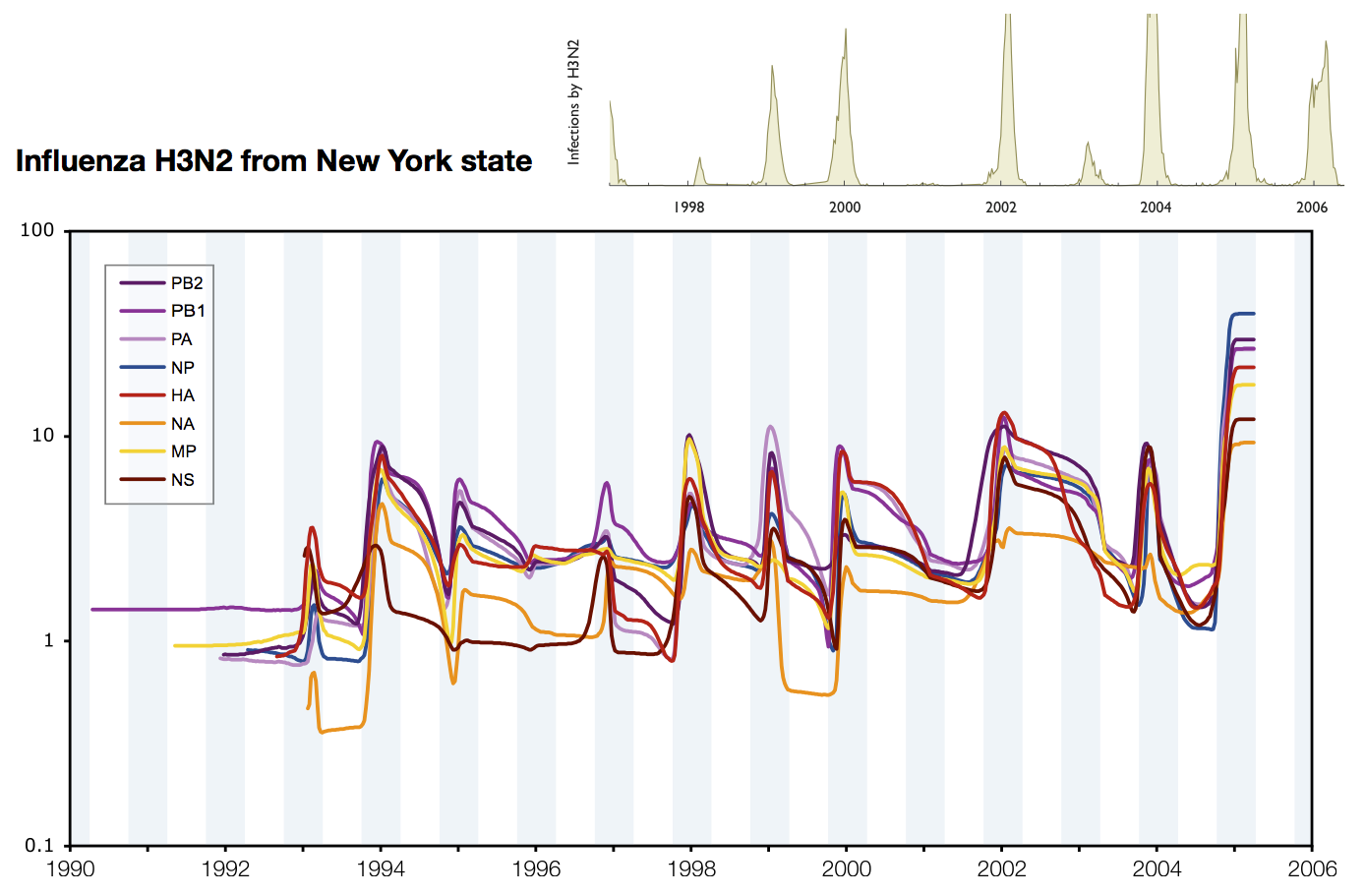
Rambaut 2008
Effective population size
Questions?
learning-hour-phylodynamics-overview
By Sidney Bell
learning-hour-phylodynamics-overview
- 1,565



