COMP2521
Data Structures & Algorithms
Week 8.1
Sorting Overview
Author: Hayden Smith 2021
In this lecture
Why?
- Sorting elements can help us speed up searching, and arranges data in a useful way (for both humans and computers)
What?
- Overview of sorting
Sorting
Sorting refers to arranging a collection of items in order.
- E.G. Sorting arrays, linked lists, files
- Typically sorted in either ascending or descending order
Typically items are sorted based on an ordering relation of that property:
- For numbers, you sort them numerically
- For characters, you sort them alphabetically
The Sorting Problem
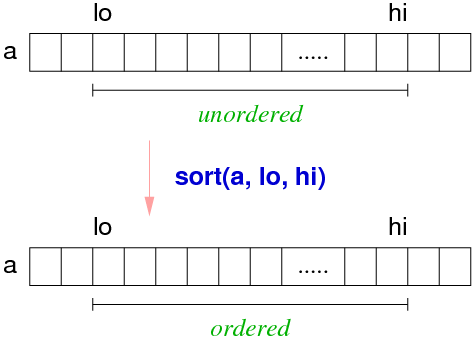
For array a[N], we would sort it by saying lo = 0, hi = N-1
The Sorting Problem
Pre-conditions:
- lo, hi are valid indexes (i.e. 0 <= lo < hi <= N-1)
- a[lo..hi] contains defined values of type Item
Post-conditions:
- a[lo..hi] contains the same set of values as before the sort
- foreach i in lo..hi-1, it's true that a[i] <= a[i + 1]
The Sorting Problem
Generally speaking, most algorithms do a sort "in-place" (consists of doing a series of intelligent swapping between elements). These swaps help move unsorted items to the beginning of the array.
Sorting Algorithm Properties
-
Stable sort: Maintains order for duplicates:
- Given that x == y, if x precedes y in an unsorted list, then x precedes y in the sorted list
-
Adaptive sort: Performance is affected by actual values of items
- Best, average, and worst case performance differs
- E.G. Bubble sort is adaptive
Sorting Complexity
- Three main cases we focus on when sorting:
- Random order
- Sorted order
- Reverse order
- When we look at an algorithm, we are trying to minimise:
- The number of comparisons between items
- The number of swaps between items
- Most sorts are of two types of complexity:
- O(n^2) -> This is totally fine for small numbers (hundreds)
- O(n * log(n)) -> This is ideal
Sorting Programming
// we deal with generic Items
typedef SomeType Item;
// abstractions to hide details of Items
#define swap(A,B) {Item t; t = A; A = B; B = t;}
// Sorts a slice of an array of Items, a[lo..hi]
void sort(Item a[], int lo, int hi); // TODO
// Check for sortedness (to validate functions)
bool isSorted(Item a[], int lo, int hi)
{
for (int i = lo; i < hi; i++) {
if (!less(a[i], a[i+1])) return false;
}
return true;
}COMP2521 21T2 - 8.1 - Sorting Overview
By Sim Mautner
COMP2521 21T2 - 8.1 - Sorting Overview
- 501



