COMP2521
Data Structures & Algorithms
Week 8.4
Quicksort
Author: Hayden Smith 2021
In this lecture
Why?
- We need to learn about n*log(n) time algorithms for a sorting algorithm suitable for large data sets
What?
- Quick Sort
Quicksort
General idea:
- Choose an item to be a "pivot"
- Re-arrange (partition) the array such that:
- All elements to the left of pivot are smaller than pivot
- All elements to the right of pivot are greater than pivot
- (recursively) sort each of the partitions
Generally implemented recursively. Though can be implemented iteratively with a stack.
Conceptual Process
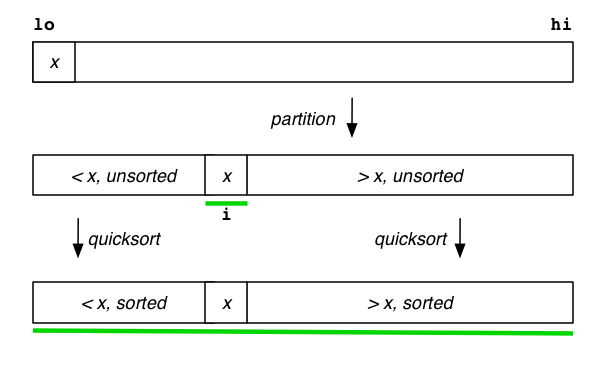
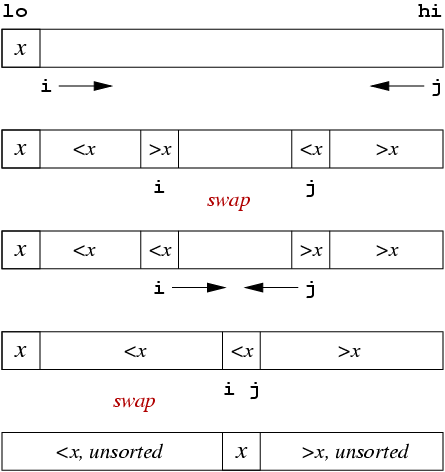
Conceptual Process
Implementation
void quicksort(Item a[], int lo, int hi) {
if (hi <= lo) return;
int i = partition(a, lo, hi);
quicksort(a, lo, i-1);
quicksort(a, i+1, hi);
}
int partition(Item a[], int lo, int hi) {
Item v = a[lo]; // pivot
int i = lo+1, j = hi;
for (;;) {
while (less(a[i],v) && i < j) i++;
while (less(v,a[j]) && j > i) j--;
if (i == j) break;
swap(a,i,j);
}
j = less(a[i],v) ? i : i-1;
swap(a,lo,j);
return j;
}Performance
-
Best case: O(n*log(n))
- EVERY choice of pivot gives two equal-sized partitions
- Essentially halving at each level (logn)
-
Worst case: O(n^2)
- EVERY choice of pivot is one of the highest or lowest values
- Results in each level requiring n comparisons
As you can see, the choice of pivot is very important
Median-of-three improvement
Rather than choosing a static or random pivot, try to find a good "intermediate" value by the median-of-three rule. Make sure the 3 elements (high, low, mid) arei nt he right order
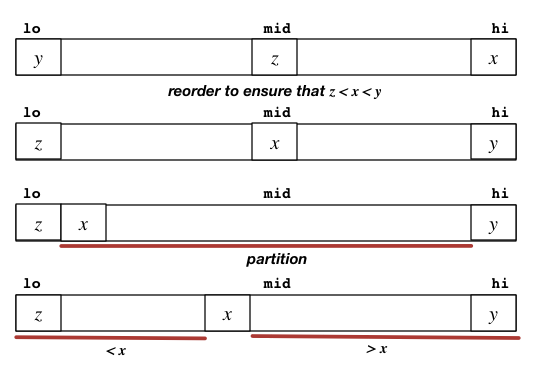
Median-of-three improvement
void medianOfThree(Item a[], int lo, int hi) {
int mid = (lo+hi)/2;
if (less(a[mid],a[lo])) swap(a, lo, mid);
if (less(a[hi],a[mid])) swap(a, mid, hi);
if (less(a[mid],a[lo])) swap(a, lo, mid);
// now, we have a[lo] < a[mid] < a[hi]
// swap a[mid] to a[lo+1] to use as pivot
swap(a, mid, lo+1);
}
void quicksort(Item a[], int lo, int hi) {
if (hi <= lo) return;
medianOfThree(a, lo, hi);
int i = partition(a, lo+1, hi-1);
quicksort(a, lo, i-1);
quicksort(a, i+1, hi);
}Insertion Sort improvement
Recursive function calls have high overhead. Quicksorting partitions with sizes < 5 (approx) have very little benefit compared to simple sorts.
Solution: Handle small partitions with insertion sort
void quicksort(Item a[], int lo, int hi) {
if (hi-lo < Threshhold) {
insertionSort(a, lo, hi);
return;
}
medianOfThree(a, lo, hi);
int i = partition(a, lo+1, hi-1);
quicksort(a, lo, i-1);
quicksort(a, i+1, hi);
}COMP2521 21T2 - 8.4 - Quick Sort
By Sim Mautner
COMP2521 21T2 - 8.4 - Quick Sort
- 661



