COMP2521
Data Structures & Algorithms
Week 8.2
Basic Sorts
Author: Hayden Smith 2021
In this lecture
Why?
- There are a handful of easy-to-implement, yet not-the-fastest sorts that are very useful to understand
What?
- Bubble Sort
- Selection Sort
- Insertion Sortt
O(n^2) sorts
A few of the popular basic sorting algorithms are:
- Bubble Sort
- Selection Sort
- Insertion Sort
These sorting algorithms all have an O(n^2) worst-case time complexity. Later we will discuss faster ones.
Bubble Sort
Moves through the list pair-wise, swapping pairs in the wrong order. Repeats this process until list is sorted.
- Worst case: O(n^2)
- Average case: O(n^2)
- Best case: O(n)
- Adaptive: Yes
- Stable: Yes
Bubble Sort
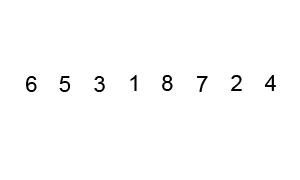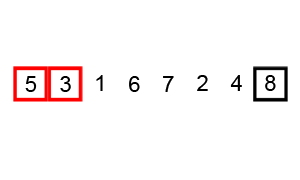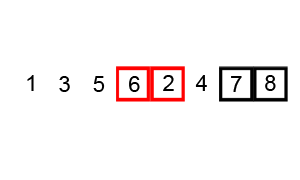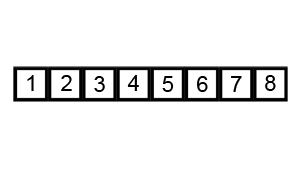
Bubble Sort
void bubbleSort(int a[], int lo, int hi) {
int i, j, nswaps;
for (i = lo; i < hi; i++) {
nswaps = 0;
for (j = hi; j > i; j--) {
if (less(a[j], a[j-1])) {
swap(a[j], a[j-1]);
nswaps++;
}
}
if (nswaps == 0) break;
}
}Selection Sort
Find the smallest element, swap it with first array slot.
Find the second smallest element, swap it with second array slot.
Etc, until traversed through entire array.
- Worst case: O(n^2)
- Average case: O(n^2)
- Best case: O(n^2)
- Adaptive: No
- Stable: No
Selection Sort

Source: https://algorithms.tutorialhorizon.com/selection-sort-java-implementation/
Selection Sort
void selectionSort(int a[], int lo, int hi) {
int i, j, min;
for (i = lo; i < hi-1; i++) {
min = i;
for (j = i+1; j <= hi; j++) {
if (less(a[j],a[min])) min = j;
}
swap(a[i], a[min]);
}
}Insertion Sort
Take first element and treat as sorted array; take next element and insert into sorted part of array so that order is preserved; repeat until whole array is sorted
- Worst case: O(n^2)
- Average case: O(n^2)
- Best case: O(n)
- Adaptive: Yes
- Stable: Yes
Insertion Sort
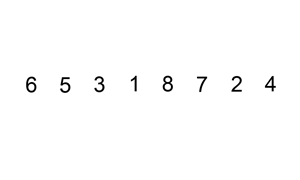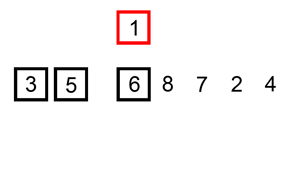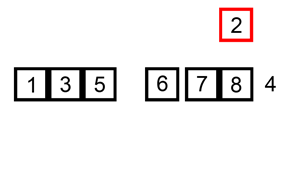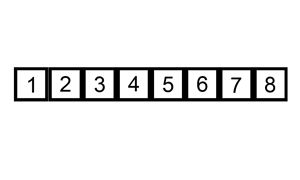
void insertionSort(int a[], int lo, int hi) {
int i, j, val;
for (i = lo+1; i <= hi; i++) {
val = a[i];
for (j = i; j > lo; j--) {
if (!less(val,a[j-1])) break;
a[j] = a[j-1];
}
a[j] = val;
}
}Insertion Sort
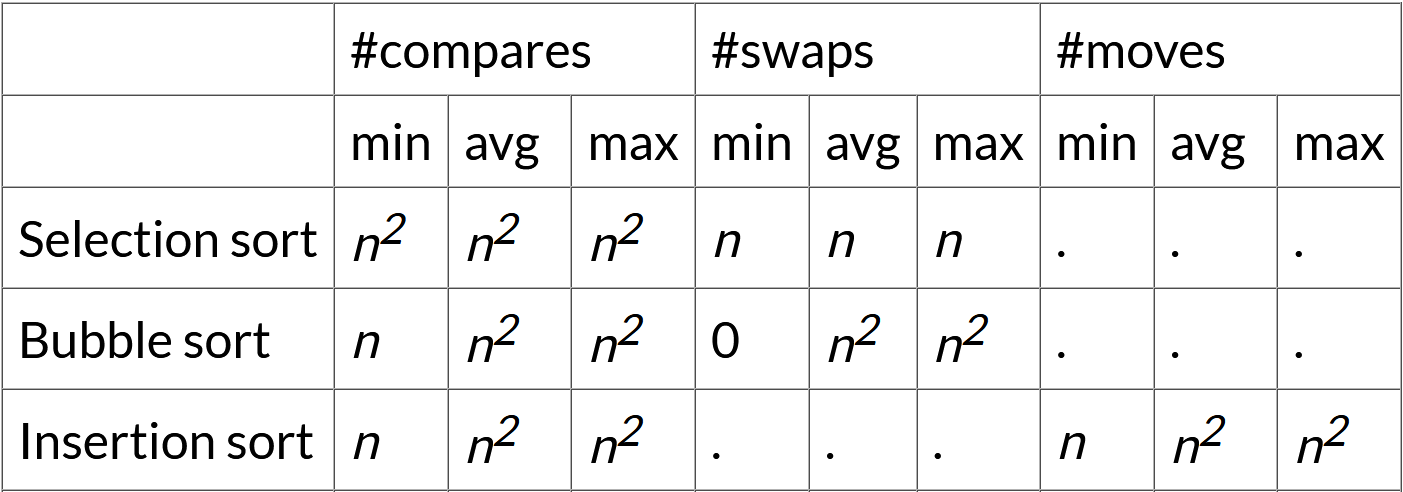
Sorting Summary
Sorting Linked Lists
Most sorts assume we work on arrays. However, we can still sort on linked lists.
COMP2521 21T2 - 8.2 - Basic Sorts
By Sim Mautner
COMP2521 21T2 - 8.2 - Basic Sorts
- 766



