Review Day!

What we've done so far!
- Git
- Command Line
- Data Types
- Conditionals
- Loops
- Functions
- Scope
- Objects
- JSON
- DOM


Let's look back at a few things

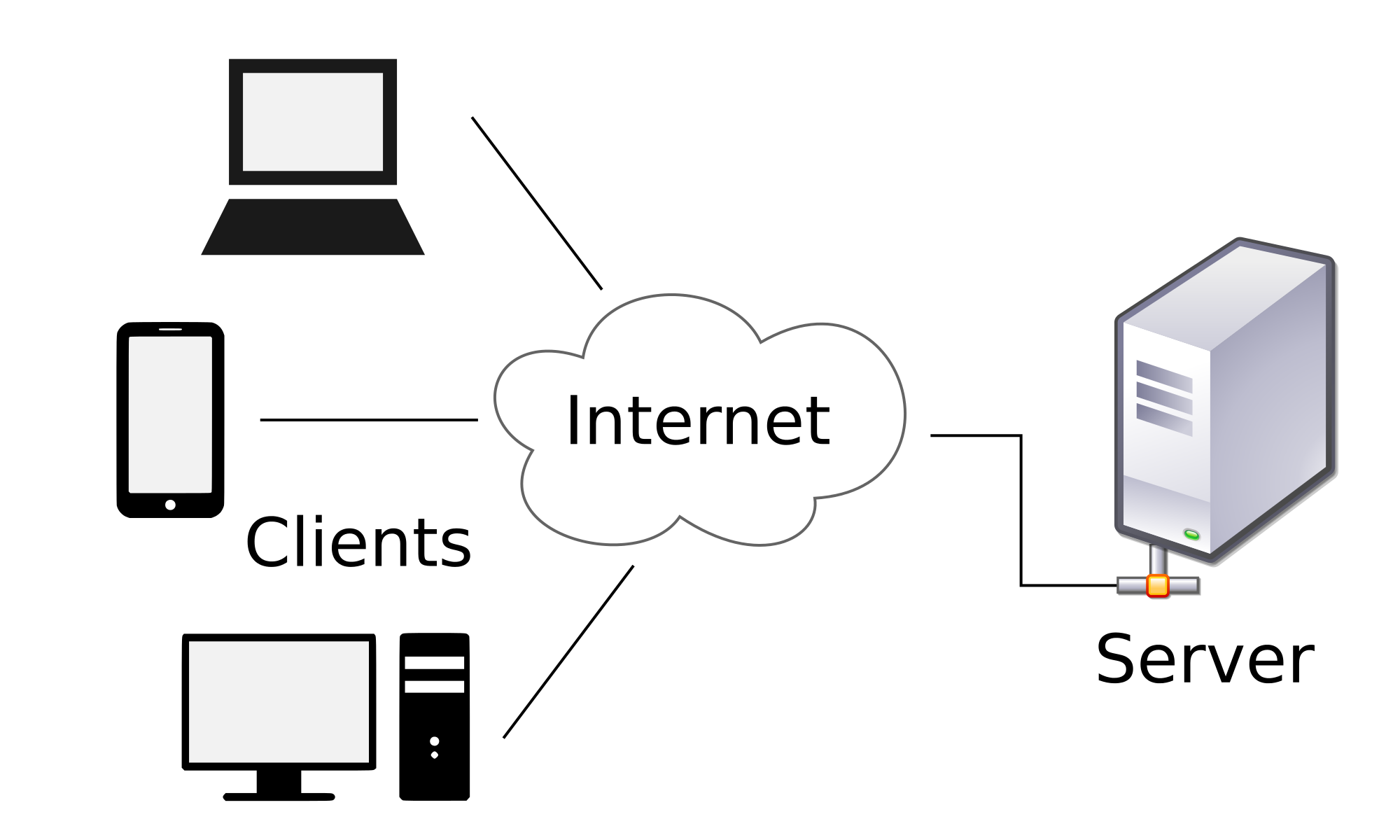
1000 ft Overview
Client/Server Model
JavaScript

What We Can Do With JavaScript
- Access Content (document.getElementById())
- Modify Content (element.style())
- Program Rules (conditionals, if/else, if/while)
- React to Events
In the Browser
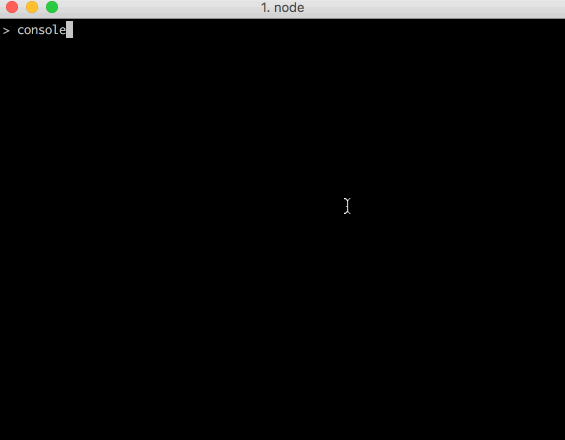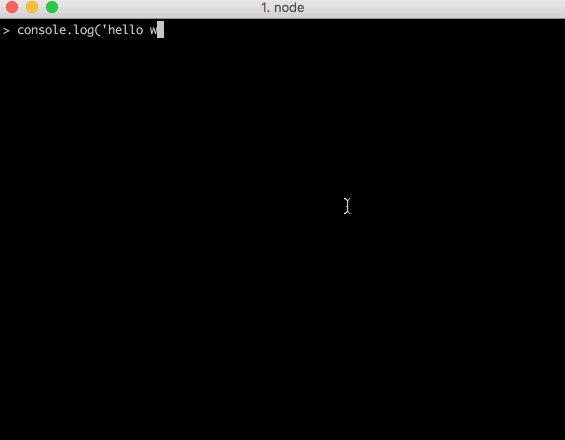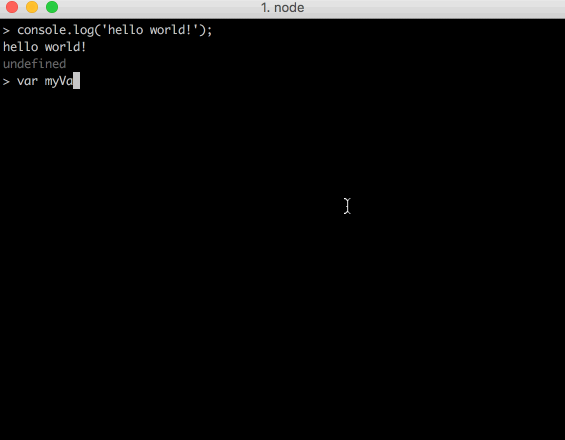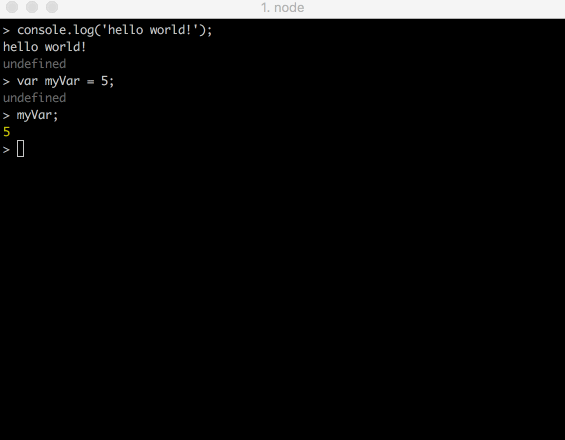
Or the console!
JavaScript Runs....
Git
Git
Version Control software that you need to install on your machine, and initiate in every project. Keeps a history of moments in time (commits) for your project (repository)
GitHub
A web platform that you can store your code files (repositories) including your git history. Has many features suited for team collaboration
Git Commands
- Git Clone (downloads the repo to local machine)
- Git Add (.) (stages changes to get ready for a commit)
- Git Commit -m 'text' (adds a message to your commit)
- Git Push (uploads your code to your remote repo)
Command Line
Commands
- ls - list contents of a directory(folder)
- cd - change directories
- mkdir - make directory
- rmdir - remote directory
- rm - remove file
- touch - create empty file
- pwd - list out current directory path
- open - opens current directory in finder
Recommended Command Line Program for Windows: Powershell
Recommended Command Line Program for Mac: iTerm
Running Node on Command Line
- cd into the directory with your JS file
- type node fileName.js
- this will start a node server on your machine and run your JS code and stop the server
Data Types
Data Types
- String
- Integers
- Booleans
- Array
- Object
Use typeOf() to check !
Array Helper Methods
- Array.pop()
- Array.shift()
- Array.unshift()
- Array.length()
- Array.reverse()
- Array.join()
Array Iteration
- For Loop
- Array.forEach()
- Array.every()
- Array.some()
- Array.filter()
- Array.map()
- Array.every()
- Array.some()
- Array.filter()
Think of variables as named buckets in which we can place one item

var adorable = 'Maru in a bucket!'
call the variable by it's name
and use = to re/assign
Conditionals
Conditionals allow us to check a condition, and respond to the answer of that condition
Comparison Operators
- <
- >
Equality Operators
- General: ==
- True: ===
- Negation: != and !==
Equality Operators
- OR: ||
- Not
- <=
- >=
Conditional Statements
- If
- If/Else
- If/Else if/Else
- Switch
Loops
- While
- Do/While
- For
- ForEach
Functions
A function is a reusable statement, or a group of reusable statements.
Creating a function
Function Declaration
function speak (words) {
console.log(words);
}Function Expressions
var speak = function (words) {
console.log(words);
}Invoke a function
myFunction();pass in argument
myFunction(myArgument);arguments take the place of perameters
function myFunction(perameter){
//do something
}Return Statement
- Returns information to wherever the function is called
- For example we can call a function in another function
- Or we can use variables to store returned data
function sum (x, y) {
return x + y;
}
function double (z) {
return z * 2;
}
var num = sum(3, 4)
=> 7
var numDbl = double(num);
=> 14
// This can also be written:
var num = double(sum(3,4));
=> 14Scope
Global Scope
Access something from ANYWHERE in the program
Local Scope
A variable with local scope cannot be referenced outside of that function.
// Global Scope
var a = "Hello";
function sayHello(name) {
// Local Scope
var b = 'kitten';
return a + " " + name;
}
sayHello("JavaScript");
=> "Hello JavaScript";
kitten;
=> undefunedObjects
myObject = {
name: 'Jessica',
age: 31,
favAnimal: 'cat',
isAwesome: true,
}Creating Objects
var myHouse = {};
var myCar = new Object();
var myMotorcycle = {
wheels: 2,
color: "blue",
maxSpeed: 300,
owners: ["Sofia", "Rose"]
}Object properties
// Setting
myCar.wheels = 4;
myCar["doors"] = 2;
// Accessing
myCar.wheels;
=> 4
myCar['doors'];
=> 2Iterate through objects
for (var i in myHouse) {
if (myHouse.hasOwnProperty(i)) {
// The "hasOwnProperty method returns true
// if an object property has a certain key"
console.log(i + " = " + myHouse[i] + "\n");
}
}Constructor Function
var Kitten = function(kittenName){
this.name = kittenName;
}
var Sam = new Kitten('sam');
Sam.name;
=> 'sam'JSON
We use JSON objects to transfer data between applications and Javascript.
To keep everything consistent, all JSON code must follow a number of strict conventions :
- Property names must be double-quoted strings.
- Trailing commas are forbidden.
- Leading zeroes are prohibited.
- In numbers, a decimal point must be followed by at least one digit.
- Most characters are allowed in strings; however, certain characters (such as ', ", \, and newline/tab) must be 'escaped' with a preceding backslash (\) in order to be read as characters (as opposed to JSON control code).
- All strings must be double-quoted.
- No comments!
Document Object Model
DOM
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming interface for HTML and XML documents.
It represents the page so that programs can change the document structure, style and content.
The DOM represents the document as nodes and objects. That way, programming languages can connect to the page.
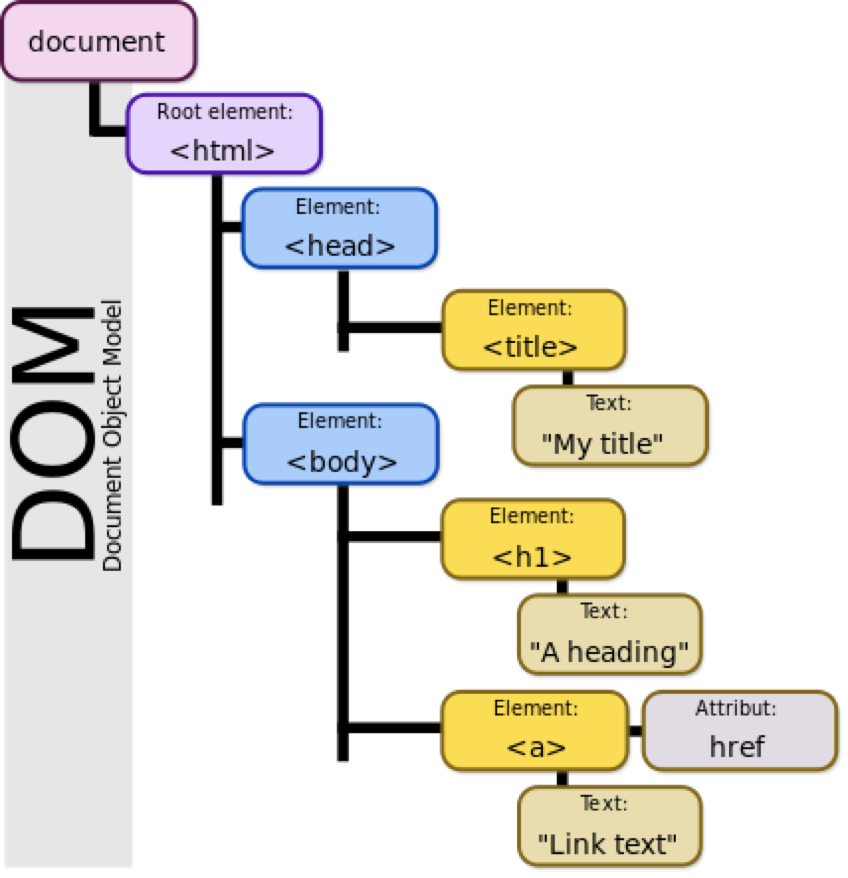
Document.getElementById(String id)
Document.querySelector(String selector)
Document.querySelectorAll(String selector)Use object dot notation to access and update elements and their styles, text, and much more using the DOM.
Aug 13th: Review Day!
By Jessica Bell
Aug 13th: Review Day!
- 126



