The Endocrine System
by Sebastian Kimberk
Introduction
- Body functions in very different ways throughout different stage of life.
- Endocrine system is responsible for creating hormones which control functions of all other organs.
- Impacts of nervous system are short-lived; effects of endocrine system can last weeks.

Endocrine vs Exocrine
- The Latin prefix "endo" means inside, while the prefix "exo" means outside.
-
Exocrine glands excrete substances out of the body through ducts.
Ex: sweat glands & tear glands
- Endocrine glands excrete substances directly into the bloodstream.

Negative Feedback Loop

Method used by glands to control bodily functions.
If organ is working too much, gland produces less hormone.
If organ is working too little, gland produces more hormone.
Video About Negative Feedback Loops
Growing Up
The endocrine system controls how an individual's organs function during the different developmental stages: infancy, childhood, adolescence, and adulthood.

Thyroid
Controls how the body uses energy, makes proteins, and adjusts the body's sensitivity to other hormones.
The thyroid is one of the largest endocrine glands. Consists of two connected lobes which are found in the neck.

Thyroid hormones determine how fast calories are consumed. They affect every single cell in the body.
Hypothalamus
Located directly above the brain stem. Is part of the limbic system.
After receiving information from nervous system, it releases hormones which control function of the pituitary gland.

Helps maintain homeostasis by regulating body temperature, hunger, thirst, fatigue, and sleep patterns.
Pituitary Gland
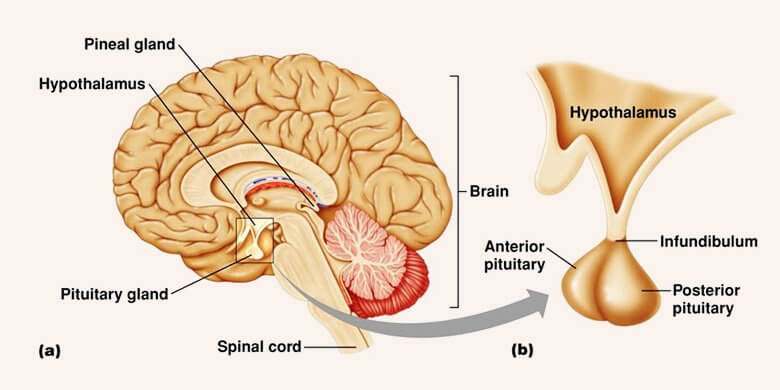
Pituitary Gland

Responsible for producing the hormones which control the rest of the endocrine glands.
Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) - Controls production of cortisol by adrenal glands (maintains blood pressure).
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) - Controls thyroid, which in turn controls the body's metabolism.
Growth Hormone (GH) - Stimulates growth during childhood and maintains muscle and bone mass during adulthood.
Growth Hormone Deficiency

Medical condition where pituitary gland does not produce enough growth hormone (AKA somatropin).
Has different effects dependent on the age of the patient.
Children generally don't grow fast enough, while adults have bone and muscle masses which are substantially below average.
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Most common causes of GHD are tumors in the pituitary gland.
It can be treated either through radiation therapy in order to eliminate tumors, or through daily injections of GH under the muscle.
Treatment Controversy

The growth hormone used for treatment of GHD used to be harvested from human pituitary glands (of dead people).
Growth hormone is now synthesized using special bacteria which were injected with human cells.
Conclusion

Most of the things which your body is doing every day are driven by hormones created by endocrine glands.
Without the endocrine system, you would not be able to live, yet, for some reason, no one really knows about it.
Bibliography
Endocrine System
By skimberk1
Endocrine System
- 956