Computation in Design
Atelier
Computation in Design
Atelier Overview
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project

Computation in Design Atelier
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
What are the current discussions around computation and contemporary technologies and how should designers respond and contribute?
How can we creatively design, apply and experience contemporary technologies so they contribute meaningful value and impact?
Where do contemporary technologies, computation, and design intersect to create positive outcomes for people and their environments?
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Josef Albers discussing Paper Sculptures presented by his students during the Preliminary Course at the Bauhaus, Dessau, Germany (1928-1929).
Atelier
Computation in Design, the Atelier.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
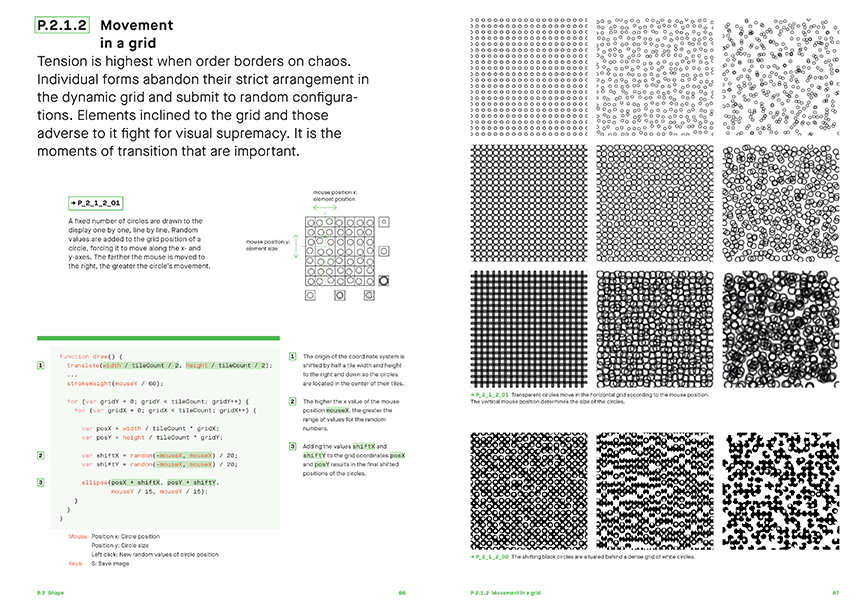
Computation in Design, as understood in the atelier, is informed by three approaches to research and design: computing, sensing and making.
It invites students on a journey where contemporary and creative technologies meet design in dynamic ways, shaping how artefacts, tools and products interact with our world.


Computation in Design, the Atelier.
In this atelier we will look at approaches, contexts and issues that relate to
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Topics that are not a priority in this atelier
- Generative Design
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Creative AI and Machine Learning
- Sensory Experiences and Physical Computing
- Experiments in Creative Coding, Making, Play
- Installation and Immersive Environments
- Computational Aesthetics
- Prototyping
- Metaverse
- Social Media
- Virtual Reality
Computation in Design, the Atelier.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Graphic Designer
Visual Artist
Interaction Designer
Creative Technologist
Design Researcher
Further your academic career
- Generative Design
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Creative AI and Machine Learning
- Sensory Experiences and Physical Computing
- Experiments in Creative Coding, Making, Play
- Installation and Immersive Environments
- Computational Aesthetics
- Prototyping
In this atelier we will look at approaches, contexts and issues that relate to
Design as a Force for Good: Lim Si Peng and Ong Kian Peng
DesignSingapore (Dsg) Scholars Lim Si Ping and Ong Kian Peng harbour a profound passion for design and the transformative impact of technology. United by a shared commitment to harmonising art, technology, and environmental consciousness, their collective aspiration is to drive positive change through their design endeavours.

Computation in Design
Computation in Design
The atelier acts as a laboratory to explore how practice and inquiry relate to human experiences, interactive environments and larger ecosystems. It is a space where hands-on experimentation meets thoughtful reflection guided by research and design.
This approach applies particularly, but not exclusively, to areas like Generative Design, Creative AI and Computational Aesthetics. It extends to Prototyping, Sensory Experiences and Human-Computer Interaction, addressing current issues while envisioning an optimistic future.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project


Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project





Graphic Design
Generative Design
Motion Graphics
Data Visualisation
Interaction Design
Computational Design
Physical Computing
Experience Design
Interface Design
Machine Learning
Computation in Design
Computing and coding addresses the aspect of applying computation to creative practices, which in this case is particularly relevant to the field of design communication. Coding is seen here as a technique, a tool, a playground and a language to communicate and interact with and through machines.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Computing
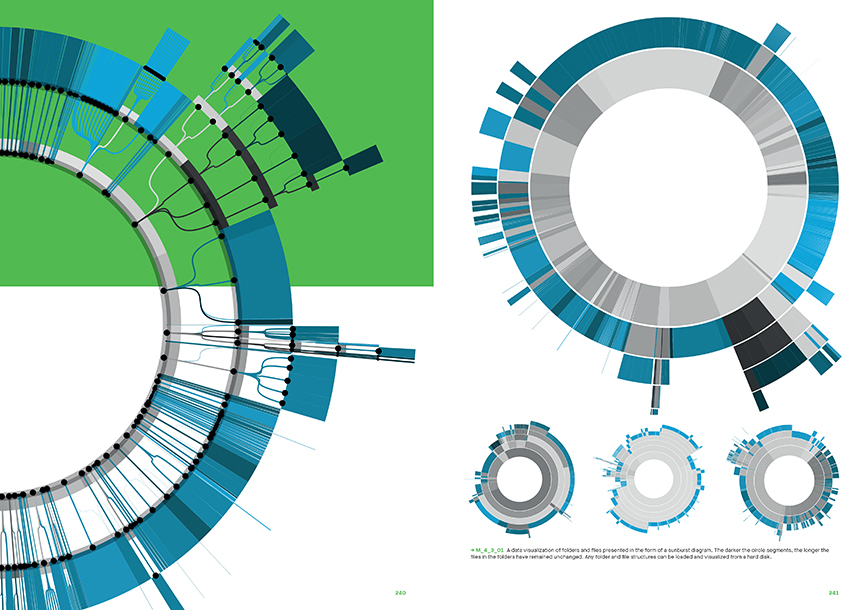
Sensing here refers to sensory experiences, sense making and sensing with our human senses or the sensors of machines. Furthermore, sensing here goes hand in hand with data acquisition, analysis, visualisation and expression when processed computationally.
Sensing
Making is understood as a hands-on approach and collaborative group work where members of a group share knowledge, learning and skills. Furthermore, one should be aware of what is being made and think critically about the context in which the making takes place and has an impact.
Making
Generative Systems, creative coding, visual communication, algorithmic behaviours, machine learning, experiences
Interaction, interfaces, sensors, data, physical computing
Tools, materials, discourse, prototypes, fabrication, immersion, expression, creative technology
Computation in Design
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Learning code can be frustrating and it requires a lot of time and a lot of failure. Time and failure and misunderstanding. To imbue a sense of optimism here is so important–to celebrate this as a new mode of working and to help students to realise that there's all these untapped ideas out there – Zach Lieberman
Coding,
its gonna be fine.
Coding Spectrum
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
No Code
Low Code
Some Code
All Code
Requires few to no code to quickly build an application. This doesn't mean there is no code involved, the code just all runs in the background. Often purely UI, pull-down and drag-and-drop based.
Similar to No Code, however, some code is exposed in the application development environment you are using. Although often related to visual programming environments, a basic understanding of coding concepts is useful.
Limited to the tool
Some customisation possible
Some coding skills required
Build your own
Wordpress
TouchDesigner
Code templates
Blender
html, css, JavaScript
Code frameworks (p5js, Processing)
Scripting
Arduino
Unity
Knowing and understanding some code as a designer allows you to innovate, collaborate better, and communicate across disciplines when technical expertise is required. Basic knowledge in software and hardware development required–can be acquired through practice.
This is when you are able to build your own software with ease. Needless to say this needs time and practice but allows you to create your own tools applied to your design practice.
Cargo and similar platforms
Figma
Spark AR
Prompting (Midjourney, Dall-e, etc.)
Pen and Paper
Text Editor
Any programming language
Command Line
Git
In this atelier, design is looked at through the lens of computation. In particular, we take a broader look at technologies and how artefacts relate to us and to others: People, machines, spaces, but, the other here may also include things, ecosystems, organisms, other species.
Much of the learning is inductive*—build and test first, gather evidence and think critically, reflect on your explorations, see what a process, an artefact, affords you as a design researcher, and decide on the next series of steps in an incremental process. Our approach here will oscillate between design practice and design research–writing and making.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Computation in Design, the Atelier.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Approach
Art+Com Studios. Futurium, permanent exhibition, invites visitors to explore potential futures through experiential artefacts in a mix of analogue and digital media.
Approach
Students go back and forth between their dissertation and their practice. Both should be carried out in tandem. If the dissertation is done before the practice, the practice becomes merely the "packaging" of the research.
New knowledge should emerge from practice. Design practice can be cross-fertilised with disciplines such as psychology, sociology, sustainability, communication studies, philosophy or literary studies, futures and foresight studies, as well as performing arts, contemporary art, music or other design disciplines, but the core of the research should be anchored in design.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Approach, in the studio.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project

Approach, in the studio.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project

Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Generativity
Interactivity
Discourse
Experimentation
Approach and Motivation
Generativity here refers to a design approach that can be regarded as computational, iterative, modular and emergent. By creating and using generative systems, a designed outcome can respond quickly to change and adapt.
An emphasis of your work may be on creating interactive scenarios that can be tested and observed in order to make the designed outcomes experiential for the audience and communicate with them through interactions.
A discursive approach can be considered a thought catalyst. The designed object’s primary role is no longer utilitarian, aesthetic or commercial but is given form and function so that it can communicate ideas—this is the goal and the measure of success. Rather than tools for living and doing, these are tools for thinking.
An experimental approach can consider unconventional materials, tools, design methods and outcomes. The centre of this approach is exploration. Often this goes in line with topics that look at future scenarios addressing artificial intelligence, climate change, sustainability or bio design.
Casey Reas
Memo Akten
Neri Oxman
Weidi Zhang
Anab Jain
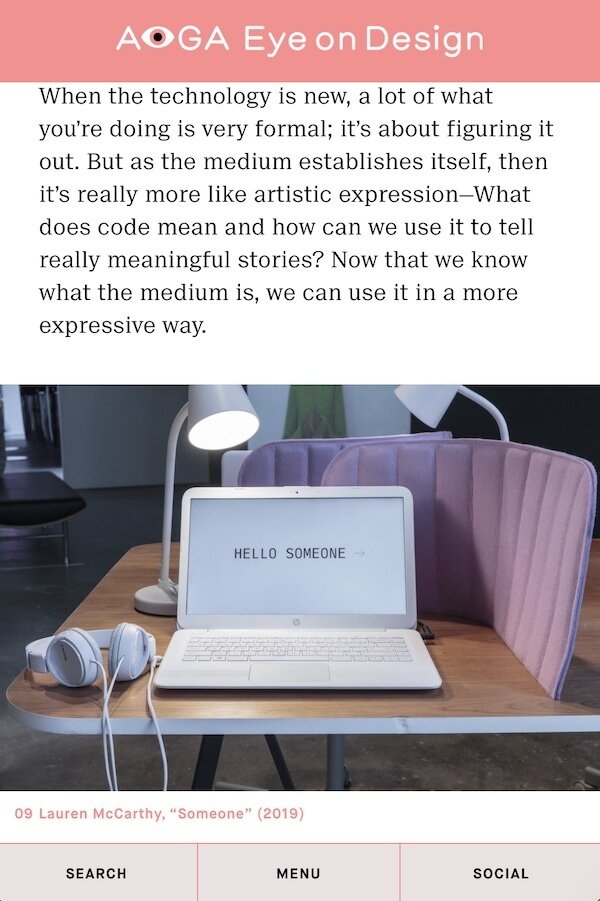
Lauren McCarthy
Stephanie and Bruce Tharp
Taeyoon Choi
Bill Moggridge
Hiroshi Ishii
Joachim Sauter, art+com
Rebecca Fiebrink
AIxDesign Community
Biodesigned
Disnovation Collective
xCoAx Conference
Final year projects here can be approached through
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Sketching
Experimenting
Prototyping
Designed Outcomes
Approach and Action
Sketching is about bringing ideas to life and putting them on paper to better communicate the nature, relationships and flow of ideas and processes through simple but meaningful mapping and diagrams. This approach is designed to help both students and their supervisors have constructive and productive discussions, critiques and feedback sessions to move the enquiry and exploration of a project forward step by step.
An experiment in the broader sense may refer to practicing by trial and error, trying and testing the unknown, and learning through a process of approximation and correction until a satisfactory state is reached. This state may mean that a particular problem has been solved, or that a state of beauty has been achieved, or some other form of successful (or possibly unsuccessful) result.
The term prototype, along with the verb prototyping, has become popular in design research. Originally, the term indicated a precursor of a mass-produced product, which shares its material qualities, but will undergo testing and development during implementation. In design research, the term prototype may also be used for all kinds of product-like physical constructions.
The outputs designed in this atelier are a collection of sketches, experiments and prototypes that are created during the course of a study. These outcomes can be stand-alone, such as a series of artefacts, an installation, a screen-based application and more, or they can be the material for a publication that documents the process and the gathered findings and outcomes in a printed or digital document.
Approach your work progressively through
Approach
Exploring
Testing
Making
Prototyping
Sketching
Documenting
Interactive
Critical
Experimental
Generative
Discursive
Playful
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Motivation
Action
Approach
Exploring
Testing
Making
Prototyping
Sketching
Documenting
Interactive
Critical
Experimental
Generative
Discursive
Playful
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Action
Motivation
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Approach

Interactive Testing
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project


Approach
Playful Prototyping
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project

Approach
Critical Making

Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project

Approach
Discursive Exploring
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Approach
Generative Sketching

Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Designed Outcomes

Generative Systems, creative coding, visual communication, publication
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Designed Outcomes


Generative Systems, tool, screen-based, real-time visuals
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project

Designed Outcomes
Creative coding, experiences, interaction, interfaces, prototypes
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project

Designed Outcomes
Augmented Reality, interactive narratives
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project

Designed Outcomes
Interaction, sensors, physical computing, experience, machine learning,immersion
Matthew Lau, Hello I am here. Matthew is currently pursuing his Master in New York at the ITP program at NYU.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Designed Outcomes
Interaction, sensors, physical computing, experience, immersion
Goh Sing Hong, Listening Lab

Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Designed Outcomes
interfaces, interactions, generative, sensors, haptics, plants
Aditi Neti, Bio-Interfaces, currently working at SIT, the Singapore Institute of Technology

Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Designed Outcomes
generative design, digital fabrication, real-time visuals, data, interfaces
Rachel Lee, Selfscapes. Currently Junior Art Director at Designory Singapore

Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Designed Outcomes
interactions, materials, making, sensors, awareness, exhibition
Aimee Junoes, Urban Plastisphere. Designer at Designory Singapore

Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Design can function at multiple levels and in different ways. Design professor Richard Buchanan captured his thinking into these ‘four orders of design’ illustrating how design as a discipline has moved from the traditional concept of the visual or tangible artefact through to orchestrating interactions and experiences, and to transforming systems.
Four Orders of Design. Symbols, Objects, Actions, Systems.
Application
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Application
Four Orders of Design
2D Graphic Design, deals with the nature, shape, and meaning of symbols and consists of four distinct but related activities: typography, illustration, photography, and print. 2
Systems and environments. Environmental design is concerned with “[t]he idea or thought that organizes a system or environment” Therefore, in the fourth order, the focus is on human systems, “the integration of information, physical artifacts, and interactions in environments of living, working, playing, and learning.” 2
4D Interaction. In interaction design, the locus of design is action. Here, the focus is on designing experiences rather than physical objects. 2
3D Industrial Design, industrial design is concerned with tangible, physical artifacts — with things. 2
1 Symbols
3 Actions
2 Objects
4 Systems
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project




1 Symbols
2 Objects
3 Actions
4 Systems
Poster
Print publication
Website
3D print
Crafted object
Device
Community
Exhibition
Platform
Spaces
Workshop
Immersive Experience
Installation
Interface
Screen
Four Orders of Design
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Supervision
Zoom Lab, prototypes by Lasalle's Media Lab and alumni. Part of the Faculty of Design exhibition Encounters, Institute of Contemporary Arts Singapore, 2019.
Supervision
Research
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Practice
Dissertation
informs
informs
individual and group consultations
workshops on sketching, experimenting, prototyping
lab sessions to address technical challenges
case studies
Supervision
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Current and past graduation projects
current graduation projects, work in progress
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Pragathi
Zarer
Alda
Jade
Alternative Web Spaces. Exploring interactivity and design to imagine alternative web spaces as a means to resist effects of commercialisation
Designing with Our Roots, Nature. A study through interaction design to bridge the ecological relationship between humans and nature during a time of environmental crisis in Singapore
Dreaming of an Interspecies Sensor. Reimagining human-nature interactions through sensory augmentation and speculative design to discuss human agency over their senses.
Gestural Interactions. Exploring the potential of gestural communication to enhance human machine collaboration in interactive art through a series of prototypes
Vanshika
Interactive Storytelling. Exploring the use of paper craft and physical computing integrated with symbolism to narrate myths and legends
Vionetta
Human-Machine Memory. Exploring the boundaries between humans and machine memory through a series of reflective experiments
Jun Liang
The Internet is a Space for Divination. A Reimagination of Divinatory Objects/Spaces on the Internet through Speculative Design.
Boon Cheong
prAI-vacy. Investigating the Oversaturation of AI and Concerns Over Data Privacy as Data Turns into a Commodity through Speculative Design
Mindy
Soundscapes of Memory. Exploring how sound influences the perception of emotions and triggers memory recall, studied through multi-sensory audio-visual experiences.
Soda
Mind in Motion. Promoting a Sense of Authorship in Contemporary Artists through Prototyping an Interface for EEG-Based Generative Art
23-24 graduation projects
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Marcus
Tanishqa
Siyoun
Ryan
Bryan
Attention Span in Brand Experience Understanding Cognitive Load and Attention Span for Brand Experience
Creativity as a Commodity Speculating the future of the Creative Industries amid the increasing adoption of generative AI technologies.
Digital Stroll Revamping digital reading for Gen Z through tailored typography and enhanced readability.
Tangible Theater Exploring a new configuration of theater experience through tangible and interactive objects and non-linear narratives.
Artefacts of Fragmentation Provoking reflections on algorithm curation dilemmas through speculative artefacts
Richard
Exhibition beyond Immersive Augmented Reality An investigation into AR interactions within contemporary museums, with the aim of enriching a meaningful experience
Ly
Tactile Playgrounds Assistive navigational tools for visually impaired children
Cheryl
Sculpting Perceptions Exploring textures in digital-physical interaction bridging realms seamlessly.
Yi Shan
Antidotes for Bruised Creatives An exploration of translating displays of expressions to visuals
Momo
Motivation Makeover Cultivating motivation through a guided experience, one challenge at a time.
22–23 graduation project topics
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Aditi
Seyoun
Ariel
Rachel
Sadhna
Farm to Fork to Phenotype Experiments in computer-mediated intervention design and mediated food behaviour during a time of global food crisis.
Selfscapes: Redefining Digital Identities Experiments into the potential of generative visual systems as visual representations of identities in the online space.
Ubiquitous Nuisance A study on how sound walks are used to understand urban noises within parks in Singapore.
Interactive Signage Explore the design of interactive signages that interpret a neighbourhood’s identity through generative visuals.
Bio-Interfaces. Facilitating human-plant interaction in a potential hybrid future to uphold urban nature as a public good
Farhan
Integrating machine learning in design An exploration into creative machine learning through the use of interactive prototypes to encourage designers to integrate design and creative technology
Matin
Promoting Healing via Interactive Positive Distractions. Utilising affective computing and ludic engagement methods to create enhanced positive stimuli for spaces of healing
Aimee
Urban Plastisphere. Exploring the role of interactive artefacts in soliciting awareness of plastic pollution.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Readings
Computation in Design, selected readings.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
1
2
3
4
5
6
Computation in Design, selected readings.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project

1
Computation in Design, selected readings.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
2
Computation in Design, selected readings.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
3
Computation in Design, selected readings.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
4
Computation in Design, selected readings.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
5
Computation in Design, selected readings.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
6
The following list of readings list is split into three sections: Coding, Sensing, Making.
Readings range from book chapters to journal and magazine articles to blog posts and interviews.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Computation in Design, more readings.
And some more readings, navigate down.
Computation in Design, more readings.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Coding addresses the aspect of applying computation to creative practices, which in this case is particularly relevant to the field of design communication. Coding is seen here as a technique, a tool, a playground and a language to communicate and interact with and through machines.
Coding
Generative Systems, creative coding, visual communication, algorithmic behaviours, machine learning, experiences
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Computation in Design, more readings: Coding
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Sensing here refers to sensory experiences as well as sense making and sensing with our human senses or the sensors of machines. Furthermore, sensing here goes hand in hand with data acquisition, analysis, visualisation and expression when processed computationally.
Sensing
Interaction, interfaces, sensors, data, physical computing
Computation in Design, more readings.
Computation in Design, readings: Sensing
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Computation in Design, readings.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Making is understood as a hands-on approach and collaborative group work where members of a group share knowledge, learning and skills. Furthermore, one should be aware of what is being made and think critically about the context in which the making takes place and has an impact.
Making
Tools, materials, discourse, prototypes, fabrication, immersion, expression, creative technology
Computation in Design, readings.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Computation in Design, other resources.
Atelier
Computation in Design
B-DC Dissertation and Graduation Project
Journals, Proceedings
Festivals, Awards
Other resources
cid-atelier-overview
By Andreas Schlegel
cid-atelier-overview
- 819