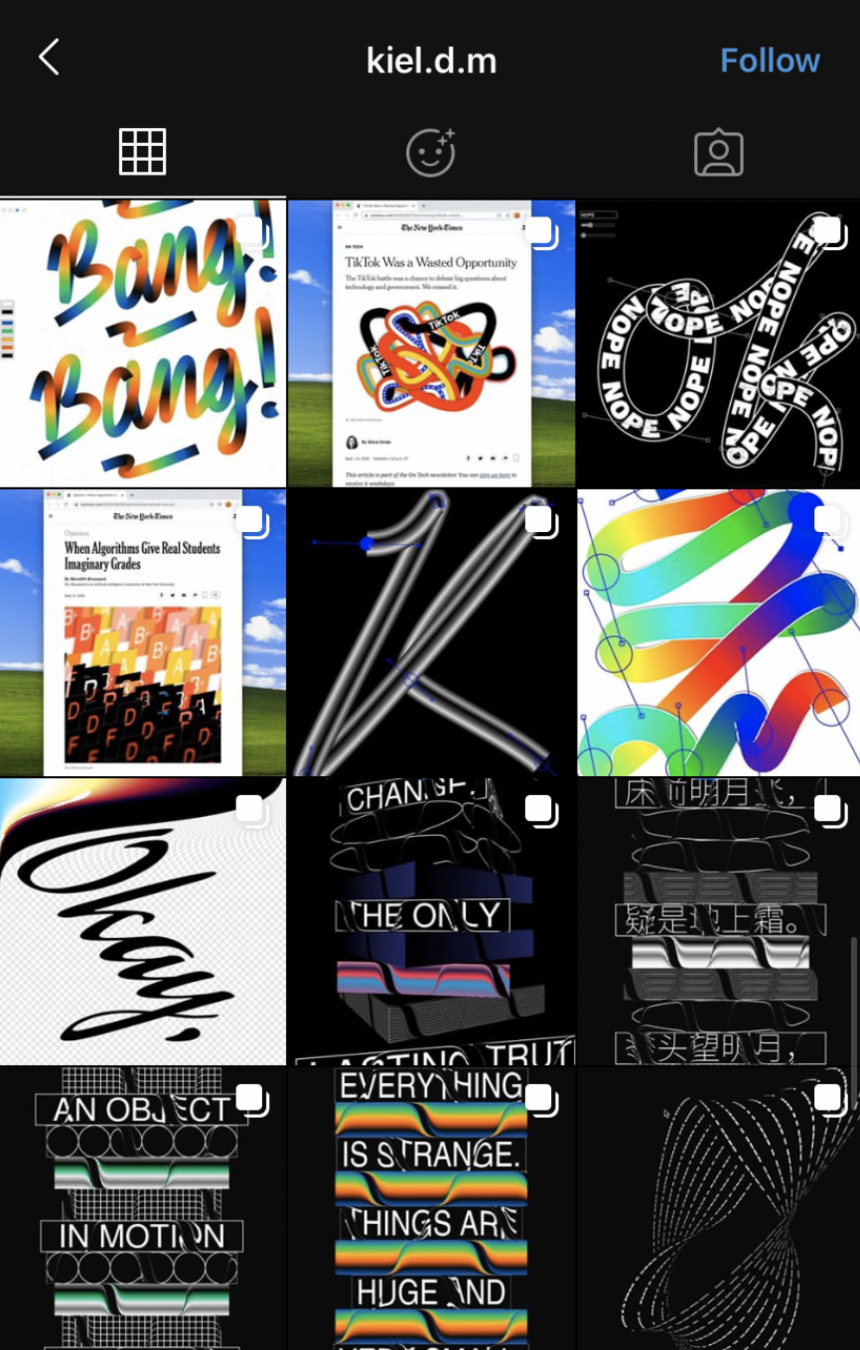
Generative Type
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1


Type and Code
Generative Type
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Type and Code
Generative Type, Type and Code.
1
The term generative can refer to a process that is executed computationally. Based on a set of rules and parametric changes, outputs are generated iteratively. Outputs here can be of many types and origins.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
In this workshop we will focus on typography as an output informed and transformed by code and change over time.
2
How can we build systems in code to create generative type? Through a series of exercises exploring the generative, dynamic and playful potential of type, students will create a series of digital outputs that will be archived and presented in an online type showcase.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Students will engage in looking at and experimenting with type from a micro view, the vertex point, to the larger view of a letter’s shape to the topology of words.
Furthermore, we will look at the emerging behaviour of type when in motion to study how this can have an effect on how we read and perceive textual and formal information.
Generative Type, Type and Code.
Explore
Ideate
Make
Test
Share
Weekly Schedule
We will meet on a weekly basis Mondays 9.30am – 12.30pm. For a breakdown of the weekly schedule, navigate downwards.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Warming up with shapes
1
Letters and vertex points
2
Pixels and buffers
3
4
This session will focus on introducing the techniques, visual directions and experiments we want to explore over the course of the workshop.
We will take a look at the structure of a letter and its vertex points which can be accessed and manipulated in code.
In this session we will cover a series of technical topics on how to load and use fonts with p5js.
Based on what we have covered and explored, participants will embark on their own code type challenge.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Code Type Challenge
5
During this last session we will do a work in progress show and tell of progress made so far. The web-template will be introduced.
Sharing and wrapping up
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Shapes and Letters
Code Type Challenge
Vertex Points
Buffers
Microsite
w1
w2
w3
w4
w5
Code Basics
This section gives an overview of basic coding concepts you should find useful to playfully explore activities and exercises for this workshop and creative coding in general.
syntax shape function variable conditional loop transformation object array .
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
p5js
code
sketch
editor
p5js is a creative coding environment, a community and a JavaScript library for creative coding, with a focus on making coding accessible and inclusive for artists, designers, educators, beginners, and anyone else.
Code, simply put, is a set of instructions for programming a computer. In Creative Coding, we use instructions to create computer-generated results. Often visual, they can be static, dynamic, poetic, interactive and they can appear on a screen or on paper, as objects among many other things.
In Creative Coding, we call a sketch a computer program. Why a sketch? In art or design, a sketch is a common term for a rough and unfinished drawing, here a coded sketch should be seen similarly, rough and unfinished, to illustrate a thought, to bring a creative idea to life.
An editor, or more precisely a code editor, is a text editor program designed for editing source code for computer programs. In our particular case this semester, we will use a browser-based editor at editor.p5js.org, a web editor for p5js. For demos and tutorials we will use p5live.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Function
Code Basics
function setup( )
function draw( )
A function is simply a “chunk” of code that you can use over and over again, rather than writing it out multiple times. Functions enable programmers to break down or decompose a problem into smaller chunks, each of which performs a particular task.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Principles and Commands to learn and remember.
setup
draw
function
rect
ellipse
line
coordinates
beginShape
endShape
vertex
Principles
Commands
The setup() function is called once when the program starts. read more
Called directly after setup(), the draw() function continuously executes the lines of code contained inside its block. read more
A function is a set of statements that perform a task. Optionally, functions can have parameters. read more
All shapes drawn to the screen have a position that is specified as a coordinate. read more
A rectangle is a four-sided closed shape. The first two parameters set the location of the upper-left corner, followed by width and height. read more
Draws an ellipse (oval) to the screen. The first two parameters set the location of center of the shape, followed by width and height. read more
Draws a line (a direct path between two points) to the screen. read more
Using the beginShape() and endShape() functions allow creating more complex forms. read more
beginShape() begins recording vertices for a shape and endShape() stops recording. read more
All shapes are constructed by connecting a series of vertices. vertex() is used to specify the vertex coordinates. read more
Code Basics
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Principles and Commands to learn and remember.
function
parameters
arguments
Principles
Example
Parameters are used in the definition of the function, between the brackets, eg. function add(x,y) here x and y are parameters.
A function is a set of statements that perform a task. Optionally, functions can have parameters. read more
Arguments are the actual values that get passed in when a function is called, eg. add(1,2) here 1 and 2 are arguments.
Code Basics
// 1. function without parameters:
// function hello1 will draw a rect at 0,0.
// that's all it can do at the moment.
function hello1() {
rect(0,0,100,100);
}
// call hello1 like this: hello1();
// 2. function with parameters
// hello2 takes 2 paramters, theX and theY
function hello2(theX, theY) {
rect(theX, theY, 100, 100);
}
// when calling hello2() with 2 arguments
// these arguments will be passed on to the
// function as parameters theX and theY
// in the following call theX will be 50 and
// theY will become 200
// call hello2 like this: hello2(50,200);
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Transformation
Code Basics
Transformation is a concept that initially leaves you scratching your head. Why? Transformations act on the coordinate system rather than on shapes, and transformations are accumulative. Allison Perish has written an extensive and useful tutorial with examples here.
translate
rotate by 180 degrees or PI
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Principles and Commands to learn and remember.
function
parameters
arguments
push
pop
translate
rotate
scale
Principles
Commands
Parameters are used in the definition of the function, between the brackets, eg. function add(x,y) here x and y are parameters.
A function is a set of statements that perform a task. Optionally, functions can have parameters. read more
Arguments are the actual values that get passed in when a function is called, eg. add(1,2) here 1 and 2 are arguments.
The push() function saves the current drawing style settings and transformations, while pop() restores these settings. read more
The push() and pop() functions can be embedded to provide more control over the positioning and rotation of shapes. read more
Specifies an amount to displace objects within the display window. read more
Rotates a shape by the amount specified by the angle parameter. read more
Increases or decreases the size of a shape by expanding or contracting vertices. read more
Code Basics
transform
When using transformations, the things you draw never change position; the coordinate system itself does. read more
mouse
We can query and use the mouse's location and button state (see interactivity) read more
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Principles and Commands to learn and remember.
Principles and Commands
Example
Code Basics
transform
When using transformations, the things you draw never change position; the coordinate system itself does. read more
push
pop
translate
rotate
scale
The push() function saves the current drawing style settings and transformations, while pop() restores these settings. read more
The push() and pop() functions can be embedded to provide more control over the positioning and rotation of shapes. read more
Specifies an amount to displace objects within the display window. read more
Rotates a shape by the amount specified by the angle parameter. read more
Increases or decreases the size of a shape by expanding or contracting vertices. read more
// use transformations to draw 2 rects
function draw() {
fill(0,0,255,100);
noStroke();
// draw a rect at coordinate 50,200
// without moving the rect but the
// coordinate system using translate
push();
translate(50,200);
rect(0,0,100,100)
pop();
// same as above but now we rotate
// the rect by 45° (using radians)
push();
translate(50,200);
rotate(HALF_PI);
rect(0,0,100,100)
pop();
}22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
A for loop repeats one or more statements a given number of times.
use a for-loop to create multiple copies
Loop
Code Basics
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Loop
Code Basics
use a for-loop to create multiple copies
for(let i=0;i<10;i++) { }
A for-loop, followed in parentheses, the for-loop takes three arguments, initialization, condition and variable modification
The first argument i.e. initialization runs only one time before the execution of the loop; It initializes a variable which is used in the condition for the loop.
The second argument i.e. condition is evaluated before every iteration; the loop terminates when this condition is satisfied. in this example when i is 10 or bigger, then the loop will exit.
The third and the last argument variable modification is used to modify the value of the variable used in condition after every iteration of the loop.
All statements go in between the curly brackets.
A for loop repeats one or more statements a given number of times.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Principles and Commands to learn and remember.
Principles and Commands
Example
Code Basics
loop
A 'for loop' consists of three different expressions inside of a parenthesis.These expressions are used to control the number of times the loop is run. read more
for
for creates a loop that is useful for executing one section of code multiple times. read more
function setup() {
createCanvas(800, 800);
}
function draw() {
background(0);
stroke(255);
noFill();
push();
translate(100,100);
// here we will use a for-loop to draw
// 10 rectangles vertically with a distance
// of 50 pixels.
for(let i=0;i<10;i++) {
push();
translate(0,i*50);
rect(0,0,600,20);
pop();
}
// the for-loop ends here after 10 rects
// have been drawn, see code between {} (above).
pop();
}22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Conditional
Code Basics
Decision making
do things when condition is false
Computers can be programmed to make decisions, to do different things in different circumstances. Decisions take the form of an if-then format. They start with a condition, which is then evaluated as either True or False.
do things when condition is true
true
false
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
22–23
Computation in Design 1
B-DC 121
Principles and Commands to learn and remember.
Principles and Commands
Example
Code Basics
if
Use if to specify a block of code to be executed, if a specified condition is met and true read more
else
else if
true
false
Use else to specify a block of code to be executed, if the same condition is false read more
The push() and pop() functions can be embedded to provide more control over the positioning and rotation of shapes. read more
Also known as boolean, true when condition is fulfilled read more
Also known as boolean, false when condition is not fulfilled read more
// if–else
// check if mouse is pressed or not
function check2() {
if (mouseIsPressed === true) {
background(0,255,0);
} else {
background(255,0,0);
}
}
// if–else if–else
// 3 checks based on the location
// of mouseX which will change the
// background color accordingly
function check3() {
if(mouseX<100) {
background(255,0,0);
} else if(mouseX>100 && mouseX<200) {
background(0,255,0);
} else {
background(0,0,255);
}
}
22–23
Computation in Design 1
B-DC 121
Computers can be programmed to make decisions, to do different things in different circumstances.
Conditional
Code Basics
Decisions take the form of an if-then format. They start with a condition, which is then evaluated as either True or False.
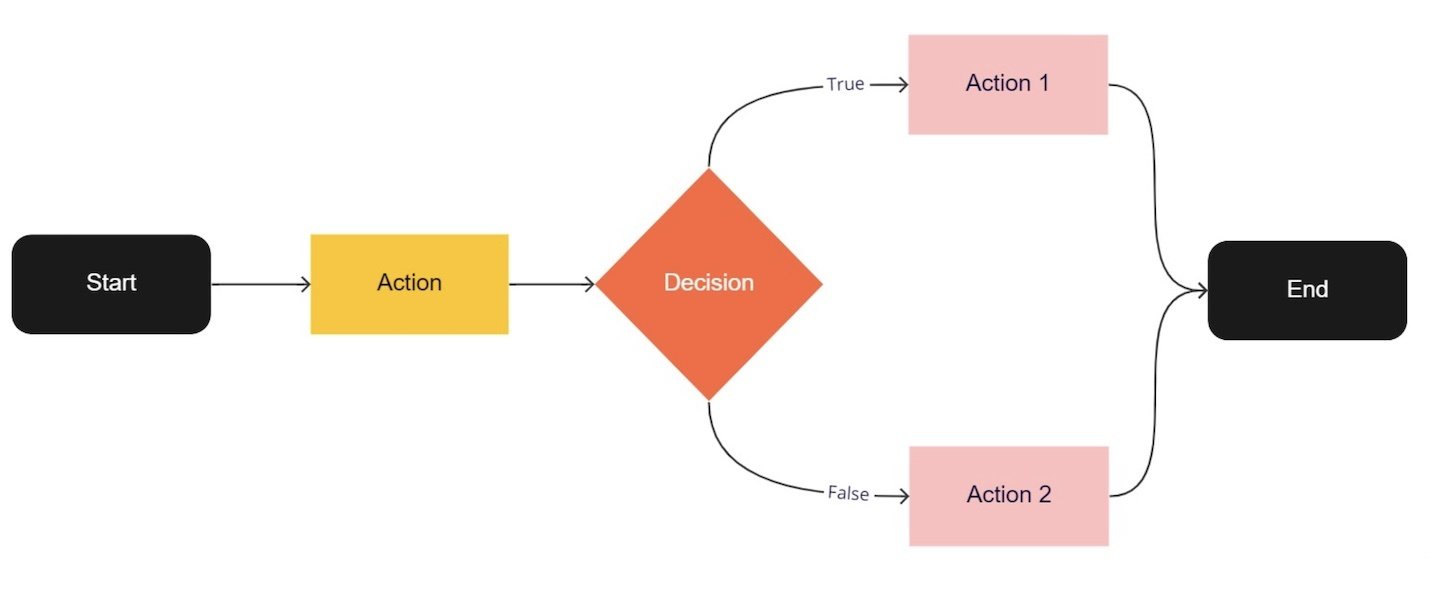
22–23
Computation in Design 1
B-DC 121
Conditional
Code Basics
When programs are allowed to make decisions, the outcome is non-linear.

22–23
Computation in Design 1
B-DC 121
Conditional
Code Basics
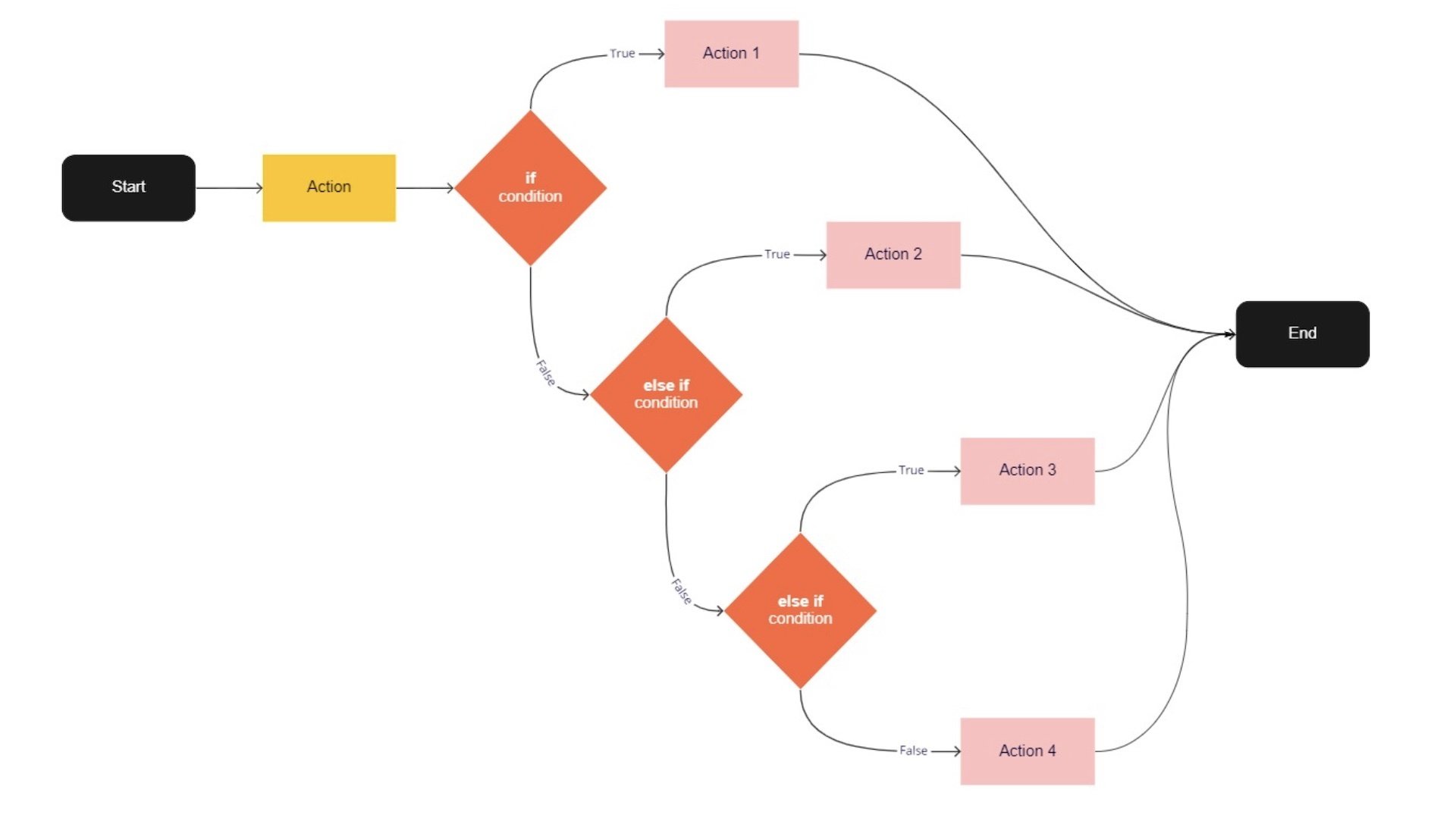
When programs are allowed to make decisions, the outcome is non-linear.
Generative Type
Resources
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Type and Code

Generative Design
Book
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Type+Code
Book
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Graphic Design the New Basics
Book


22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Form+Code
Book

22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Analog Algorithm
Book
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
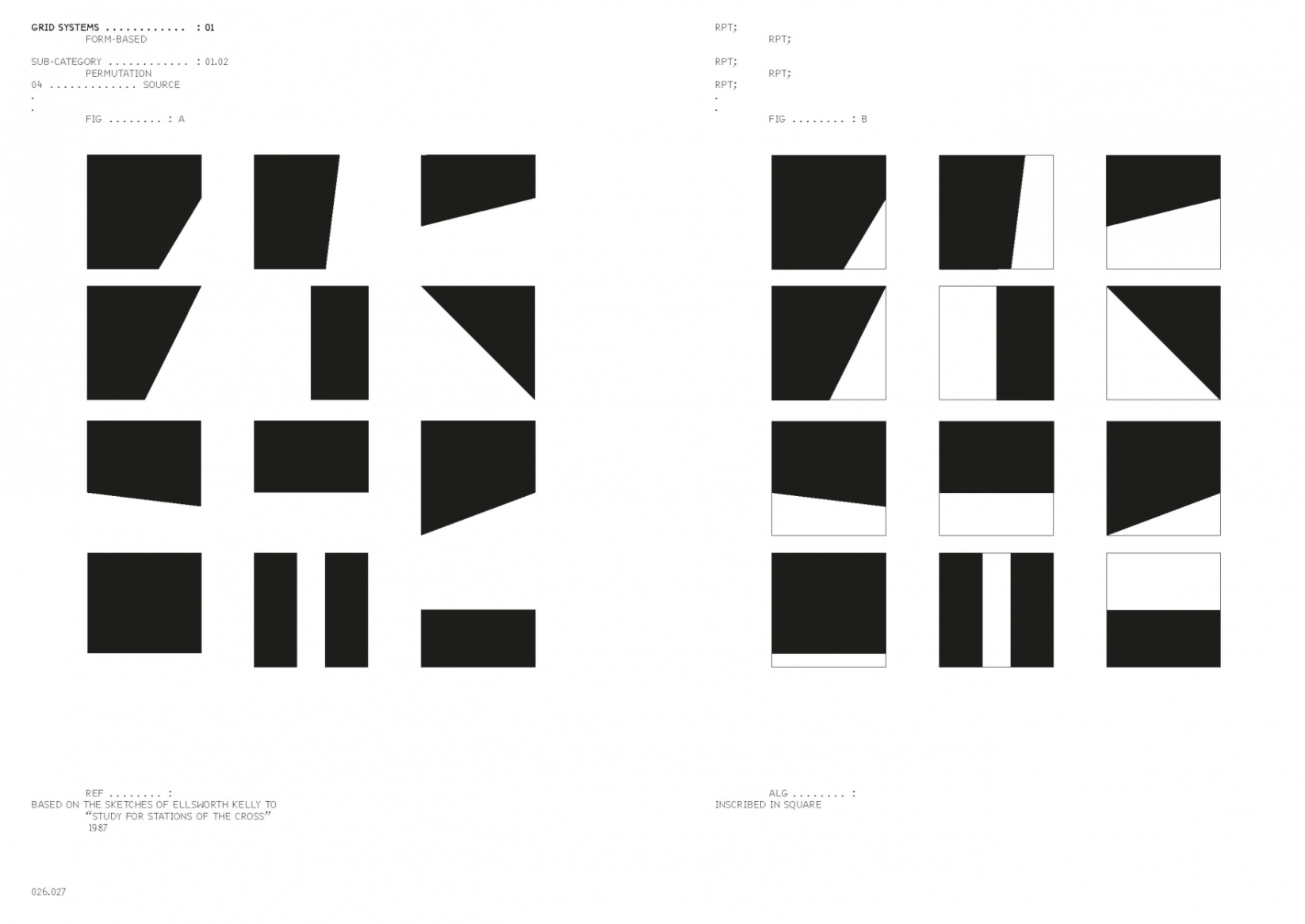
Grid Systems
Book
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Making and breaking the Grid
Book
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Book
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Project
Arial Bold
Project

In October 2014, Benedikt and Joey decide to use the alphabet shaped letterforms found in aerial imagery as their vehicle to show how people - artists, designers, scientists, etc - can make data from aerial images. Looking to reach out to a larger community for support and bring attention to their efforts, the duo decide to start a Kickstarter campaign.

22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Font Map
Project
Designers at IDEO wanted to bring artificial intelligence to the world of fonts, so they created Font Map, a quick experiment to see how machine learning can address challenges in design. They created a tool that helps designers understand and see relationships across more than 750 web fonts.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Dimensions of Two
Project
A publication and exhibition in black and white, two and three dimensions. Lots to learn from.
In a voluminous yet easy-to-handle self-publication with a white softcover, the three designers who make up Norm sum up their many years of unique practical research into the fundamental principles of graphic design. The nine chapters, most in black and white, deal with topics such as size ratios, page divisions, graphic objects and letter shapes. They are densely packed with a wide variety of drawings and schemata elucidated with minimalist textual information.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Flexible Visual Systems
Project
“Flexible Visual Systems” is the design manual for contemporary visual identities. It teaches you a variety of approaches on how to design flexible systems, adjustable to any aesthetic or project in need of an identifiable visual language.
To learn how to design flexible systems is not just learning another craft, it is going to change the way you think and work entirely. It is an approach, how to design. If you would place system design into a curriculum it would be the foundation course, putting you in the right mindset. You can apply the systemic approach to any discipline you will later specialize in, from corporate design, communication design, user experience design to textile design.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Type me, type me not
Project
These experiments in computational typography were based on Peter Cho's coursework from a class John Maeda taught at the MIT Media Laboratory in the fall of 1997. Type me, Type me not received a gold award from the 1998 ID Magazine Interactive Media Design Review. The original project was a Java Applet, and he ported it to P5.js in 2016.
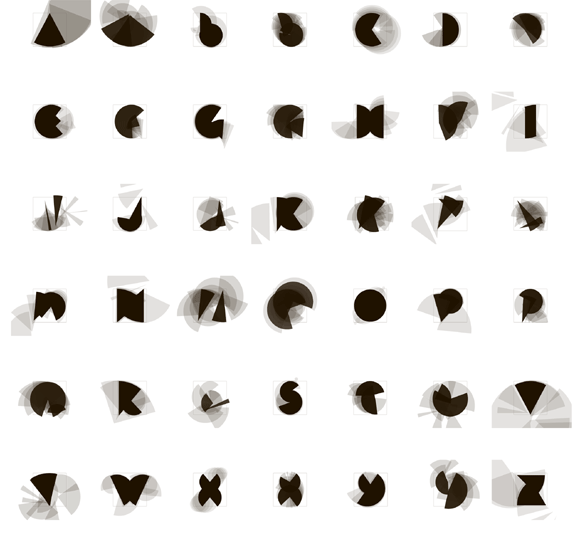
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Robotype
Project
Humans use letters, which are two-dimensional static symbols, for communication. Writing these letters requires body movement as well as spending a certain amount of time; therefore, it can be demonstrated that a letter is a trajectory of movement and time. Based on this notion, Yuichiro Katsumoto conducted studies regarding multidimensional kinetic typography, primarily using robots to display a letter and visualize its time and movement simultaneously.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
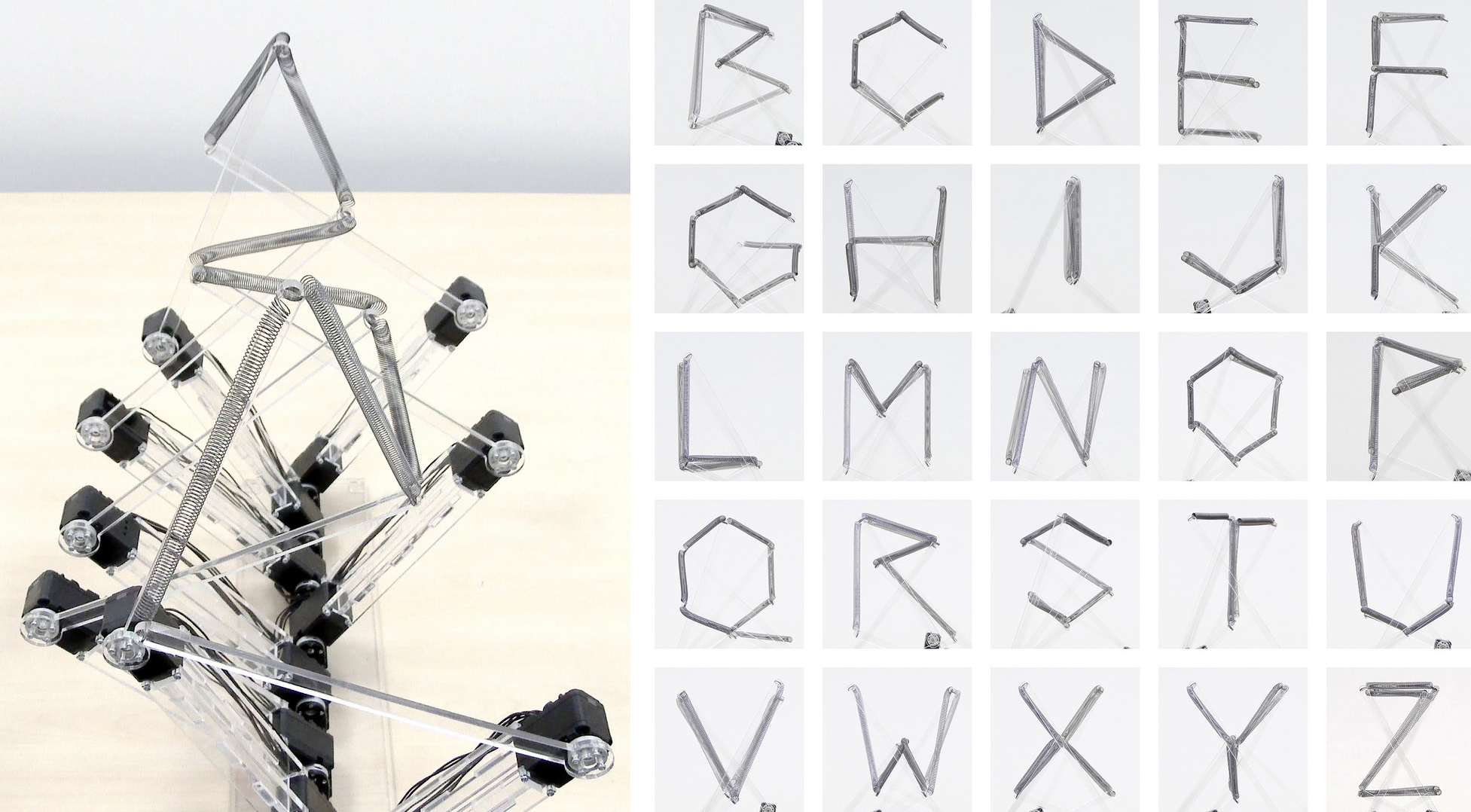
Project
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Studio
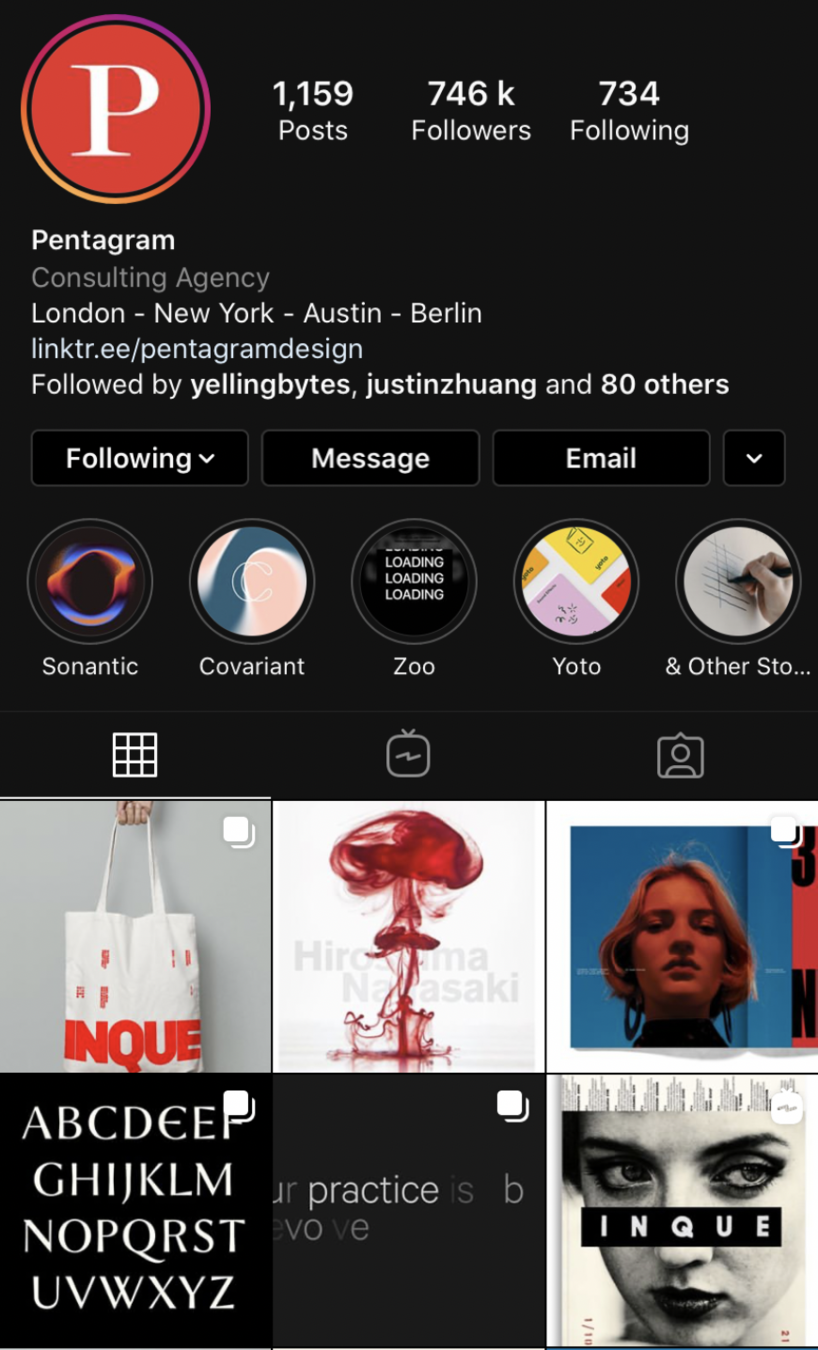
Pentagram
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
See how the visual identity unfolds and applies to a wide range of outcomes.
Andreas Gysin
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1


Tim Rodenbroecker
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1

Obys
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1

Dia Studio
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Luca Banchelli
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Wait for it.
loackme
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Andre Burnier
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Design Systems International
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
A design studio that uses code as their primary material. They turn ideas into prototypes and experiences, create visual systems, build custom design tools and improve workflows.
Backgrounds in Computer Science, Graphic Design, Cognitive Science, and Interior Design power the studio's fresh and unique perspective, while a shared passion to explore, learn, and create unique visual solutions unites the people at designsystems international.
Demo Festival
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
About the demo festival: "On a dark stormy night, after endlessly scrolling through our Instagram feeds, we dreamt of all the beautiful motion design we had seen. And we kept dreaming: what if we could show all this great work on hundreds of giant screens? Not just for our fellow designers, but for everyone! That dream came true."
DEMO was founded by Studio Dumbar/DEPT® and Global.

More
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
And more
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Studio
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Week 1
1
This session will focus on introducing the techniques, visual directions and experiments we want to explore over the course of the workshop.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Warming up with shapes

A bit of context and history.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Design by Numbers. John Maeda
Scriptographer. Juerg Lehni
Processing. Casey Reas, Ben Fry and Community
Generative Design. Benedikt Gross et al.
1990s
2002–2012
since 2001
2009 and 2018
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1

I created Design By Numbers during in a time when getting artists and designers to program the computer was just beginning to become in vogue. I spent most of the earlier half of the 1990's espousing the importance of getting beyond the tools, and into the medium of programming itself. Working on Design By Numbers was a kind of revelation for me. I realized how uninteresting it is to program. The actual point of the book was to get more non-programmers to program as a means to hopefully realize how boring programming can be. And then to re-imagine, re-envision, and realize a superior form of programming for the non-mathematically inclined.
– John Maeda
Design by Numbers
1990s
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Scriptographer is an open-source scripting plugin for Adobe Illustrator, available as a free download at Scriptographer.org. The software was created to give the user the possibility to extend Illustrator’s functionality by writing simple scripts in the JavaScript language, with a focus on ease of use, simplicity and clarity of the provided vocabulary.
Scriptographer
2002–2012
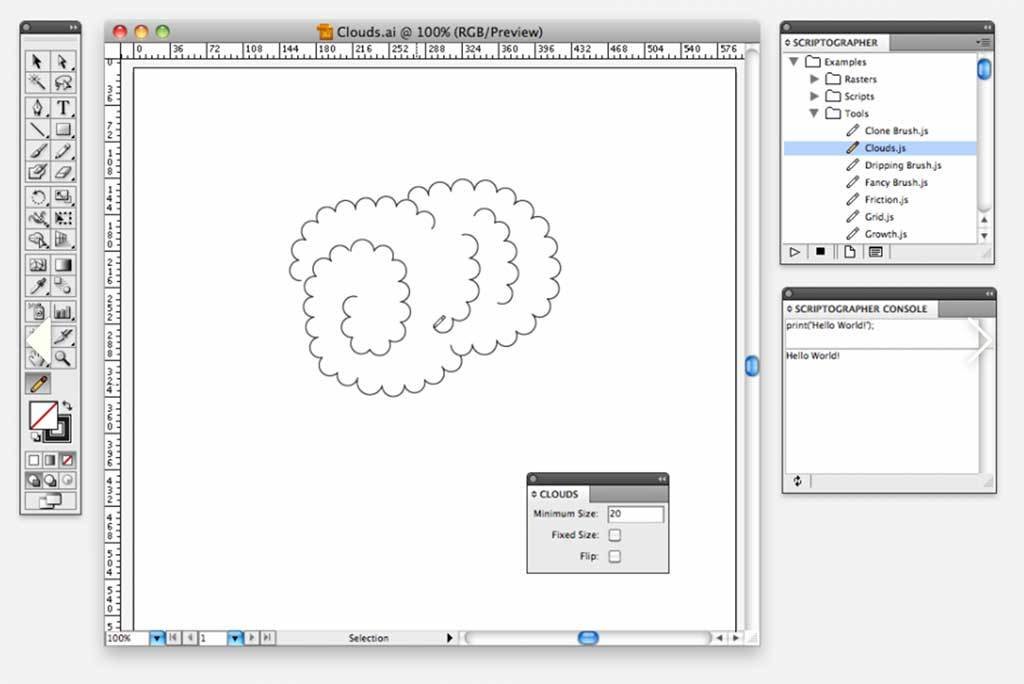
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Processing is a free, open-source coding language for visual art developed by Ben Fry and Casey Reas, former classmates at the MIT Media Lab. Launched in 2001 as Proce55ing, the project encompasses a programming environment designed for artists’ use, and a community of practitioners. Processing has grown into the Processing Foundation, an organisation that oversees a larger family of software that aim to empower users to work creatively with code, as well as promote software literacy – especially for those who have not had access to programming education.
Processing
since 2001
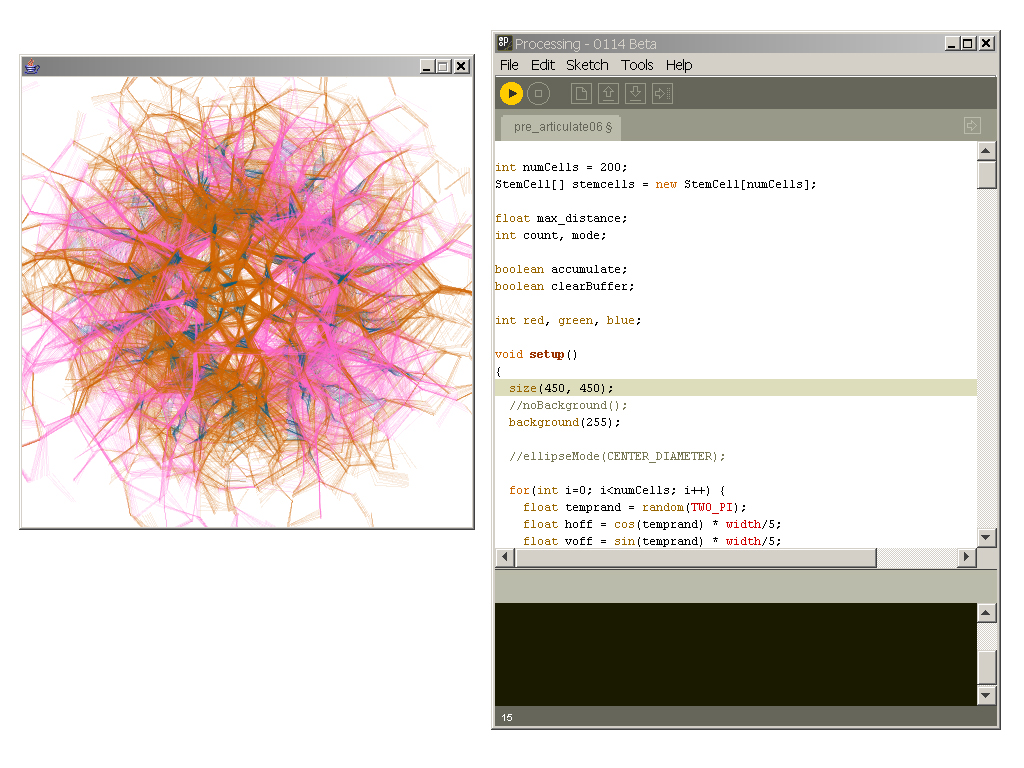
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Generative design fundamentally changes the design process: the designer shifts from being a performer of tasks to being a conductor, effectively orchestrating the decision-making process of the computer. This is what generative design is all about: iteratively developing different processes and then selecting those that produce the most visually compelling results. Designers and artists no longer have to use the tools dictated by computers and powerful but prescriptive design software and can now create their own tools, which generate amazing results independently, as many of the examples in the book demonstrate.
Generative Design Book
2009 and 2018


22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Code
Form
Iterate
Modular
Parameter
Simple to complex
System
Tool
Takeaway points
Warming up and Session 1
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
1 Let's start with drawing some shapes
2 Take a look at the Processing Community Day open call from Coimbra
3 Make our own alphabet
Let's start with drawing some shapes
Warming up
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1


Create an adaptation from one of the images on the right. Here look for patterns in the image and apply them in code, but first, analyse with pen and paper before you head over to the code editor.
You can work in pairs. The purpose is to analyse and understand the image in structure and then translate into code.
30
1
Take a look at the Processing Community Day open call from Coimbra
Warming up
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
This could be a small but rewarding outside of class exercise, more details can be found under the Call section on their website. Extended deadline is 16 October 2022.
The Processing Community Day @ Coimbra 2022 invites professionals, researchers, students, designers and artists to submit individual or collective projects that visually and / or conceptually explore techniques or subjects related to the theme “Community”.
2
Making our own alphabet
Warming up
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Using simple shapes, each participant will draw two assigned letters in code using a canvas of size 540x540. Use black and white only.
3


45
continues on next page
Making our own alphabet
Warming up
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
3
Follow the links
Code template

Approach
Code template
Freestyle
Sketch on paper
Systematic
Use a grid
Don't stop here and follow your own heros and inspirations.
45
Making our own alphabet
Warming up
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
3
Challenge
For each of your assigned letters, create a coded poster with the coded letter in the foreground.
Support the foreground with a composition of basic shapes and colors arranged in the background.
Before you start: come up with a simple narrative–a fleeting moment–that your posters are based on.
Format
600 x 850 pixels
primitive shapes
maximum 5 colors
coded
p5js sketch, png (svg if possible)
Homework
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Complete assigned letters and coded posters
Review Resources and Code Basics
From session 1 to session 2
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
2
We will take a look at the structure of a letter and its vertex points which can be accessed and manipulated in code.
Letters, words and vertex points
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Shapes and Letters
Code Type Challenge
Letters, words and vertex points
Buffers
Microsite
w1
w2
w3
w4
w5
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Observations
Follow instructions and requirements, for example use required dimensions
When you copy a link to a spreadsheet, give it a label by editing the link and change its text.
Transition from using static numbers (e.g. vertex(100,200)) to using variables instead (e.g. vertex(x1, y2)) to make you sketch more flexible
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Lets first review the outcomes from last week's session: the letterforms and Exploration 1, posters. In session 1 we have looked at playing with simple shapes to create and practice generating graphics using code.
Review Session 1


Session 2
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
1 Loading fonts in 2D and 3D
2 Static text
3 Letterforms and vertex points
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 2
In session 2 we will continue to look at simple shapes and then continue with manipulating vertex points of a letter. Outcomes here can be rendered as images or .svg files.
Furthermore, we will look at reading and loading fonts in p5js. Ideally the fonts are uploaded in ttf format into your sketch. For example, you can download a font from Google Fonts as a ttf file and then upload this file into your sketch. With the commands to the right you can control the font-settings of letters after a font has been loaded.
Continues on the next slide
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 2
In session 2 we will continue to look at simple shapes and then continue with manipulating vertex points of a letter. Outcomes here can be rendered as images or .svg files.
Furthermore, we will look at reading and loading fonts in p5js. Ideally the fonts are uploaded in ttf format into your sketch. For example, you can download a font from Google Fonts as a ttf file and then upload this file into your sketch. With the commands to the right you can control the font-settings of letters after a font has been loaded.
Continues on the next slide
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 2
Create a sketch that loads a font and displays the font in 2D and 3D. You can create two sketches here, one for 2D and one for 3D.
Use up to 5 words. Use the references and demos provided. For each sketch only use black and white.
Reference
Demo
540x540 pixels
font, text, 2D, 3D
Up to 5 words
black on white only
Requirements
Loading Fonts
20
1
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 2
Select one out of the three reference images to the right and create a sketch that follows its particular style. If unsure, do a quick search on the designer and design style to view more examples for that particular period and style.
Requirements
Static Text
40
540x540 or 1080x1080 pixels
font, text, 2D
black on white only
save to .jpg
Demo



Raoul Hausmann, Grün, 1918.
Poetry, Dada.
Josef Mueller Brockmann, 1971.
Studio Dumbar, 2019.
Dutch Design.
2
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 2
Using the vertex point details of a letter you are able to create a custom letterform by replacing and animating a vertex point's visual representation.
In this activity play with the number of vertex points and the visual representation of a point using different shapes, movement and color. The final letter should be saved as .svg and .png file.
Letterforms and vertex points
margin of 20px
Canvas
height 540px
width can vary
Continues on the next slide
3
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 2
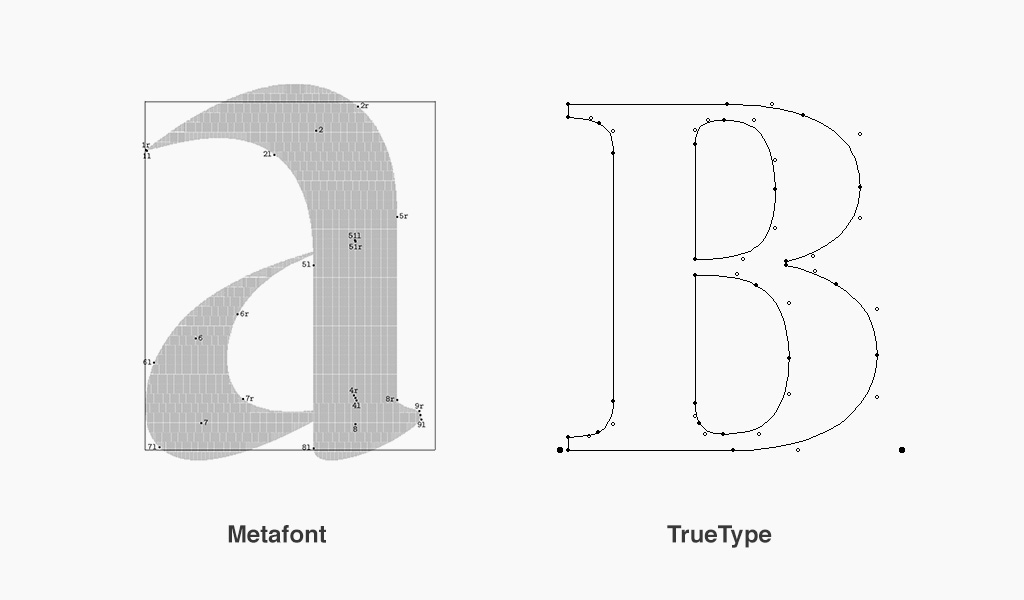
Vertex points, or vectors, are the building blocks of a single letter of a typeface. Letters here can also be referred to as glyphs – the specific shape, design or representation of a character. In code we can access the vertex points of a glyph and manipulate and customise a glyph.
Letterforms and vertex points
Continues on the next slide
Read more
3
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 2
Letterforms and vertex points
Continues on the next slide
To what extend can we ________ so that the letter is still readable?
Manipulate a letter
Reduce vertex points
Animate the letter
Experiment with shapes
Interact with form
How can we ________ so that the process and outcome can be considered playful?
Code templates
3
Homework Challenge
Session 2
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Challenge
Build on Exercise 2 Static Text and create a 5 to 10-second animation. Use up to 5 words that describe one or more sounds, for example: broken glass or wrrroommhh or click clack. You can use multiple sketches and then edit them together in post-production.
From exercise 3 Letterforms and vertex points create an animation to your taste, it can last up to 20 seconds. If you want to use sound, use non-copyrighted tracks from freesound.org
Format
540 x 540 or 1080 x 1080 pixels
shapes and fonts
maximum 5 colors
coded
For each challenge
1. a p5js sketch
2. png(s) or svg(s) (process)
3. a mp4
In this second session we looked at how to load fonts, how to display words using code and how to animate letters.
Each of you should have created static and animated letters and words in black and white.
1
2
Homework
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Complete homework challenge
Review Resources and Code Basics
From session 2 to session 3
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
3
In this session we will cover a series of technical topics on how to load and use fonts with p5js.
Pixels and buffers Review and redo session 2

Please see slides under session 2, especially part 3 and homework.
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Observations
Commitment, motivation, completeness
Ideas, study, reference, inspiration, interpretation, aesthetics, consistency
Variety, iterations, small but many steps of progress
To do well in this workshop, you must demonstrate the above points and be committed to them in the remaining sessions.

Where you see shapes, I see code.
Max Bill, Poster, 1980s.
Iterations click letters to view
Demo
Demonstrating and understanding iteration. Click on a to f on the right to open code at different stages of a sketches' development process.
Small but many steps of progress
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
How to save an image
General
Easy right click into the canvas, then 'save image as ...'
Or, more challenging, use saveCanvas() on keyPressed in your code to save the canvas to image (this option is included in many of the sketch samples provided in this slide deck)
How tos
How to record video
Use quicktime's screen recording option to record videos from a running sketch.
How to go into fullscreen mode
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 3
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
1 Buffers
2 Reactive
If you feel comfortable with what was covered in session 1 and session 2, do continue with the following
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
A buffer is equivalent to a layer in Photoshop or Illustrator. In p5js such a layer is created using the createGraphics command. We can then access this buffer and draw into it. Buffers can then be treated like images and we can apply filters using blendMode() or use them as textures applied to 3D objects.
The examples provided in this section will demonstrate the following:
Session 3
1 create a buffer with createGraphics()
2 draw into a buffer and render it using image()
3 apply buffers to texture()
4 draw buffer multiple times and use blendMode()
Buffers
1
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
A buffer is equivalent to a layer in Photoshop or Illustrator. In p5js such a layer is created using the createGraphics command. We can then access this buffer and draw into it. Buffers can then be treated like images and we can apply filters using blendMode() or use them as textures applied to 3D objects.
The examples provided in this section will demonstrate the following:
1 create a buffer with createGraphics()
2 draw into a buffer and render using image()
3 apply buffers to texture()
4 draw buffer multiple times and use blendMode()
Mouse: mouse-click to toggle lighting
Session 3
Buffers
1
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
A buffer is equivalent to a layer in Photoshop or Illustrator. In p5js such a layer is created using the createGraphics command. We can then access this buffer and draw into it. Buffers can then be treated like images and we can apply filters using blendMode() or use them as textures applied to 3D objects.
The examples provided in this section will demonstrate the following:
1 create a buffer with createGraphics()
2 draw into a buffer and render using image()
3 apply buffers to texture()
4 draw buffer multiple times and use blendMode()
Session 3
Buffers
1
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
A buffer is equivalent to a layer in Photoshop or Illustrator. In p5js such a layer is created using the createGraphics command. We can then access this buffer and draw into it. Buffers can then be treated like images and we can apply filters using blendMode() or use them as textures applied to 3D objects.
The examples provided in this section will demonstrate the following:
1 create a buffer with createGraphics()
2 draw into a buffer and render using image()
3 apply buffers to texture()
4 draw buffer multiple times and use blendMode()
Session 3
Buffers
1
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
A buffer is equivalent to a layer in Photoshop or Illustrator. In p5js such a layer is created using the createGraphics command. We can then access this buffer and draw into it. Buffers can then be treated like images and we can apply filters using blendMode() or use them as textures applied to 3D objects.
The examples provided in this section will demonstrate the following:
1 create a buffer with createGraphics()
2 draw into a buffer and render using image()
3 apply buffers to texture()
4 draw buffer multiple times and use blendMode()
Session 3
Buffers
1
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
We can read sound input using the p5js sound library and then analyse it using the fft method. An fft analysis extracts the intensity for a range of frequencies which we can then use to manipulate visuals on the screen.
Both examples linked to on the right demonstrate how to read sound from the microphone and then read the intensity of frequencies as well as the sound level.
Session 3
Sound Reactive
2
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 3
Some more samples
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 3
Some more samples
Homework Challenge
Session 3
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Challenge
Review the challenge from session 2 and improve on it as necessary (optional)
Create a series of sketches that address one or more of the topics and code samples covered in this session. You can choose to work with one or more of the following options: Buffer, 2D, 3D, reactive. If you are using sound, use non-copyrighted soundtracks, for example from freesound.org
Format
fullscreen
shapes and fonts
maximum 5 colors
coded
For challenge 2
1. one or more p5js sketch(es)
2. png(s) or svg(s) (process)
3. a video in .mp4
In this third session we did review and redo the challenge introduced in session 2. Furthermore we have looked at two more topics, buffers and sound reactivity.
1
2
Homework
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Complete homework challenge session 3
Review and improve previous challenges
From session 3 to session 4
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
4
Based on what we have covered and explored, participants will embark on their own code type challenge.
Code Type Challenge

Session 4
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Based on the given brief and techniques learned in previous sessions, start working on your self-directed mini-project for this workshop
While we start working on your mini-projects, you can ask for individual feedback and comments on previous exercises
Letterforms
Vertex points
Words
Pixels
Buffers
What we have covered
Code Experiments
Mockups
Short description
What is required for the Mini-Project
many examples and references have been shared and shown in previous slides. Use those as a starting point and inspiration if you find them useful.
References
Mini-Project
Arrays
Buffers
frameCount, sin, tan
loops
Shapes
Sound input
textToPoints
Transformations
Code topics addressed
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Mini-Project
Briefing, intro.
In this mini project you will extend and apply your typographic experiments to 1) or 2)
1) a mock-up of a spatial scenario, for example a poster, billboard, animation, exhibition design, virtual space or a combination of these
2) An interactive application, such as a camera- or sound-reactive application, a generative tool or similar that can be user-tested.
optionally you can combine 1) and 2)
1/3
1) can be achieved by overlaying coded experiments in a p5js sketch over a photograph.
2) can be achieved by testing and video recording an interactive sketch with one or more of your peers.
Alternatively use a video editing tool, or 3D application to superimpose coded visual (as rendered video)
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Mini-Project
Briefing, approach.
Start by sketching visual ideas on paper. Your approach can be purely visual or thematic.
A visual approach, for example, looks at a series of explorations into the representation of typographic elements where composition, complexity, iteration, movement and generativity are central to the experiments and outcomes.
A thematic approach, for example, focuses on the interpretation of an imaginary event such as a festival, conference or exhibition. Experiments and outcomes here can be derived and guided by visual interpretations of the theme. Outcomes should be static and animated, they can be interactive if applicable.
pen-on-paper sketch(es)
windowWidth, windowHeight
fullscreen
shapes, words, letters
2D or 3D
frameCount, sin, tan, loop
transformations (rotate, translate, scale)
up to 5 colours
short project description
Requirements
2/3
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Mini-Project
Briefing, for example, spatial scenario.
3/3
Dynamic poster in public
Jenny Holzer

Typographic objects
Barbara Kruger

Exhibition design
Virtual space


22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Mini-Project
Briefing, for example, interactivity and tool.
3/3
p5js sketch, facial features tracking




p5js sketch, microphone input
p5js sketch, midi keyboard to control sound and type on screen
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Mini Project
Session 4
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Challenge
Work on a mockup of a spatial scenario or an interactive application with focus on generative type.
Use a visual or thematic approach
Document your process from initial sketches on paper to a series of p5js sketches to images and videos.
Finished outcome
Requirements
fullscreen (16x9) or square
shapes, words, letters
2D or 3D, max. 5 colours
frameCount, sin, tan, loop
1. pen on paper sketches
2. series of p5js sketches
3. final sketch
4. png(s) or svg(s) (process)
5. mp4
6. short description
1
2
3
4
Homework
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Complete homework challenge session 4
Review and improve previous challenges
From session 4 to session 5
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
5
During this last session we will do a show-and-tell of progress made so far. The web-template will be introduced.
Sharing and wrapping up
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Session 5
Generative Type
Outcomes
22–23
B-DC 221
Generative Type Workshop
Computation in Design
Semester 1
Type and Code
cid-generative-type-2223
By Andreas Schlegel
cid-generative-type-2223
- 1,027