Functional Programming
in JavaScript

函数式编程本质
-
支持 高阶函数 (higher-order functions)
- 追求 函数调用没有副作用 (no side-effect)
Related Concepts
-
First-class & Higher-order Functions
-
Pure Functions
-
Currying
-
Function Composition
-
Hindley-Milner
-
Pattern Matching
-
Lambda Calculus
-
Lazy Evaluation
-
Functor、Applicative Functor & Monad
First-class Functions
First-class functions are values, and can be used in every way that typical expressions can.
assigning to variables
const foo = funxtion() { return 'Hey, js-functional' }
foo() // => 'Hey, js-functional'storing in data structures
const obj = {
foo: function() { return 'Hey, js-functional' },
}
obj.foo() // => 'Hey, js-functional'returning by functions
const bar = function() {
return function() { return 'Hey, js-functional' }
}
const foo = bar()
foo() // => 'Hey, js-functional'
passing as arguments to other functions
const baz = function(func) { return func() }
baz(function() { return 'Hey, js-functional' })
// => 'Hey, js-functional'
Higher-order functions
A higher-order function is a function that does at least one of the following:
- takes one or more functions as arguments.
- returns a function as its result.
function noisy(fun) {
return function() { return fun.apply(null, arguments) }
}
noisy(Boolean)(0) // => false
noisy(Boolean)(1) // => true
Pure Functions
A function where the return value is only determined by its input values, without observable side effects.
- Given the same input, will always return the same output.
- Produces no side effects.
- Relies on no external state.
Math.random() // => 0.1599823728657992
Math.random() // => 0.10539394558259518
// `Math.random()` is not pure.
Math.sqrt(2) // => 1.4142135623730951A function is only pure if, given the same input, it will always produce the same output.
关于函数副作用(side-effect)
变更了更高作用域的的变量
let glob = 1
function foo(x) { return ++glob + x }
console.log(foo(1)) // => 3关于函数副作用(side-effect)
“隐晦”地修改了引用参数
let glob = 1
const obj = {glob}
function foo(x) { return ++x.glob }
foo(obj)
console.log(glob) // => 2
Benefits of Pure Functions
- Cacheable & Memoization
- portable, easier to test & parallelize
- Referential Transparent
- can be lazy
memoize技术: 递归函数性能优化
/**
f(0) = 0
f(1) = 1
f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2) (n > 1)
**/
function fibonacci(n) {
if (n === 0 || n === 1) return n
return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)
}
console.log(fibonacci(7))
console.log(fibonacci(40))
以存储空间换执行效率
const fibonacci = (function() {
const cache = {}
return function fib(n) {
if (n in cache) return cache[n]
return (cache[n] = (n === 0 || n === 1) ? n : fib(n-1) + fib(n-2))
}
})()
console.log(fibonacci(7))
console.log(fibonacci(40))
memoize函数的JS实现
function memoize(func) {
const memo = {}
const slice = Array.prototype.slice
return function() {
const args = slice.call(arguments)
if (args in memo) return memo[args]
return (memo[args] = func.apply(this, args))
}
}
const memoizedFibonacci = memoize(fibonacci)
console.log(memoizedFibonacci(7))
console.log(memoizedFibonacci(40))引用透明(Referential Transparent)
An expression is said to be referentially transparent if it can be replaced with its corresponding value without changing the program’s behavior.
# 中国的首都是个美丽的城市。
# 北京是个美丽的城市。
function foo(n, fun) { return fun(n) + fun(n) }
foo(10, fibonacci)举例:函数推导
function foo(n, fun) { return fun(n) * 2 }
foo(10, fibonacci)
# 编程领域
fibonacci(n) + fibonacci(n) => 2*fibonacci(n)
# 数学领域
f(x) = g(x) + g(x) = 2 * g(x)如何理解 Curry 化函数?
In mathematics and computer science, currying is the technique of translating the evaluation of a function that takes multiple arguments (or a tuple of arguments) into evaluating a sequence of functions, each with a single argument.
一個函數当且仅当只能容许拥有一个参数
假設, js 語法有這樣的限制:
function max(a, b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
max(10086, 10010);
// => 10086
function max(a) {
return function(b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
}
max(10086)(10010);
// => 10086继续举例
function addFourNumbers(a, b, c, d) {
return a + b + c + d;
}
addFourNumbers(1, 3, 5, 7);
// => 16
function curriedAddFourNumbers(a) {
return function(b) {
return function(c) {
return function(d) {
return a + b + c + d;
}
};
}
}
curriedAddFourNumbers(2)(4)(6)(8);
// => 20借助一些工具:ramdajs
const R = require('ramda')
const addFourNumbers = function(a, b, c, d) {
return a + b + c + d
}
const curriedAddFourNumbers = R.curry(addFourNumbers)
curriedAddFourNumbers(1)(3)(5)(7)
//=> 16
// 或
const f = curriedAddFourNumbers(1)
const g = f(3)
const h = g(5)
h(7)
//=> 16Why Curry Needs
Heron's Formula
Calculate the area of a triangle while only knowing the length of all three sides.
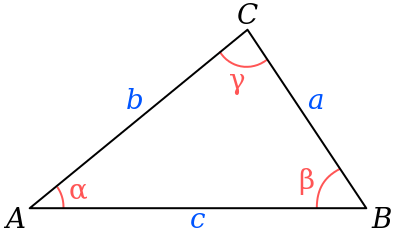
// 根据三条边的长度判断是否能够构成一个三角形
function isTriangle(a, b, c) {
return (a>0 && b > 0 && c > 0 && a+b > c && a+c > b && b+c > a)
}
// 根据三角形三条边的边长计算其面积
function heronFormula(a, b, c) {
if (!isTriangle(a, b, c)) throw new Error('Illegal triangle')
const p = (a+b+c) / 2
return Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c))
}
// 计算已知一条边长为3,其它两条边未知的的三角形面积
function foo(x, y) {
return heronFormula(3, x, y)
}
/**
*
* 如果已知边长为4,其它两条边未知的求其三角形面积
* 是不是要再实现一遍与foo(x,y)结构完全类似的函数?
*
**/
const R = require('ramda')
// 对 heronFormula() 函数进行Curry化
const curriedHeronFormula = R.curry(heronFormula)
// 〔新函数〕计算其中一个边长为3的三角形面积
const foo = curriedHeronFormula(3)
// 〔新函数〕计算其中两条边长分别为3,4的三角形面积
const bar = foo(4)
// 〔结果〕计算边长分别为3,4,5的三角形面积
console.log(bar(5))
// => 6
通过Curry化,能够更加精简地实现函数复用
当然,Curry本质意义在于:将函数完全变成「接受一个参数;返回一个值」的固定形式,这样对于讨论和优化更加方便。
Partial Functions
Function Composition
const compose = (f, g) => x => f(g(x))pointfree
const getAdminEmails = function(users) {
const emails = [];
for (var i = 0; i < users.length; i++) {
if (users[i].role === 'admin') {
emails.push(users[i].email)
}
}
return emails
}pointfree
const getAdminEmails = users =>
users
.filter(u => u.role === 'admin')
.map(u => u.email)pointfree
const getAdminEmails = users =>
users
.filter(u => u.role === 'admin')
.map(u => u.email)Hindley-Milner
大家都知道 1加1等于2;但是一个苹果加一个板凳等于什么呢?
λ-calculus
Lazy Evaluation
js-functional
By Ivan Lyons
js-functional
js-functional
- 2,851



