Android Mobile Development
First Application
Tools to use
-
Android SDK
-
Android Emulator GenyMotion
-
Android Studio
-
Gradle build system
Appendix
-
Web Services
-
RESTful Web Services
-
Event Driven
-
Dependency Injection
Web services
A Web service is a method of communication between two electronic devices over a network. It is a software function provided at a network address over the Web with the service always on as in the concept of utility computing.
-
REST-compliant Web services
-
Arbitrary Web services
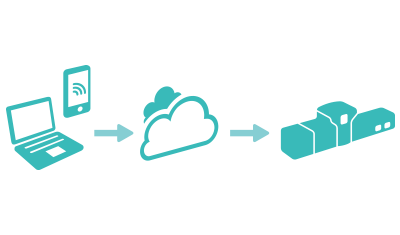
RESTful Web Services (1)
RESTful web services are built to work best on the Web. Representational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style that specifies constraints, such as the uniform interface. In REST Architecture everything is a resource.
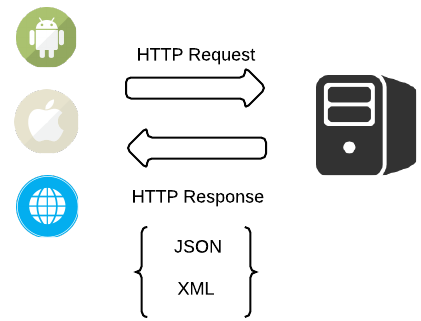
RESTful Web Services (2)
GET /tickets - Retrieves a list of tickets
GET /tickets/12 - Retrieves a specific ticket
POST /tickets - Creates a new ticket
PUT /tickets/12 - Updates ticket #12
PATCH /tickets/12 - Partially updates ticket #12
DELETE /tickets/12 - Deletes ticket #12
Event Driven
Event-driven programming is a programming paradigm in which the flow of the program is determined by events such as user actions (mouse clicks, key presses), sensor outputs, or messages from other programs/threads.
Dependency injection
Dependency injection is a software design pattern that implements inversion of control for resolving dependencies.
A dependency is an object that can be used (a service). An injection is the passing of a dependency to a dependent object (a client) that would use it. The service is made part of the client's state. Passing the service to the client, rather than allowing a client to build or find the service, is the fundamental requirement of the pattern.
Dependency injection allows a program design to follow the dependency inversion principle. The client delegates to external code (the injector) the responsibility of providing its dependencies
Application
A basic client of Forsquare's REST api
SPECS
-
Login into the app with standard credentials
-
List of places for specific location
-
Show a place with details
Project Breakdown
- Write and read the specs
- Naive mockup and definition of use cases
- Number of Screens
- Revise & define the flow diagram of screens
- Final Mockup
- Read Forsquare API
- Detailed define use cases
- App Architecture
- Backward Compatibility
- Setup environment
- Decide + Setup library gradle dependencies
- Dev - Test
- RELEASEEEE!!!!!!!
Naive Use Cases
User Login Use Case
data
- username
- password
result
- redirects to places list
Places list Use Case
data
- location
result
- show places list
- user authenticated
Place Show Use Case
data
- placeId
result
- show place with details
Number of screens
User Login Screen has -> 1 Activity + 1 Fragment
Places list -> 1 Activity + 1 Fragment
Places list -> 1 Activity + 1 Fragment
Advise
Prefer screen by each feature separately
Flow diagram of screens
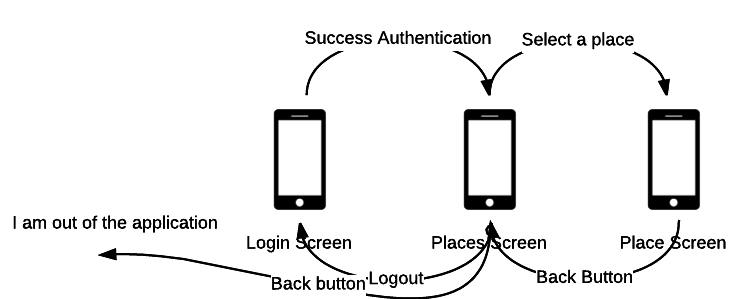
Mockup
-
InVision
-
Balsamiq
-
Prototype.io
-
FuildUI
Detailed Use cases
User Login
Data
- <user username>
- <user password>
Primary Course
1. Fill form and request login with above data
2. System validates data
3. System authenticates user
4. System redirects to main screen
Exception Course
1. System delivers validation error
2. System delivers auth error
App Architecture
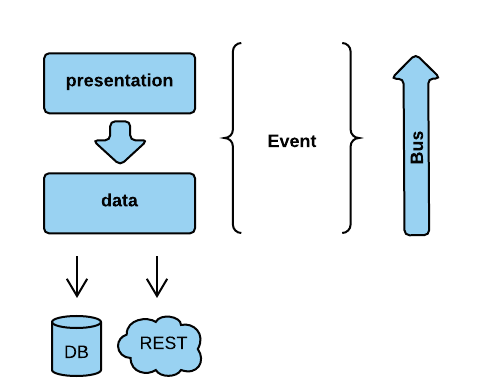
In the next presentation we will show MVP and cleaner layers
Decide & Setup libraries
RESTful API library
Retrofit by Square
Event Driven
Otto by Square
Dependency Injection
Dagger2 by Google
// RETROFIT //
// Define API
public interface GitHubService {
@GET("/users/{user}/repos")
Call<List<Repo>> listRepos(@Path("user") String user);
}
// Define service client to use for calls
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl("https://api.github.com")
.build();
GitHubService service = retrofit.create(GitHubService.class);
// Make Asynchronous HTTP Call
Call<List<Repo>> repos = service.listRepos("octocat");// OTTO //
// Bus to send events
Bus bus = new Bus();
// Sends an event
bus.post(new AnswerAvailableEvent(42));
// Listen for an Event
@Subscribe public void answerAvailable(AnswerAvailableEvent event) {
// TODO: React to the event somehow!
}// DAGGER2 //
// Inject Constructor
class Thermosiphon implements Pump {
private final Heater heater;
@Inject
Thermosiphon(Heater heater) {
this.heater = heater;
}
...
}
// Inject fields
class CoffeeMaker {
@Inject Heater heater;
@Inject Pump pump;
...
}Views
Butterknife by Square
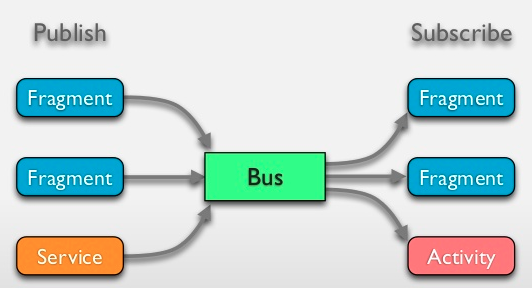
Image fetcher
Picasso
// This is the DEFAULT
activity.subtitle = (android.widget.TextView) activity.findViewById(R.id.title);
activity.footer = (android.widget.TextView) activity.findViewById(R.id.subtitle);
activity.title = (android.widget.TextView) activity.findViewById(R.id.footer);
// BUT This is COOL
class ExampleActivity extends Activity {
@Bind(R.id.title) TextView title;
@Bind(R.id.subtitle) TextView subtitle;
@Bind(R.id.footer) TextView footer;
@Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.simple_activity);
ButterKnife.bind(this);
// TODO Use fields...
}
}
Picasso.with(context).load("http://i.imgur.com/DvpvklR.png")
.into(imageView);Dev - Test
Advise
Package by feature
Use Espresso & Robolectric for test
Jump steps - No time

Clean Architecture for Padawans

“Before software can be reusable it first has to be usable.”
Ralph Johnson (computer scientist)
Android Mobile Development - Part 2
By Spiros Oikonomakis
Android Mobile Development - Part 2
- 1,837


