Earthsys 144: Fundamentals of GIScience
Projections and Coordinate Systems
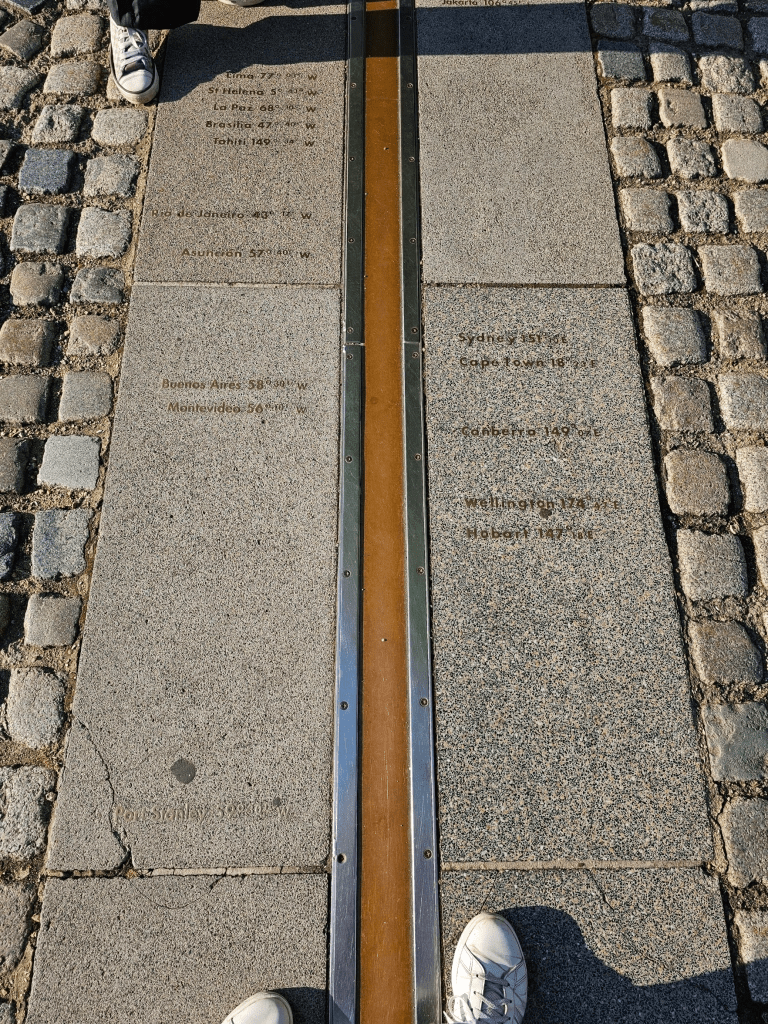
where is your data? gis.stanford.edu


The Size & Shape
of the Earth
(Less complicated, but somehow more complicated, than you think)
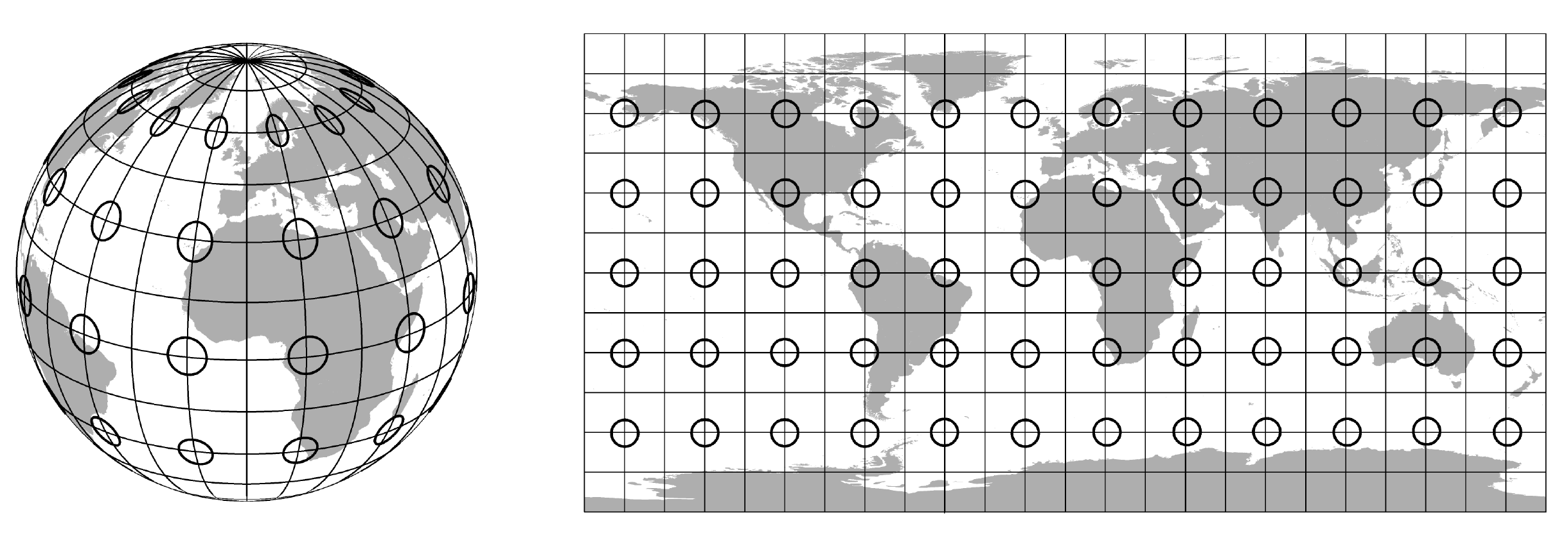
spherical vs ellipsoid?
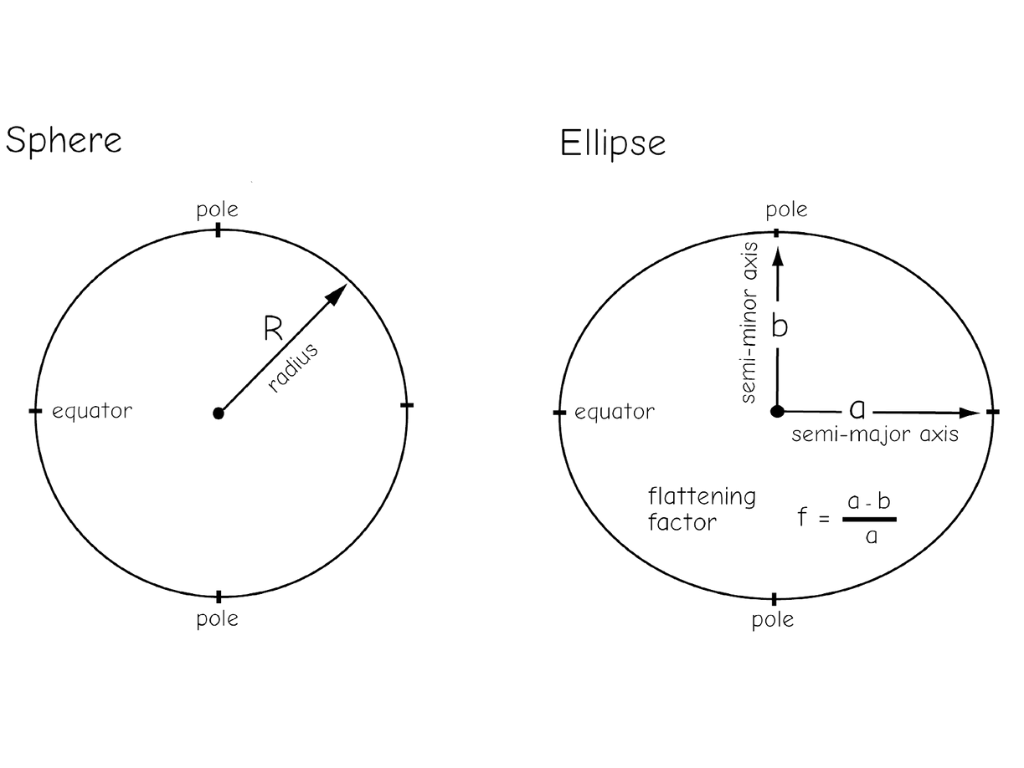
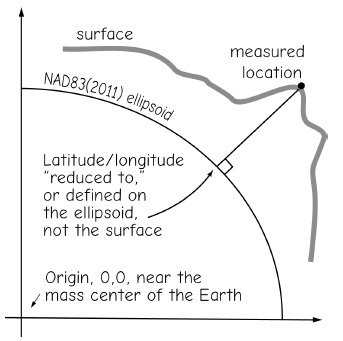
surface & ellipsoid coordinates
the geoid
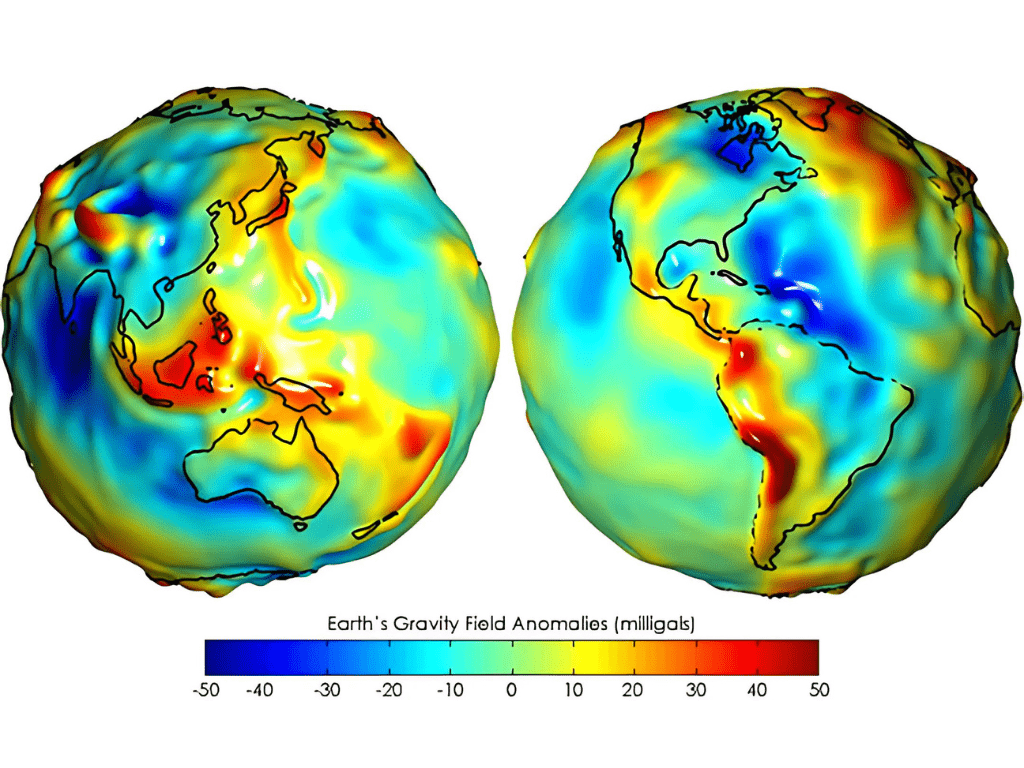
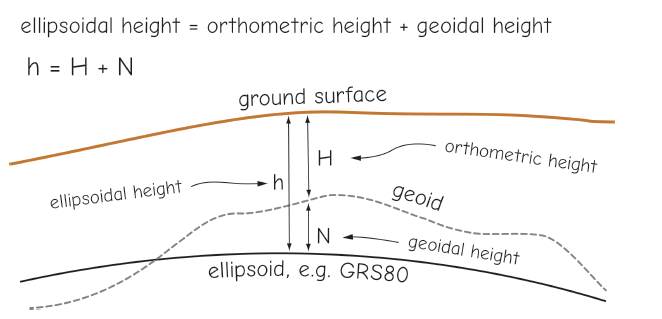
But, really...
If the Earth were scaled down to the size of a billiard ball, the variance in its surface "smoothness" would be less than 0.089 mm.
World Pool-Billiard Association (WPA) equipment specifications, a billiard ball must be uniform with a tolerance of +/- 0.127 mm

geographic coordinate systems
(Laying a "frame of reference" on the Earth)
coordinates
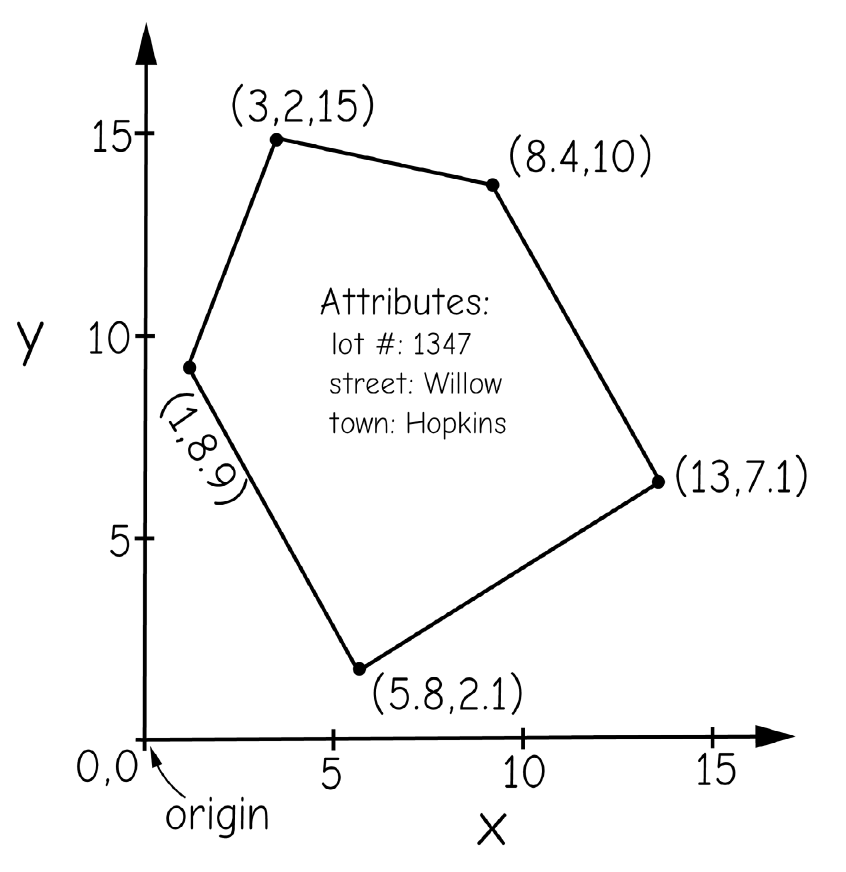

Geographic Coordinate Systems
longitude, con't
coordinate notation
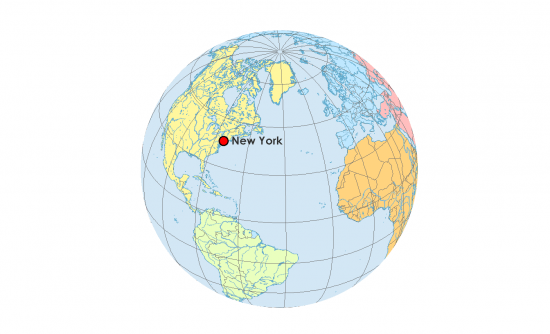
Degrees Minutes Seconds (DMS)
📍 Latitude: 40° 42′ 51″ N
📍 Longitude: 74° 00′ 21″ W
Decimal Degrees (DD)
📍 Latitude: 40.714
📍 Longitude: -74.006

Precision
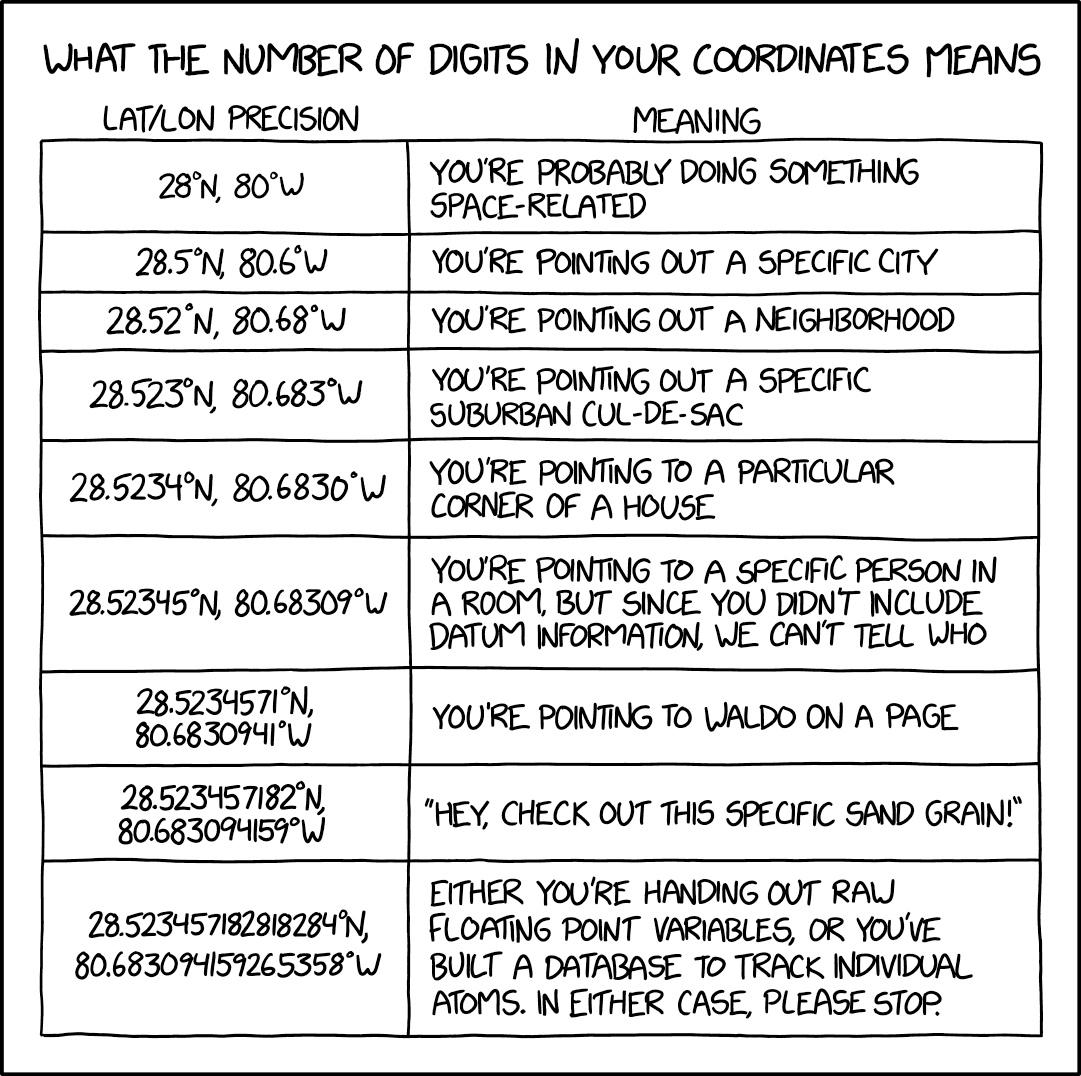
Precision
decimal
places degrees distance
------- ------- --------
0 1 111 km
1 0.1 11.1 km
2 0.01 1.11 km
3 0.001 111 m
4 0.0001 11.1 m
5 0.00001 1.11 m
6 0.000001 0.111 m
7 0.0000001 1.11 cm
8 0.00000001 1.11 mmHow many locations can one place have?
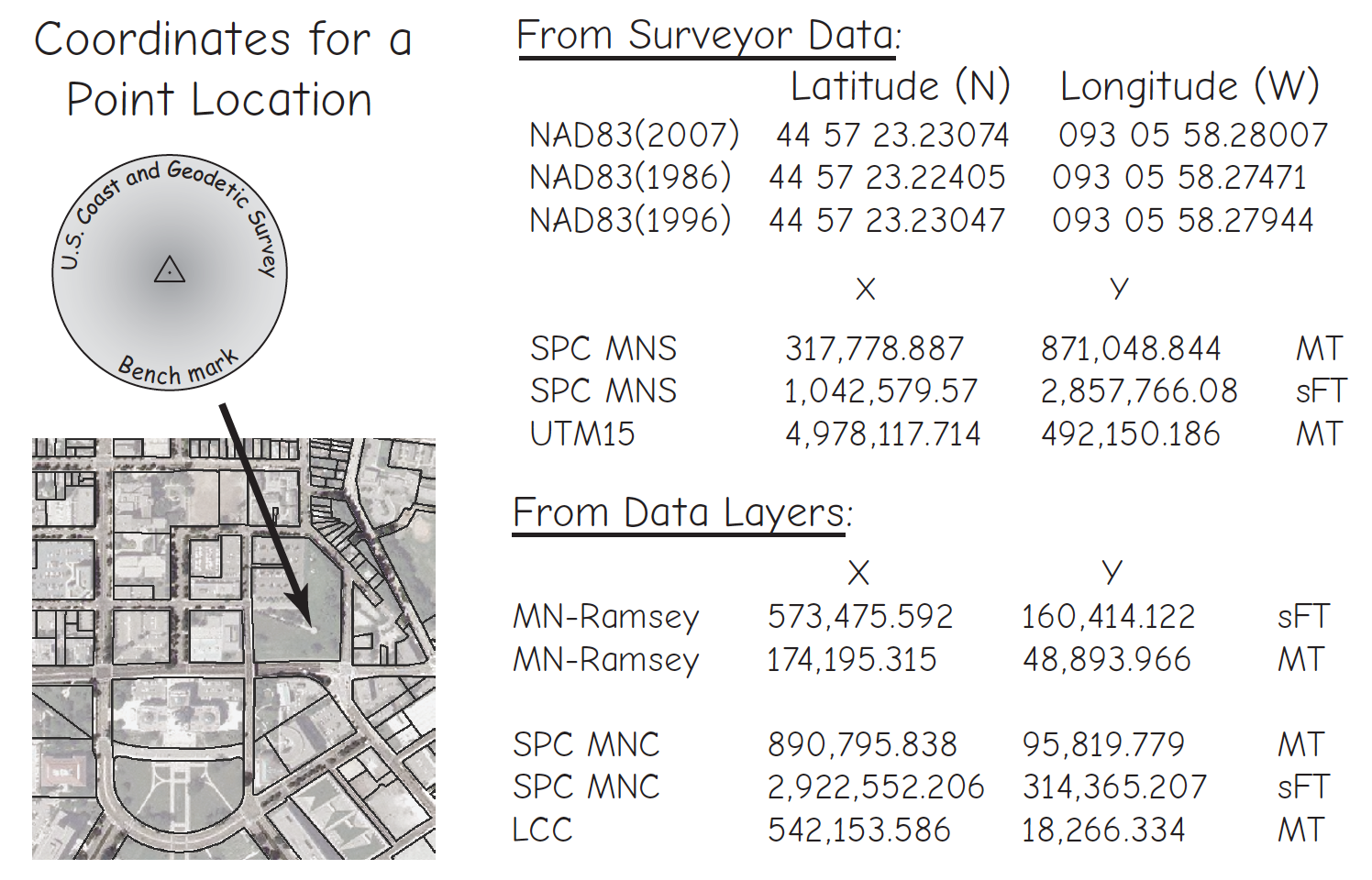
datums & (geographic) transformations
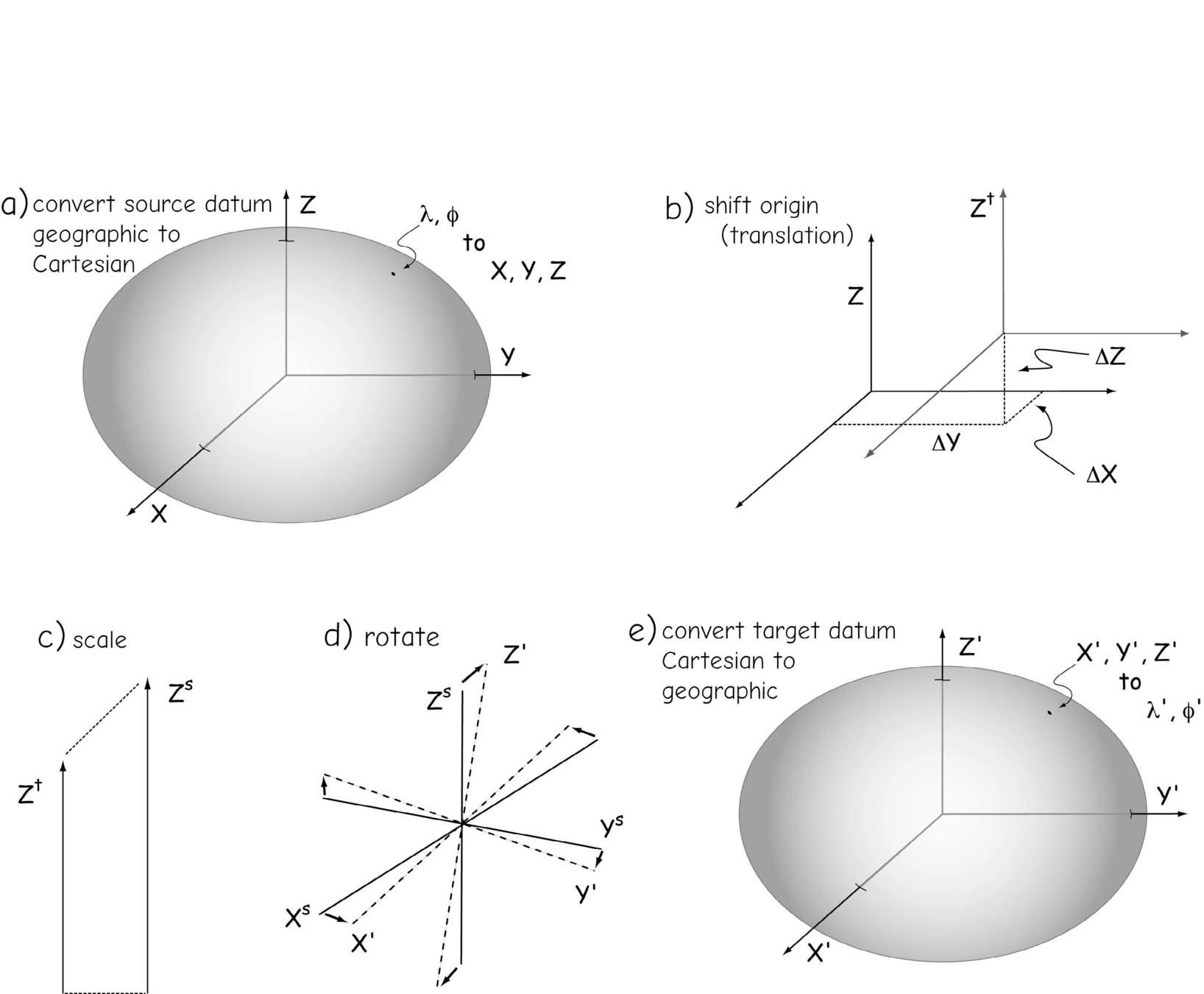
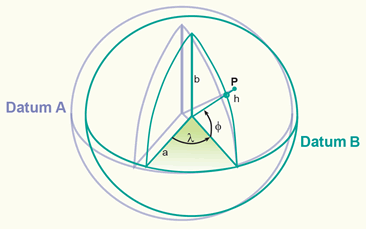
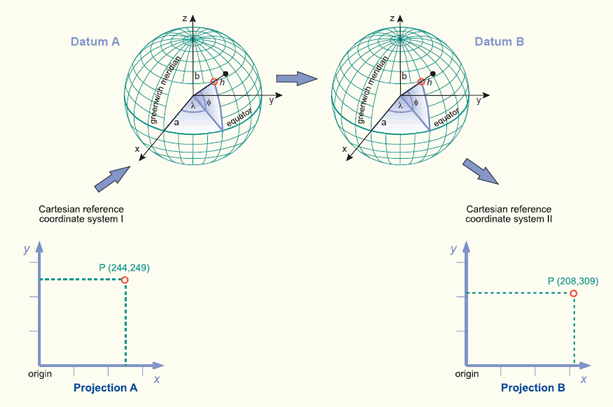
projected coordinate systems
(because the Earth isn't flat, but our desktops are.)

Projected Coordinate Systems
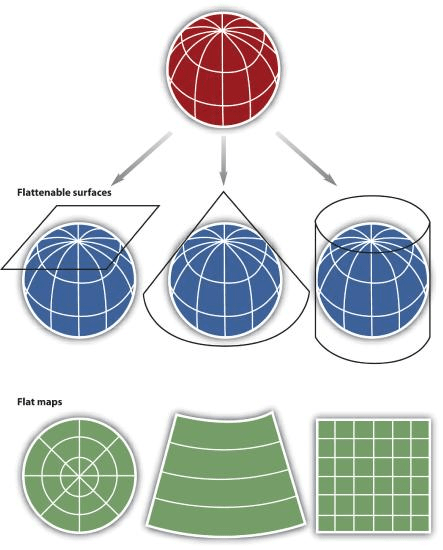
projections & coordinate systems
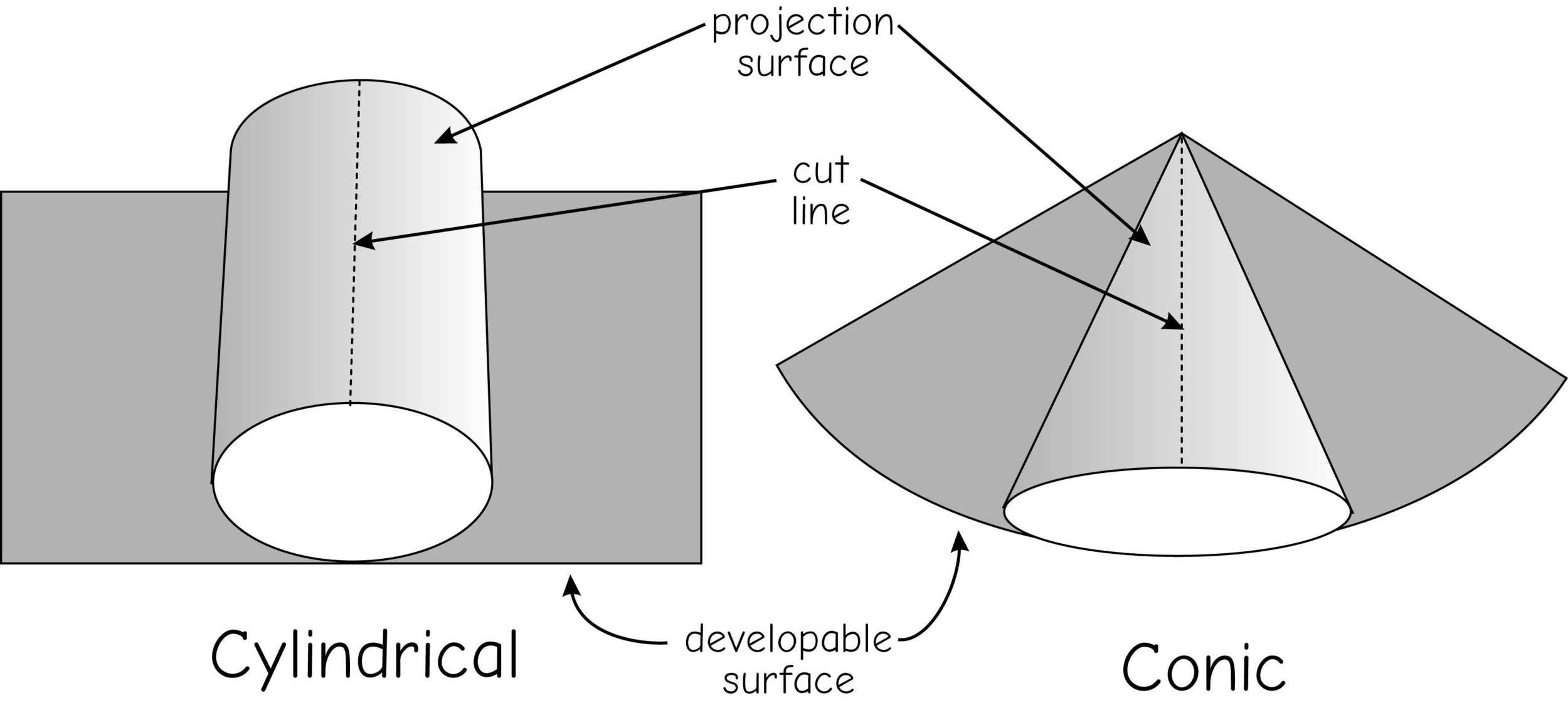
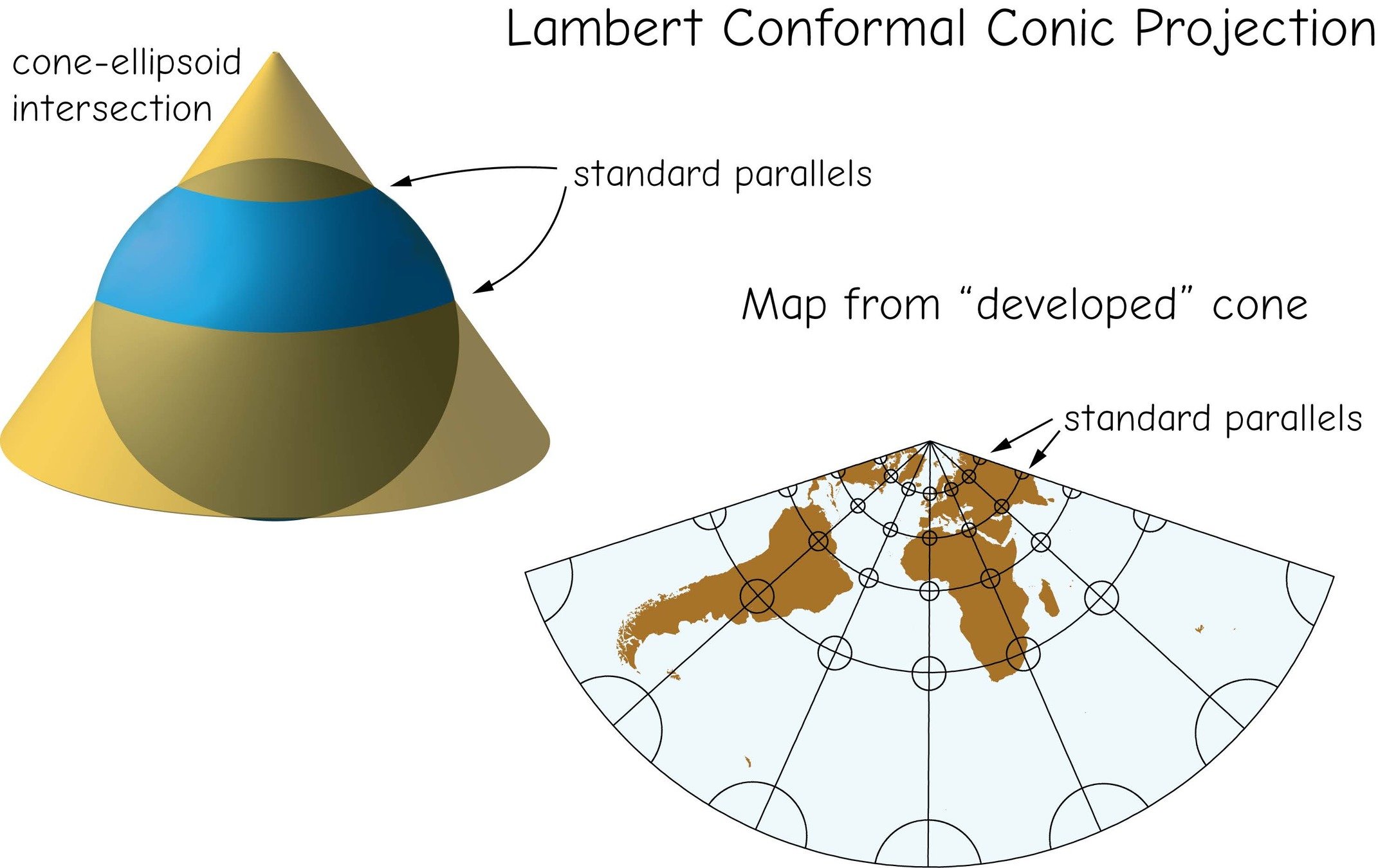
Lambert conformal conic
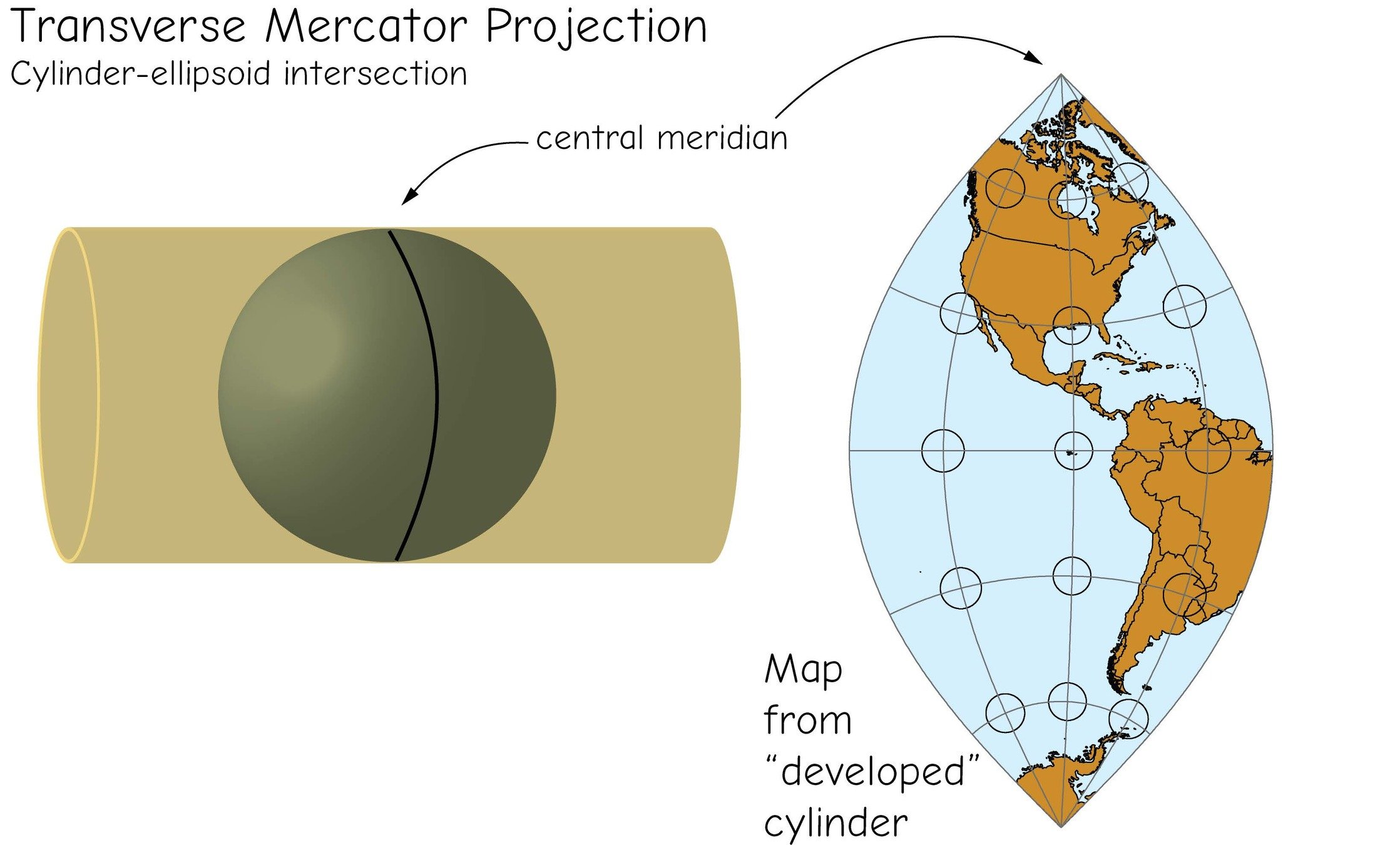
Transverse Mercator
projections & coordinate systems
projections & coordinate systems
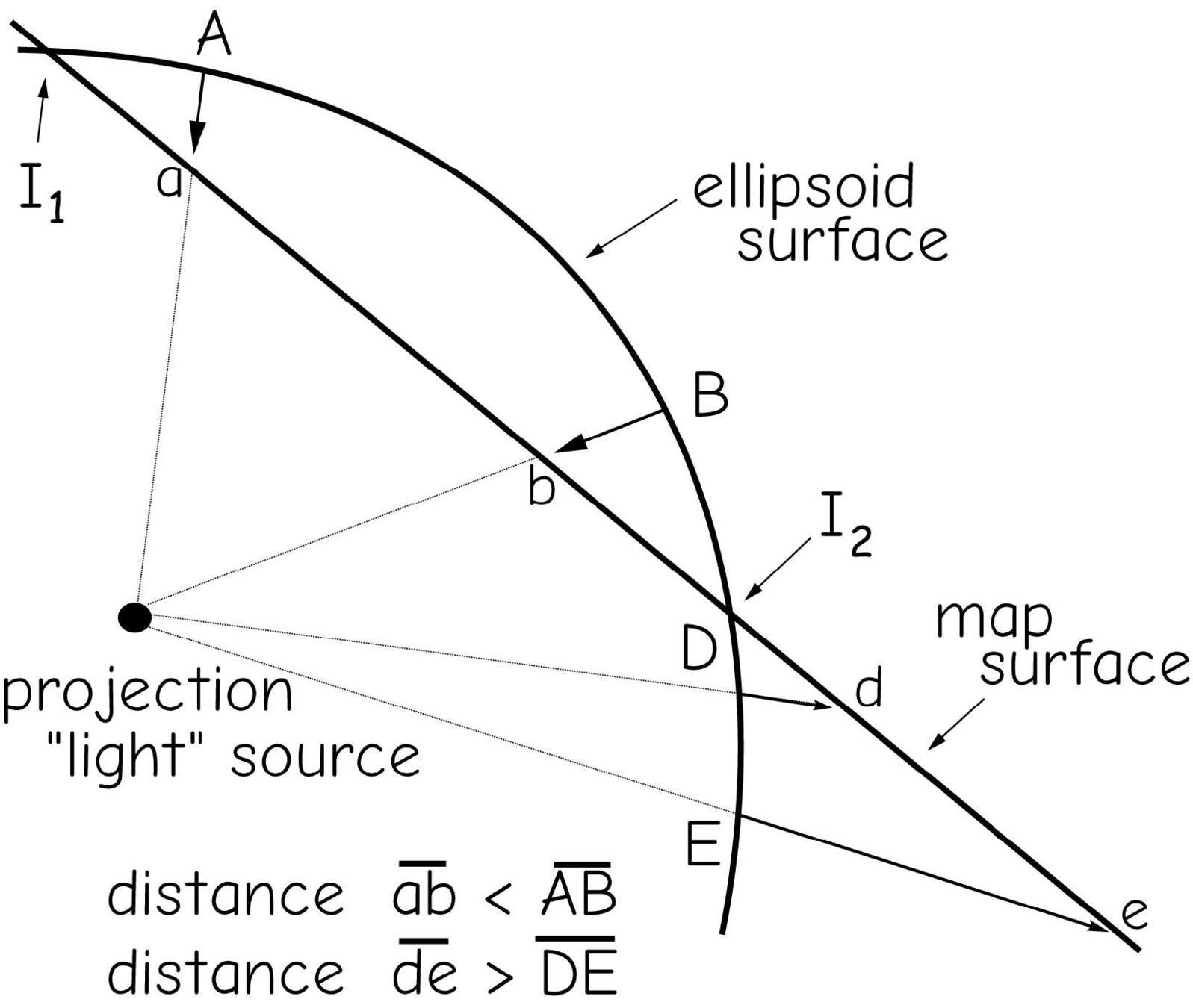
projections & coordinate systems

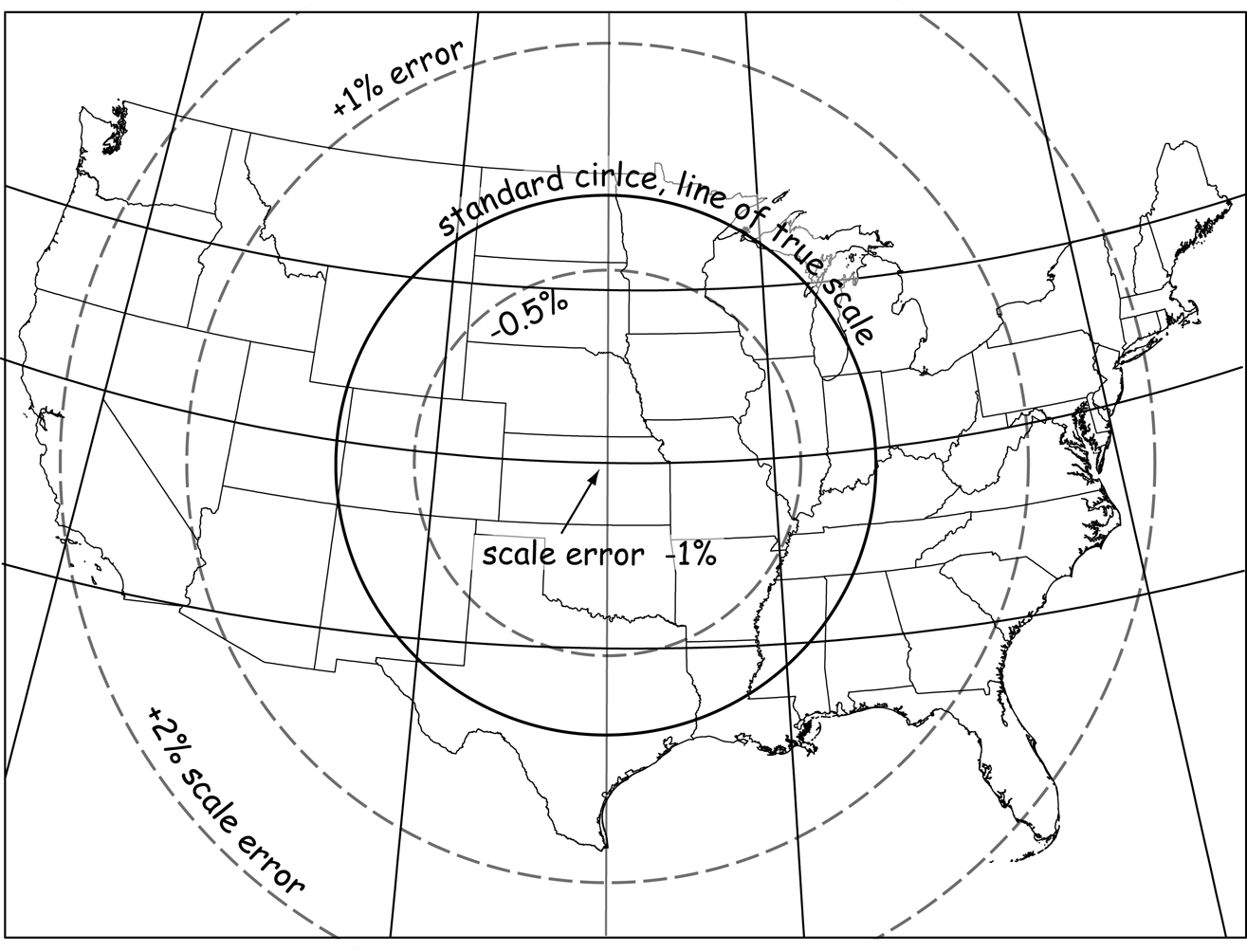
projections & coordinate systems

projections & coordinate systems
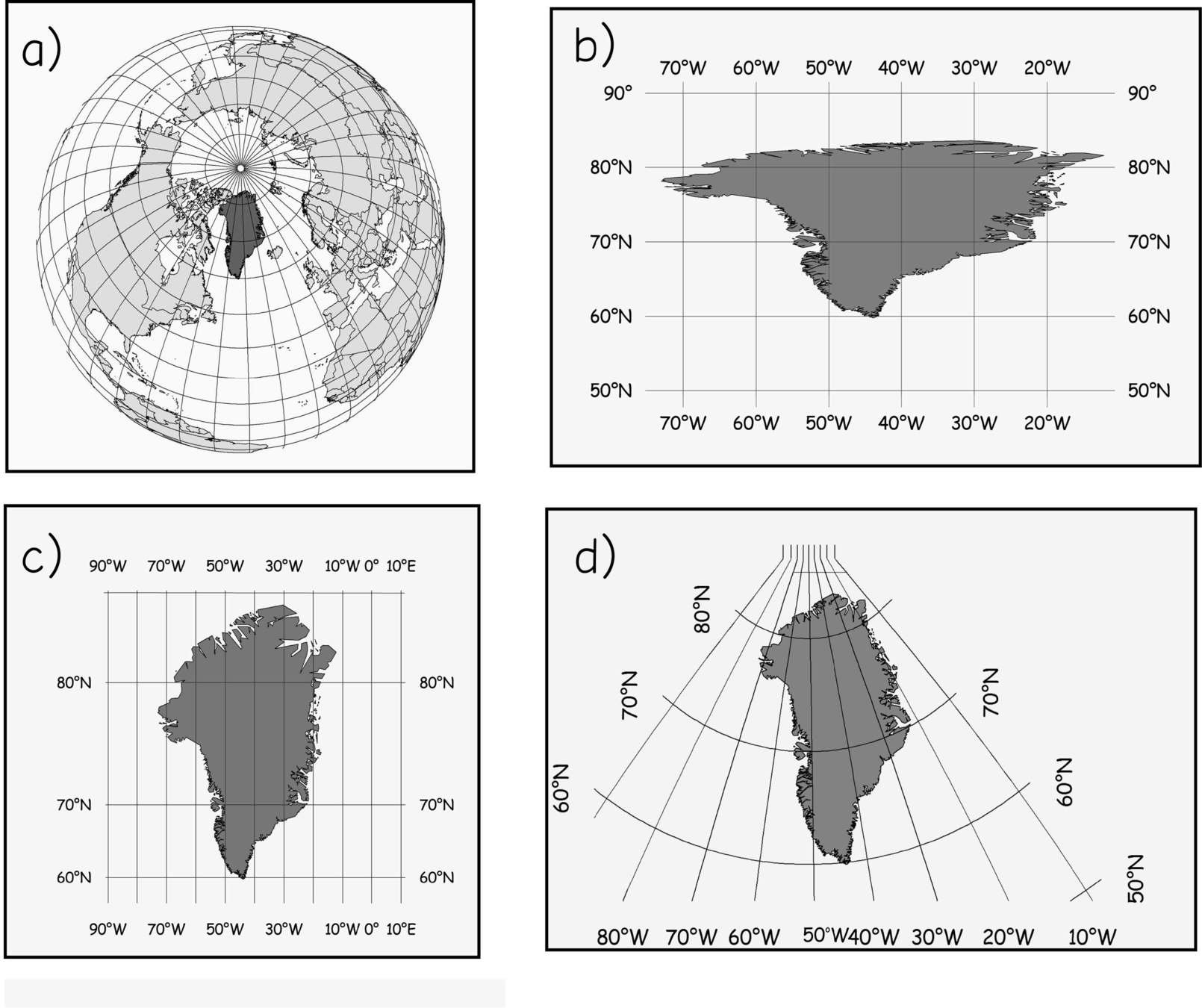
state plane coordinate systems

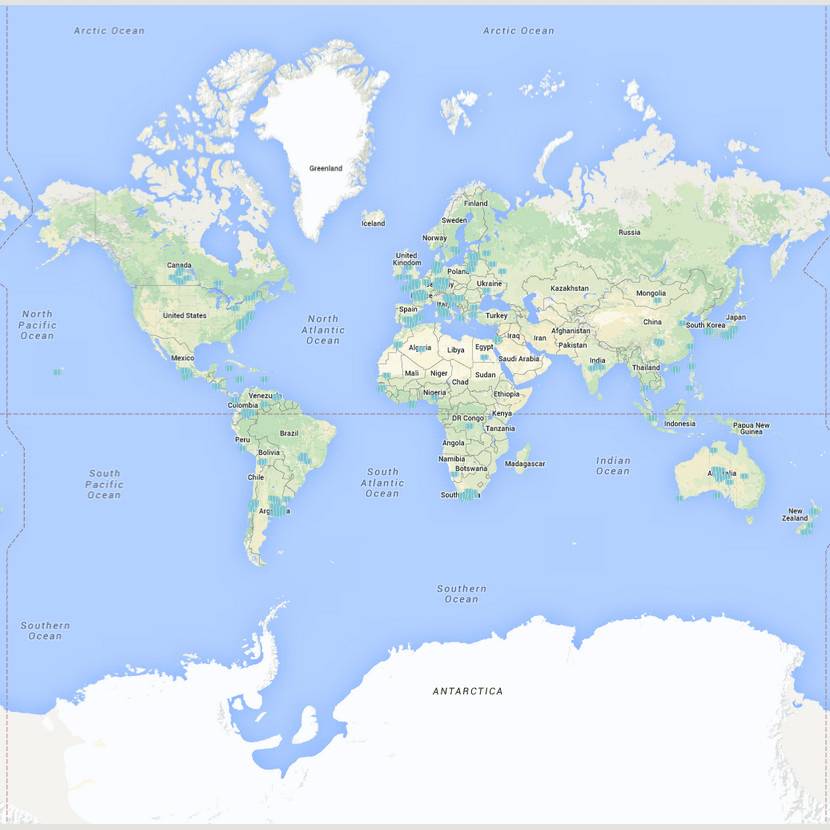
The "special" case of Web Mercator
(The "Map Projection" you are most familiar with!)

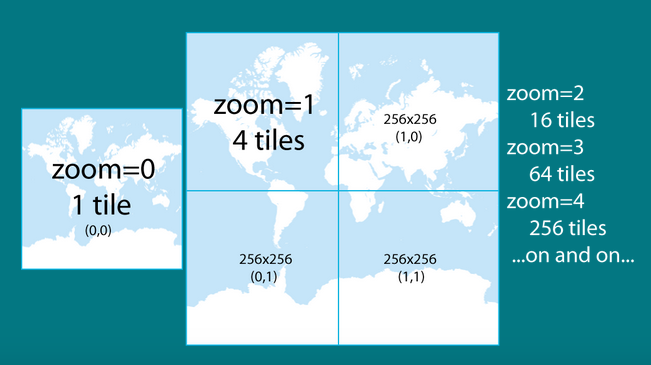
web map tiling schema






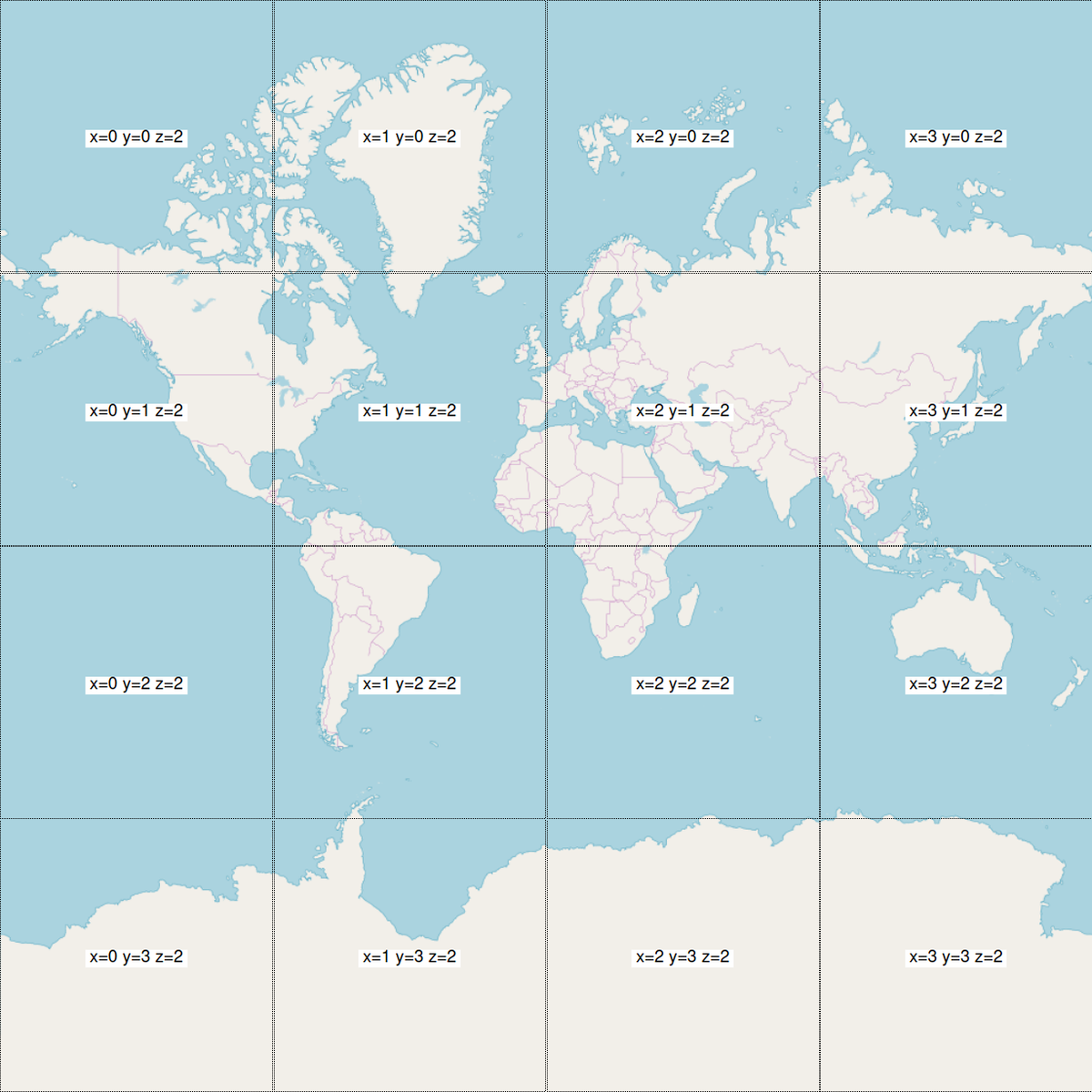
https://a.tile.openstreetmap.org/2/2/1.png
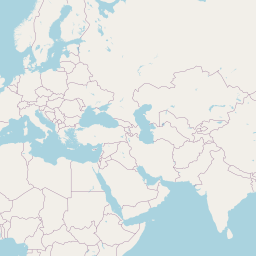
https://a.tiles.mapbox.com/v4/mapbox.satellite/2/2/1.jpg


Credit: @chris_whong

Odds & Ends
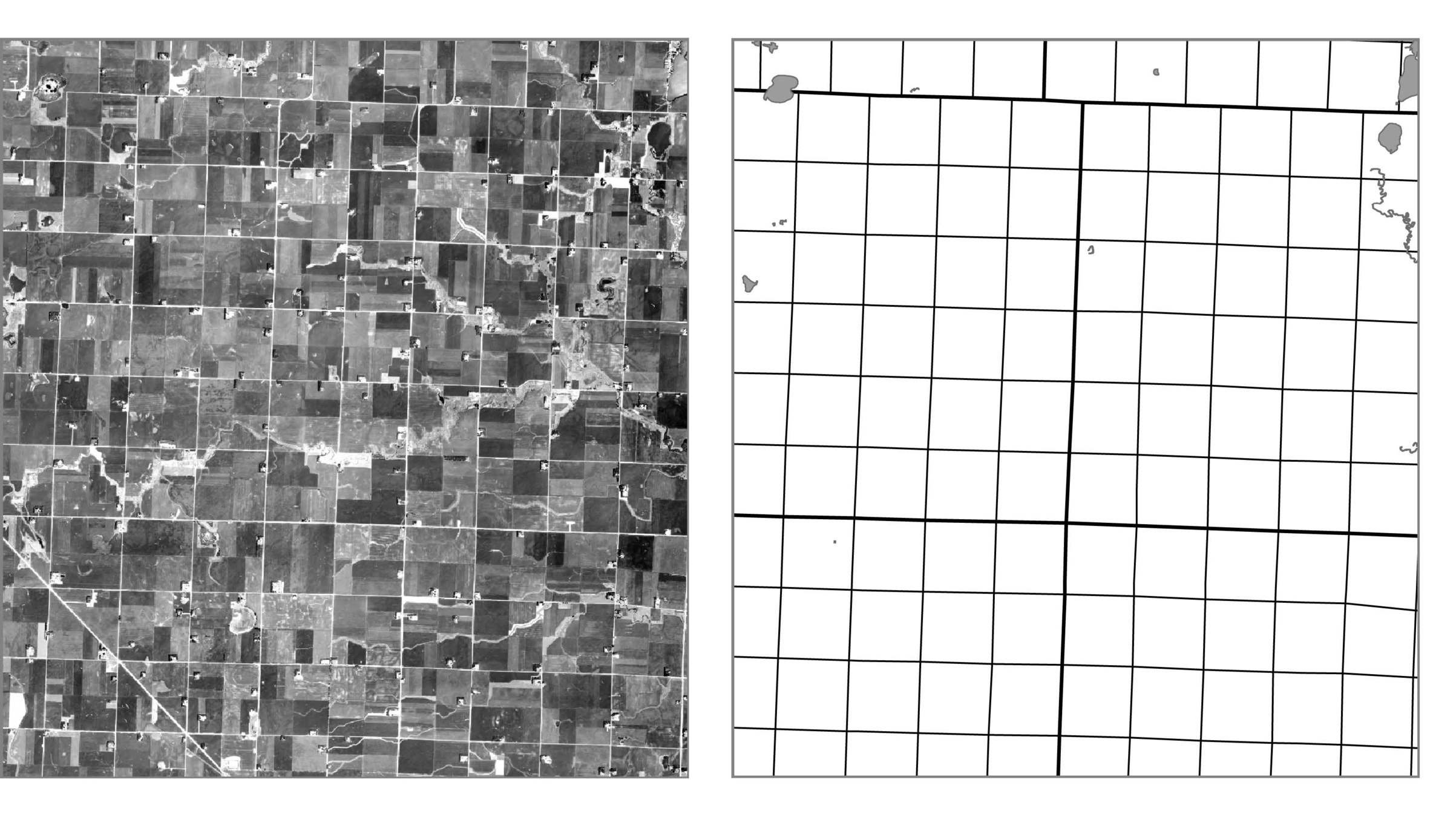
Public Land Survey System (PLSS)
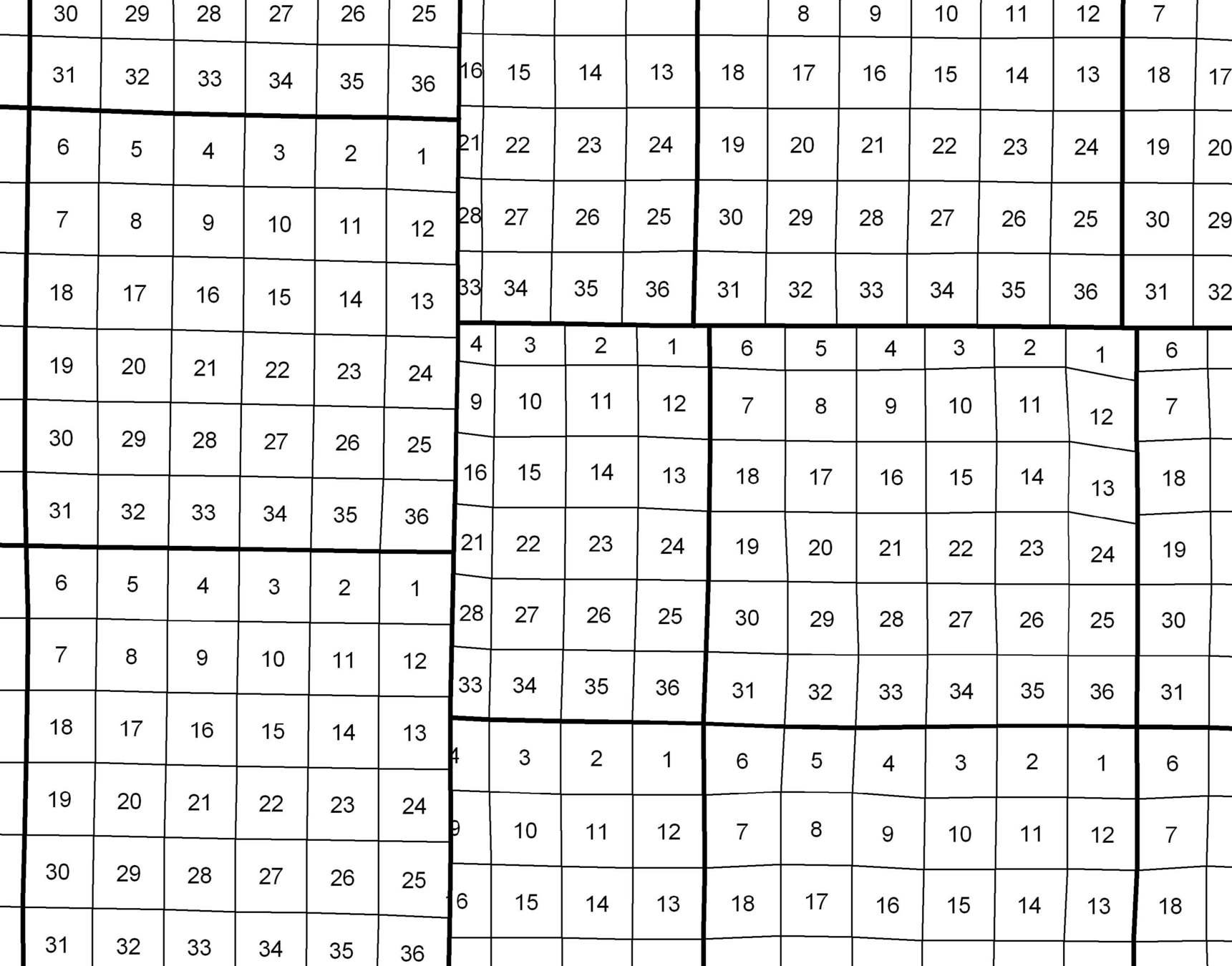
Public Land Survey System (PLSS)
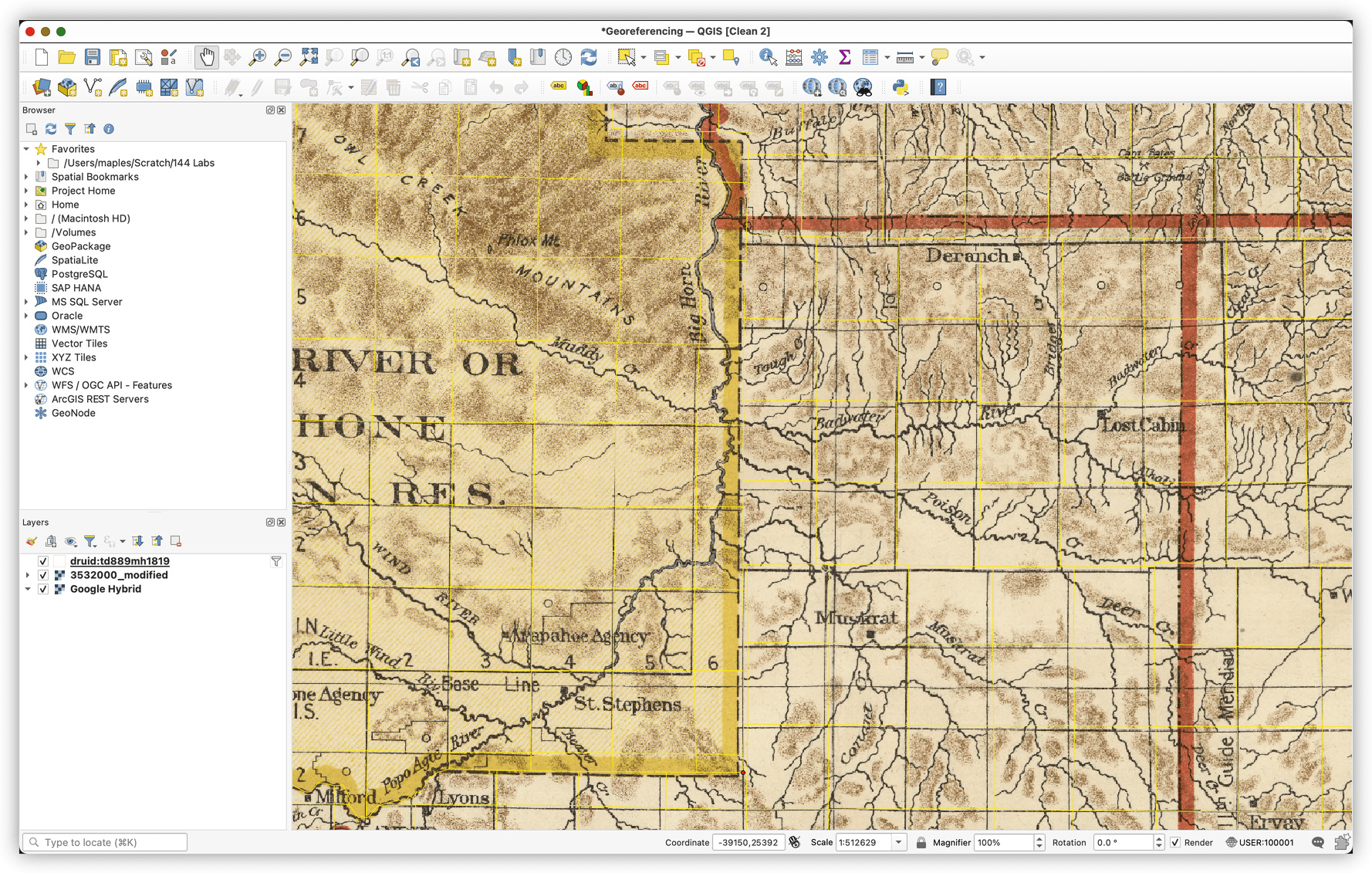
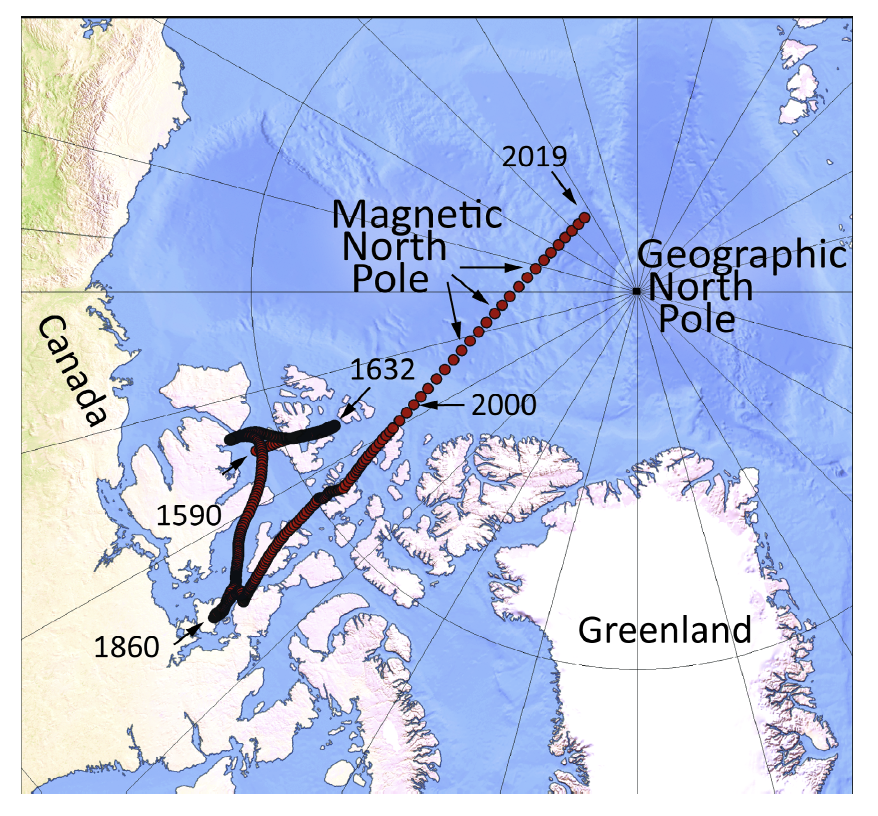
geographic vs magnetic north
All Lab Sections will meet in the Mitchell A65 Computer Lab, located in the basement.
Facilitator Day & Time Location
| Maya (Monday Morning) | Monday 9:00–11:00 AM | Mitchell A65 Computer lab |
| Stace (Monday Afternoon) | Monday 3:00–5:00 PM | Mitchell A65 Computer lab |
| Nona (Wednesday Afternoon) | Wednesday 3:00–5:00 PM | Mitchell A65 Computer lab |
| Marielle (Friday Afternoon) | Friday 3:00–5:00 PM | Mitchell A65 Computer lab |
Labs!
Coordinate Systems & Geodesy
By Stace Maples
Coordinate Systems & Geodesy
- 903



