From Chaos to Control
Automating Data Workflows with Prefect & GCP

Automating Data Workflows
with Prefect & GCP


What this talk is, and is not!?
🙅♂️ Not a tutorial
✅ Trip around bird's eye view Workflow orchestration for Dataflow
✅ About Prefect and how to use it
✅ Quick tour of how Prefect can be used with GCP
Workflow?
System for managing repetitive processes and tasks which occur in a particular order.
Dataflow?
-
A data flow represents the movement of data from one component or system to another.
-
Also, be described as the transport of data from a source to a destination.
-
Example: ETL
Workflow
Orchestration?
-
Tool that turns code into a workflow that can be scheduled, run and observed.
-
Provides functionality such as data passing between task, scheduling, alerting, caching and visibility for monitoring workflow execution and failures.
agenda_workflow.yaml
Abhishek
🥑 Developer Advocate @Dozer
🐍 Pythonista
👨👩👧👦 Community first person 💛
connect with me:
👨💻 "1x.engineer"

Know more about Dozer: getdozer.io
Existing Tools ⚒️
-
Apache Airflow -
Dagster -
Prefect✨ -
KubeFlow
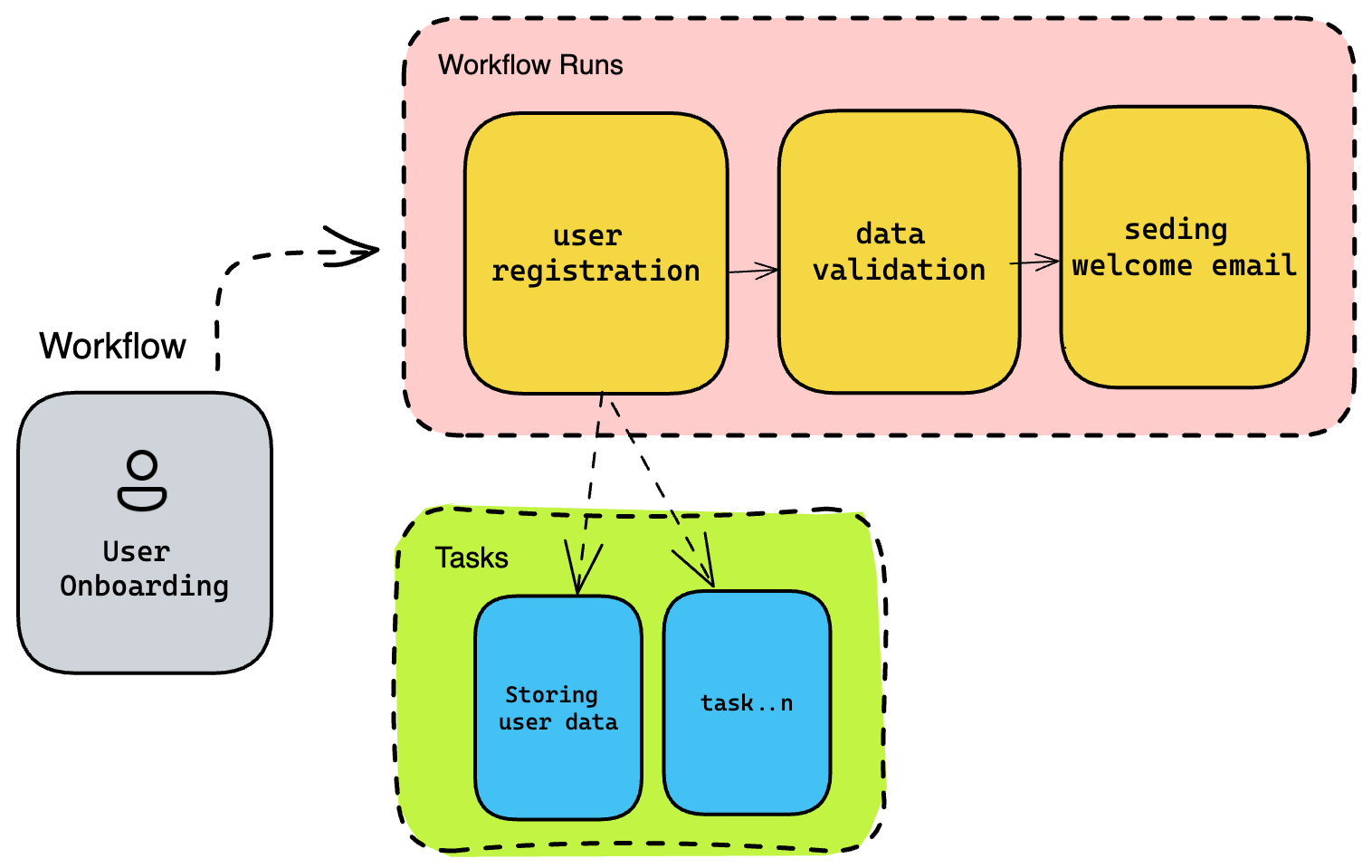
(An user onboarding workflow example)
Why Prefect & !Airflow
Did you say Airflow?

*Nightmare*
Also keep in mind 🧠
Modern Data Stack
Current MLOps Process
-
Data collection -
Feature engineering -
Modeling (training, validation, testing, inference) -
Deployment -
Monitoring

Ease Of Setup
Dynamic DAGs
Parallel Scaling
Version Control
Event Driven Workflow

- Modern workflow orchestration tool (OSS).
- Automates and manages complex workflows.
- Monitor, coordinate, and orchestrate dataflows.
- Deploy anywhere, configure remotely.
Actors:
- A “Flow” in Prefect refers to a DAG of tasks that represent the steps of a workflow.
- A “Task” in Prefect is a unit of work that performs a specific action.
Let's have a look at long ingestion script 👇
Let’s transform this into a Prefect flow.
- We breakdown the whole
ingest_data()function into tasks:
@task(log_prints=True, tags=["extract"], cache_key_fn=task_input_hash, cache_expiration=timedelta(days=1))
def extract_data(url: str):
.....
@task(log_prints=True)
def transform_data(df):
.....
@task(log_prints=True, retries=3)
def load_data(table_name, df):
.....2. Then we put the tasks in the main flow function. We use the flow decorator to indicate that main_flow() is a Prefect flow
@flow(name="Subflow", log_prints=True)
def log_subflow(table_name: str):
print(f"Logging Subflow for: {table_name}")
@flow(name="Ingest Data")
def main_flow(table_name: str = "yellow_taxi_trips"):
user = "postgres"
password = "postgres"
host = "localhost"
port = "5432"
db = "postgres"
table_name = "yellow_taxi_trips"
csv_url = "https://github.com/DataTalksClub/nyc-tlc-data/releases/download/yellow/yellow_tripdata_2021-01.csv.gz"
log_subflow(table_name)
raw_data = extract_data(csv_url)
data = transform_data(raw_data)
load_data(table_name, data)View code here:
python ingest_data_flow.pyRun:

Orion UI with the command prefect orion start
Then we can see the UI dashboard at http://127.0.0.1:4200
- First, we need to create a GCP Bucket Block. For my case, I named my bucket
de-gcs.
- Then we need to create another block for GCP Credentials. Remember to link your service account file to the JSON key file you had.
- After setting up the Block for GCP we would be able to run
etl_web_to_gcs.py(script here)
python etl_web_to_gcs.py
ETL with Prefect and GCP ✨
Checkout - prefect-gcp library

You should be able to see your data loaded to GCS here.
- Now we will implement the ETL script to extract data from GCS and load them into BigQuery.
- We need to add two tasks,
extract_From_gcsandwrite_bq. - See the full script here.
GCS to BigQuery
@task(retries=3)
def extract_from_gcs(color: str, year: int, month: int) -> Path:
"""Download trip data from GCS"""
gcs_path = f'data/{color}/{color}_tripdata_{year}-{month:02}.parquet'
gcs_block = GcsBucket.load('de-gcs')
gcs_block.get_directory(from_path=gcs_path, local_path='./')
return Path(gcs_path)
@task()
def write_bq(df: pd.DataFrame) -> None:
"""Write DataFrame to BigQuery"""
gcp_credentials_block = GcpCredentials.load('gcp-credentials')
df.to_gbq(
destination_table='trips_data_all.yellow_taxi_trips',
project_id='crafty-elf-376416',
credentials=gcp_credentials_block.get_credentials_from_service_account(),
chunksize=500_000,
if_exists='append'
)Next we need to create a table in BigQuery.

Now let’s try to run our ETL script! Before that we need to delete all of the data populated by BigQuery.


You will see our records in table preview:
Now run:
python etl_gcs_to_bq.py

Parametrizing Flow and Deployments

With Google Cloud Run
👇

Prefect*Me*Prefect gave me a deal, I could not refuse.

From Chaos to Control: Prefect + GCP
By Abhishek Mishra
From Chaos to Control: Prefect + GCP
- 318





